The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- review of medical records
- physical examination
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- general urine analysis
- biochemical analysis of blood
- TSH-basal, fT3, fT4
- tumor markers (AFP, CEA, СА-19-9)
- inflammation indicators (CRP, ESR)
- indicators of blood coagulation
- abdominal ultrasound scan
- CT/MRI of abdomen
- preoperative care
- percutaneous embolization (coiling) or chemoembolization
- symptomatic treatment
- cost of essential medicines
- nursing services
- elaboration of further recommendations
Indications
- Inoperable liver metastases
- Poor response to systemic chemotherapy
Treatment is not indicated in:
- Presence of extrahepatic metastases
- Affection of more than 70% of the liver
How program is carried out
During the first visit, the doctor will conduct a clinical examination and go through the results of the available diagnostic tests. After that, you will undergo the necessary additional examination, such as the assessment of liver and kidney function, ultrasound scan, CT scan and MRI. This will allow the doctor to determine which vessels are feeding the tumor and its metastases, as well as determine how well you will tolerate the procedure.
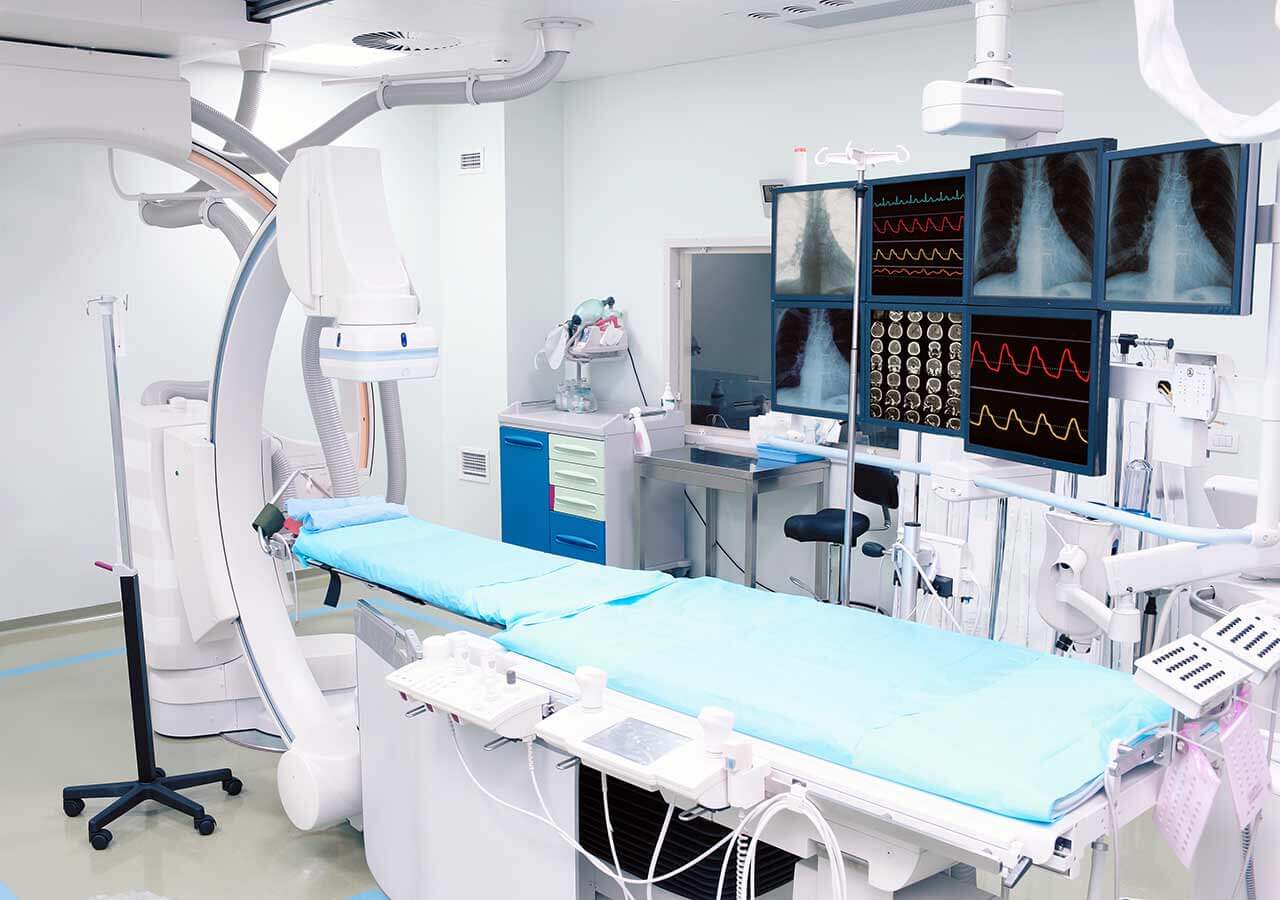
Chemoembolization begins with local anesthesia and catheterization of the femoral artery. The thin catheter is inserted through a few centimeters long incision of the blood vessel. The doctor gradually moves the catheter to the vessel feeding the primary tumor or its metastases. The procedure is carried out under visual control, an angiographic device is used for this. The vascular bed and the position of the catheter in it are displayed on the screen of the angiograph.
