About the Department of Pediatric Epileptology at University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich
The Department of Pediatric Epileptology at the University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich provides comprehensive medical care for children with all types of epilepsy. The primary task of the doctors of the medical facility when a child is admitted to the department is to confirm or exclude the diagnosis of epilepsy. As a rule, long-term video-EEG monitoring is used for this purpose, which allows not only to detect the presence of pathological changes in the brain of a young patient but also to determine the size and location of epileptic foci. Whenever required, the department's doctors cooperate with neuropediatricians, neurologists, and neurosurgeons to provide young patients with differential diagnostics of epilepsy and carry out neurological tests for a comprehensive assessment of the functioning of the nervous system. In most cases, the department's team of doctors uses only drug therapy and other conservative treatments. Epilepsy surgery may be required only in complex cases if drug therapy does not give the desired result and seizures do not disappear after a certain period of time. Surgical procedures for epilepsy are performed in state-of-the-art operating rooms in collaboration with neurosurgeons who have vast experience in the surgical treatment of this pathology. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Ingo Borggräfe.
Epilepsy is a severe brain disorder. The condition is associated with impaired neuronal activity and the development of seizures, the intensity and duration of which may vary. During an epileptic seizure, a child experiences a clouding of consciousness, accompanied by motor and sensory disturbances. The child falls asleep for a few minutes after an epileptic seizure and, after waking up, cannot remember the seizure that happened. It is noteworthy that epilepsy can also develop in infants under the age of 1 year, but not only in young children and adolescents.
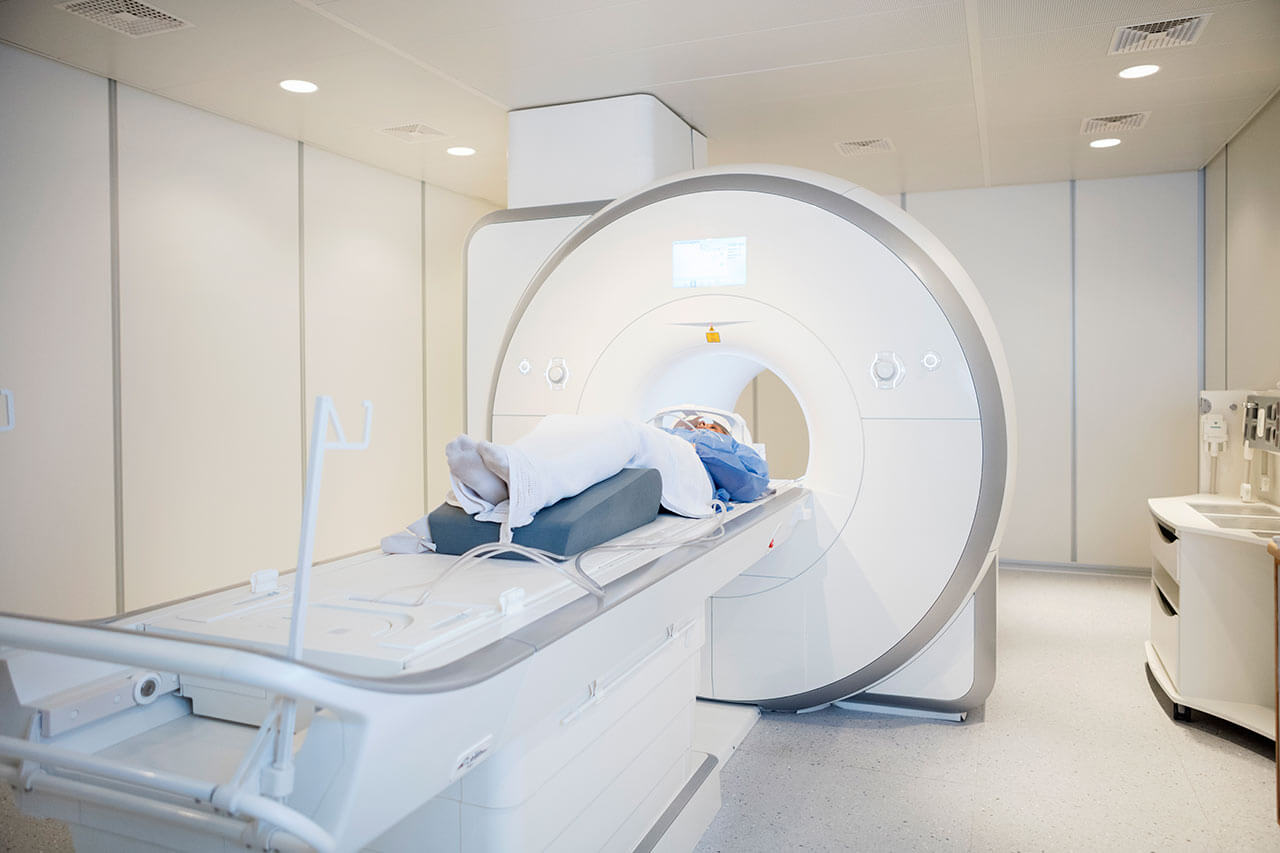
The first stage of the diagnostic process is the collection of a child's medical history, during which doctors clarify the circumstances under which a seizure usually occurs, the characteristics of the prenatal and postnatal periods, the child's daily regimen, the presence of epilepsy in the family, and other data. This is followed by laboratory tests and instrumental examinations such as complete blood count and urinalysis, biochemical profile, electroencephalography, including long-term video-EEG monitoring, CT and/or MRI. The attending physician may prescribe other diagnostic procedures whenever required.
