About the Department of Neurology and Epileptology at Hospital Kassel
The Department of Neurology and Epileptology at the Hospital Kassel offers the full range of medical services for the effective detection and treatment of pathologies of the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord), peripheral nervous system and muscles. The treatment of patients with epilepsy is of particular interest to the department's doctors. The priority focuses of the department's clinical practice also include stroke treatment, which is carried out within a specialized Stroke Unit – the best in the State of Hesse. In addition, the department's team of neurologists is distinguished by outstanding success in the treatment of inflammatory and infectious diseases of the nervous system, dystonia, dementia and neuromuscular diseases. The department has at its disposal state-of-the-art medical equipment, which makes it possible to establish a diagnosis with high accuracy and provide timely treatment with maximum efficiency. The high professionalism of the department's specialists allows them to competently combine the very latest treatment methods available in the department to achieve a favorable treatment outcome. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Julian Bösel.
Stroke is one of the most common and dangerous neurological disorders, and therefore the department has a modern Stroke Unit, the medical team of which has colossal experience and excellent technical capabilities to provide emergency care to patients with this pathology. The Stroke Unit of the department is designed for 14 beds, each of which is equipped with a progressive monitoring system that ensures continuous monitoring of blood pressure, electrocardiography indicators and blood oxygen levels. The specialists of the Stroke Unit provide emergency medical care around the clock. This is especially important in the case of admission of patients in the so-called "golden hour", when the effectiveness of therapeutic measures is maximally high and allows avoiding irreversible processes in the body. After stabilizing the patient's condition, he is transferred to the Post-Stroke Unit, where he undergoes the following stages of treatment aimed at preventing repeated strokes. At this stage, the patient undergoes secondary prevention, which involves taking medications to improve blood flow or anticoagulants, lipid-lowering drugs, as well as drugs to lower blood pressure. In addition, physiotherapists, occupational therapists and speech therapists work intensively with the patient. It is worth noting that the department's Stroke Unit is the largest and best in the State of Hesse, while the highest quality of medical care in it has been awarded by the certificate of the German Stroke Society.
The neurologists working in the department regularly deal with the treatment of patients with epilepsy of various origins. The treatment of this disease can be provided both on an outpatient and inpatient basis. When admitted to the department, the patient undergoes an initial consultation followed by the comprehensive diagnostics and assessment of status epilepticus. The diagnostics involves not only routine studies such as electroencephalography and sleep-deprived EEG tests, but also long-term video-EEG monitoring and examinations using a portable EEG apparatus. Particular attention is paid to pregnant women with epilepsy. The treatment program is developed individually for each patient, taking into account the frequency and intensity of epileptic seizures, the characteristics of the patient's body and his general state of health. The department also conducts vagus nerve stimulation for drug-resistant epilepsy. Whenever required, the specialists from related medical fields are involved.
The department also demonstrates excellent results in the treatment of such complex neurological disorders as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson's disease, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, polyneuropathy, normal pressure hydrocephalus, idiopathic intracranial hypertension, dementia, meningitis, encephalitis and others. In the case of a severe course of the disease, the patient requires hospitalization, while the patients with a stable condition can be treated outpatiently. The treatment is based on drug therapy with the latest generation drugs. The department's doctors provide each patient with an individual treatment regimen, taking into account the specific clinical indications and the rate of progression of the disease.