When the catheter reaches a suspected artery, a contrast agent is injected through it. Due to the introduction of the contrast agent, the doctor clearly sees the smallest vessels of the tumor and the surrounding healthy tissues on the screen of the angiograph. After that, he injects emboli into the tumor vessels through the same catheter.
Emboli are the spirals or the liquid microspheres. The type of embolus is selected individually, taking into account the diameter of the target vessel. When carrying out chemoembolization, a solution of a chemotherapy drug is additionally injected into the tumor vessel. Due to the subsequent closure of the vessel lumen with an embolus, the chemotherapy drug influences the tumor for a long time. In addition, the drug does not enter the systemic circulation, which allows doctors to use high doses of chemotherapeutic agents without the development of serious side effects. Chemoembolization leads to the destruction of the tumor or slowing down its progression.
After that, the catheter is removed from the artery. The doctor puts a vascular suture on the femoral artery and closes it with a sterile dressing. During chemoembolization, you will be awake. General anesthesia is not used, which significantly reduces the risks of the procedure and allows performing it on an outpatient basis, avoiding long hospital stay.
After the first procedure, you will stay under the supervision of an interventional oncologist and general practitioner. If necessary, you will receive symptomatic treatment. As a rule, a second chemoembolization procedure is performed in 3-5 days after the first one in order to consolidate the therapeutic effect. After that, you will receive recommendations for further follow-up and treatment.
Required documents
- Medical records
- Abdominal ultrasound (if available)
- MRI/CT scan of the abdomen (if available)
- Biopsy results (if available)
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Adult and Pediatric Diagnostic, Interventional Radiology, Neuroradiology at the University Hospital Jena offers the full range of services in these medical fields. Here patients can undergo all modern imaging diagnostic studies and therapeutic procedures, the quality of which corresponds to high international standards. The department also specializes in conducting radiological studies in children and adolescents. The cutting-edge technical equipment and the rich clinical experience of doctors contribute to the successful work of the department. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Ulf Teichgräber.
The department is part of three modern interdisciplinary centers: the Center for Diagnostics and Prevention of Breast Cancer, the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Prostate Cancer and the Center for Diagnostics and Treatment of Uterine Fibroids. The centers cooperate with the relevant departments of the hospital (for example, the Department of Urology, Gynecology), and thus provide accurate diagnostics and comprehensive, effective treatment even in the most complex clinical cases.
A special feature of the department is the performance of radiological studies in infants, young children and adolescents (the only department of its kind in the federal state of Thuringia). To this end, doctors use special equipment that meets the needs of young patients. Most often, specialists of the department resort to imaging diagnostics in children to detect bone fractures or pathological changes in the structure of tissues and organs. The main diagnostic methods in the field of pediatric radiology include X-ray, ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT). All studies are conducted with the best possible safety for the child's organism, which guarantees a minimal radiation dose.
Also, priority clinical focuses of the department include neuroradiology. In close cooperation with the Department of Neurology and Neurosurgery, as well as with the Department of Neuropathology, doctors provide quality neuroradiologic diagnostics and therapy. The focus is on endovascular treatment of vascular malformations of the head and neck, spinal cord, endovascular treatment of ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke, and analgesic therapy.
Since 2013, the department has a specialized outpatient clinic for minimally invasive interventions and postoperative care. Any kind of therapy is prescribed individually, with due consideration of a specific clinical situation. The main therapeutic options of the outpatient clinic include the following minimally invasive procedures (interventional radiology):
- Percutaneous transluminal angioplasty (PTA)
- Laser angioplasty
- Angioplasty with stenting
- Atherectomy
- Thrombectomy with the use of Rotarex system
- Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS)
- Port system implantation
- Chemoembolization
- Radioembolization
- Other treatments
The service range of the department includes:
- All types of X-ray studies
- Ultrasound examinations
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Breast cancer screening with the use of magnetic resonance imaging/MR mammography (within the interdisciplinary center)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the prostate to detect prostate cancer and determine its stage, prostate biopsy (within the interdisciplinary center)
- Prostate embolization for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia (within the interdisciplinary center)
- Uterine fibroid embolization (within the interdisciplinary center)
- Neuroradiology
- Conventional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain and spinal cord
- Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging
- Doppler tissue imaging
- Functional MRI
- Spectroscopy
- Computer tomography (CT) of the brain and spinal cord
- Angiography (contrast-enhanced X-ray diagnostics of vascular disease)
- Digital subtraction angiography
- Conventional X-ray studies of the brain and spinal cord
- Other services
- Pediatric radiology
- X-ray and fluoroscopy (for example, to examine lungs, musculoskeletal system, spine, skull, etc.)
- Computed tomography, including contrast-enhanced one (for example, to examine the skull, lungs, abdominal organs, spine, musculoskeletal system, etc.)
- Magnetic resonance imaging (for example, to examine all organs of the abdominal cavity, brain, musculoskeletal system, lungs, whole body, functional diagnostics of the brain, gastrointestinal tract, heart, vessels, kidneys and urinary tract)
- Ultrasound examinations (for example, to examine brain, joints, soft tissues, thyroid gland, blood vessels (Doppler and duplex sonography), bones in suspected osteoporosis, bone decalcification, etc.)
- Other services
Curriculum vitae
Education
- 2005 - 2007 Master of Business Administration, Frankfurt School of Finance.
- 1997 Harvard School of Public Health.
- 1996 - 1997 Faculty of Medicine, University of California, San Francisco, Clerkship.
- 1990 - 1997 Master of Business Administration, State Examination in Human Medicine.
- 1990 - 1997 Study of Human Medicine, Hannover Medical School.
Positions
- May 2003 - July 2010 Senior Physician, Head of the Section of Interventional Radiology, Charite University Hospital Berlin.
- October 1990 - May 1997 Student/Doctoral Fellow, Hannover Medical School.
- 1996 - 1996 Clerkship, Harvard Medical School, Massachusetts General Hospital.
Licenses and Certificates
- June 2007 Certificate of the Head of the Seminar of the German Society of Ultrasound in Medicine (without expiration).
Photo of the doctor: (c) Universitätsklinikum Jena
About hospital
According to the prestigious Focus magazine, the University Hospital Jena regularly ranks among the top German medical facilities!
The hospital has positioned itself as a multidisciplinary medical facility with a long history of more than 200 years. Since its foundation, the hospital has been constantly developing and modernizing, thanks to which nowadays it offers patients the highest level of treatment in Germany based on the use of innovative technologies and the very latest therapeutic techniques. The hospital consists of 26 specialized departments and 25 research institutes. It treats more than 53,600 inpatients and about 274,000 outpatients every year. The staff of the hospital includes more than 5,600 competent doctors.
The extensive resources of the university hospital, high treatment standards, and the introduction of new research developments provide first-class treatment in Germany meeting the stringent international standards. The hospital has an excellent reputation not only in Germany, but also far beyond its borders, due to which it accepts a large number of foreign patients for the diagnostics and treatment.
Despite the technical progress and the availability of accurate computerized systems, the patient’s physical health and emotional state is the main value of each employee of the hospital, since some diagnoses cause emotional distress in patients. The doctors of the hospital believe that the key to a successful result is a comprehensive and individual approach, so they spend a lot of time talking with patients, listen carefully to all their wishes and support at all stages of the therapeutic process. All this in combination with high-precision diagnostic techniques and the very latest types of therapy forms a solid basis for the achievement of an optimal treatment result.
Photo: (c) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
Patients rooms
The patients of the University Hospital Jena live in comfortable single and double rooms made in a modern design. Each patient room is equipped with an ensuite bathroom with shower and toilet. The room has enough space to store personal belongings, as well as a table and chairs for receiving visitors. A bedside table can be converted into a table so that patients can eat right in their bed. Each room has a TV, and there is also access to the Internet. In addition, the hospital offers enhanced-comfort rooms.
Meals and Menus
The patient and his accompanying person have a daily choice of three menus. If for some reason the patient does not eat all the foods, he will be offered an individual menu. Please inform the medical staff about your dietary preferences prior to the treatment.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Religion
Religious services are available upon request.
Accompanying person
During the inpatient program, an accompanying person may stay with you in a room or at the hotel of your choice.
Hotel
During the outpatient program, you can live at a hotel of your choice. Managers will help you to choose the most suitable options.