The program includes:
- Initial presentation in the clinic
- clinical history taking
- review of medical records
- physical examination
- laboratory tests:
- complete blood count
- general urine analysis
- biochemical analysis of blood
- TSH-basal, fT3, fT4
- tumor markers (AFP, CEA, СА-19-9)
- inflammation indicators (CRP, ESR)
- indicators of blood coagulation
- abdominal ultrasound scan
- CT/MRI of abdomen
- preoperative care
- percutaneous embolization (coiling) or chemoembolization
- symptomatic treatment
- cost of essential medicines
- nursing services
- elaboration of further recommendations
Indications
- Inoperable liver metastases
- Poor response to systemic chemotherapy
Treatment is not indicated in:
- Presence of extrahepatic metastases
- Affection of more than 70% of the liver
How program is carried out
During the first visit, the doctor will conduct a clinical examination and go through the results of the available diagnostic tests. After that, you will undergo the necessary additional examination, such as the assessment of liver and kidney function, ultrasound scan, CT scan and MRI. This will allow the doctor to determine which vessels are feeding the tumor and its metastases, as well as determine how well you will tolerate the procedure.
Chemoembolization begins with local anesthesia and catheterization of the femoral artery. The thin catheter is inserted through a few centimeters long incision of the blood vessel. The doctor gradually moves the catheter to the vessel feeding the primary tumor or its metastases. The procedure is carried out under visual control, an angiographic device is used for this. The vascular bed and the position of the catheter in it are displayed on the screen of the angiograph.
When the catheter reaches a suspected artery, a contrast agent is injected through it. Due to the introduction of the contrast agent, the doctor clearly sees the smallest vessels of the tumor and the surrounding healthy tissues on the screen of the angiograph. After that, he injects emboli into the tumor vessels through the same catheter.
Emboli are the spirals or the liquid microspheres. The type of embolus is selected individually, taking into account the diameter of the target vessel. When carrying out chemoembolization, a solution of a chemotherapy drug is additionally injected into the tumor vessel. Due to the subsequent closure of the vessel lumen with an embolus, the chemotherapy drug influences the tumor for a long time. In addition, the drug does not enter the systemic circulation, which allows doctors to use high doses of chemotherapeutic agents without the development of serious side effects. Chemoembolization leads to the destruction of the tumor or slowing down its progression.
After that, the catheter is removed from the artery. The doctor puts a vascular suture on the femoral artery and closes it with a sterile dressing. During chemoembolization, you will be awake. General anesthesia is not used, which significantly reduces the risks of the procedure and allows performing it on an outpatient basis, avoiding long hospital stay.
After the first procedure, you will stay under the supervision of an interventional oncologist and general practitioner. If necessary, you will receive symptomatic treatment. As a rule, a second chemoembolization procedure is performed in 3-5 days after the first one in order to consolidate the therapeutic effect. After that, you will receive recommendations for further follow-up and treatment.
Required documents
- Medical records
- Abdominal ultrasound (if available)
- MRI/CT scan of the abdomen (if available)
- Biopsy results (if available)
Service
You may also book:
 BookingHealth Price from:
BookingHealth Price from:
About the department
The Department of Adult and Pediatric Interventional Radiology, Neuroradiology at the Municipal Hospital Karlsruhe provides the full range of imaging diagnostics and image-guided minimally invasive treatment. The medical facility admits patients of all age groups, including children and adolescents. In the field of interventional radiology, special attention is paid to the treatment of vascular diseases and cancers, and pain management for chronic pain. An integral part of the department's clinical practice is the interventional treatment of neurological disorders, including stroke, carotid stenosis, and cerebral aneurysms. Medical care is provided both on an inpatient and outpatient basis. The department is one of the largest medical facilities of this kind in Germany and has been awarded a prestigious certificate from the German Society for Interventional Radiology and Minimally Invasive Therapy (DeGIR). The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Peter Reimer.
The department is proud of its advanced equipment: 5 devices for computed tomography (CT), 4 devices for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), 3 devices for angiography, 2 mammography systems, 5 X-ray systems, 3 ultrasound devices and 1 device for digital volume tomography. The department also cooperates closely with the Department of Nuclear Medicine, thanks to which patients have the opportunity to undergo PET/CT and SPECT/CT scans. The results of the performed examinations are recorded and stored using a modern picture archiving and communication system. The department also participates in the telemedicine project, in cooperation with the University Hospitals of Mannheim and Heidelberg. In addition, this equipment is used for imaging-guided interventional diagnostic and therapeutic procedures. The department's doctors take a responsible approach to compliance with radiation protection standards, so all examinations and treatment are absolutely safe.
The department performs many imaging-guided interventional therapeutic procedures. These procedures are an excellent alternative to open surgery, as only a skin puncture is needed for access, without any incisions or sutures. In addition, interventions are performed using local anesthesia. Therefore, this type of treatment significantly reduces the risks to the patient's health and contributes to the shortest possible hospital stay.
The most common scope of interventional treatment is catheter-based procedures for vascular pathologies: stenosis and occlusion of the blood vessels of the pelvis and lower limbs, arteries of the kidneys, bowel, lungs, aorta, deep vein thrombosis and other diseases. The department's doctors also successfully perform embolization (local injection of emboli to occlude blood vessels) for the treatment of uterine fibroids, benign prostatic hyperplasia, varicocele, internal bleeding, and hemorrhoids. Transarterial embolization and transarterial chemoembolization are successfully used for cancer treatment. The essence of these procedures is to block the blood vessels supplying the tumor, due to which the tumor is deprived of nutrition and thereby is destroyed. Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT) is also available in the department and involves the introduction of radiation sources in close proximity to the tumor, due to which the tumor is destroyed, and healthy adjacent tissues are practically not affected. This type of therapy is most often used for liver tumor and metastasis treatment.
The department's physicians often resort to image-guided interventional procedures to drain abscesses, ascites, form dialysis access, and place port systems. The specialists also use interventional manipulations to treat chronic pain syndromes, for example, facet joint block can effectively eliminate back pain without resorting to surgical interventions.
Neuroradiology is responsible for the interventional treatment of neurological disorders. Doctors most often deal with strokes, carotid stenosis, cerebral aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, and dural fistulas. Despite the achievements of modern medicine and the availability of innovative navigation systems, catheter-based treatment of neurological pathologies remains safer, since the risk of damage to vital brain structures is negligible. In addition, patients recover much quicker after interventional treatment.
The department's diagnostic options include:
- Classic X-ray tests
- Computed tomography (also with contrast enhancement)
- Diagnostics of tumors
- Diagnostics of vascular pathologies
- Diagnostics of heart pathologies
- Emergency diagnostics
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Diagnostics of brain and spinal pathologies
- Diagnostics of heart pathologies
- Diagnostics of breast pathologies
- Diagnostics of abdominal and small pelvis pathologies
- Diagnostics of vascular pathologies
- Diagnostics of musculoskeletal pathologies
- Fetal MRI diagnostics
- Ultrasound scans
- Color-coded duplex sonography of the carotid artery and other vessels
- Ultrasound scanning of the neck and thyroid soft tissues
- Abdominal and pelvic ultrasound scans
- Ultrasound-guided fusion biopsy of the prostate gland
- Diagnostics of breast pathologies
- Digital mammography
- High resolution breast sonography
- Tomosynthesis
- Contrast-enhanced spectral mammography
- Magnetic resonance imaging of the breast
- Imaging tests in children
- X-ray scans
- Diagnostics of skeletal pathologies
- Diagnostics of scoliosis
- Measurement of the length of the lower limbs and axial parameters of the lower limbs
- Lung examinations
- Bone examinations
- Fluorography
- Esophageal scans
- Gastrointestinal scans
- Contrast enema
- Urethral and bladder pressure testing
- Magnetic resonance imaging
- Skull scans
- Chest scans
- Abdominal scans
- Vascular imaging
- Whole-body magnetic resonance imaging
- Spectroscopy
- Fetal MRI
- Computed tomography
- Chest scans
- Abdominal scans
- Limb scans
- Digital volume tomography
- CT-guided interventional procedures
- Ultrasound examinations
- X-ray scans
- Other diagnostic services
The department's range of therapeutic services includes:
- Interventional radiology
- Image-guided interventions for stenoses and occlusions of the blood vessels of the pelvis and lower limbs, arteries of the kidneys, bowel, lungs, aorta, and deep vein thrombosis
- Embolization for uterine fibroids, benign prostatic hyperplasia, varicocele, internal bleeding, hemorrhoids, and vascular malformations
- Image-guided interventions for abscess and ascite drainage, dialysis access and port system placement
- Image-guided interventions for cancer treatment
- Transarterial embolization
- Transarterial chemoembolization
- Selective internal radiation therapy (SIRT)
- Ablation
- Pain management for chronic pain syndromes
- Periradicular therapy
- Facet joint block
- Nerve plexus block
- Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty
- Interventional neuroradiology
- Image-guided interventions for stroke
- Image-guided interventions for cerebral aneurysms
- Image-guided interventions vascular malformations
- Image-guided interventions for carotid stenosis
- Image-guided interventions for dural fistulas
- Image-guided interventions for cerebral vein diseases
- Image-guided interventions for brain and spinal cord tumors
- Other medical services
Curriculum vitae
Higher Education and Professional Career
- 2009 Master of Health Services Administration, Koblenz University of Applied Sciences.
