The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- case history collection
- general clinical examination
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- general urine analysis
- biochemical analysis of blood
- TSH-basal, fT3, fT4
- tumor markers (thyroglobulin (TG),
TG antibodies (TgAb)) - indicators of inflammation
- indicators of blood coagulation
- ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland
- thyroid scintigraphy
- radioiodine therapy
- symptomatic treatment
- cost of essential medicines
- nursing services
- stay in the hospital with full board in 2-bed room
- elaboration of further recommendations
How program is carried out
During the first visit, the doctor will conduct a clinical examination and go through the results of the available diagnostic tests. After that, you will undergo the necessary additional examination, such as the assessment of liver and kidney function, ultrasound scan of the thyroid gland and lymph nodes of the neck, thyroid scintigraphy. This will allow your doctor to assess how effective radioiodine therapy will be and how well you will tolerate it. In addition, the doctor will calculate the dosage of the drug you need.
Radioiodine therapy with I-131 includes oral administration of the drug. You will take 1 to 4 radioactive iodine capsules or drink about a teaspoon of liquid with radioactive iodine. You will take the drug in your ward, without visiting the manipulation room or operating room.
After taking radioactive iodine, you will stay in your ward for 24 to 48 hours. The next morning after the procedure, the dosimetrist will determine the amount of radiation in your body. If the amount is low, you will be allowed to leave your ward and will be discharged from the hospital. If the amount is high, then the dosimetric control will continue for another day, until a low amount of radiation in your body is detected.
The isotope I-131 can accumulate not only in the thyroid gland, but also partially in the salivary glands. This can cause dry mouth. To get rid of this side effect, you will dissolve sour candies, as this stimulates the work of salivary glands.
The drug is quickly excreted by the kidneys, and after 48 hours you will no longer pose a danger to others. After the procedure, you should drink at least 1 glass of water per hour and visit the toilet regularly. This will allow you to quickly remove radioactive iodine from the body. Food can be usual, without excess iodine in the diet.
During these 48 hours, you can read, use a mobile phone, tablet or computer. All these devices will not be a source of radiation in the future.
Control examination includes scintigraphy, which is performed 7-10 days after radioiodine therapy. Based on the results of the examination, the doctor will determine how well the cells of the thyroid gland (or cancer metastases) have accumulated radioactive iodine. In a few weeks after the procedure, you will have a control blood test for thyroid hormones. In the future, you will visit an endocrinologist regularly.
Required documents
- Medical records
- MRI/CT scan (not older than 3 months)
- Biopsy results (if available)
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Adult and Pediatric Interventional Radiology, Neuroradiology and Nuclear Medicine at the Nuremberg Hospital offers the full range of medical services in these areas at the highest technical and scientific levels. The department specializes in imaging and radioisotope diagnostic tests and various types of therapy for patients of all age groups with cancer, injuries and diseases of the musculoskeletal system, brain, etc. Diagnostic tests are available in the department, including angiography, CT, MRI, PET/CT, SPECT, ultrasound, digital radiography, digital mammography, and scintigraphy. The department's therapeutic options include modern image-guided interventional procedures and radioisotope therapy. The specialists at the medical facility have unique skills in microwave ablation, transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT), uterine artery embolization, prostate artery embolization, mechanical thrombectomy, and other procedures. Patients receive medical care from highly qualified physicians with a wealth of expert knowledge and vast clinical experience. The cornerstone of successful practice is also a state-of-the-art medical and technical base. The Head Physician of the department is Prof. Dr. med. Michael Lell.
The department's team of interventional radiologists treats patients suffering from cancer. Microwave ablation is often performed here to destroy malignant tumors. During this procedure, a thin needle is used through which microwave energy is directed to the tumor, which can heat the tissue of the malignant tumor to extremely high temperatures of 100°C and above. Under the influence of high temperatures, malignant cells are destroyed. Microwave ablation is an innovative method, but it has already proven itself in the treatment of tumors and metastases in the liver, lungs, kidneys, bones, soft tissues, etc. In most cases, the procedure is performed under general anesthesia under CT guidance with an approach through a skin puncture (without any incisions). A hospital stay does not exceed 2 days. Microwave ablation is usually used as a complementary treatment to surgical interventions, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy. The decision on the advisability of this therapeutic procedure is made during interdisciplinary tumor boards.
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is successfully performed in the department for liver cancer and liver metastases. This method involves puncturing the common femoral artery in the groin and the subsequent delivery of emboli (miniature balls) containing a chemotherapy agent into the blood vessels supplying the malignant tumor using catheter-based techniques. The emboli block the blood circulation of the tumor, additionally acting on it with a chemotherapy drug, which subsequently leads to its destruction. The TACE procedure is performed under angiography guidance, which ensures maximum manipulation accuracy and excludes damage to healthy liver segments. Transarterial chemoembolization is most often performed for advanced cancer when surgery is contraindicated. TACE cannot cure liver cancer, but it can normalize the patient's condition and prolong their life.
