The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- review of medical records
- physical examination
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- biochemical analysis of blood
- inflammation indicators (CRP, ESR)
- indicators blood coagulation
- TSH-basal
- blood gas analysis
- chest x-ray examination
- measurement of arterial blood pressure
- electrocardiogram (ECG)
- high-resolution computed tomography (HR-CT)
- pulmonary function test
- bronchoscopy with biopsy
- histological and microbiological examination
- preoperative care
- surgical pleurectomy
- histologically and immunohistochemically
- examination of the remote tissues
- symptomatic treatment
- control examinations
- the cost of essential medicines and materials
- nursing services
- full hospital accommodation
- explanation of future recommendations
Required documents
- Medical records
- X-ray examination, MRI/CT scan (if available)
- Pleural biopsy (if available)
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Vascular Surgery at the University Hospital Ulm provides effective surgical treatment for diseases of the heart, respiratory system, and blood vessels. The team of cardiac surgeons operates on patients with heart valve pathologies, coronary heart disease, heart failure, and heart rhythm disturbances. In the field of thoracic surgery, the key focus is on the surgical removal of lung tumors and lung metastases. The specialists in this area also perform surgery to repair chest wall deformities. In the field of vascular surgery, interventions for abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms are most often performed here. The department's vascular surgeons are also exceptionally competent in the treatment of peripheral occlusive arterial disease. A great advantage for the department's patients is that almost all surgical interventions are performed using minimally invasive techniques, so there is no need for a long postoperative recovery. The department's operating rooms are equipped with state-of-the-art technology. This allows for effective and safe treatment. The priority is always personalized medical care for patients. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Andreas Liebold.
Coronary heart disease is one of the most common causes of death worldwide, and therefore the department performs coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG) almost daily. This operation is considered to be the most effective method of restoring normal blood supply to the myocardium. The department's cardiac surgeons have a perfect command of all modern CABG techniques, including the classical method with the use of a heart-lung machine, the minimally invasive method with the use of a heart-lung machine, and off-pump coronary artery bypass (OPCAB) without the use of a heart-lung machine. The optimal CABG option is selected on an individual basis after a thorough study of the patient's clinical data and potential surgical risks. Preference is always given to minimally invasive surgery if possible.
The department also regularly admits patients with heart failure. In the early stages of the disease, conservative treatment is provided, but as heart failure progresses, only a surgical procedure may be helpful. The department's specialists perform operations for resecting left ventricular aneurysms, which significantly improves the pumping function of the heart and the quality of life of the patient. Another surgical method to improve the pumping function of the heart in heart failure is reconstructive plastic surgery of the left ventricle, including the replacement of part of its wall using autologous tissue or artificial material. The department also regularly performs surgery to implant single-, dual-, and triple-chamber pacemakers and cardioverter-defibrillators. Doctors individually adjust the assistive device depending on the patient's condition, improving ventricular performance and atrial coordination.
The department's thoracic surgeons are highly skilled in performing surgery for lung cancer and lung metastases. The scope of surgery for lung cancer depends on the tumor size and the spread of the oncological process. Localized tumors are treated using tumor resection, while in advanced stages of cancer, segmental resection (the tumor is removed with part of the lung) or lobectomy (resection of a lobe of the lung) may be required. The last-line surgical treatment for lung cancer is a pneumonectomy (removal of the entire lung). To remove lung metastases, both open surgical interventions and sparing surgical procedures are performed, the most effective of which are considered to be radiofrequency and microwave ablation.
The department's team of vascular surgeons brilliantly performs operations on abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms. An aortic aneurysm is its pathological local expansion due to the weakening of the walls. The risk of developing pathology increases with age. The main etiologic causes include atherosclerosis, arterial hypertension, smoking, and diabetes mellitus. In some cases, aneurysm development may be caused by bacterial infections and inflammation. An aneurysm is a life-threatening condition because its rupture causes severe internal bleeding, which is potentially fatal. In most cases, aortic aneurysms do not cause any symptoms, but when they become large, they put pressure on the adjacent structures. If the aneurysm ruptures, the patient will experience sharp pain in the thorax, back, or abdomen, and the resulting internal bleeding may cause unconsciousness. Surgical treatment is indicated if the aneurysm is 5 cm or more in diameter or if the aneurysm is rapidly enlarging. The department's vascular surgeons perform classical and endovascular operations to treat aneurysms. In the first case, a special Y-prosthesis is implanted through an open approach, and in the second case, the doctor approaches the pathological focus through a femoral artery puncture, after which a stent-graft is implanted. Both interventions are performed under general anesthesia, and the duration of a hospital stay is 5-10 days.
