The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the hospital
- Clinical history taking
- Review of available medical records
- Physical examination
- Laboratory tests:
- Complete blood count
- General urine analysis
- Biochemical analysis of blood
- Tumor markers
- Inflammation indicators (CRP, ESR)
- Coagulogram
- Ultrasound scan
- CT scan / MRI
- Preoperative care
- Embolization or chemoembolization, 2 procedures
- Symptomatic treatment
- Cost of essential medicines
- Nursing services
- Elaboration of further recommendations
How program is carried out
During the first visit, the doctor will conduct a clinical examination and go through the results of the available diagnostic tests. After that, you will undergo the necessary additional examination, such as the assessment of liver and kidney function, ultrasound scan, CT scan and MRI. This will allow the doctor to determine which vessels are feeding the tumor and its metastases, as well as determine how well you will tolerate the procedure.
Chemoembolization begins with local anesthesia and catheterization of the femoral artery. The thin catheter is inserted through a few centimeters long incision of the blood vessel. The doctor gradually moves the catheter to the vessel feeding the primary tumor or its metastases. The procedure is carried out under visual control, an angiographic device is used for this. The vascular bed and the position of the catheter in it are displayed on the screen of the angiograph.
When the catheter reaches a suspected artery, a contrast agent is injected through it. Due to the introduction of the contrast agent, the doctor clearly sees the smallest vessels of the tumor and the surrounding healthy tissues on the screen of the angiograph. After that, he injects emboli into the tumor vessels through the same catheter.
Emboli are the spirals or the liquid microspheres. The type of embolus is selected individually, taking into account the diameter of the target vessel. When carrying out chemoembolization, a solution of a chemotherapy drug is additionally injected into the tumor vessel. Due to the subsequent closure of the vessel lumen with an embolus, the chemotherapy drug influences the tumor for a long time. In addition, the drug does not enter the systemic circulation, which allows doctors to use high doses of chemotherapeutic agents without the development of serious side effects. Chemoembolization leads to the destruction of the tumor or slowing down its progression.
After that, the catheter is removed from the artery. The doctor puts a vascular suture on the femoral artery and closes it with a sterile dressing. During chemoembolization, you will be awake. General anesthesia is not used, which significantly reduces the risks of the procedure and allows performing it on an outpatient basis, avoiding long hospital stay.
After the first procedure, you will stay under the supervision of an interventional oncologist and general practitioner. If necessary, you will receive symptomatic treatment. As a rule, a second chemoembolization procedure is performed in 3-5 days after the first one in order to consolidate the therapeutic effect. After that, you will receive recommendations for further follow-up and treatment.
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Adult and Pediatric Diagnostic, Interventional Radiology at the University Hospital Marburg UKGM offers the full range of services in these fields and specializes in all modern radiological examinations, imaging-guided minimally invasive interventions. The department has advanced technical equipment, including specially adapted devices for examination in children. In the field of interventional radiology, of particular interest is minimally invasive treatment of oncological and vascular diseases. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med Andreas Mahnken.
The service range of the department includes:
- Diagnostic radiology
- X-ray examinations
- Ultrasound examinations
- Fluoroscopy
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Combined PET-CT method
- Pediatric radiology
- Ultrasound examinations
- X-ray examinations
- Fluoroscopy
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Interventions in children (for example, radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of osteoid osteomas)
- Interventional treatment of vascular malformations in children (hemangiomas and lymphangiomas)
- Interventional radiology
- Embolization and sclerotherapy for the treatment of vascular malformations
- Cryoablation and cryotherapy for cancer and benign tumors
- MRI-guided breast vacuum biopsy
- Therapy of arteriovenous malformations (for example, embolization, installation of special metal coils)
- Uterine artery embolization for the treatment of uterine myomas
- Radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation for the treatment of liver tumors
- Radiofrequency ablation, cryotherapy and cryoablation for the treatment of osteoid osteomas
- Prostate artery embolization for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia
- MRI-guided focal cryotherapy for prostate cancer treatment
- Selective internal radiation therapy for the treatment of liver cancer and liver metastases
- Transarterial chemoembolization for the treatment of liver cancer and liver metastases
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunting for portal hypertension treatment
- Treatment of malignant tumors of the kidneys, liver, bones and lungs with the help of cryotherapy, radiofrequency and microwave ablation, irreversible electroporation
- Sclerotherapy for varicocele treatment
- Interventional therapy for chronic venous diseases
- Placement of long-term venous catheters and port systems (for example, for chemotherapy)
- Other diagnostic and therapeutic procedures in adults and children
Curriculum vitae
- 05.1991 - 03.1993 Study of Human Medicine, Julius Maximilian University of Würzburg.
- 04.1993 - 09.1994 Study of Human Medicine, Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn.
- 10.1994 - 03.1995 Study of Human Medicine, Karl Franzens University Graz.
