The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- review of medical records
- physical examination
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- general urine analysis
- biochemical analysis of blood
- inflammation indicators (CRP, ESR)
- indicators of blood coagulation
- neurological examination
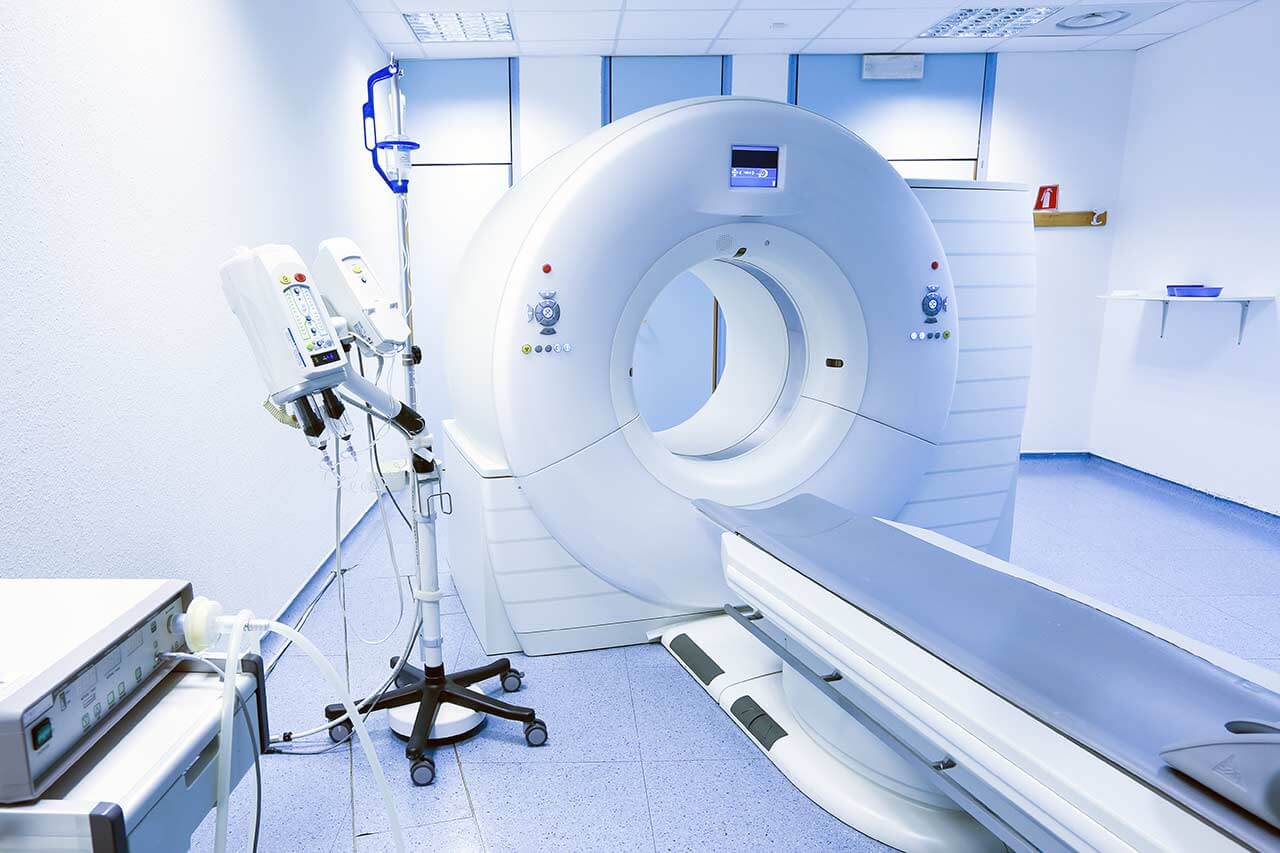
- CT/MRI scan
- neuropsychological tests (if indicated):
- ENMG (electroneuromyography)
- EEG (electroencephalography)
- SEPs (somatosensory evoked potentials)
- VEPs (visually evoked potentials)
- BAEP tests (brainstem auditory evoked potentials)
- preoperative care
- MRI-guided laser ablation of brain metastases
- postoperative MRI control
- symptomatic treatment
- control examinations
- the cost of essential medicines and materials
- nursing services
- full hospital accommodation
- developing of further guidance by specialists
in oncology and radiotherapy
How program is carried out
During the first visit, the physician will conduct a clinical examination and neurological examination, and go through the results of the available diagnostic tests. After that, you will undergo the necessary additional examination, such as the laboratory blood and urine tests, MRI scan with obtaining 3D images and creating volumetric images of the whole brain. Based on the results of an additional examination, the physician will clarify the localization of brain metastases. After that, the preparation according to the preoperative standard will begin.
