The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- review of medical records
- physical examination
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- biochemical analysis of blood
- indicators of inflammation
- indicators blood coagulation
- ophthalmologic examination:
- slit-lamp examination
- pupil function tests
- ocular motility test
- ophthalmoscopy
- perimetry (visual field test)
- computer perimetry
- visometry (without correction and with correction)
- keratometry
- pachymetry
- refractometry (objective, subjective, cycloplegic)
- autorefractometry
- non-contact tonometer
- biomicroscopy
- preparation according to preoperative standard
- corneal transplantation
- symptomatic treatment
- control examinations
- the cost of essential medicines and materials
- nursing services
- explanation of future recommendations
Required documents
- Medical records
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Adult and Pediatric Ophthalmology at the University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden offers the full range of services in the field of diagnostics and treatment of diseases of the eye and its appendages. Medical care is provided both on an inpatient and outpatient basis. The department has 42 beds, three state-of-the-art operating rooms, a laser surgery unit, as well as perfectly equipped rooms for diagnostic examinations. The department's priority focuses are on the treatment of glaucoma, including in children, as well as cataract, intraocular lens implantation, keratoplasty, reconstructive surgery after injuries, surgical correction of refractive errors, laser vision correction, etc. All experts of the department have long clinical experience and high professionalism, and they also practice the most effective and modern treatment methods. More than 6,000 inpatients undergo treatment in the department annually. More than 14,400 outpatients receive medical care here every year. The department's medical team aims to provide each patient with an individualized treatment at the highest level of university medicine. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Lutz E. Pillunat.
Cataract is one of the most common ophthalmic diseases, so the department's doctors have rich and successful experience in dealing with this pathology. Cataract is a partial or complete clouding of the lens located between the vitreous body and the iris. The lens is responsible for the refraction of rays and their follow up projection onto the retina. The clouding of the lens disrupts this process, which leads to a decrease in visual acuity or even its complete loss. The department's specialists deal with the treatment of cataract in adults and congenital cataract in children. Early diagnostics of cataract significantly improves the prognosis for the patient, therefore, the department's doctors strongly recommend contacting an ophthalmologist at the first manifestations of visual impairment. The diagnostics usually involves the use of such methods as slit lamp biomicroscopy, examination of the fundus and determination of intraocular pressure, as well as the assessment of visual acuity and visual fields. Cataract is treated with surgery – this is the only 100% effective therapeutic technique. As a rule, doctors perform ultrasound phacoemulsification of the affected lens. During the surgical intervention, the clouded lens is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens. The duration of the operation is 15-20 minutes. The surgical procedure is performed under local anesthesia – it is absolutely painless and well tolerated. Drug therapy is carried out at the initial stages of cataract to prevent the progression of the pathology, but today there are no drugs that could cure the pathology completely.
The department's ophthalmologists also often admit patients with glaucoma, which is a progressive disease that causes irreversible blindness. Pathology is initially manifested by an increase in intraocular pressure, which in turn causes the development of optic nerve atrophy. At the stage of diagnostics, tonometry, perimetry, gonioscopy, biomicroscopy, pachymetry, optical coherence tomography are performed. An optimal treatment regimen is developed based on the diagnostic results. Drug therapy assumes the intake of the very latest antiglaucoma drugs in order to reduce the production of intraocular fluid, as well as to improve its outflow. However, conservative treatment is not suitable for all patients, so surgical intervention is the main treatment method. The optimal type of surgery is determined by the ophthalmologist based on the specific clinical case.
The department also admits young patients with ophthalmic diseases. The specialists most often deal with diseases of the lacrimal ducts, ptosis, uveitis, congenital cataract and glaucoma, nystagmus, retinopathy of prematurity, inflammatory eye lesions, eye malformations, etc. With appropriate indications, conservative treatment with modern medicines is carried out. If drug therapy does not give a positive result, doctors resort to surgical treatment of an ophthalmic disease in a child.
The department's range of medical services includes:
- Diagnostic options
- Ultrasound examinations (A-, B-mode ultrasound, Doppler scanning)
- Fluorescein angiography
- Binocular vision dysfunction diagnostics
- Electrophysiological tests (electroretinography, electrooculography)
- Corneal topography
- Retinal nerve fiber layer thickness assessment
- Pachymetry
- Heidelberg retinal tomography
- Intraocular pressure measurement
- Color Doppler imaging of the eye and orbit
- Preliminary diagnostics before refractive eye surgery
- Heidelberg retinal flowmeter examination
- Visual field testing
- Visually evoked cortical potentials (VECP)
- Multifocal electroretinography
- Therapeutic options
- Surgical treatment of cataract
- Surgical treatment of glaucoma (also in children of all age groups)
- Intraocular lens implantation
- Keratoplasty
- Reconstructive surgery and treatment of eye injuries
- Vitreoretinal surgery
- Macular surgery
- Surgical treatment of diseases of the eye muscles and orbit
- Cryosurgery
- Laser surgery
- Refractive eye surgery
- Correction of strabismus in adults and children
- Treatment of neuro-ophthalmic diseases
- Treatment of ophthalmic diseases in children
- Diseases of the lacrimal ducts
- Uveitis
- Glaucoma
- Congenital cataract
- Ptosis
- Hemangiomas of the eyelids
- Congenital dermoid cysts
- Retinopathy of prematurity (monitoring and corrective interventions, such as prescribing glasses at an older age)
- Nystagmus
- Children with developmental disabilities that require diagnostics and monitoring by an ophthalmologist
- Eye malformations (coloboma, optic nerve abnormalities)
- Acute inflammation of the eye and its appendages (for example, redness and swelling of the eyelids or conjunctiva)
- Other diagnostic and therapeutic methods, other ophthalmic diseases in adults and children
Curriculum vitae
Professional Career
- 1977 - 1983 Study of Human Medicine at the University of Duesseldorf.