- 04.1995 - 04.1997 Study of Human Medicine and Economics, Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn.
- 04.2004 - 07.2006 Study of Health Administration Management, Osnabrueck University of Applied Sciences.
- 10.2008 - 12.2012 Medical education, Ruprecht Karls University of Heidelberg.
Clinical Activities
- Since 01.11.2012 Head of the Department of Adult and Pediatric Diagnostic, Interventional Radiology at the University Hospital Marburg.
- 01.05.2010 - 31.10.2012 Leading Senior Physician and Deputy Head of the Department of Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology at the University Hospital Aachen.
- 01.01.2006 - 31.10.2012 Leader of the Working Group on "Interventional Therapy Technologies" in the Department of Applied Medical Technology, Rhine-Westphalian Technical University Aachen.
- 01.11.2004 - 30.04.2010 Senior Physician of the Department of Radiological Diagnostics, University Hospital Aachen.
- 01.05.1999 - 31.10.2004 Assistant Physician of the Department of Radiological Diagnostics, University Hospital Aachen.
- 01.06.1998 - 28.2.1999 Intern, Department of Urology, Robert Koch Clinic, Gehrden.
- 01.06.1997 - 31.05.1998 Department of Surgery, Hegau Singen Clinic.
Academic Titles
- Since 01.11.2012 Department of Radiology (W3 Professor), University Hospital Marburg.
- 27.12.2010 Master of Medical Education (MME), Ruprecht Karls University of Heidelberg.
- 14.04.2008 Visiting Professor, Rhine-Westphalian Technical University Aachen.
- 07.07.2006 Master of Business Administration (MBA), Osnabrueck University of Applied Sciences.
- 14.06.2004 Habilitation, Rhine-Westphalian Technical University Aachen.
- 30.05.1997 Doctoral degree, Medical History Institute, Rhenish Friedrich Wilhelm University of Bonn.
Professional Qualifications
- 23.08.2007 Additional qualification, Health Care Quality Management.
- 06.08.2003 Theoretical foundations of radiation protection.
- 28.07.2003 Vascular sonography of the abdominal cavity and retroperitoneal space.
- 28.07.2003 Mammary gland sonography.
- 16.07.2003 Medical Specialist in Diagnostic Radiology.
- 25.01.2013 Additional training, Physician-Monitor for MPG examinations.
- 26.11.2012 Lecturer in Interventional Radiology, DeGIR.
- 11.02.2011 European Board of Interventional Radiology (EBIR).
- 07.02.2011 Q3 Coach, cardiac CT and MRI (German Society of Radiology).
- 03.05.2010 Interventional Radiology, DeGIR.
- 07.04.2004 Total Quality Management (TQM) in accordance with EFQM.
Awards
- 29.05.2014 Eugenia and Felix Wachsmann Prize.
- 10.06.2009 CIRSE Foundation Education Grant.
- 20.05.2009 Hermann Holthusen Award (Hermann-Holthusen-Ring) of the German Society of Radiology.
- 01.08.2007 Scholarship of the German Research Foundation (RSNA 2007).
- 27.05.2006 Werner Porstmann Scholarship of the German Society of Radiology.
- 05.05.2005 Walter Friedrich Prize of the German Society of Radiology.
- 06.03.2005 ECR Foundation for Research and Education.
- 20.05.2004 11th Coolidge Award.
- 13.05.2004 Hans Langendorff Prize.
Memberships
- German Society of Radiology.
- German Society of Interventional Radiology.
- European Society of Radiology.
- European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology.
- European Society of Cardiovascular and Interventional Surgery.
- German Society of Neuroradiology.
Photo of the doctor: (c) UKGM - Universitätsklinikum Gießen und Marburg GmbH
About hospital
The University Hospital Marburg UKGM offers patients modern diagnostics and comprehensive therapy at the international level. As a maximum care hospital, the medical facility specializes in all fields of modern medicine ranging from ophthalmology to traumatology and dentistry. The main areas of specialization of the hospital are surgery, neurosurgery, oncology, nephrology with kidney transplantation and children's medicine.
The hospital is the third largest in Germany. Every year, more than 436,000 patients are treated in two locations of the hospital (Giessen and Marburg): 342,000 in outpatient and 94,000 inpatient settings. The medical facility is the first privatized university hospital in the country.
The hospital staff makes a significant contribution to the development of research activities at the Faculty of Medicine of the Justus Liebig University Giessen and the Philipps University of Marburg. To develop new diagnostic and therapeutic methods, as well as to implement them into clinical practice, the specialists maintain active cooperation in a large number of areas.
The widest range of diagnostic and therapeutic services, the advanced infrastructure and technical base, high quality of treatment and professionalism of health workers contribute to the fact that the medical facility has an excellent reputation not only in Germany, but also far beyond its borders.