Neuroradiology is represented by a specially trained team of doctors who perform both image-guided diagnostic procedures and minimally invasive treatment of diseases of the brain and spinal cord. The main clinical focus is mechanical thrombectomy for stroke, coiling for brain aneurysms, embolization for brain meningiomas, endovascular repair of cerebral arteriovenous malformations, and interventional pain management for chronic back pain. All of the above-mentioned procedures are minimally invasive and are performed using catheter-based techniques through an endovascular approach under angiography, CT, or MRI guidance. Imaging guidance guarantees high accuracy and safety of manipulations, which is especially important in the treatment of pathologies of the central nervous system. The high treatment success rates in this area are confirmed by the quality certificate from the German Society of Neuroradiology (DGNR).
The specialists in the field of nuclear medicine offer the widest range of services, including diagnostic examinations with radioisotopes and radionuclide therapy. The most popular diagnostic procedures are scintigraphy, positron emission tomography, computed tomography combined with positron emission tomography, and single-photon emission computed tomography. The key focus of the treatment is radioiodine therapy. Radioiodine therapy may be indicated for patients with both benign and malignant thyroid diseases and involves the intake of an individually prescribed dose of radioactive iodine (orally or in the form of capsules or liquid). Since radioactive iodine is actively absorbed by thyroid cells, the drug easily targets and affects the altered cells. Radioiodine therapy is an effective and safe treatment method with minimal side effects. An essential requirement for radioactive iodine therapy is a hospital stay of 3-5 days.
The department's therapeutic options include:
- Adult and pediatric interventional radiology
- Interventional cancer therapy
- Microwave ablation
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE)
- Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT)
- Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty for circulatory disorders
- Prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia
- Embolization for acute and life-threatening arterial bleeding (for example, in the abdomen, pelvis, lungs, head, or neck)
- Renal artery dilatation with balloon catheters and stents for nephrogenic arterial hypertension
- Interventional cancer therapy
- Neuroradiology
- Mechanical thrombectomy for stroke
- Coiling for brain aneurysms
- Embolization for intracranial meningiomas
- Endovascular repair of brain arteriovenous malformations
- Endovascular treatment of subdural hematomas
- Interventional pain management for chronic back pain
- Nuclear medicine
- Radioisotope therapy with a special focus on radioiodine therapy
- Other medical services
Curriculum vitae
Since May 2016, Prof. Dr. med. Michael Lell has been the Head Physician of the Department of Adult and Pediatric Interventional Radiology, Neuroradiology and Nuclear Medicine at the Nuremberg Hospital, as well as the Head of the Department of Radiology at the Paracelsus Private Medical University.
Prof. Lell graduated from the Universities of Regensburg and Munich. After his thesis defense on the subject "Signal changes in magnetic resonance imaging during and after radiation therapy / chemotherapy for tumor treatment", in 1998, he became an Assistant Physician and a Research Fellow at the Institute of Radiology at the University Hospital Erlangen. In 2003, he was board certified in Diagnostic Radiology and was appointed as a Senior Physician there. Prior to working at the Nuremberg Hospital, he worked as a Senior Consultant and Permanent Representative of the Director of the Institute.
The specialist's priority clinical and research focuses include imaging diagnostics of the cardiovascular system, imaging tests in cancer patients, and interventional procedures for cancer treatment.
Photo of the doctor: (c) Klinikum Nürnberg
About hospital
According to the reputable Focus magazine, the Nuremberg Hospital ranks among the top German medical facilities!
The hospital is one of the largest, highly specialized medical centers in Europe and positions itself as the maximum care hospital. The healthcare facility is an academic hospital of the Paracelsus Medical University in Nuremberg. It houses 42 departments, institutes, and highly specialized centers focusing on various medical fields. All the hospital's employees work hand in hand for the benefit of their patients. The specialists strive to provide top-class medical care for every patient. Moreover, the medical team always shows a humane attitude and understanding towards the patient's life situation, making every effort to support them during the entire therapeutic process.
The total number of beds in the hospital is 2,233. The medical team consists of more than 8,400 employees, including many world-famous doctors and professors who had their clinical training at the best medical facilities in Germany, other European countries, and the USA. The hospital admits more than 100,000 inpatients and more than 170,000 outpatients annually. The number of patients who come to the hospital steadily increases every year, which is the best confirmation of its high standards and outstanding treatment results.
The cornerstone of successful clinical practice is state-of-the-art technical infrastructure. The hospital offers its patients innovative technologies such as the Da Vinci surgical system, devices for stereotactic procedures, intraoperative radiation therapy, angiography, PET CT devices, high-intensity focused ultrasound, 64-slice CT scanners, and other advanced medical devices. The combination of cutting-edge technical facilities and the high competence of the physicians allows for the provision of effective treatment even in the most complex cases.