- Since 2000 Head Physician of the Department of Adult and Pediatric Interventional Radiology, Neuroradiology at the Municipal Hospital Karlsruhe.
- 1993 - 1999 Senior Physician and Assistant Professor in Radiology, Department of Radiology at the University Hospital Muenster.
- 1989 - 1991 Research Fellow, Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, USA.
- 1986 - 1989, 1991 - 1992 Internships, Hannover Medical School.
- 1978 - 1985 Study of Medicine, Faculty of Medicine, University of Cologne.
Memberships in Professional Societies
- German Radiological Society (DRG).
- German Society of Ultrasound in Medicine (DEGUM).
- Society of Southwest Germany Radiologists and Nuclear Medicine Specialists.
- International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (ISMRM).
- Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
- European Society of Cardiology (ESCR).
- European Society of Cardiovascular Radiology (ESCR).
- European Congress of Radiology (ECR).
- European Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine and Biology.
- Academy of Radiology.
- Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE).
- European Society of Urogenital Radiology.
- German Society for Interventional Radiology and Minimally Invasive Therapy (DeGIR).
- Working Group on the Diagnostics of the Heart and Blood Vessels.
- Working Group on Radiological Tests of the Musculoskeletal System.
Photo of the doctor: (c) Städtische Klinikum Karlsruhe
About hospital
The Municipal Hospital Karlsruhe is a modern maximum care medical facility, which combines a long tradition and the advanced achievements of modern medicine. The hospital operates on the basis of the University of Freiburg, so scientific innovations in the field of diagnostics and treatment are continuously introduced into practice here. The hospital presents almost all areas of modern medicine, including many medical services for young patients.
A highly qualified and experienced team of more than 4,500 employees provides impeccable medical care. The medical facility has 1,571 beds for the hospitalization of its patients. The hospital admits more than 63,000 inpatients and about 186,000 outpatients annually. A large number of patients wishing to receive medical care in the hospital speak for themselves and are a confirmation of the exceptional service, as well as the effectiveness of the treatment provided.
The quality management system of the hospital's medical care is certified in accordance with the DIN EN ISO 9001 standards. Since 2016, the hospital has implemented a regular quality control in compliance with the strict standards of the Initiative Quality Medicine (IQM). In addition, almost all departments of the hospital have numerous certificates in their areas of specialization, including certificates from the German Cancer Society (DKG), the German Society for General and Visceral Surgery (DGAV), the German Cardiac Society (DGK), the German Diabetes Society (DDG), the German Society of Nephrology (DGN), the German Trauma Society (DGU), etc.
The main value of the hospital's staff is the health and satisfaction of their patients, so a respect and a humane attitude towards each patient remain priorities. The doctors and nursing staff support each patient in every possible way on their path to recovery. The specialists also strive to perform the most sparing, but at the same time the most effective and safe treatment.
Photo: (с) depositphotos
Accommodation in hospital
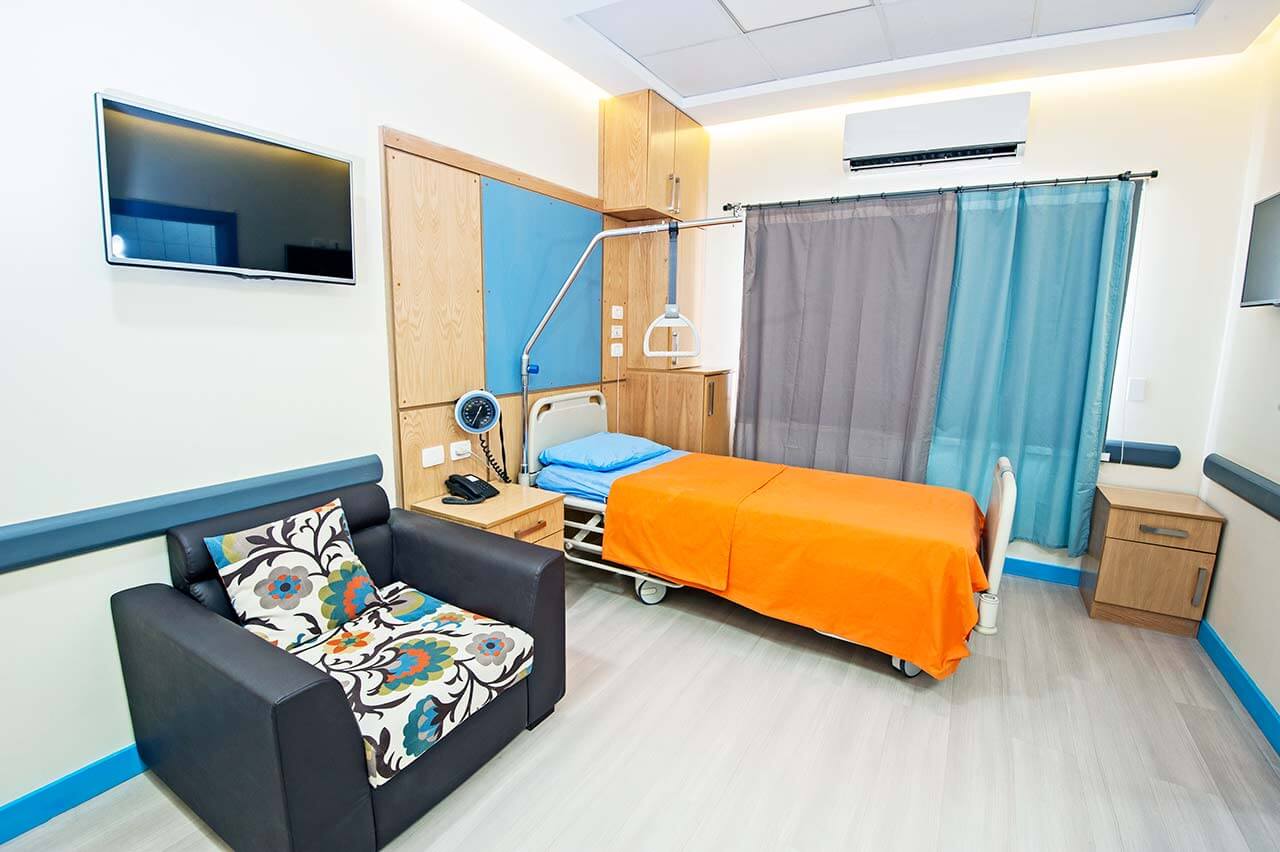
Patients rooms
The patients of the Municipal Hospital Karlsruhe live in cozy patient rooms with everything necessary for a comfortable stay. Standard patient room furnishing includes an automatically adjustable bed, a bedside table, a TV, and a telephone. The patient rooms have Wi-Fi. Each patient room also has an ensuite bathroom with a shower and a toilet.
The patient rooms in the pediatric departments are specially designed for children, so that young patients feel at home. Children can live in their patient room with one of their parents. There are also special playrooms designed for children.
Meals and Menus
The patients of the hospital are offered tasty and varied three meals a day: breakfast, lunch and dinner. The menu also features dietary meals. The kitchen staff will gladly accept all the individual wishes of patients.
The hospital also has a cozy cafe where one can have a tasty snack, drink tea, coffee and soft drinks.
Further details
Standard rooms include:
Religion
The hospital has two chapels that regularly host Protestant, Catholic, and Ecumenical worship services. A patient can watch the broadcast of the worship on TV channels in his own room, if desired.
Accompanying person
Your accompanying person may stay with you in your patient room or at the hotel of your choice during the inpatient program.
Hotel
You may stay at the hotel of your choice during the outpatient program. Our managers will support you for selecting the best option.