About the Department of Interventional Neuroradiology at University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich
The Department of Interventional Neuroradiology at the University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University Munich offers the full range of medical services at the highest level of university medicine. The patients of the medical facility can undergo imaging diagnostics and image-guided interventional treatment of diseases of the nervous system. The focus of the department's specialists is on patients with strokes, cerebral vascular stenosis, vascular malformations of the brain and spinal cord, and cerebral aneurysms. Medical care includes counseling, emergency care, inpatient and outpatient care. The department's diagnostic options include computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, and digital subtraction angiography. Imaging equipment can also be used for therapeutic manipulations on the brain and spinal cord. Experts from the Departments of Neurology and Neurosurgery are often engaged in the therapeutic process, especially at the stage of treatment planning. The unique competencies of doctors and the excellent equipment of the medical facility are the keys to medical service of the highest European standard. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Thomas Liebig.
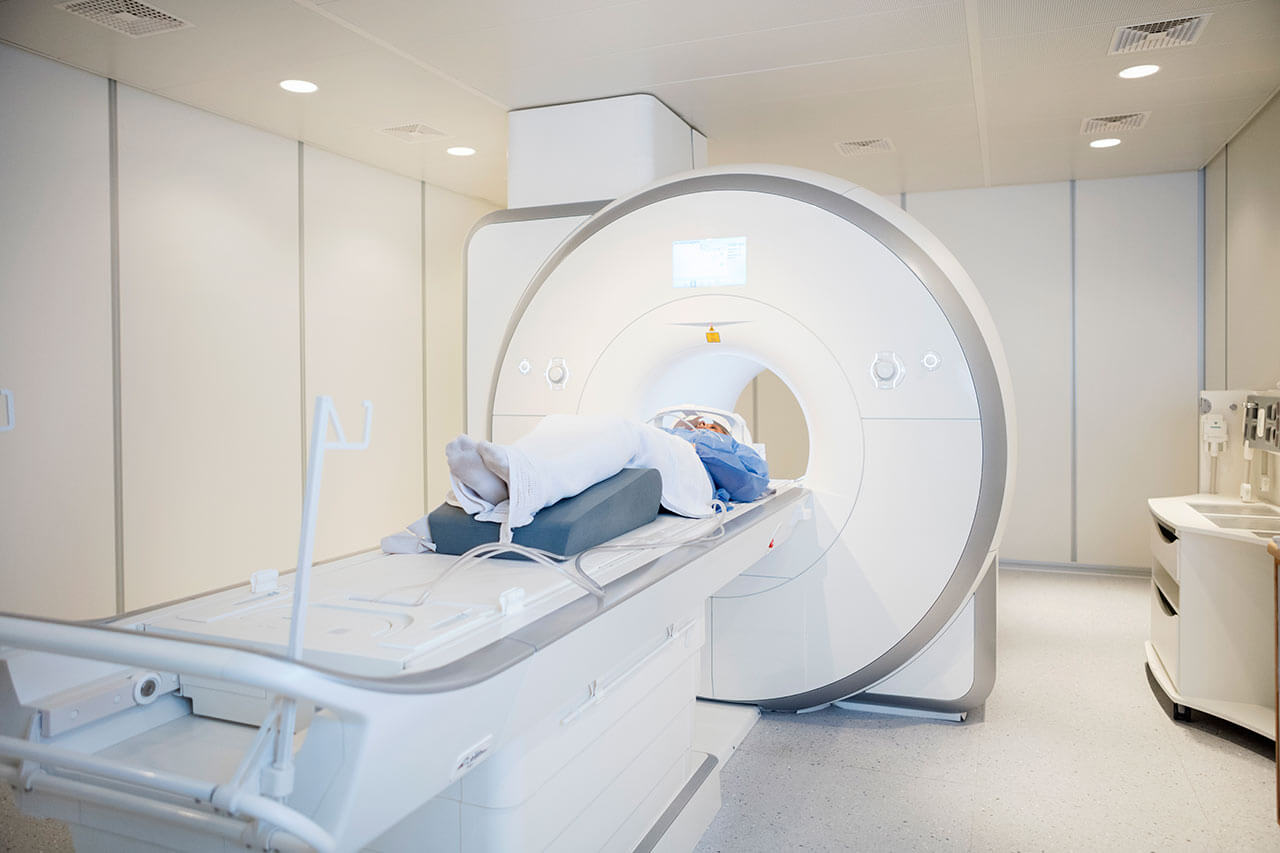
The department's doctors have advanced technical resources to perform high-precision examinations of the central nervous system, that is, the brain and spinal cord. Computed tomography is carried out on the devices of world-famous companies, such as Siemens and General Electric. Doctors perform magnetic resonance imaging using a 3 Tesla scanner, thanks to which they can obtain thin-sliced high-resolution images and ascertain the presence of pathological changes at early stages. An indispensable diagnostic method in the department is digital subtraction angiography, with the help of which physicians receive data on the state and patency of the blood vessels of the brain.