The Nuremberg Hospital is undoubtedly one of Germany's leading medical facilities, where patients benefit from modern infrastructure, precise diagnostics, effective treatment, and responsive care.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
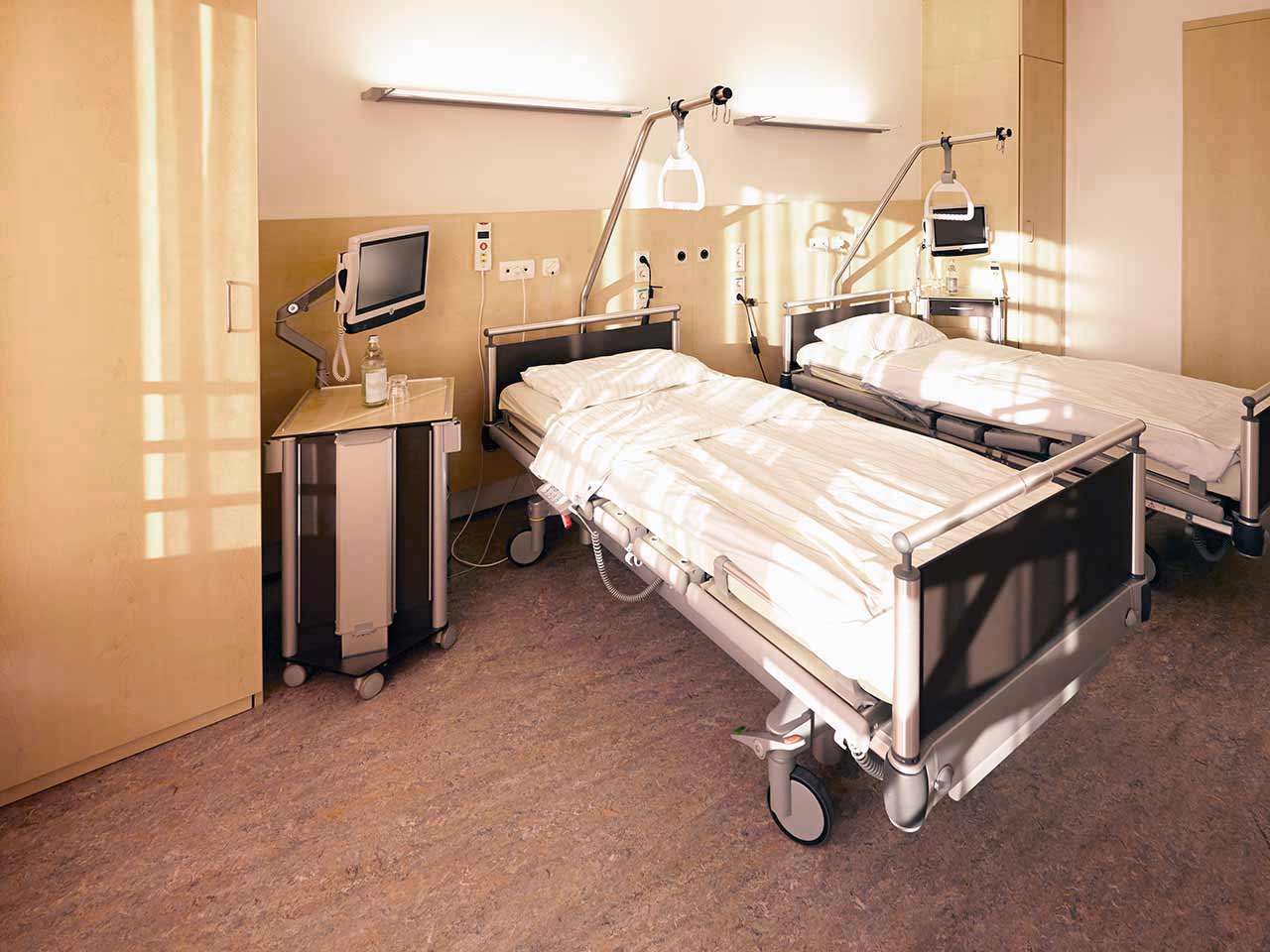
Patients rooms
The patients at the Nuremberg Hospital live in comfortable single and double rooms. Each patient room is equipped with an ensuite bathroom with a shower and a toilet. Standard rooms include an automatically adjustable bed, a bedside table, a wardrobe for storing clothes, a table and chairs for receiving visitors, a TV, and a radio. The hospital also offers Wi-Fi.
If desired, patients can live in enhanced-comfort rooms. Such patient rooms are more spacious, and their furnishings correspond to the level of an upscale hotel.
Meals and Menus
The patients at the hospital are offered tasty and balanced meals three times a day: breakfast, lunch, and dinner. The patients have a daily choice of three dishes for lunch and dinner, while breakfast is served as a buffet.
If, for some reason, you do not eat all foods, you will be offered an individual menu. Please inform the medical staff about your food preferences prior to treatment.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Accompanying person
Your accompanying person may stay with you in your patient room or at the hotel of your choice during the inpatient program.
Hotel
You may stay at the hotel of your choice during the outpatient program. Our managers will support you for selecting the best option.