As for treatment, the department's specialists mainly carry out drug therapy with anticonvulsants, which helps the doctors to reduce the pathological activity of the brain. As a rule, the department's epileptologists prefer to prescribe a single drug (monotherapy), as clinical trials show that such an approach to treatment achieves the best results. The department's specialists have rich clinical experience in the individual prescription of the most effective drug and its optimal dosage to achieve control over epilepsy. Treatment with anticonvulsants usually takes one to several years. If a doctor sees a positive trend in the child, the dosage of the drug will be gradually reduced. In some cases, it may be necessary to increase the dose.
An important part of the therapeutic process is compliance with the daily regime, since fatigue, poor sleep, stress, and malnutrition may trigger the development of epileptic seizures. Particular attention is paid to the diet. The department's doctors often prescribe a ketogenic diet for children, the essence of which is to give up sugar and sweets and increase the intake of fats, including animal ones. The child is also recommended to drink plenty of fluids. The therapeutic effect is achieved by converting fats into ketone bodies (lipid metabolism products), which, once in the brain, help to reduce abnormal neural activity and reduce the onset of seizures. In most cases, physical therapy is also widely used during the therapeutic process.
The last-line therapy for epilepsy is surgery. It is performed by highly specialized neurosurgeons who cooperate closely with the department's specialists. Epilepsy surgery is the method of choice in cases where drug therapy is ineffective or in patients with complex forms of the neurological disorder. Prior to surgery, preoperative diagnostics are mandatory: video-EEG monitoring, including an invasive one, and various brain imaging tests. Young patients undergoing their treatment in the department are offered the following operations for epilepsy: a focal resection of the epileptic focus, a hemispherectomy, and a callosotomy. Alternative treatments in the presence of contraindications to neurosurgical intervention are vagus nerve electrostimulation and thalamic stimulator implantation.
The department's main clinical activities are as follows:
- Epilepsy diagnostics
- Laboratory tests: complete blood count, urinalysis, and biochemical profile
- Electroencephalography, including long-term video-EEG monitoring and invasive EEG monitoring
- Computed tomography
- Magnetic resonance imaging, including functional MRI
- Tractography
- 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron emission tomography
- Ictal single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)
- Epilepsy treatment
- Conservative treatment
- Drug therapy with anticonvulsants
- Ketogenic diet and daily regime normalization
- Therapeutic exercises
- Surgical treatment
- Focal resection of the epileptic focus
- Hemispherectomy
- Callosotomy
- Alternative treatments in the case of contraindications to surgery: vagus nerve electrical stimulation and thalamic stimulator implantation
- Conservative treatment
- Other medical services