The department's team of doctors specializes in the interventional treatment of neurological diseases. This type of therapy is an excellent alternative to invasive neurosurgical intervention. Angioplasty followed by stent implantation is one of the most popular procedures. Such treatment is indicated for patients with cerebral vascular stenosis. The essence of the procedure is to dilate the narrowed blood vessel with a follow-up stent implantation (a special metal structure resembling a frame) under the guidance of an imaging system. The stent will keep the blood vessel open. Angioplasty can completely eliminate the stenosis in the long term, thereby preventing the development of a stroke in a patient.
The specialists working at the medical facility successfully treat vascular malformations such as arteriovenous malformations and arteriovenous fistulas. Both pathologies can cause potentially life-threatening bleeding. To eliminate them, doctors use endovascular techniques (embolization) and neurosurgical interventions. In some cases, the specialists combine the two above-mentioned techniques, namely, they perform hybrid interventions. The optimal type of treatment is determined during the board with the participation of neuroradiologists, neurologists, and neurosurgeons. Neuroradiologists are responsible for catheter-based embolization, during which they block the affected blood vessels with polymeric substances. The department's specialists also take part in performing hybrid surgery.
The department has vast experience in the endovascular treatment of cerebral aneurysms and thrombectomy in patients with stroke. Patients can be sure of its effectiveness because the doctors at the medical facility regularly conduct this type of treatment.
The department's range of medical services includes:
- Diagnostic options
- Computed tomography (CT)
- Magnetic resonance imaging, including with contrast enhancement
- Contrast-enhanced digital subtraction angiography (to detect pathologies of the cerebral blood vessels, in particular, cerebral artery aneurysms, arteriovenous malformations, arteriovenous fistulas, and stenoses)
- Therapeutic options
- Thrombectomy for ischemic stroke
- Angioplasty with stent implantation for cerebral vascular stenosis
- Embolization for vascular malformations of the brain and spinal cord (for example, arteriovenous malformations and arteriovenous fistulas)
- Endovascular treatment of aneurysms
- Other medical services
Curriculum vitae
Prof. Thomas Liebig studied Human Medicine at the Hannover Medical School. He also completed his internships in Gainesville (Florida) and at the Harvard Medical School in Boston (Massachusetts), USA. In 1993, he began his internship at the Charite University Hospital Berlin. In 1995, he defended his thesis and received full admission to medical practice. The doctor then held the position of a Research Fellow in the Department of Radiology and Neurosurgery at the Charite University Hospital Berlin. In 2000, he had his board certification in Radiology. Prof. Liebig then held the position of a Senior Physician at the International Neuroscience Institute in Hannover, and a Senior Physician at the Alfried Krupp Hospital Essen. In 2006, he had his board certification in Neuroradiology. From 2006 to 2010, he held the position of a Managing Senior Physician at the University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich. In 2008, he had his habilitation (thesis devoted to the treatment of cerebral artery aneurysms). In 2010, Dr. Liebig received W2 Professorship and became the Head of the Department of Neuroradiology at the University Hospital Cologne. In 2015, he was offered to move to the Charite University Hospital Berlin, where he headed the Institute of Neuroradiology. Since April 1, 2018, the Doctor has been Professor in the Department of Neurosurgery at Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, and the Head of the Department of Interventional Neuroradiology at the University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich.
Photo of the doctor: (c) LMU Klinikum