The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- physical examination
- review of medical records
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- general urine analysis
- biochemical analysis of blood
- indicators of inflammation (CRP, ESR)
- indicators blood coagulation
- x-ray examination of the hip
- MRI scan of the hip
- preoperative care
- hip replacement (hip endoprosthesis)
- symptomatic treatment
- control examinations
- physiotherapeutic procedures
- orthopedic appliances
- the cost of essential medicines and materials
- nursing services
- full hospital accommodation
- explanation of future recommendations
How program is carried out
Preliminary preparation for hip replacement includes quitting smoking and drinking alcohol; cancelling non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen); cancelling anticoagulants (warfarin); normalization of body mass, if possible.
Preoperative examination, including consultation with an anesthesiologist and necessary related specialists, takes 1-2 days. According to its results, the most suitable endoprosthesis is selected.
Hip replacement. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The patient lies on his side, the affected leg is bent and fixed in this position. The surgeon makes an incision 15-20 cm long, minimally traumatizing the muscles and nerve endings. Through this incision, miniature instruments are inserted to remove the damaged joint structures. Healthy bone is adjusted for further reliable implant fixation.
The surgeon installs a femoral stem in the center of the upper part of the femur. Ball-shaped head of the joint is fixed on it. The surgeon also implants a special liner that facilitates movement of the leg and protects the structures of the prosthesis. After the primary fixation of the prosthesis components, the doctor assesses the joint range of motion, as well as the length and symmetry of the lower limb.
The implant is fixed with cement or cementless method. The doctor treats the operating field with antiseptics, conducts its final revision and sutures the wound layer by layer. A temporary drainage is installed in the joint, and a bandage is applied on top.
Postoperative care. During the first day after the intervention the patient stays in the intensive care unit, under round-the-clock medical supervision. After that, with a smooth course of the postoperative period, the patient is transferred to a regular ward and the drains are removed. The range of motion expands gradually, from light toes movements to walking. Walking with the use of walking aids is allowed in 3-5 days after the operation.
Required documents
- X-ray examination of the hip joints
- MRI scan of the hip joints, if available
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Adult and Pediatric Orthopedics, Trauma Surgery, Foot Surgery at the University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden offers the full range of diagnostics, conservative and surgical treatment of musculoskeletal diseases and injuries. The department is a certified Endoprosthetics Center – more than 1,000 primary joint replacement surgeries are performed here annually. The surgeons of the Endoprosthetics Center also specialize in particularly complex clinical cases and revision procedures for the replacement of previously implanted artificial joints. In addition, the department has the status of the interregional Trauma Center certified in accordance with the standards of the German Trauma Society. The department has also been awarded a Certificate of Excellence from the German Orthopedic Foot and Ankle Society (DAF) in the field of foot surgery. A separate area of clinical activity is the treatment of diseases, injuries and congenital malformations of the musculoskeletal system in children. Depending on the severity of the clinical case, both conservative and surgical techniques are used in the treatment of orthopedic pathologies in children. The department's medical team prefers sparing low-traumatic surgery, while open operations are performed only if other therapeutic options are ineffective. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Klaus-Dieter Schaser.
The department's orthopedists pay special attention to the treatment of primary and secondary musculoskeletal tumors. The department most often deals with the treatment of patients with bone tumors, bone metastases and sarcomas. The specialists perform tumor resection surgery followed by bone and soft tissue reconstruction with the use of biological materials, endoprostheses, etc. Conservative therapeutic measures are carried out in collaboration with oncologists, radiation therapists and other specialists. Whenever possible, tumor resection surgery is performed using minimally invasive surgical techniques, which significantly speeds up and facilitates the recovery process after the intervention.
The department also successfully treats shoulder and elbow diseases. The department's medical team specializes in the treatment of shoulder and elbow arthrosis, rotator cuff tear, shoulder joint instability, impingement syndrome, calcific tendinitis, frozen shoulder and other pathologies. At the early stages of the disease, it is often possible to avoid surgery and provide conservative treatment, including drug therapy, manual therapy, physiotherapy, therapeutic exercises, electrotherapy and other techniques. If surgical treatment is indicated for the patient, surgeons always strive to perform arthroscopic or minimally invasive interventions that exclude extensive skin and soft tissue incisions.
