The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- physical examination
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- general urine analysis
- biochemical analysis of blood
- tumor markers
- indicators of blood coagulation
- CT scan (on indication 650 €)
- MRI scan (on indication 1200 €)
- biopsy and histological examination (on indication 1800 €)
- nursing services
- consultation of related specialists
- consultation of all leading experts
- development of individual treatment plan
- written statement
Required documents
- Medical records
- MRI/CT scan (if available)
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Pediatric Otolaryngology at the Children's Hospital Nuremberg offers diagnostics and treatment of ear, throat, and nose diseases to young patients. Conservative therapy and surgical treatment of otolaryngologic diseases are provided here. The department's team of doctors has rich experience in the surgical removal of adenoids and palatine tonsils and interventions for middle ear and paranasal sinus pathologies. Almost all operations on the ENT organs in children are performed on an outpatient basis without a mandatory hospital stay. This approach allows children to avoid stress and fear of the upcoming treatment, as they can spend most of the time with one of their parents. Surgical procedures are performed using endoscopic and other minimally invasive techniques, which ensure minimal postoperative pain for the child. Otolaryngologists collaborate closely with pediatric surgeons, and complex clinical cases are discussed during joint medical boards. The doctors and nursing staff are very friendly and easily get along with young patients. The department is headed by Dr. med. Mathias Heissenberg.
One of the most popular surgical interventions in the department's clinical practice is a tonsillectomy, a procedure for the removal of the palatine tonsils. In most cases, such treatment is prescribed for recurrent tonsillitis. The pathology is associated with inflammation of the tonsils and often has a complex course with the formation of purulent plugs. Before the prescription of a tonsillectomy, the child undergoes comprehensive diagnostics, including a clinical examination by a pediatrician, advanced blood testing, electrocardiography, and a chest X-ray. The department's otolaryngologists then begin to plan the surgical intervention and determine the optimal technique for performing the operation. Doctors use radio wave ablation, radiofrequency ablation, electrocoagulation, ultrasound excision, cryodestruction, or perform a classical tonsillectomy with a scalpel. Despite the availability of various state-of-the-art techniques in the arsenal of specialists, the excision of inflamed areas of the palatine tonsils with a scalpel remains relevant. All of the above-mentioned techniques also give a good result, but mainly in cases of mildly enlarged palatine tonsils due to inflammation. The child stays under medical supervision after a tonsillectomy. Parents receive recommendations on nutrition in the postoperative period and the care of the child at home. For example, the child's diet for 3-6 days after the operation should consist of pureed dishes that are easily chewed and swallowed.
The department's specialists also regularly perform an adenoidectomy to remove adenoids in children. The operation is prescribed for young patients with significantly enlarged tonsils due to inflammatory processes. Adenoid hypertrophy (adenoid vegetation) adversely affects the child's general health condition, hindering the work of the respiratory system, provoking speech disorders and hearing loss, and making the child distracted and inattentive. Preoperative diagnostics include comprehensive laboratory testing, electrocardiography, chest X-ray, pharyngoscopy, rhinoscopy, and nasopharyngeal endoscopy. The department's otolaryngologists perform a classical adenoidectomy with the help of an adenotome (a surgical instrument with a loop-shaped working part), as well as endoscopic and laser types of the intervention. Priority is always given to adenoid removal using minimally traumatic methods, and a classical adenoidectomy is a last-line option. After the procedure, the child remains under medical supervision for some time before being discharged. During the first 4-8 days, parents should carefully monitor the child's condition and strictly follow the recommendations provided by the doctor.
The department's team of doctors specializes in interventions for middle ear pathologies. Of particular interest in this area is tympanoplasty, an operation to restore the integrity of the tympanic membrane (eardrum). The primary indications for this intervention are chronic suppurative or adhesive otitis media, conductive hearing loss, and connective tissue overgrowth in the middle ear mucosa (tympanosclerosis). Tympanoplasty aims to repair the eardrum and auditory ossicles in order to restore or improve hearing and cease pus flow from the ear. The surgical intervention is performed under general or local anesthesia using a postauricular approach. As a rule, a short-term hospital stay (2-3 days) is required.
The department's key focuses include:
- Tonsillectomy
- Adenotomy
- Tonsillotomy
- Tympanostomy tube insertion surgery
- Tympanoplasty
- Endoscopic paranasal sinus surgery
- Other medical services
Curriculum vitae
Higher Education
- 2000 Specialization in Special Otolaryngology, Christian Albrecht University of Kiel.
- 1999 Additional qualification in Plastic Surgery, Christian Albrecht University of Kiel.
- 1996 Board certification in Otolaryngology, Christian Albrecht University of Kiel.
- 1994 Thesis defense, summa cum laude, Eberhard Karl University of Tuebingen.
- 1992 Admission to medical practice, Eberhard Karl University of Tuebingen.
- 1985 Medical studies, Georg August University of Goettingen.
Professional Career
- 1994 - 1996 Preparation for board certification in Otolaryngology, Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, University Hospital Kiel.
- 1998 - 2001 Senior Physician, Department of Otolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery, University Hospital Kiel.
- Since 2001 Otolaryngologist in his own private practice in Nuremberg.
- Since 2010 Head Physician, Department of Pediatric Otolaryngology, Children's Hospital Nuremberg.
- Since 2005 Medical Advisor, Dr. Erler Otolaryngology Clinic in Nuremberg.
- 2001 - 2010 Physician, Department of Otolaryngology, Martha Maria Hospital Nuremberg.
Memberships in Professional Societies
- Working Group on Plastic, Reconstructive and Aesthetic Head and Neck Surgery (APKO).
- Working Group on Pediatric Otolaryngology (PädHNO).
- Working Group on Applied Sleep Medicine (AfaS).
- German Society of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery (DGHNO-KHC).
- German Association of Otorhinolaryngologists (HNO).
- European Academy of Facial Plastic Surgery (EAFPS).
- North German Society of Otorhinolaryngology, Head and Neck Surgery.
Photo of the doctor: (c) Klinik Hallerwiese-Cnopfsche Kinderklinik
About hospital
The Children's Hospital Nuremberg is a maximum care health facility that focuses on providing effective care for young patients in a pleasant and comfortable environment. The hospital admits children and adolescents up to 18 years old. Medical care can be provided on an inpatient or outpatient basis. Highly qualified doctors and experienced nursing staff work with children. The specialists get along well with young patients. The goal of the hospital's medical team is to provide patients with modern and most sparing treatment. It is also important for doctors to eliminate pain and discomfort during the therapeutic process. The key to successful clinical practice in the medical facility is the close cooperation of doctors, their high competence and vast experience, as well as the hospital's state-of-the-art medical equipment and modern infrastructure.
The hospital has more than ten specialized departments. Priority areas include pediatric otolaryngology, surgery, urology, orthopedics, endocrinology, oncology, hematology, pulmonology, and neuropediatrics. Patients are offered innovative treatments that have proven themselves at the international level. Surgical treatment involves the wide use of sparing, minimally invasive techniques, after which children recover quickly and experience virtually no pain.
The hospital admits more than 15,000 young patients every year, most of whom are treated on an outpatient basis without mandatory hospitalization. Each child receives personalized care. The treatment is accurately planned, and the doctor tells the parents about its specifics. An important aspect is a friendly and attentive attitude towards children, as well as understanding their fears and needs.
The Children's Hospital Nuremberg has repeatedly received the "Ausgezeichnet. FÜR KINDER" quality certificate. This certification is granted to the best children's hospitals in Germany, which regularly demonstrate high treatment success rates.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
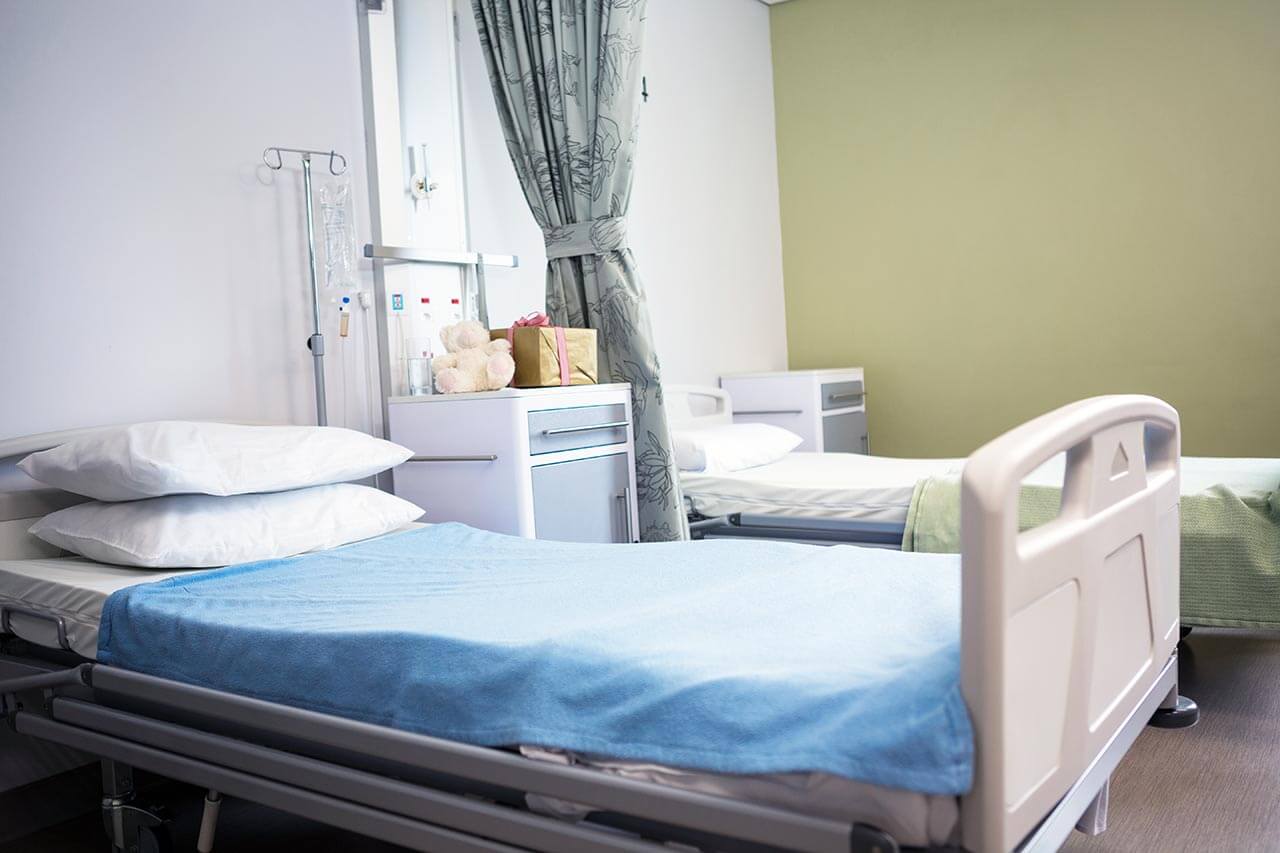
Patients rooms
The patients of the Children's Hospital Nuremberg live in comfortable rooms designed in a child-friendly style. The furnishing of a patient room includes a comfortable automatically adjustable bed, a bedside table, a table, chairs, and a wardrobe. The hospital has a Rooming-in system, thanks to which parents can stay in the same room with their child. To ensure interesting and pleasant leisure time for children, the hospital has excellent playrooms, where every child can find something to do and toys to their liking.
Meals and Menus
The patients at the hospital are offered three tasty and balanced meals a day: breakfast, lunch, and dinner. With appropriate clinical indications, an individual menu may be developed for the child.
Further details
Standard rooms include: