The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- physical examination
- review of medical records
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- general urine analysis
- biochemical analysis of blood
- indicators of inflammation (CRP, ESR)
- indicators blood coagulation
- x-ray examination of the hip
- MRI scan of the hip
- preoperative care
- hip replacement (hip endoprosthesis)
- symptomatic treatment
- control examinations
- physiotherapeutic procedures
- orthopedic appliances
- the cost of essential medicines and materials
- nursing services
- full hospital accommodation
- explanation of future recommendations
How program is carried out
Preliminary preparation for hip replacement includes quitting smoking and drinking alcohol; cancelling non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, ibuprofen); cancelling anticoagulants (warfarin); normalization of body mass, if possible.
Preoperative examination, including consultation with an anesthesiologist and necessary related specialists, takes 1-2 days. According to its results, the most suitable endoprosthesis is selected.
Hip replacement. The operation is performed under general anesthesia. The patient lies on his side, the affected leg is bent and fixed in this position. The surgeon makes an incision 15-20 cm long, minimally traumatizing the muscles and nerve endings. Through this incision, miniature instruments are inserted to remove the damaged joint structures. Healthy bone is adjusted for further reliable implant fixation.
The surgeon installs a femoral stem in the center of the upper part of the femur. Ball-shaped head of the joint is fixed on it. The surgeon also implants a special liner that facilitates movement of the leg and protects the structures of the prosthesis. After the primary fixation of the prosthesis components, the doctor assesses the joint range of motion, as well as the length and symmetry of the lower limb.
The implant is fixed with cement or cementless method. The doctor treats the operating field with antiseptics, conducts its final revision and sutures the wound layer by layer. A temporary drainage is installed in the joint, and a bandage is applied on top.
Postoperative care. During the first day after the intervention the patient stays in the intensive care unit, under round-the-clock medical supervision. After that, with a smooth course of the postoperative period, the patient is transferred to a regular ward and the drains are removed. The range of motion expands gradually, from light toes movements to walking. Walking with the use of walking aids is allowed in 3-5 days after the operation.
Required documents
- Medical records
- X-ray examination (if available)
- MRI/CT scan (if available)
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Adult and Pediatric Orthopedics, Trauma Surgery at the University Hospital Mainz offers the full range of diagnostics, treatment and follow-up care for diseases and injuries of the musculoskeletal system in adults and children. The department has modern operating rooms equipped with advanced navigation systems to ensure the most effective surgical treatment. The outstanding quality of medical services is confirmed by prestigious certificates of the German Cancer Society, certificates of professional societies in traumatology and endoprosthetics. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Dr. h.c. Pol Maria Rommens.
One of the priorities of the department’s clinical focuses is hip and knee arthroplasty. Surgical interventions are performed by competent specialists with tremendous experience in this field. Also, high-quality endoprostheses of the best world manufacturers are used. A unique offer in this field is the postoperative Rapid Recovery Program, which aims to improve patients’ quality of life and achieve optimal results after surgery.
The service range of the department includes:
- Surgical treatment of polytrauma, pelvic and acetabular injuries
- Surgical treatment of extremity injuries of any severity (the department is a supraregional Trauma Center, certified by the German Society of Traumatology)
- Surgical treatment of injuries in the elderly (in comorbidities, such as diabetes mellitus, hypertension, heart failure, etc.)
- Hip endoprosthetics and revision interventions
- Knee endoprosthetics and revision interventions
- Treatment of spinal injuries and diseases (conservative, interventional and surgical treatment methods)
- Spinal injuries (for example, due to traffic accidents)
- Osteoporotic vertebral fractures
- Degenerative spinal diseases (for example, degeneration of intervertebral discs and intervertebral joints, spinal canal stenosis)
- Spinal malformations and deformities (for example, scoliosis, spina bifida)
- Infectious diseases affecting the spine
- Spinal tumors (interdisciplinary treatment concept)
- Shoulder surgery (including modern arthroscopic techniques for shoulder reconstruction and prosthetics)
- Surgical treatment of degenerative and traumatic elbow injuries
- Elbow arthroscopy
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Stabilizing operations
- Osteosynthesis
- Total and partial elbow endoprosthetics
- Hand surgery (open, arthroscopic, microsurgical interventions and endoprosthetics) in
- Congenital malformations
- Injuries of finger tendons and ligaments
- Hand and wrist fractures
- Formation of false joints (pseudoarthrosis)
- Rheumatic changes in the hand
- Compression syndromes (carpal tunnel syndrome, cubital tunnel syndrome)
- Rhizarthrosis
- Trigger fingers
- Ganglia
- Foot surgery
- Degenerative tendon damage
- Ankle cartilage damage (cartilage transplantation, joint replacement surgery)
- Rheumatic deformities
- Reconstruction of the incorrect position of the tibia and calcaneus
- Correction of complex foot deformities
- Minimally invasive surgery
- Diabetic foot syndrome (in progressive stage)
- Pediatric traumatology (treatment of children under 14 years old)
- Injuries of the musculoskeletal system and their consequences
- Skin lesions
- Abdominal trauma
- Traumatic brain injuries
- Pediatric orthopedics (conservative and surgical treatments)
- Treatment of congenital hip dysplasia
- Treatment of congenital clubfoot and other foot deformities
- Treatment of deformities or differences in leg length
- Treatment of spinal diseases and injuries (for example, scoliosis)
- Care for children with severe disabilities (in cerebral palsy, spina bifida, various forms of muscular diseases, metabolic disorders and their complications, skeletal dysplasia)
- Spastic diseases (botulinum toxin A injection therapy)
- Conservative and surgical treatment of sports injuries
- Treatment of oncological diseases of the musculoskeletal system (orthopedic oncology)
- Septic surgery (treatment of posttraumatic and postoperative infections, as well as the repair of bone and soft tissue defects)
- Osteoporosis treatment
- Physiotherapy
- Other medical services
Curriculum vitae
- 1972 - 1979 Study of Medicine at the Catholic University of Leuven.
- 1979 - 1984 Training in General Surgery in the Department of Surgery of the University Hospital of
- the Catholic University of Leuven.
- 1984 - 1986 Postgraduate Training in Traumatology in the Department of Traumatology at the University Hospital Essen, Germany.
- 1985 Medical Specialist in Surgery.
- 1986 Medical Specialist in Trauma Surgery.
- 1995 Medical Specialist in Emergency Medicine.
- 1998 Medical Specialist in Physical Therapy.
- 2006 Medical Specialist in Orthopedics and Trauma Surgery.
- 2007 Medical Specialist in Special Trauma Surgery.
- 1999 European Board of Surgery, Qualification in Traumatology.
- 1986 - 1996 Staff Member of the Department of Traumatology and Emergency Surgery at the University Hospital Gasthuisberg in Leuven, Belgium.
- 1990 Thesis defense: "The tibial shaft fracture with severe soft tissue damage".
- 1996 - 2013 Ordinary Professor and Chief Physician of the Department of Trauma Surgery at the University Hospital Mainz, Germany.
- Since 2013 Head of the Department of Adult and Pediatric Orthopedics, Trauma Surgery, University Hospital Mainz.
Awards and Honors
- 1993 - 1997 Founder and First President of the Belgian Trauma Society.
- 1997 - 2003 President of the Küntscher Society.
- 2009 - 2010 President of the European Society of Trauma and Emergency Surgery (ESTES).
- 2011 - 2017 Secretary General of the European Society of Trauma and Emergency Surgery (ESTES).
- 2005 Editor of the European Journal of Trauma and Emergency Surgery.
- 2005 Doctor honoris causa of the University of Patras, Greece.
- 1999 - 2014 Member of the Pelvic Expert Group.
Photo of the doctor: (c) Universitätsmedizin der Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz
About hospital
The University Hospital Mainz is one of the best maximum care medical facilities in Germany and an internationally recognized scientific center. There are more than 60 departments and institutes, which represent all fields of modern medicine. The hospital serves more than 68,000 inpatients and more than 273,000 outpatients annually, which testifies to the excellent reputation of this medical institution.
The key to the successful clinical practice is also a highly qualified medical staff, which consists of 7.800 employees from various fields. The doctors of the hospital are convinced that each clinical case requires an individual approach, therefore, they devote much time to consultations and communication with patients. The main goal of all hospital employees is to provide an optimal medical care based on the use of the state-of-art diagnostic and therapeutic measures, as well as the introduction of the latest scientific achievements into the medical practice.
The best interns and assistant physicians are trained here. The world-famous leading physicians of the hospital share their long experience and professional skills. Naturally, an integral part of the university hospital work is research, thanks to which many innovative possibilities in the field of diagnostics and therapy have been developed.
Photo: (c) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
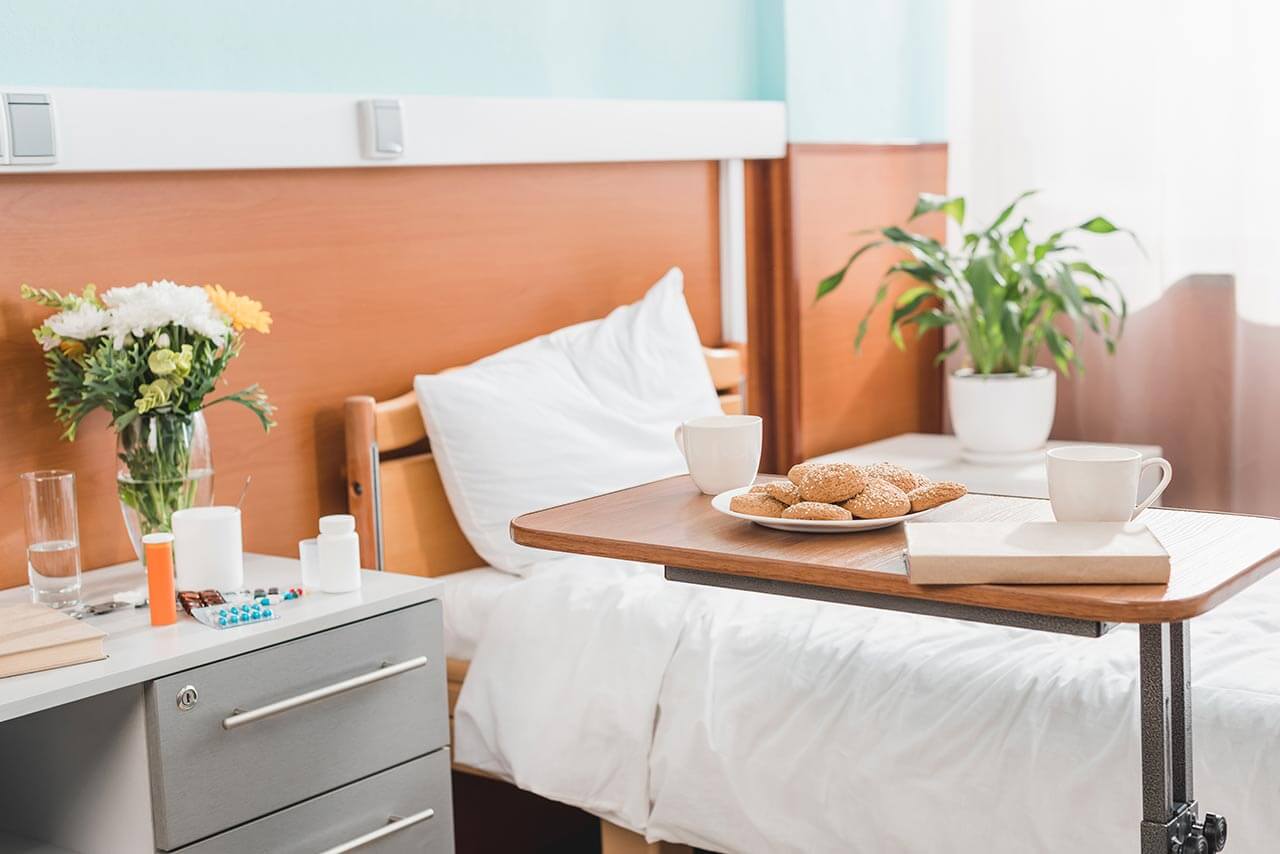
Patients rooms
The patients of the University Hospital Mainz live in bright, spacious and comfortable rooms. The patient rooms are equipped with modern electronically adjustable beds, which at the touch of a button automatically assume a specified position. Also, there is a TV and a telephone in the patient rooms. To use them, it is necessary to get a prepaid card (in vending machines at the entrance to the hospital). The use of a TV is free, but the patient will need headphones. Telephone calls are made for a fixed fee, which will be withdrawn from the prepaid card at discharge from the hospital. Also, each patient room is equipped with an ensuite bathroom with shower, washbasin and toilet.
Meals and Menus
The patients of the hospital are offered a tasty and balanced three meals a day: breakfast, lunch and dinner. The menu also includes vegetarian and dietary dishes. In addition, for both patients and their visitors there are available cafeterias and bakeries, where one can buy baked goods, snacks, hot and cold drinks.
Further details
Standard rooms include: