The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the hospital
- Clinical history taking
- Review of available medical records
- Physical examination
- Laboratory tests:
- Complete blood count
- General urine analysis
- Biochemical analysis of blood
- Tumor markers
- Inflammation indicators (CRP, ESR)
- Coagulogram
- Ultrasound scan
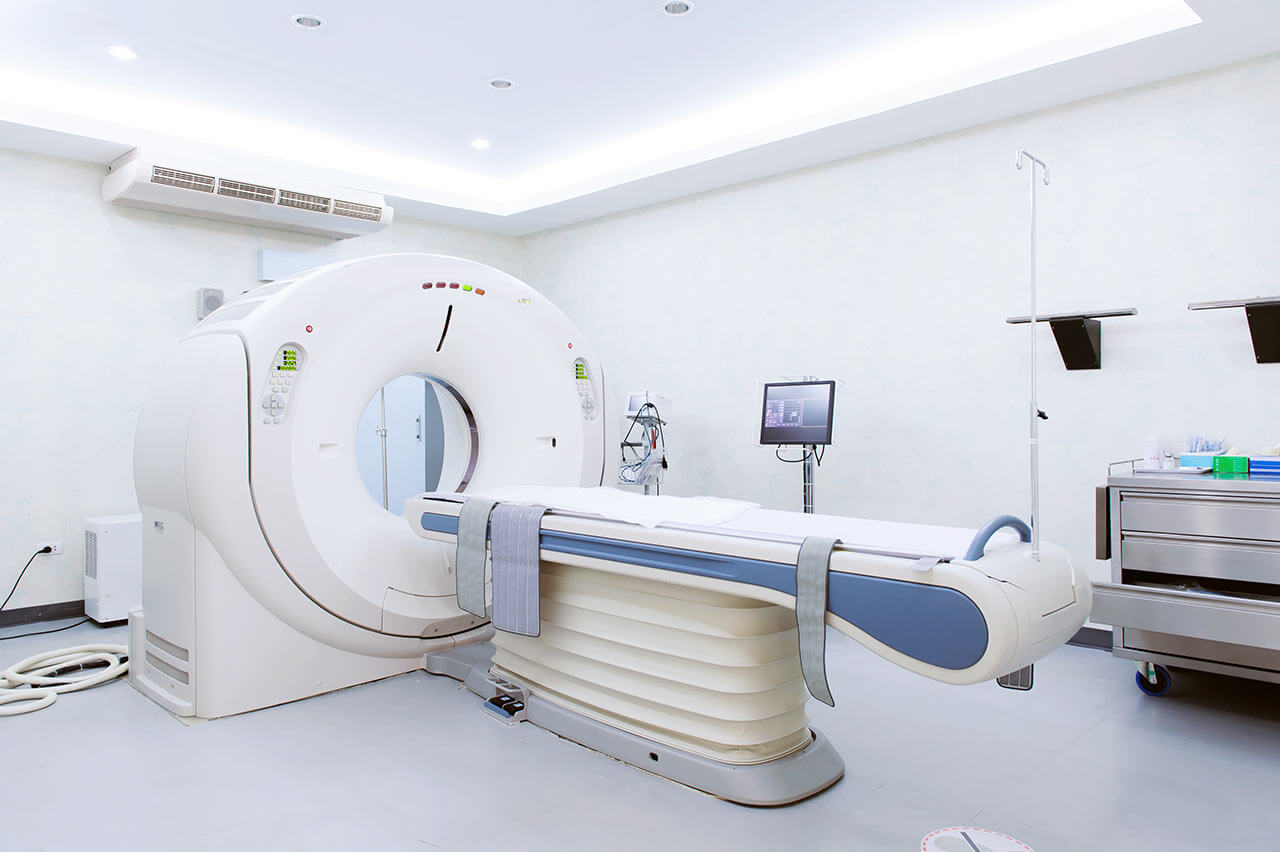
- CT scan / MRI
- Preoperative care
- Embolization or chemoembolization, 2 procedures
- Symptomatic treatment
- Cost of essential medicines
- Nursing services
- Elaboration of further recommendations
How program is carried out
During the first visit, the doctor will conduct a clinical examination and go through the results of the available diagnostic tests. After that, you will undergo the necessary additional examination, such as the assessment of liver and kidney function, ultrasound scan, CT scan and MRI. This will allow the doctor to determine which vessels are feeding the tumor and its metastases, as well as determine how well you will tolerate the procedure.
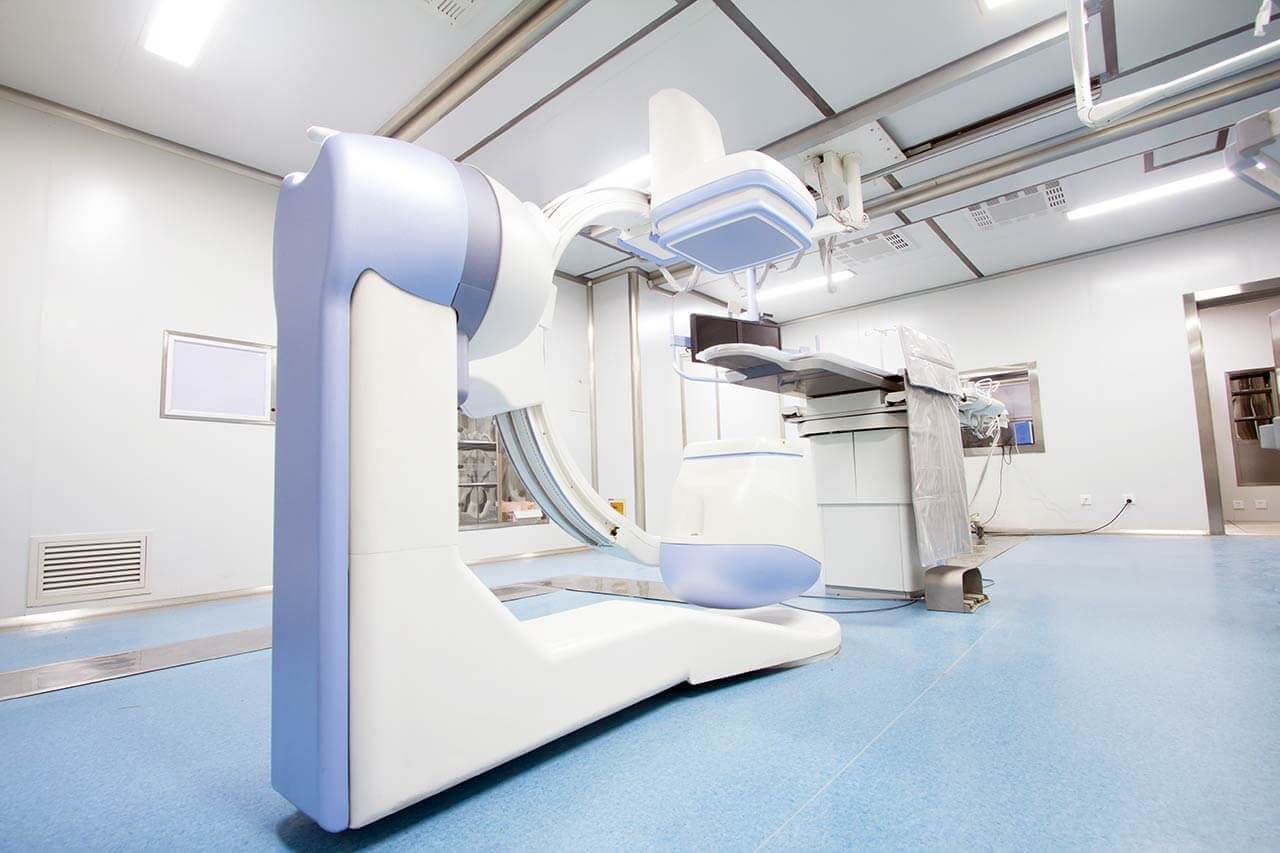
Chemoembolization begins with local anesthesia and catheterization of the femoral artery. The thin catheter is inserted through a few centimeters long incision of the blood vessel. The doctor gradually moves the catheter to the vessel feeding the primary tumor or its metastases. The procedure is carried out under visual control, an angiographic device is used for this. The vascular bed and the position of the catheter in it are displayed on the screen of the angiograph.
When the catheter reaches a suspected artery, a contrast agent is injected through it. Due to the introduction of the contrast agent, the doctor clearly sees the smallest vessels of the tumor and the surrounding healthy tissues on the screen of the angiograph. After that, he injects emboli into the tumor vessels through the same catheter.
Emboli are the spirals or the liquid microspheres. The type of embolus is selected individually, taking into account the diameter of the target vessel. When carrying out chemoembolization, a solution of a chemotherapy drug is additionally injected into the tumor vessel. Due to the subsequent closure of the vessel lumen with an embolus, the chemotherapy drug influences the tumor for a long time. In addition, the drug does not enter the systemic circulation, which allows doctors to use high doses of chemotherapeutic agents without the development of serious side effects. Chemoembolization leads to the destruction of the tumor or slowing down its progression.
After that, the catheter is removed from the artery. The doctor puts a vascular suture on the femoral artery and closes it with a sterile dressing. During chemoembolization, you will be awake. General anesthesia is not used, which significantly reduces the risks of the procedure and allows performing it on an outpatient basis, avoiding long hospital stay.
After the first procedure, you will stay under the supervision of an interventional oncologist and general practitioner. If necessary, you will receive symptomatic treatment. As a rule, a second chemoembolization procedure is performed in 3-5 days after the first one in order to consolidate the therapeutic effect. After that, you will receive recommendations for further follow-up and treatment.
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
According to the Focus magazine, the Department of Adult and Pediatric Urology, Andrology at the Charite University Hospital Berlin is one of the best medical facilities in Germany for prostate cancer treatment!
The department provides the full range of diagnostic and therapeutic services for men and women with diseases of the urinary system, representatives of the stronger sex with pathologies of the reproductive system, and children with congenital and acquired urological conditions. The department specializes in conservative and surgical treatment of malignant tumors of the male genitals, kidneys, and bladder. The specialists at the healthcare facility are proud of the status as a Training Center for Robotic Urological Surgery with certification by the European Association of Urology (EAU). Robotic surgery with the da Vinci system is an integral part of the daily clinical practice of the department's doctors, and the presence here of one of the best da Vinci surgery training centers in Europe testifies to the advanced experience of the department's medical team in this field. Together with the Department of Nephrology and the Department of Surgery, it is part of the Kidney Transplant Center, the largest of its kind in Germany. The unique feature of this center is that almost all operations to remove a kidney from a living donor are minimally invasive procedures. Men with andrological problems can also be treated in the department. Special attention is given to the treatment of erectile dysfunction, infertility, and hormonal imbalances.
The Head Physician of the department is Prof. Dr. med. Thorsten Schlomm. The doctor enjoys a reputation as a highly competent expert in minimally invasive and da Vinci robot-assisted surgery for prostate cancer. In his more than 15 years of clinical practice, he has performed more than 3,000 of the above surgical procedures. It is very important for the doctor not only to perform the operation as efficiently as possible but also to preserve potency. In addition to his successful clinical activities, Prof. Thorsten Schlomm works on scientific publications (he has almost 400 of them) and books and is a member of the German, European, and American Societies of Urology.
The department specializes in uro-oncology, providing conservative and surgical treatment for prostate cancer, testicular cancer, kidney cancer, bladder cancer, and urethral cancer. Prostate cancer is the most common malignancy in men. Most cases of oncopathology occur in men over the age of 65. The therapeutic process begins with a diagnostic evaluation that includes a digital rectal examination and a prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test. If PSA levels are elevated, the department performs transrectal ultrasound (TRUS)-guided prostate biopsy, MRI/ultrasound fusion-guided biopsy, transperineal biopsy, or micro-ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy. For maximum patient comfort, the biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. If the biopsy results are negative, additional imaging studies are performed: CT, MRI, bone scintigraphy, and PET-CT. The department offers all modern therapeutic methods – the healthcare facility is one of the largest centers for prostate cancer treatment in Germany, certified by the German Cancer Society (DKG). In most cases, the first-line treatment is surgery called a prostatectomy. When clinically indicated, prostatectomy is performed using the innovative da Vinci robotic system. Robotic procedures are characterized by low trauma and high precision, due to which potency and the function of the sphincter of the bladder can be preserved. In addition, the department is one of the few in Germany to use the NeuroSAFE technique in prostate cancer surgery, which allows surgeons to pinpoint the presence of tumor cells in the tissues involved in erection, thereby preserving erectile function. Surgery is complemented by conservative methods: hormone therapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy (external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy), and other types of treatment. Each patient is treated according to an individually developed regimen in accordance with current clinical protocols. The priority of the department's doctors is to achieve an effective therapeutic result, while it is important to provide the patient with a decent quality of life after the treatment.
Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) seek medical attention from the department almost every day. This condition is also one of the most common urological pathologies in men. Despite the fact that prostate adenoma is a benign neoplasm, it causes urinary problems and other symptoms. The department's team of urologists offers its patients effective conservative and surgical treatment methods, with the optimal therapeutic tactics being determined depending on the stage of the pathology and the severity of symptoms. At the early stages of prostate adenoma, the department's doctors prescribe drug therapy. At advanced stages, surgical treatment is recommended: thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP), Greenlight Laser laser vaporization of the prostate, transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), and REZUM water vapor prostate ablation. All of the above procedures are minimally invasive and require only a few days of hospitalization. The optimal procedure for each patient is selected after a personal consultation with the treating physician, based on the patient's clinical data and individual preferences.
The department has a highly professional team of pediatric urologists whose area of responsibility includes the treatment of phimosis, hypospadias, epispadias, hydrocele, varicocele, megaureter, ureterocele, duplicated kidney, enuresis, and other urological pathologies in young patients. Most of the diseases require reconstructive plastic surgery. Whenever possible, such surgeries are performed using minimally invasive surgical techniques, which allow for rapid recovery of the child in the postoperative period. In cooperation with nephrologists and pediatric urologists, the department's specialists successfully perform kidney transplants in children, including from living donors.
Andrology occupies an important place in the clinical practice of the department. Of particular interest in this area is the medical care for men with erectile dysfunction, hormonal imbalances, and infertility. Erectile dysfunction (ED) is the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for complete sexual intercourse. During the initial consultation, the andrologist studies the patient's medical history, since in many cases ED occurs against the background of diabetes mellitus, vascular pathologies, psychological problems, and other diseases. Next, the doctor conducts a clinical examination, an ultrasound scan of the penis, and hormonal tests. If there is a suspicion that ED is a secondary disease due to vascular pathology, a SKAT test is performed. This consists of injecting a drug into the cavernous bodies of the penis to stimulate an erection. Based on the diagnostic results, the patient is prescribed an optimal treatment plan: the department's therapeutic options include drug therapy, vacuum therapy, and penile prosthetics, with surgery being the last-line treatment and being recommended only if conservative therapy fails. It should be noted that the department's specialists regularly perform penile prosthetic surgery and have many years of experience in this field.
The range of medical services provided by the department includes the following:
- Urology
- Diagnostics and treatment of malignant urological diseases
- Diagnostics and treatment of prostate cancer
- Surgical treatment
- Prostatectomy using da Vinci robotic technology and open surgical techniques
- Conservative treatment
- High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) treatment
- Hormone therapy
- Radiation therapy: external beam radiation therapy and brachytherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of bladder cancer
- Surgical treatment
- Transurethral resection (Hexvix®)
- Partial cystectomy: open, minimally invasive, and robotic da Vinci surgery
- Radical cystectomy with ileal bladder reconstruction: open, minimally invasive, and robotic da Vinci surgery
- Conservative treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Immunotherapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of kidney cancer
- Surgical treatment
- Kidney resection: open, minimally invasive, and robotic da Vinci surgery
- Nephrectomy: open, minimally invasive, and robotic da Vinci surgery
- Ureterorenoscopy and local laser therapy or local resection of renal pelvic tumors through a percutaneous approach: open, minimally invasive, and robotic da Vinci surgery
- Conservative treatment
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Cryotherapy
- Drug therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of testicular cancer
- Surgical treatment
- Orchiectomy
- Residual tumor resection in the case of the development of metastases after the completion of chemotherapy
- Testicular prosthetics
- Conservative treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of penile cancer
- Surgical treatment
- Partial penectomy
- Radical penectomy
- Inguinal and pelvic lymph node removal: open, minimally invasive, and robotic da Vinci surgery
- Conservative treatment
- Chemotherapy
- Radiation therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of prostate cancer
- Diagnostics and treatment of benign urological diseases
- Diagnostics and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Surgical treatment
- Thulium laser enucleation of the prostate (ThuLEP)
- Greenlight Laser vaporization of the prostate
- Transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP)
- REZUM water vapor prostate ablation
- Conservative treatment
- Drug therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of hydrocele and varicocele
- Surgical treatment
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of Peyronie's disease
- Surgical treatment
- Penile corporoplasty
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of urinary incontinence in women
- Surgical treatment
- TVT and TVT-O sling procedures
- Colposuspension
- Botox injections
- Sacral neurostimulation
- Conservative treatment
- Pelvic floor muscle training
- Pelvic floor electrical stimulation
- Biofeedback
- Drug therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of urinary incontinence in men
- Surgical treatment
- Advance Band sling procedures
- AMS and VICTOR artificial sphincter implantation
- Conservative treatment
- Pelvic floor muscle training
- Pelvic floor electrical stimulation
- Biofeedback
- Drug therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of urolithiasis
- Surgical treatment
- Ureterorenoscopy
- Percutaneous nephrolitholapaxy
- Conservative treatment
- Extracorporeal shock wave therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of urological diseases in children
- Open surgical procedures
- Kidney transplant, including from a living donor
- Reconstructive plastic surgery for hypospadias and epispadias
- Reconstructive urethral plastic surgery
- Orchidopexy
- Surgical correction of hydrocele and varicocele
- Surgery for megaureter, ureterocele, and duplex kidney
- Renal pelvic plastic surgery
- Nephrectomy
- Varicocelectomy
- Bladder enlargement surgery
- Minimally invasive surgical procedures
- Kidney harvesting surgery from a living donor
- Nephrectomy
- Pyeloplasty
- Orchiopexy
- Surgery for megaureter, ureterocele, and duplex kidney
- Varicocelectomy
- Open surgical procedures
- Diagnostics and treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Kidney transplant surgery
- Diagnostics and treatment of malignant urological diseases
- Andrology
- Diagnostics and treatment of erectile dysfunction
- Surgical treatment
- Penile implant surgery
- Conservative treatment
- Drug therapy
- Vacuum therapy
- Surgical treatment
- Diagnostics and treatment of hormonal imbalances in men
- Testosterone replacement therapy
- Diagnostics and treatment of male infertility
- Diagnostics and treatment of erectile dysfunction
- Diagnostics and treatment of other urological and andrological conditions
Curriculum vitae
Higher Education and Professional Career
- 1995 - 2001 Medical studies, Georg August University of Goettingen (Germany); professional training in urology at the University Hospital Goettingen and the University Hospital Hamburg.
- 2003 - 2007 Assistant Physician, Department of Urology, University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf, with clinical and scientific specialization in the diagnosis and treatment of prostate cancer.
- 2007 - 2018 Managing Physician, Department of Urology, Martini Clinic at the University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf.
- 2007 - 2018 Coordinator of the Prostate Cancer Center certified by the German Cancer Society (DKG), Martini Clinic at the University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf.
- 2009 Habilitation in Urology. Subject: "High-throughput clinical validation of prognostic and therapeutic biomarkers in prostate cancer using the chromosomal microarray analysis method".
- 2010 - 2018 Scientific Director of the Martini Clinic at the University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf.
- 2011 W3 Professorship, Department of Urology, University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf.
- Since 2016 Associate Professor for Molecular Urology, Center for Cancer Biomarkers (CCBIO), University of Bergen, Norway.
- Since 2018 W3 Professorship and Head of the Department of Adult and Pediatric Urology, Andrology at the Charite University Hospital Berlin.
Memberships in Professional Societies
- German Society of Urology (DGU).
- European Association of Urology (EAU).
- American Urological Association (AUA).
- American Association for Cancer Research (AACR).
Clinical Focuses
- Prostate cancer treatment: open and robotic (da Vinci) nerve-sparing prostatectomy.
- Metastatic prostate cancer therapy.
- Cancer gene therapy.
Research Focuses
- Cancer research.
- Clinical Coordinator of the International Cancer Genome Consortium and the Cancer Genome Atlas.
Photo of the doctor: (c) Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin
Sources:
About hospital
According to the reputable Focus magazine, the Charite University Hospital Berlin ranks 1st among the best healthcare facilities in Germany!
The hospital is one of the largest and leading university medical complexes in Europe, and also consistently holds leading positions in the international medical arena. The Charite operates on the basis of the Faculty of Medicine of the Free University of Berlin and the Humboldt University of Berlin. Patients are offered modern diagnostics and treatment with the very latest methods, many of which were developed by professors and scientists of the medical complex. More than half of all German Nobel Prize winners in medicine and physiology, such as Emil von Behring, Robert Koch, and Paul Ehrlich, studied and worked at the Charite University Hospital Berlin. The medical complex includes more than 100 specialized departments and institutes, which helps to ensure that patients receive care in all existing medical specialties. The hospital has exceptional experience in treating complex clinical cases.
Each year, the hospital treats more than 137,800 inpatients and more than 787,700 outpatients. The hospital has a bed capacity of 3,293 beds. A huge medical team consisting of 5,670 scientists and doctors and more than 6,000 nurses work for the benefit of the patients. The main task of all specialists of the medical facility is to restore the patient's health or save his life in critical cases. The hospital has a friendly atmosphere where every patient feels care, respect and empathy.
The Charite University Hospital Berlin is generously funded by the German government, which is why it offers patients the latest generation of excellent equipment and comfortable infrastructure. The Charite medical complex is equipped with da Vinci robotic surgery systems, laser technologies, equipment for endovascular catheter-based interventions, neuronavigation devices, intraoperative monitoring systems, equipment for proton therapy available only in the most advanced medical centers in the world, and many other technologies. All these resources, combined with the experience and professional skills of the hospital's doctors, are the key to providing the most effective and safe treatment in accordance with the highest international medical standards.
The hospital is recognized with a huge number of quality certificates, including DIN EN ISO 9001:2015, certificates from the German Cancer Society (DKG), the German Society for General and Visceral Surgery (DGAV), the German Society for Thoracic Surgery (DGT), the German Hernia Society (DHG), and the ERAS Society.
The Charite University Hospital Berlin is a benchmark in the European healthcare system. Patients therefore receive impeccable medical service, quality care, and personalized service that puts the patient and their individual needs first.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
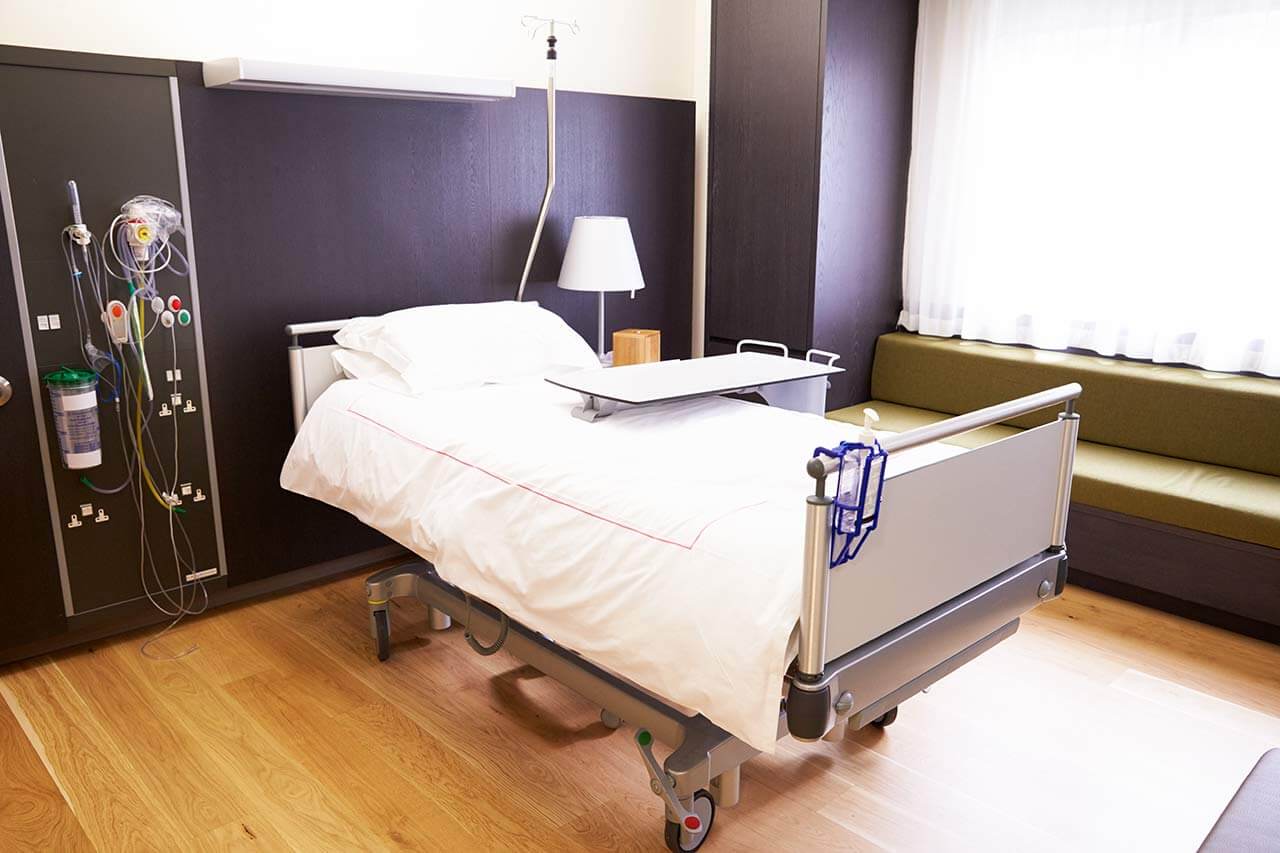
Patients rooms
The patients of the Charite University Hospital Berlin live in comfortable rooms made of modern design. Each room is equipped with an ensuite bathroom with a toilet and a shower. The standard room furnishing includes an automatically adjustable bed, a bedside table, a wardrobe for storing clothes, a table and chairs for receiving visitors, and a TV. If desired, Wi-Fi access can be provided. The hospital also offers enhanced-comfort rooms.
Meals and Menus
The patient and his accompanying person have a daily choice of three menus. If for any reason, you do not like the food, you will be offered an individual menu. Please inform the medical staff about your dietary preferences before the treatment.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Religion
Religious services are available upon request.
Accompanying person
During the inpatient program, an accompanying person may stay with you in a patient room or at the hotel of your choice.
Hotel
During the outpatient program, you can live at a hotel of your choice. Managers will help you to choose the most suitable options.
The hospital offers a full range of laboratory tests (general, hormonal, tests for infections, antibodies, tumor markers, etc.), genetic tests, various modifications of ultrasound scans, CT scans, MRI and PET / CT, angiography, myelography, biopsy and other examinations. Treatment with medications, endoscopic and robotic operations, stereotaxic interventions is carried out here, modern types of radiation therapy are also used. The hospital offers patients all the necessary therapeutic techniques.
- Proton therapy
- CyberKnife treatment
- Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC)
- PSMA therapy with Lutetium-177
- Joint replacement in adults and children
These are oncological diseases, benign neoplasms of the brain and spinal cord, heart valve defects, diabetes mellitus and its complications, joint diseases and other pathologies.
- Neurosurgery
- Oncology
- Plastic and reconstructive surgery
- Interventional radiology
- Proton therapy (Proton Therapy Center BerlinProtonen)
The medical team includes more than 4,225 highly qualified scientists and doctors.