- 1978 - 1983 Study of Psychology at the University of Duesseldorf.
- 1983 - 1987 Assistant Physician, Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital Ulm.
- 1987 - 1991 Senior Physician, Department of Ophthalmology, University Hospital Ulm.
- 1991 - 1993 Appointed as Managing Senior Physician of the Department of Ophthalmology at the University Hospital Ulm.
- 1993 - 1995 Glaucoma Research Scholarship, Bascom Palmer Eye Institute, University of Miami, USA (Scholarship of the German Research Foundation).
- 1995 Invitation to the position of C3 Professor, Department of Ophthalmology, University of Hamburg.
- 1996 - 2001 Professor of Ophthalmology and Deputy Head of the Department of Ophthalmology at the University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf.
- 2000 Invitation to the position of C4 Professor of Ophthalmology, Faculty of Medicine Carl Gustav Carus, Dresden University of Technology.
- Since 01.05.2001 Head of the Department of Adult and Pediatric Ophthalmology at the University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden.
- 09.2001 Elected President of the Saxon Ophthalmologic Society.
- 11.2001 Recognized as Ophthalmologist by the federal state of Saxony.
Awards and Honors
- 1986 Merckle Research Prize, Ulm University.
- 1987 Laureate of the International Chibret Award.
- 1992 Award for work on video materials of the German Society of Ophthalmology.
- 1993 Honorary Membership of the Italian Glaucoma Society.
Memberships in Professional Societies
- German Society of Ophthalmology.
- Association of German Ophthalmologists.
- German-speaking Society of Intraocular Lens Implantation, Interventional and Refractive Surgery (DGII).
- Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology (ARVO).
- American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO).
- European Glaucoma Society (EGS).
- International Glaucoma Society (IGS).
- Italian Glaucoma Society (Honorary Membership).
Research Focuses
- Physiology and pathophysiology of the blood supply to the eye.
- Pathogenesis of optic nerve damage in glaucoma.
- Surgical treatment of glaucoma.
- The role of vascular factors in glaucoma.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
About hospital
According to the reputable Focus magazine, the University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden ranks among the top five German hospitals!
The hospital is the benchmark for modern high-quality medicine. Positioning itself as a maximum care medical facility, the hospital represents all medical fields. There are 26 specialized departments, 6 institutes and 17 interdisciplinary centers, which cooperate closely with the clinical and scientific facilities of the Faculty of Medicine. The basis of successful practice is excellent equipment, which is regularly updated, as well as highly qualified, experienced medical personnel: world famous doctors and professors work here for the benefit of patients.
In addition to its main goal of caring for patients, the hospital is also active in training and professional development of medical personnel, as well as in the field of public health care. The priority focus of the work is research activity, which allows the doctors to introduce the innovative diagnostic and therapeutic techniques into clinical practice.
A special feature of the hospital is also the diagnostics and treatment of rare diseases. State-of-the-art equipment and well-coordinated work of doctors of various medical specialties make it possible to timely recognize pathologies rarely encountered in medical practice and select the most effective therapy. Specialization in rare diseases include neurology, endocrinology, hematology/oncology, and rare autoimmune diseases.
The hospital has 1,410 beds for patient hospitalization. About 55,900 inpatients and more than 233,975 outpatients undergo treatment here annually. A large medical team, consisting of about 1,000 highly qualified doctors, as well as over 2,000 nursing staff take care of the patients' health. Each patient is guaranteed an individual approach and the most effective treatment in accordance with current clinical protocols.
It should be noted that the university hospital enjoys an impeccable reputation not only in Germany, but also far beyond its borders, including Arab countries, post-Soviet states, Great Britain and the United States. Patients from different parts of the world come here for high-quality treatment for diseases of any severity. The highest credit of patient confidence is the main indicator of the fruitful work of doctors.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
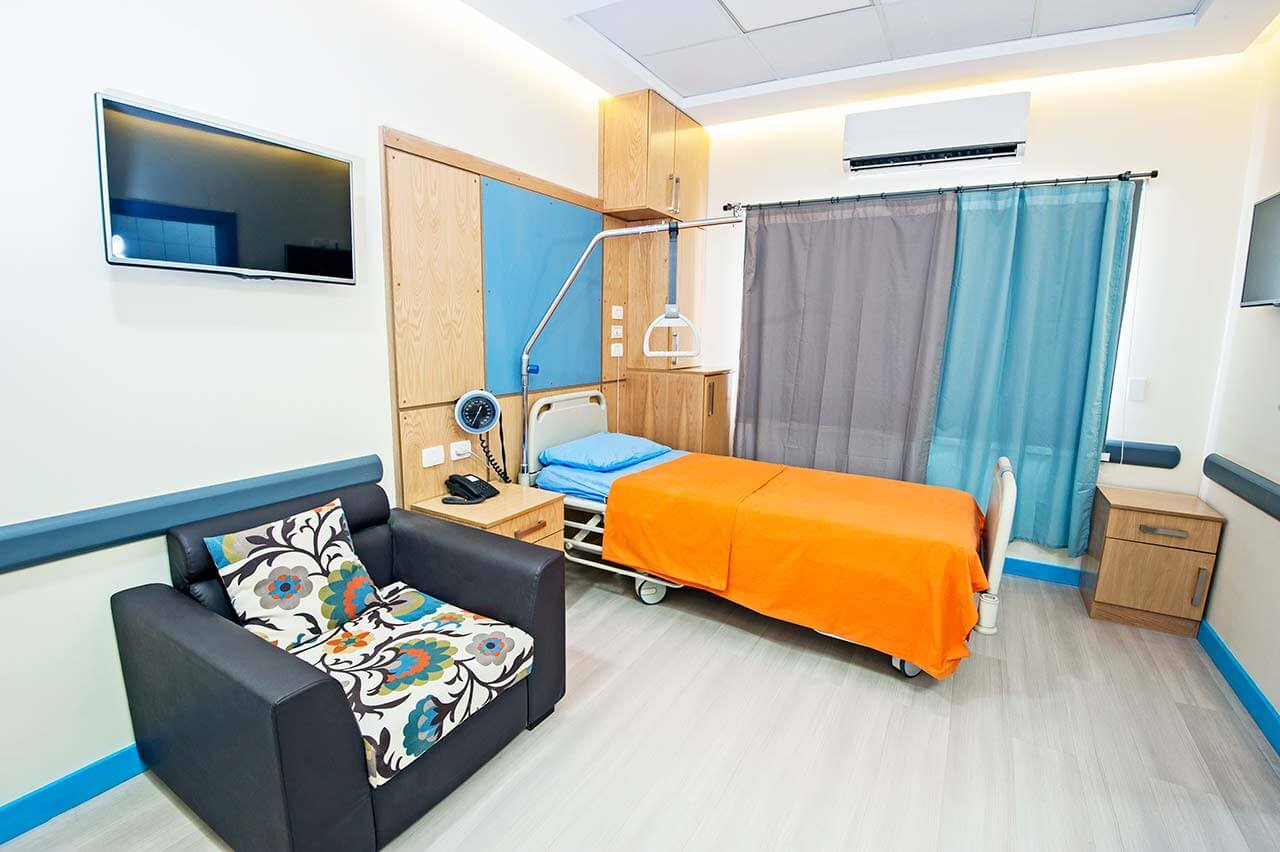
Patients rooms
The patients of the University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden live in comfortable rooms made in bright colors and equipped with everything necessary. The standard patient room includes an automatically adjustable bed, a bedside table with a sliding table, a wardrobe, a telephone and a TV. There is also Wi-Fi (free) in the patient rooms.
If desired, patients may live in enhanced comfort patient rooms. These patient rooms have a more sophisticated design, upholstered furniture and a safe for storing valuables.
Meals and Menus
The patients of the hospital are offered a tasty, healthy and varied three meals a day. The menu is based on local cuisine and seasonal food. If you for some reason do not eat certain products, please inform the medical staff of the hospital in advance, and you will be offered an individual menu. The nutrition provided in the hospital is certified in accordance with the quality standards of the German Nutrition Society (DGE) for catering in German hospitals.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Religion
The religious services are available upon request.
Accompanying person
Your accompanying person may stay with you in your patient room or at the hotel of your choice during the inpatient program.
Hotel
You may stay at the hotel of your choice during the outpatient program. Our managers will support you for selecting the best option.
The hospital offers a full range of laboratory diagnostic procedures (general, hormonal, tests for tumor markers, infections, antibodies, etc.), genetic tests, various modifications of ultrasound scans, CT scans, MRI and PET / CT, angiography, myelography, biopsy and other examinations. Treatment with medications, endoscopic and robotic operations, stereotaxic interventions is carried out here, modern types of radiation therapy are also used. The hospital offers patients all the necessary therapeutic techniques.
- Cochlear implantation
- Deep brain stimulation
- Treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia with green laser
- Da Vinci prostatectomy
- Bone marrow transplantation
These are head and neck tumors, hearloss, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, epilepsy, Parkinson disease, infertility, malignant tumors of the reproductive system, congenital anomalies of the genital organs and the urinary system, urinary incontinence, blood clotting disorders, leukemia and other pathologies.
- Otolaryngology (Center for Cochlear Implantation)
- Neurology and Epileptology
- Urology
- Oncology
- Gastroenterology and Hepatology
About 1,000 highly qualified doctors work at the hospital.