The department specializes in the diagnostics and treatment of the following neurological disorders:
- Stroke
- Epilepsy
- Inflammatory diseases of the central and peripheral nervous system, including multiple sclerosis, inflammatory polyneuropathies
- Infectious diseases of the nervous system
- Meningitis
- Encephalitis
- Neuroborreliosis
- Parkinson's disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Myasthenia gravis and other muscle diseases
- Normal pressure hydrocephalus
- Idiopathic intracranial hypertension
- Dementia
- Diseases of the peripheral nervous system, including compression syndromes
- Other diseases of the nervous system
The department's range of medical services includes:
- Diagnostics
- Electrophysiological studies
- Electroencephalography
- Electromyography
- Electronystagmography
- Recording of somatosensory, auditory and visual evoked potentials
- Extended electroencephalography
- Sleep-deprived EEG test
- Continuous EEG monitoring
- Long-term video EEG monitoring
- Neurosonography
- Parenchymal ultrasound
- Doppler sonography and duplex sonography of the extra- and intracranial arteries supplying the brain
- Intensive neuromonitoring
- Intracranial pressure measurement
- Cerebral perfusion pressure measurement
- Cerebral oxygenation monitoring
- Cerebral oximetry using near-infrared spectroscopy
- Pupillometry
- Cerebrospinal fluid testing
- Neuropsychological testing
- Imaging studies of the brain and spinal cord (in collaboration with the Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Neuroradiology)
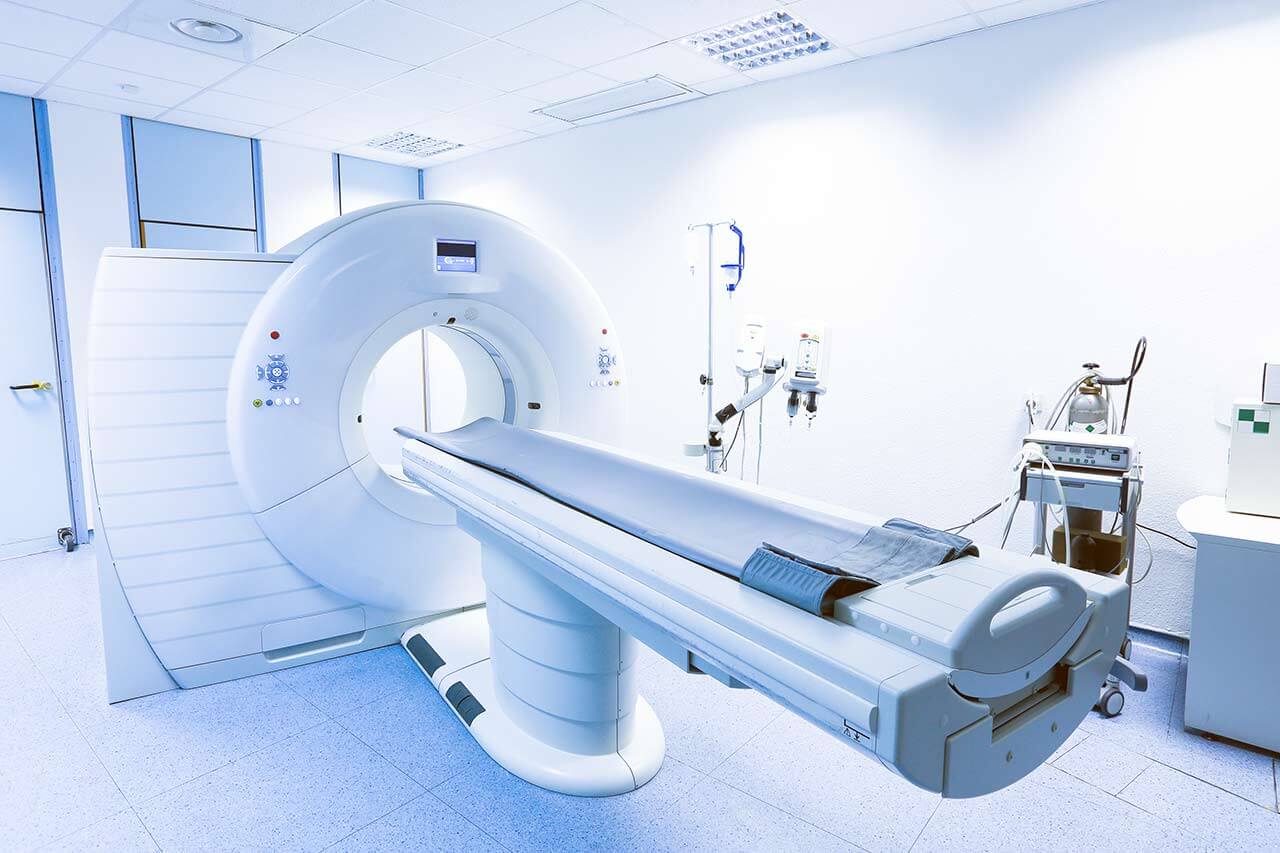
- Computed tomography
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Digital subtraction angiography
- Biopsy
- Electrophysiological studies
- Treatment
- Emergency neurological care
- Intensive neurological care
- Medical treatment with modern drugs
- Botulinum toxin injections (for example, for the treatment of focal dystonia, hemifacial spasm, some forms of spasticity)
- Other diagnostic and therapeutic options
Photo of the doctor: (c) Klinikum Kassel