The department's specialists also perform surgical treatment of carotid artery stenosis using classical and endovascular methods. Carotid artery stenosis occurs due to the formation of atherosclerotic plaques on the blood vessel walls. The main risk factors for pathology include smoking, elevated cholesterol levels, diabetes mellitus, and arterial hypertension. Carotid artery stenosis mostly does not cause any symptoms, so it is diagnosed accidentally during an ultrasound scan for other complaints. At the same time, carotid artery stenosis may provoke a stroke, a life-threatening condition. The department's vascular surgeons effectively eliminate carotid artery narrowing with thromboendarterectomy (classical surgery) or balloon dilatation with stent implantation (endovascular surgery). During thromboendarterectomy, the affected carotid artery is approached through an incision in the neck. The surgeon isolates the affected artery, removes the atherosclerotic plaque, and closes the incision area with a synthetic patch. The operation is performed under general anesthesia, and the duration of a hospital stay is just a few days. Balloon dilatation involves the placement of a special balloon into the blood vessel through a puncture in the femoral artery. Once positioned correctly, the balloon is inflated to eliminate the artery stenosis. The final stage of the intervention is the implantation of a stent, which keeps the blood vessel open. Endovascular intervention is performed under local anesthesia.
The department's range of surgical services includes:
- Cardiac surgery
- Surgical treatment of coronary artery diseases
- Conventional coronary artery bypass grafting
- Total arterial myocardial revascularization
- Minimally invasive coronary artery bypass grafting
- Off-pump coronary artery bypass surgery on a beating heart
- Surgical treatment of mitral valve diseases
- Mitral valve reconstructive plastic surgery
- Mitral valve replacement surgery with biological or mechanical prostheses, including minimally invasive techniques
- Surgical treatment of aortic valve diseases
- Aortic valve reconstructive plastic surgery
- Aortic valve replacement with biological or mechanical prosthesis, including minimally invasive techniques
- Surgical treatment of heart failure
- Resection of a left ventricular aneurysm
- Differentiated remodeling of the heart ventricles, including reduction plastic surgery
- Implantation of single-, dual-, and triple-chamber pacemakers and cardioverter-defibrillators
- Implantation of extra- and intracorporeal mechanical cardiac support systems
- Surgical treatment of thoracic aortic diseases
- Ascending aorta replacement surgery
- Yakub and David procedures
- Surgical treatment of arrhythmias
- Implantation of cardiac recorders, pacemakers, and defibrillators with the subsequent continuous monitoring of implanted devices
- Endoscopic radiofrequency ablation for atrial fibrillation
- Surgical treatment of coronary artery diseases
- Thoracic surgery
- Surgical treatment of lung cancer and lung metastases
- Malignant tumor resection
- Segmental lung resection
- Lobectomy (lung lobe resection)
- Pneumonectomy (whole lung surgical removal)
- Classical surgery, radiofrequency, and microwave ablation to remove lung metastases
- Video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) to treat lung tumors, pneumothorax, and pleural adhesions
- Sympathectomy using VATS to treat excessive sweating (hyperhidrosis)
- Surgery for pleural empyema
- Chest wall surgery for the treatment of accidental injuries and other pathologic conditions
- Lung volume reduction surgery using VATS
- Pleurodesis using VATS (artificial obliteration of the pleural cavity)
- Surgery for a spontaneous pneumothorax
- Surgical treatment of lung cancer and lung metastases
- Vascular surgery
- Open and endovascular surgery for abdominal and thoracic aortic aneurysms and thoracoabdominal aneurysms.
- Open and endovascular surgery for acute and chronic type B aortic dissection (according to the Stanford classification).
- Endovascular bypass surgery and stent implantation for the treatment of peripheral occlusive arterial disease
- Thromboendarterectomy (open surgery) and balloon dilatation followed by stent implantation (endovascular surgery) for the treatment of carotid artery stenosis
- Other medical services
Curriculum vitae
Higher Education and Postgraduate Training
- 1984 - 1989 Medical studies, Leipzig University.
- 1989 Admission to medical practice.
- 1990 Thesis defense, Leipzig University. Subject: "Ischemic heart disease and acute reduction of left ventricular function: results of a surgical intervention compared to drug therapy".
- 1989 - 1991 Training in Surgery (General Surgery and Neurosurgery), clinics in Chemnitz and Bad Neustadt.
- 1997 Board certification in Cardiac Surgery.
- 2001 Habilitation and Venia Legendi, University of Regensburg. Subject: "Research on minimized extracorporeal blood circulation".
- 2015 Certified Specialist in Transcatheter Aortic Valve Implantation.
Professional Career
- 1990 - 1995 Assistant Physician, clinics in Chemnitz, Bad Neustadt, and Regensburg.
- 1995 - 2004 Senior Physician, Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, University Hospital Regensburg.
- 2004 - 2010 Professor for Cardiac Surgery, University of Rostock.
- 2004 - 2011 Deputy Head Physician, Department of Cardiac Surgery, University Hospital Rostock.
- Since 2011 Head Physician, Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery and Vascular Surgery, University Hospital Ulm.
Clinical Interests
- Minimally invasive reconstructive plastic surgery of the mitral and tricuspid valves.
- Minimally invasive closure of an atrial septal defect.
- Minimally invasive cardiac surgery using 3D technology.
- Aortic root surgery.
- Heart valve replacement surgery.
- Aortocoronary bypass surgery.
- Artificial heart implantation.
Awards and Honors
- 2019 Included in the list of outstanding physicians according to the Focus medical magazine.
- 2020 Included in the list of outstanding cardiac surgeons according to the Focus medical magazine.
Memberships in Professional Societies
- International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT).
- European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery (EACTS).
- German Society for Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery (DGTHG).
- German Transplantation Society (DTG).
- Eurotransplant International Foundation (ET).
- International Society for Minimally Invasive Cardiothoracic Surgery (ISMICS).
- German Association of Universities (DHV).
Photo of the doctor: (c) Universitätsklinikum Ulm
About hospital
The University Hospital Ulm is an advanced medical complex that provides patients with high-class medical care using the very latest scientific achievements. The medical facility has been performing successful clinical activities for more than 40 years and has long earned an excellent reputation throughout Europe. The hospital regularly demonstrates high treatment success rates, takes an active part in the training of medical students, and works tirelessly on promising research projects.
The university hospital consists of 29 specialized departments and 16 scientific institutes, where more than 7,000 highly qualified employees work for the benefit of their patients. More than 55,000 inpatients and about 300,000 outpatients are treated here every year. The hospital has 1,274 beds. The medical team of the hospital is focused on providing personalized medical services using the most modern and sparing diagnostic and treatment methods.
The University Hospital Ulm is the largest medical complex in the region, and practically all areas of modern medicine are represented here. Transplantology and oncology are among the priority areas of clinical activity in the medical facility. The hospital holds leading positions in the world in bone marrow transplantation. In addition, the hospital has advanced experience in cancer treatment. The Comprehensive Cancer Center is recognized as the leading facility of this kind in the country, and it is certified by the German Cancer Society (DKG). It provides effective treatment for various types of cancer. The center also offers innovative CAR T-cell therapy. In addition, the Cancer Center is actively engaged in research activities to improve available treatment methods and develop innovative therapeutic techniques to fight cancer.
Along with the use of advanced technologies, doctors show respect, understanding, and a humane attitude toward the patient. The medical team includes competent psychologists, who are always ready to provide assistance and support to the patients and their families during the therapeutic process.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
Patients rooms
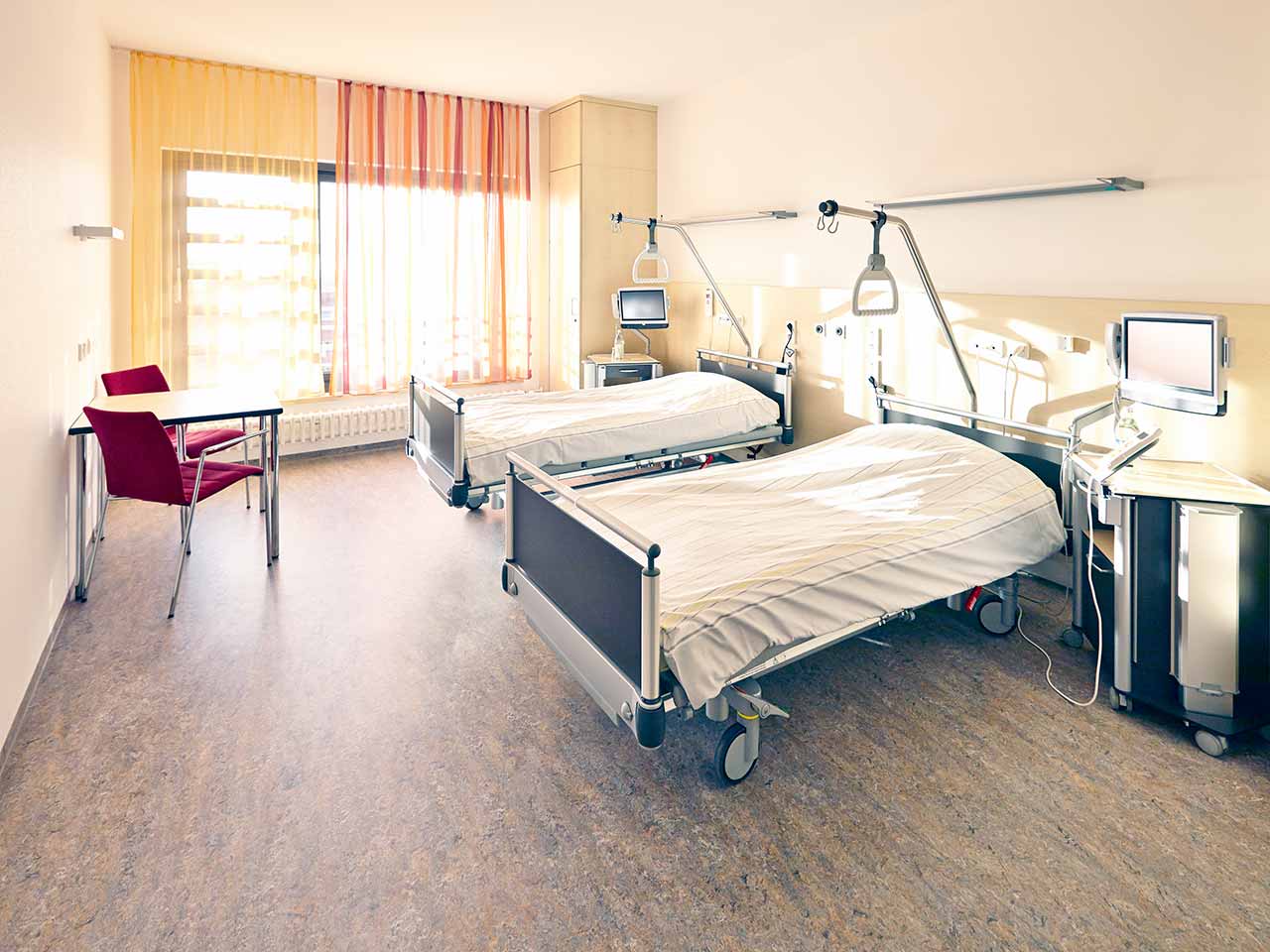
The patients of the University Hospital Ulm live in comfortable single and double rooms with a modern design and light colors. All patient rooms have an ensuite bathroom with a toilet and a shower. The patient room furnishings include a comfortable automatically adjustable bed, a bedside table, a wardrobe, a table and chairs, a telephone, a radio, and a TV. Wi-Fi access is also available in patient rooms.
The hospital also offers enhanced-comfort rooms, which additionally have a safe, a refrigerator, and upholstered furniture. The bathroom in the enhanced-comfort room has changeable towels, a cosmetic mirror, a hairdryer, and toiletries.
Meals and Menus
Patients and their accompanying person are offered three meals a day: breakfast, lunch, and dinner. The patient and accompanying person have a choice of three menus every day, including a vegetarian menu. Patients staying in the enhanced-comfort rooms are also offered light snacks, fruits, desserts, and hot and cold drinks in the comfortable lounge area.
If, for some reason, you do not eat all the foods, you will be offered an individual menu. Please inform the medical staff about your dietary preferences prior to treatment.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
![]() Shower
Shower
![]() Toilet
Toilet
![]() Wi-Fi
Wi-Fi
![]() TV
TV
Religion
The hospital has a chapel where Catholic and Protestant services are held weekly. The services are also broadcast on the internal television channel of the hospital. The chapel is open 24 hours a day for visits and prayers.
The services of other religious representatives are available upon request.
Accompanying person
Your accompanying person may stay with you in your patient room or at the hotel of your choice during the inpatient program.
Hotel
You may stay at the hotel of your choice during the outpatient program. Our managers will support you for selecting the best option.