The team of traumatologists of the medical facility has vast experience in the treatment of musculoskeletal injuries, including those of high severity. The department deals with the treatment of bone fractures, traumatic brain injuries, ankle sprains, distal radius fractures, dislocations and other traumatic lesions.
An integral part of the department's clinical practice is foot and ankle surgery. The specialists in this medical field admit patients with foot injuries, ankle and toe arthrosis, acute and chronic inflammatory ankle diseases, foot bone congenital malformations, compression syndromes, foot tumors and diabetic foot syndrome. The department's doctors use in their work an individual approach to each clinical case and select the optimal treatment methods based on the diagnostic results of a particular patient. The goal of any treatment is to relieve pain, restore foot function and patient's mobility.
The team of pediatric orthopedists provides treatment of the full range of musculoskeletal diseases and injuries in children and adolescents. The medical facility carries out conservative and surgical treatment of shoulder and elbow pathologies, spinal diseases and chronic back pain, O-shaped and X-shaped deformities of the lower extremities, leg length discrepancy, hip and knee diseases, foot deformities and diseases. The specialists have particular expertise in the treatment of musculoskeletal tumors in children. The department's doctors get along well with young patients and support them in every possible manner on their way to recovery.
The department's clinical focuses include:
- Joint replacement surgery
- Hip replacement surgery, including follow-up conservative therapy (physiotherapy, injection therapy, drug therapy, special pain therapy)
- Joint-preserving operations
- Implantation of cementless and cemented prostheses
- Revision interventions for extensive defects, up to bone replacement, for example, the femur
- Knee replacement surgery
- Partial joint replacement
- Total joint replacement (total endoprosthesis)
- Revision interventions (even in extensive bone defects)
- Hip replacement surgery, including follow-up conservative therapy (physiotherapy, injection therapy, drug therapy, special pain therapy)
- Shoulder surgery
- Rotator cuff tear (arthroscopic treatment methods)
- Arthroscopic articular lip reconstruction (SLAP technique)
- Shoulder instability
- Acromioclavicular joint lesion (arthroscopic techniques)
- Subacromial pain syndrome (arthroscopic techniques)
- Shoulder arthrosis (various types of arthroplasty)
- Shoulder sports injuries
- Elbow surgery
- Elbow arthroscopy
- Limited radius of elbow movements (arthroscopic or open arthrolysis)
- Ligament plastic repair
- Elbow arthrosis (implantation of elbow prostheses)
- Tennis elbow (denervation and elimination of necrosis)
- Surgical treatment of primary and secondary malignant musculoskeletal tumors (bone tumors, bone metastases, soft tissue sarcomas)
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Implantation of endoprostheses for tumors
- Implantation of custom-made prostheses
- Limb sparing surgery
- Function-preserving reconstructive surgery after soft tissue and bone resection
- Implantation of artificial materials for bone tissue replacement
- Surgical and conservative treatment of musculoskeletal injuries
- Bone fractures
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Ankle sprains
- Distal radius fractures
- Dislocations
- Surgical treatment of spinal pathologies
- Treatment-resistant spinal pain, vertebral dislocation
- Degenerative scoliosis
- Surgical treatment: dorsal fusion, ventral derotation spondylodesis
- Conservative treatment: the use of orthoses, physiotherapy on an outpatient basis
- Spinal disc herniation
- Spinal stenosis
- Spondylitis/spondylodiscitis
- Vertebral fractures
- Cervical spinal cord pathologies and injuries
- Spinal tumors
- Special orthopedic pain management
- Reconstructive hip surgery
- Arthroscopic interventions (also diagnostic)
- Arthroscopic reconstruction and surgical repair of the hip position in severe forms of hip impingement syndrome
- Transpositional interventions to repair the incorrect hip position
- Acetabular roof plastic surgery and pelvic osteotomy (minimally invasive methods)
- Surgical treatment of pelvic and acetabular injuries
- 3D X-ray-guided stabilization operations on the anterior and posterior parts of the pelvic ring, as well as acetabular reconstruction
- Sacroiliac joint navigational surgery
- Revision interventions for pseudoarthrosis (also with the use of transposition osteotomy, plastic surgery for the cancellous bone or the use of osteoinductive growth factors)
- Femoral derotation osteotomy
- Joint replacement surgery for posttraumatic coxarthrosis