Photo: (c) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
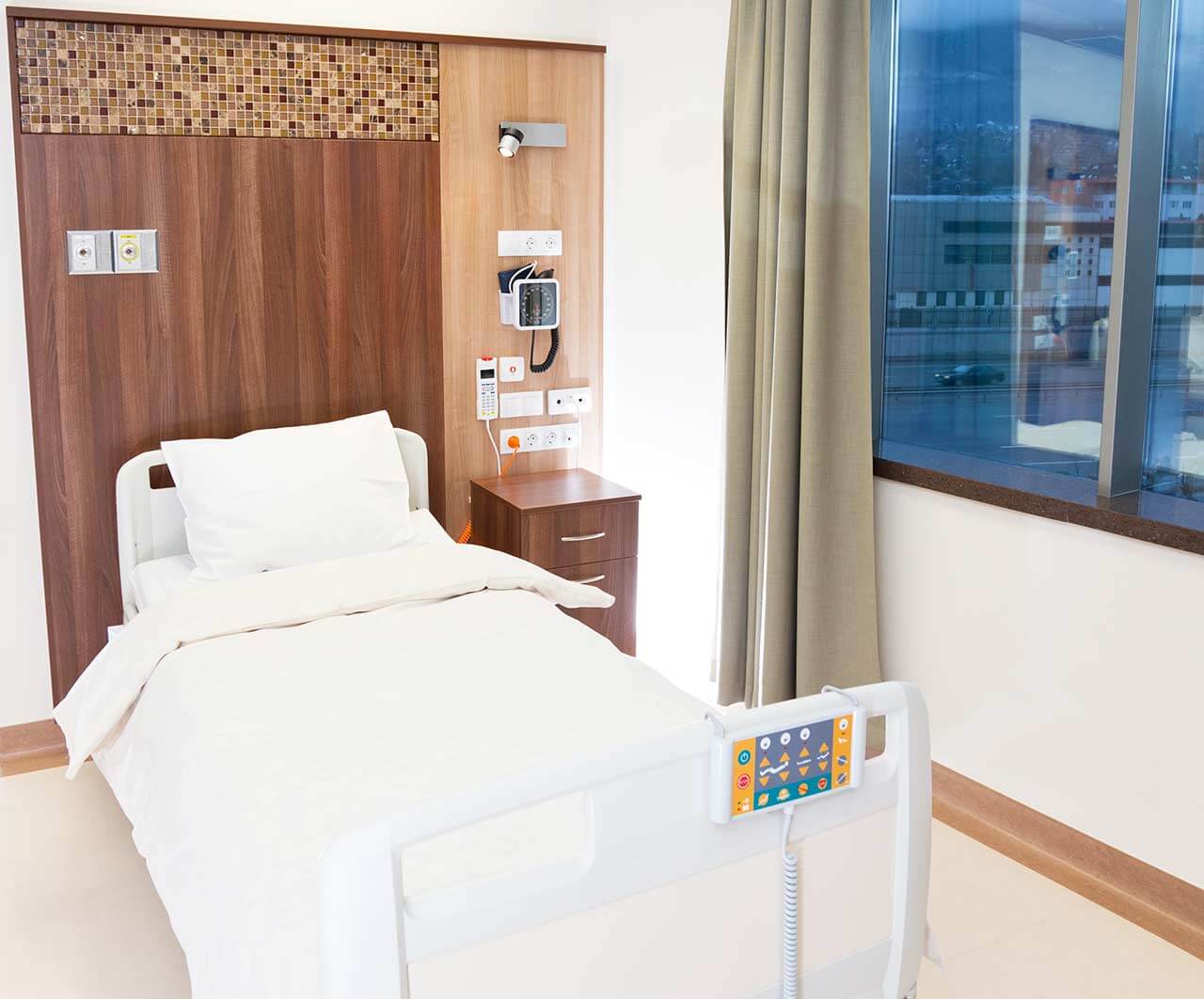
Patients rooms
The patients of the University Hospital Marburg UKGM live in comfortable single and double rooms made in a modern design and light colors. Each room has an ensuite bathroom with shower and toilet. The pediatric departments provide patient rooms for the joint accommodation of mother and child. The standard room furnishing includes an automatically adjustable bed, bedside table, wardrobe, TV, telephone.
Meals and Menus
The patients of the hospital are offered balanced, healthy three meals a day: buffet breakfast, lunch and dinner. The private kitchen, certified according to DIN EN ISO 9001: 2000, is responsible for providing patients with food and drinks.
If for some reason you do not eat all foods, you will be offered an individual menu. The hospital also has a cafeteria with a large assortment of hot and cold drinks, snacks and desserts.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Television
All patient rooms are equipped with TV sets. If you have some questions about TV use, please contact medical personnel.
Religion
Religious services can be provided upon request.
Accompanying person
During an inpatient program, an accompanying person can stay with you in a patient room or in a hotel of your choice.
Hotel
During the outpatient program, you can stay at the hotel of your choice. Our managers will help you choose the most suitable option.