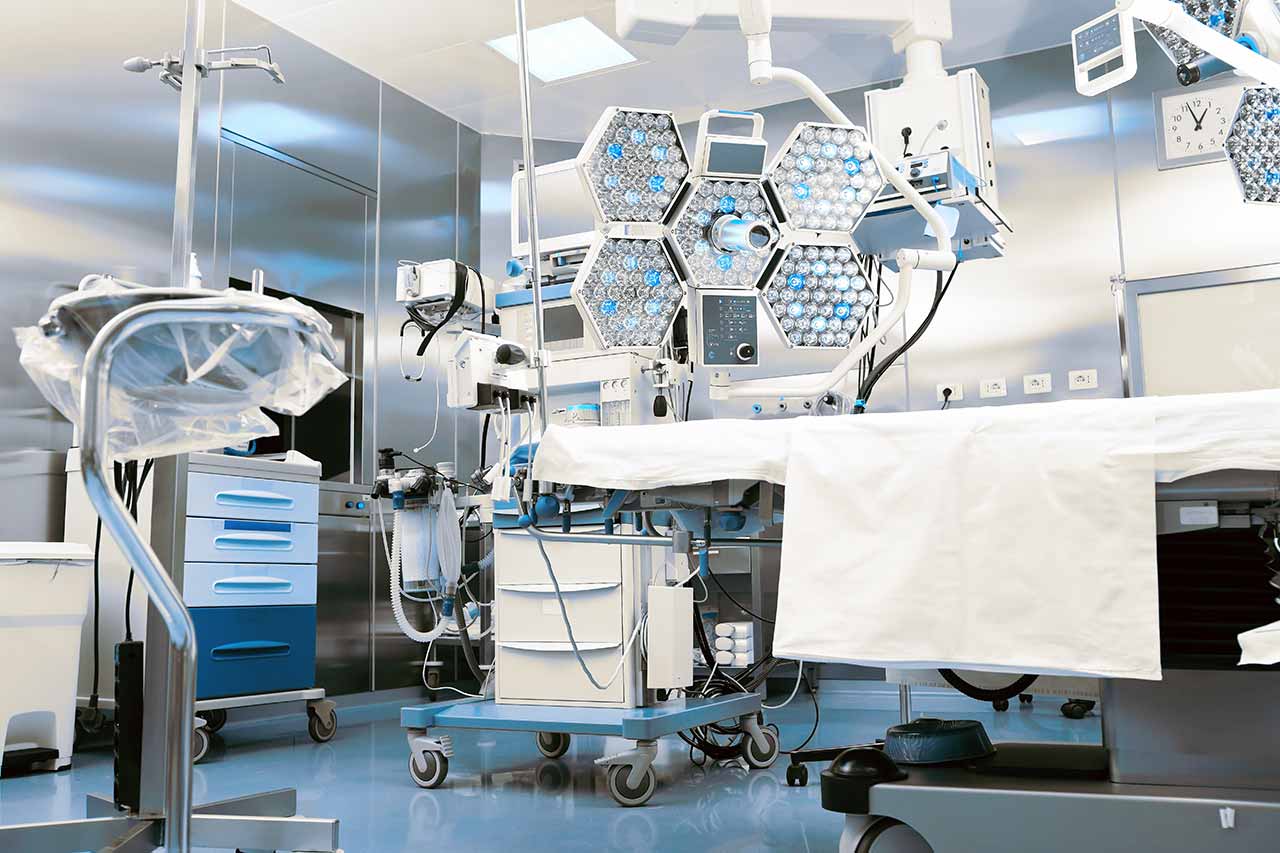
Laser ablation of metastases begins with the formation of access to the brain. When using a catheter with a laser fiber, a hole with a diameter of 3.2 mm is sufficient for this. The miniature size and flexibility of the catheter help preserve healthy brain tissue.
When the catheter reaches metastasis, energy is delivered through the laser fiber. Under the influence of high temperature, metastases are destroyed. The procedure is guided by real-time MRI. Surgeons also assess the temperature of healthy brain tissue using thermographic images to avoid overheating.
After the completion of the operation, you will be transferred to the ward, under the round-the-clock supervision of doctors and nurses. In several days, the attending physician will evaluate the results of the postoperative MRI scans, schedule the date of discharge from the hospital and give you detailed recommendations for further follow-up and treatment.
Required documents
- Medical records
- MRI/CT scan (not older than 3 months)
- Biopsy results (if available)
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Neurosurgery and Spinal Surgery at the Beta Clinic Bonn offers the full range of modern surgical procedures for patients with diseases of the brain, spinal cord, spine, and peripheral nervous system. The department has state-of-the-art equipment, including navigation systems, monitoring devices, surgical microscopes, intraoperative X-ray diagnostic systems, angiography systems, and laser equipment. In addition, a system for minimally invasive stereotactic interventions has been installed in the department's operating room. The department's neurosurgeons use the latest microsurgical and endoscopic techniques in their work. The medical facility is one of only three in Europe to successfully use the VISUALASE™ device for MRI-guided laser ablation to treat epilepsy. This minimally invasive procedure is highly effective and represents a real breakthrough in epilepsy surgery. The department's neurosurgeons always strive to provide the patient with optimal medical care. They talk in detail about each stage of treatment and are happy to answer the patient's questions. Neurologists and specialists in the field of neuroradiology are often involved in the therapeutic process, which guarantees a comprehensive approach to treatment.
The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Thomas Gasser. According to the prestigious Focus magazine, Prof. Gasser is one of the best neurosurgeons in Bonn. In addition, according to the Jameda website rating, the doctor ranks among the top five neurosurgeons in Bonn based on patient reviews.
The department's team of neurosurgeons focuses on patients with brain diseases, such as tumors, dystonia, essential tremor, trigeminal neuralgia, headaches, dizziness, tinnitus, and other pathologies. The treatment of brain tumors is a rather complex task because it is important for doctors not only to remove the neoplasm but also to preserve the integrity of healthy anatomical structures of the brain. Among benign brain neoplasms, acoustic neuromas and meningiomas are most often encountered in the clinical practice of the department's neurosurgeons, and among malignant ones, these are gliomas, astrocytomas, and metastases of lung, colon, or breast cancer, etc. In many cases, a patient is unaware of the presence of a tumor for a long time, since there are no symptoms in the early stages. As the tumor grows, complaints such as headaches, epileptic seizures, difficulty concentrating, chronic fatigue, speech disorders, movement disorders, etc. may appear. Diagnostics for a suspected brain tumor include imaging tests, such as CT and/or MRI. As a rule, contrast-enhanced MRI is preferred, while a CT scan is used for planning tumor resection surgery. A biopsy is an integral part of the diagnostic process. As for the treatment of brain tumors, the goal of a neurosurgical intervention is to completely remove the tumor if possible. The specialists at the medical facility perform brain tumor resections using microsurgical techniques, which help preserve the integrity of the vital anatomical structures of the brain. During operations, navigation systems and neuromonitoring are used, which contributes to the high safety of surgical treatment. Stereotactic surgery is successfully used to remove brain tumors located in hard-to-reach places. In most cases, patients with malignant brain tumors are additionally prescribed chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
The department can boast of its successful experience in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. The pathology is a progressive neurological disorder that impairs body movement, coordination, and especially the ability to control muscles. This is due to the impairment of the excitability of brain neurons that control movement and coordination functions. Initial symptoms may include hand tremors and movement problems. Later, painful muscle cramps and balance problems may appear. Parkinson's disease usually develops after the age of 50 and is one of the most common neurological diseases. Patients with suspected Parkinson's disease undergo comprehensive diagnostics that include a neurological examination, motor coordination tests, balance tests, cognitive function tests, and brain MRI and PET scans. Parkinson's disease is still an incurable disease, but the department's neurosurgeons have many methods for its control and progression prevention. The first-line treatment is drug therapy, which is complemented by physiotherapy, occupational therapy, and speech therapy. Patients with advanced stages of Parkinson's disease are offered deep brain stimulation. The technique involves the implantation of electrodes in the area of the brain that is responsible for motor functions. The stimulator generates electrical impulses to activate it and eliminate the symptoms of Parkinson's disease. Stimulator implantation is a stereotactic intervention (a minimally invasive technique) under local anesthesia. Surgical manipulations are planned using CT and MRI scans. The department's neurosurgeons regularly perform deep brain stimulation, so patients can be sure that they will get the best result.
The team of the department's neurosurgeons admits patients with diseases of the peripheral nervous system. Particular attention is paid to the care of patients with carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome, Morton's neuroma, and traumatic injuries of the peripheral nerves. Diagnostic options for examining the peripheral nervous system include electrophysiological studies, peripheral nerve conduction testing, magnetic resonance imaging, and other tests. The treatment of pathologies of the peripheral nerves can be either conservative or surgical, depending on the stage and severity of the disease. The department's neurosurgeons perform surgical treatment of peripheral nerve diseases, including decompression surgery (neurolysis), reconstructive surgical procedures, and surgery to remove peripheral nerve tumors.
A separate focus of the department's work is spinal surgery. In this area, the neurosurgeons of the medical facility perform operations for spinal disc herniation, spondylolisthesis, vertebral fractures, spinal stenosis, chronic back pain, and facet syndrome. Surgery for cervical and lumbar disc herniation is the most demanded in the department. The integral diagnostic methods for a patient with suspected spinal disc herniation are the study of anamnesis, a clinical examination, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). It is worth noting that the department uses an innovative open MRI system, which is a great advantage for patients with a fear of closed spaces. Based on the diagnostic results, the department's specialists assess the advisability of the operation because a good result for spinal disc herniation can often be achieved with the help of conservative therapy. If a decision is made to perform an operation, the department offers three options for low-traumatic and effective interventions: CT-guided microtherapy, a microsurgical intervention, and an endoscopic intervention. During microtherapy, a thin needle is inserted into the affected area of the spine under CT guidance to inject decongestants and painkillers. The procedure of microtherapy should be repeated 2-3 times with an interval of a week. During a microsurgical intervention, the doctor makes small incisions. This treatment is also sparing and safe. Endoscopic surgery for a herniated disc does not require any tissue incisions, and natural bone holes in the spine are used as a surgical approach for inserting an endoscope. This version of the operation is also minimally traumatic, but at the same time, it has a high efficiency.
The department performs the diagnostics and treatment of the following diseases:
- Brain diseases
- Benign and malignant brain tumors
- Dystonia
- Essential tremor
- Trigeminal neuralgia
- Chronic headaches
- Dizziness
- Parkinson's disease
- Tinnitus
- Peripheral nerve diseases
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Cubital tunnel syndrome
- Morton's neuroma
- Traumatic injuries of peripheral nerves
- Spinal diseases
- Cervical and lumbar disc herniation
- Spondylolisthesis
- Vertebral fractures
- Spinal stenosis
- Chronic back pain
- Facet syndrome
- Other neurological disorders
The department's surgical options include:
- Surgery for brain diseases
- Microvascular decompression (Jannetta procedure) for trigeminal neuralgia
- Microsurgical interventions for benign and malignant brain tumors
- MRI-guided laser ablation with the VISUALASE™ device for epilepsy (an innovative technique)
- Microtherapy for chronic headaches and dizziness caused by spinal diseases
- Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson's disease, dystonia, and essential tremor
- Surgery for diseases of the peripheral nervous system
- Decompression operations (neurolysis)
- Reconstructive interventions
- Surgery to remove peripheral nerve tumors
- Surgery for spinal diseases
- CT-guided microtherapy, microsurgical and endoscopic interventions for cervical and lumbar disc herniation
- Minimally invasive endoscopic abrasion for herniated discs
- Intervertebral disc replacement surgery for hernias
- Decompression for spinal stenosis
- Spinal cord stimulation for chronic back pain
- Spinal stabilization (spondylodesis) for spondylolisthesis
- Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty for vertebral fractures
- Other surgical interventions
Curriculum vitae
Prof. Thomas Gasser studied medicine at the Semmelweis University in Budapest, and he also trained at the University Hospital Essen and repeatedly trained abroad. He has served as a visiting physician at the Groote Schuur Hospital in Cape Town. Having defended his thesis on epidural scarring after an intraspinal intervention, he received admission to medical practice. This was followed by preparation for board certification and habilitation on the development and clinical significance of functional magnetic resonance imaging in neurosurgery.