- Reconstructive knee surgery
- Stabilizing patellar interventions
- Cartilage transplantation (including autologous cartilage cell transplantation)
- Correction of axial disorders (transposition osteotomy)
- Cruciate ligament surgery
- Surgical treatment of foot pathologies
- Corrective toe interventions (hallux valgus), including corrective osteotomy and soft tissue interventions
- Surgical repair of soft tissues and bones of the rare foot and midfoot
- Implantation of endoprostheses and arthrodeses of the big toe
- Implantation of arthrodesis on the rare foot and midfoot
- Amputation
- Synovectomy, tenosynovectomy
- Arthroscopic ankle surgery
- Pediatric orthopedics
- Shoulder and arm diseases
- Shoulder instability
- Shoulder dislocation
- Elbow osteochondrosis
- Deformities (congenital or due to an accident)
- Head, neck and spinal diseases
- Malformations and postural disorders (for example, torticollis, scoliosis, vertebral dislocation, Scheuermann's disease)
- Back pain
- Diseases and deformities of the lower extremities
- O-shaped and X-shaped deformities, leg length discrepancy (congenital deformities or consequences of an accident)
- Hip joint diseases
- Hip dislocation
- Late effects of residual hip dysplasia
- Perthes disease
- Hip pain
- Knee and knee joint diseases
- Osteoarthritis
- Meniscus tear
- Patellar dislocation
- Knee pain
- Foot and ankle diseases
- Clubfoot (Ponseti method)
- Planovalgus foot deformity
- Pes cavus
- Musculoskeletal tumors in children
- Neuromuscular disorders (children with disabilities)
- Fractures and injuries due to metabolic and skeletal diseases (for example, osteogenesis imperfecta)
- Shoulder and arm diseases
- Other medical services, other orthopedic diseases and injuries
Curriculum vitae
In 1990, Prof. Klaus-Dieter Schase entered the Faculty of Medicine at the University of Erlangen-Nuremberg, where he studied until 1996. In 1995 and 1996, he completed an internship at the University of Regensburg. After completing his education in 1996 and 1998, he completed a residency in the Department of Traumatology and Reconstructive Surgery at the Faculty of the Humboldt University of Berlin, where Prof. Haas became his supervisor. In 1998, the doctor received a medical license. Between 1998 and 2004, he worked as an Assistant Physician and Research Fellow in the Department of Traumatology and Reconstructive Surgery at the Charite University Hospital under the guidance of Prof. Haas. In 2002, he completed his board certification in Surgery. From 2002 to 2009, he held the position of Head Physician, Deputy Head of the Department of Spinal Tumor Surgery at the Charite University Hospital Berlin, the Musculoskeletal Surgery Center at the Charite University Hospital Berlin, and also received the title of University Professor. In 2006, he became the Head of the Department of Spinal Surgery at the Musculoskeletal Surgery Center of the Charite University Hospital Berlin. In 2009, the doctor had board certification in Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery. In 2009, he became the Deputy Head Physician and the Head of the Department of Traumatology and Reconstructive Spinal Surgery at the Charite University Hospital Berlin. In 2010, he completed his specialization in Special Trauma Surgery. Currently, Dr. Klaus-Dieter Schaser provides treatment and has medical specialization in the following areas: degenerative spinal surgery, spinal tumor surgery (surgical treatment of primary spinal tumors and metastases), musculoskeletal tumor surgery, surgical treatment of spinal injuries, pelvic reconstructive surgery, surgical treatment of complex injuries of the extremities (open and closed fractures, soft tissue injuries, reconstructive surgery of musculoskeletal defects). Dr. Klaus-Dieter Schaser is a member of a number of well-known and respected organizations and scientific societies. He is a member of the German Trauma Society, the German Society of Surgery, the German Society for Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery, the German Spine Society and the Orthopaedic Research Society. The doctor is also a member of the European Society for Surgical Research, the Association for Bone Tumors, the Joint Consortium, founder and representative of the Berlin Trauma Network. Prof. Klaus-Dieter Schaser is the Deputy Speaker of the Regional Surgery Center at the Charite University Hospital Berlin. In 1998, the doctor was awarded the Orthopedic Research Society Award for Research in Microvascular Medicine for closed soft tissue injuries in New Orleans.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
About hospital
According to the reputable Focus magazine, the University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden ranks among the top five German hospitals!
The hospital is the benchmark for modern high-quality medicine. Positioning itself as a maximum care medical facility, the hospital represents all medical fields. There are 26 specialized departments, 6 institutes and 17 interdisciplinary centers, which cooperate closely with the clinical and scientific facilities of the Faculty of Medicine. The basis of successful practice is excellent equipment, which is regularly updated, as well as highly qualified, experienced medical personnel: world famous doctors and professors work here for the benefit of patients.
In addition to its main goal of caring for patients, the hospital is also active in training and professional development of medical personnel, as well as in the field of public health care. The priority focus of the work is research activity, which allows the doctors to introduce the innovative diagnostic and therapeutic techniques into clinical practice.
A special feature of the hospital is also the diagnostics and treatment of rare diseases. State-of-the-art equipment and well-coordinated work of doctors of various medical specialties make it possible to timely recognize pathologies rarely encountered in medical practice and select the most effective therapy. Specialization in rare diseases include neurology, endocrinology, hematology/oncology, and rare autoimmune diseases.
The hospital has 1,410 beds for patient hospitalization. About 55,900 inpatients and more than 233,975 outpatients undergo treatment here annually. A large medical team, consisting of about 1,000 highly qualified doctors, as well as over 2,000 nursing staff take care of the patients' health. Each patient is guaranteed an individual approach and the most effective treatment in accordance with current clinical protocols.
It should be noted that the university hospital enjoys an impeccable reputation not only in Germany, but also far beyond its borders, including Arab countries, post-Soviet states, Great Britain and the United States. Patients from different parts of the world come here for high-quality treatment for diseases of any severity. The highest credit of patient confidence is the main indicator of the fruitful work of doctors.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
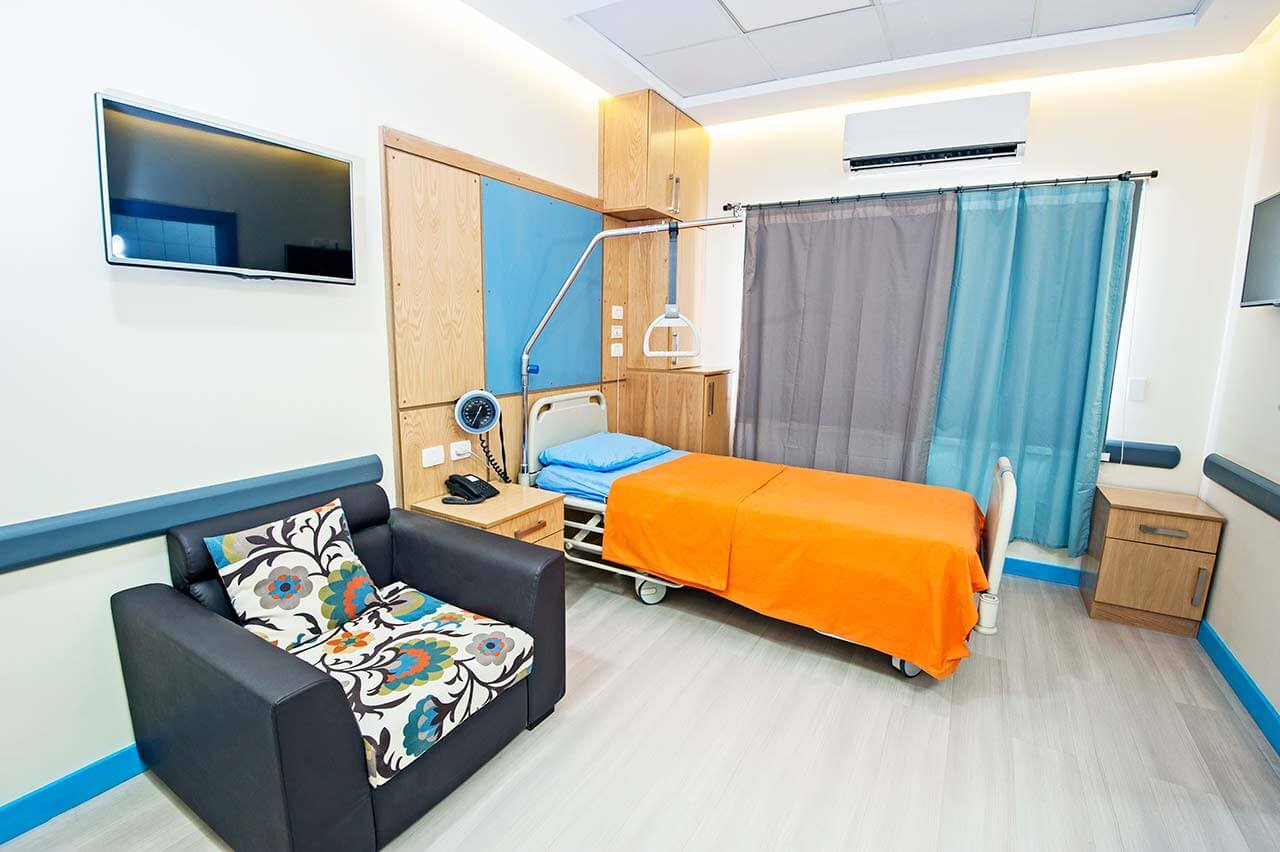
Patients rooms
The patients of the University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden live in comfortable rooms made in bright colors and equipped with everything necessary. The standard patient room includes an automatically adjustable bed, a bedside table with a sliding table, a wardrobe, a telephone and a TV. There is also Wi-Fi (free) in the patient rooms.
If desired, patients may live in enhanced comfort patient rooms. These patient rooms have a more sophisticated design, upholstered furniture and a safe for storing valuables.
Meals and Menus
The patients of the hospital are offered a tasty, healthy and varied three meals a day. The menu is based on local cuisine and seasonal food. If you for some reason do not eat certain products, please inform the medical staff of the hospital in advance, and you will be offered an individual menu. The nutrition provided in the hospital is certified in accordance with the quality standards of the German Nutrition Society (DGE) for catering in German hospitals.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Religion
The religious services are available upon request.
Accompanying person
Your accompanying person may stay with you in your patient room or at the hotel of your choice during the inpatient program.
Hotel
You may stay at the hotel of your choice during the outpatient program. Our managers will support you for selecting the best option.
The hospital offers a full range of laboratory diagnostic procedures (general, hormonal, tests for tumor markers, infections, antibodies, etc.), genetic tests, various modifications of ultrasound scans, CT scans, MRI and PET / CT, angiography, myelography, biopsy and other examinations. Treatment with medications, endoscopic and robotic operations, stereotaxic interventions is carried out here, modern types of radiation therapy are also used. The hospital offers patients all the necessary therapeutic techniques.
- Cochlear implantation
- Deep brain stimulation
- Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with green laser
- Da Vinci prostatectomy
- Bone marrow transplantation
These are head and neck tumors, hearloss, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, epilepsy, Parkinson disease, infertility, malignant tumors of the reproductive system, congenital anomalies of the genital organs and the urinary system, urinary incontinence, blood clotting disorders, leukemia and other pathologies.
- Otolaryngology (Center for Cochlear Implantation)
- Neurology and Epileptology
- Urology
- Oncology
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
About 1,000 highly qualified doctors work at the hospital.