Prof. Thomas Gasser founded the Faculty of Functional Neurosurgery and Intraoperative Imaging at the Goethe University in Frankfurt (Germany), and since 2008 he has also held a position at the Faculty of Functional Neurosurgery at the University Hospital Essen.
The priority of the professor's medical practice is the use of modern therapeutic methods for treating pain syndromes and movement disorders (for example, spinal cord stimulation and deep brain stimulation).
Prof. Gasser's scientific activity is focused on the application of sophisticated imaging techniques in neurosurgery. In 2005, he was awarded the International Exchange Grant from the German and Japanese Neurosurgical Societies, which enabled him to implement a successful research project at the Tokyo Women's Medical University (Japan).
Prof. Gasser is the author and co-author of more than 130 scientific publications. He has two patents for medicines, and he regularly lectures at international congresses. In addition, he is a Scientific Advisor and Member of the Scientific Advisory Board of Medtronic Navigation, Louisville, USA. He is also a Member of several specialized associations, including the German Society of Neurosurgery, World Congress of Neurosurgery (WCNS), and the World Society for Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery (WSSFN). Since 2018, Prof. Gasser has been a Member of the Leopoldina, the German National Academy of Sciences.
Photo of the doctor: (c) Beta Klinik Service-, Verwaltungs- und Forschungs- GmbH
About hospital
The Beta Clinic Bonn is a modern private healthcare facility with 20 specialized departments. In addition, the clinic cooperates with 30 independent doctors of various specializations, most of whom have their own private practices. The doors of the clinic first opened for patients in 2008. Since that time, the medical facility has expanded significantly and achieved outstanding success. It harmoniously combines state-of-the-art equipment, high levels of competence among doctors, and comfortable infrastructure. All these possibilities make it possible to provide patients with high-quality medical care in accordance with modern European standards. The work of the medical team at the clinic is based on the following principle: "Our task is to take care of the health of patients." The clinic provides comprehensive treatment, taking into account the individual needs and wishes of each patient.
The hospital has an excellent diagnostic base: rooms for instrumental diagnostics, imaging tests, and endoscopic procedures. The medical complex also has in-house laboratories with advanced equipment. The clinic's doctors have the opportunity to perform comprehensive diagnostics in the shortest possible time and detect the slightest pathological changes in the work and structure of the internal organs. When considering the diagnostic results in complex clinical cases, physicians from related specialties are often involved in the process so that all important aspects are taken into account when developing a treatment regimen for a patient.
The therapeutic options at the clinic are quite diverse. At the same time, doctors always strive to keep pace with innovations, carrying out treatment using the most modern and sparing techniques. The operating rooms at the clinic have advanced computer equipment, navigation devices, monitoring systems, surgical microscopes, special tools, and equipment for laparoscopic and endoscopic interventions, as well as laser systems. The clinic also has an in-house Rehabilitation Center, where patients undergo physiotherapy and therapeutic exercises.
The clinic is expanding more and more every year. Innovative developments in diagnostics and treatment are immediately introduced here. It is worth noting that the clinic is a pioneer in Germany in advanced laser treatment for epilepsy. The therapy was implemented into clinical practice in 2019 and has been successfully applied here since then.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
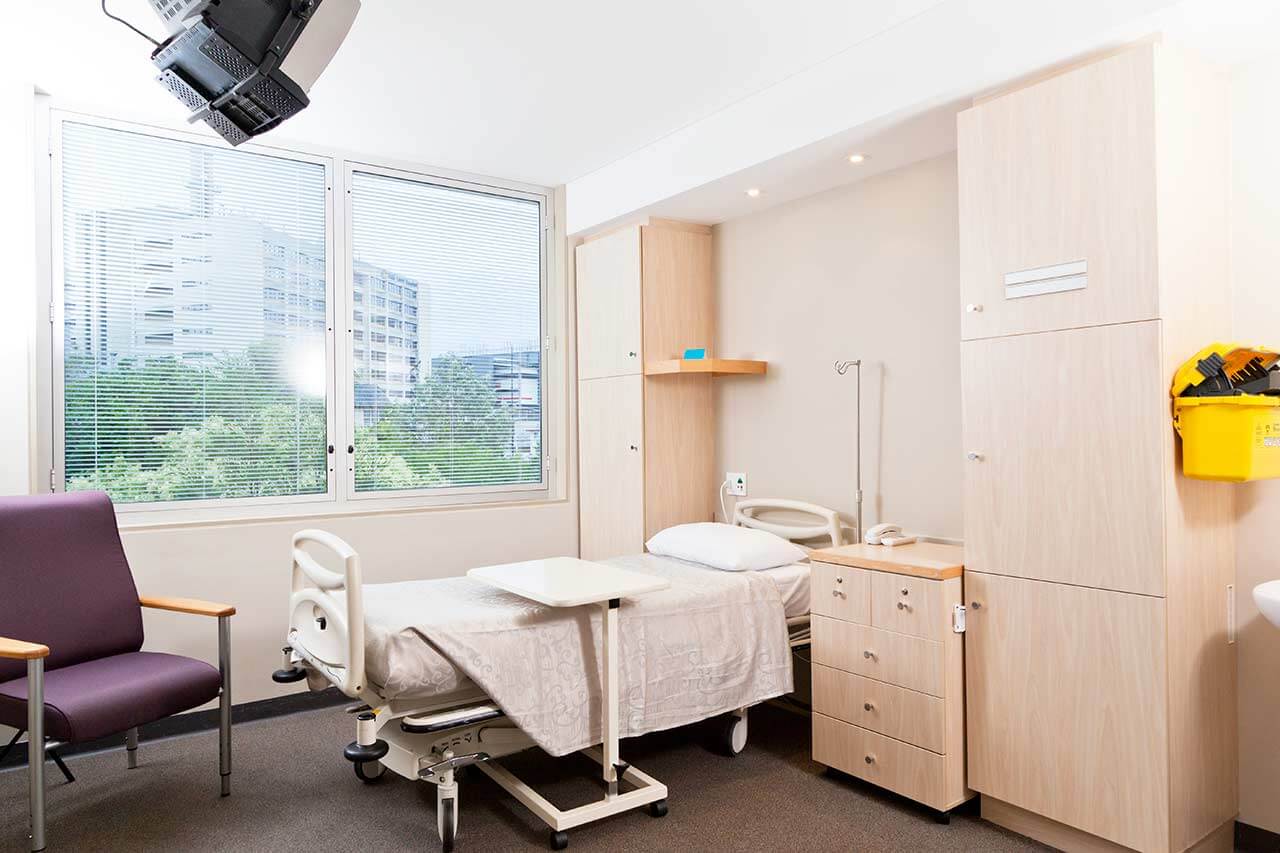
Patients rooms
The patients of the Beta Clinic Bonn live in comfortable single rooms. Each room has a separate bathroom with a shower and toilet. The rooms have a modern design and meet the standards of a high-class hotel. For the convenience of patients, the rooms are equipped with electrically adjustable beds, air conditioning, satellite and Internet TV, a telephone, and Wi-Fi.
The clinic also offers accommodations in enhanced comfort rooms. Such patient rooms have a more refined design. In addition, they are very spacious. Enhanced comfort rooms have a minibar, daily fresh fruit, and a special dinner menu. Most windows of the clinic's patient rooms offer a beautiful view of the Rhine River and beautiful green landscapes.
Meals and Menus
The patients of the clinic are offered balanced, delicious food: a buffet breakfast, a hearty three-course lunch, and a light dinner. Also, for dinner, one can taste special offers from the chef at the hospital restaurant, which, if desired, can be served to the patient room.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Accompanying person
Your accompanying person may stay with you in your patient room or at the hotel of your choice during the inpatient program.
Hotel
You may stay at the hotel of your choice during the outpatient program. Our managers will support you for selecting the best option.
In the immediate vicinity of the clinic is the Kameha Grand, a five-star hotel. The exterior and interior of the hotel impress with their beauty. In addition, the hotel is famous for its excellent service. The hotel is located on the banks of the Rhine and offers picturesque views from its windows.