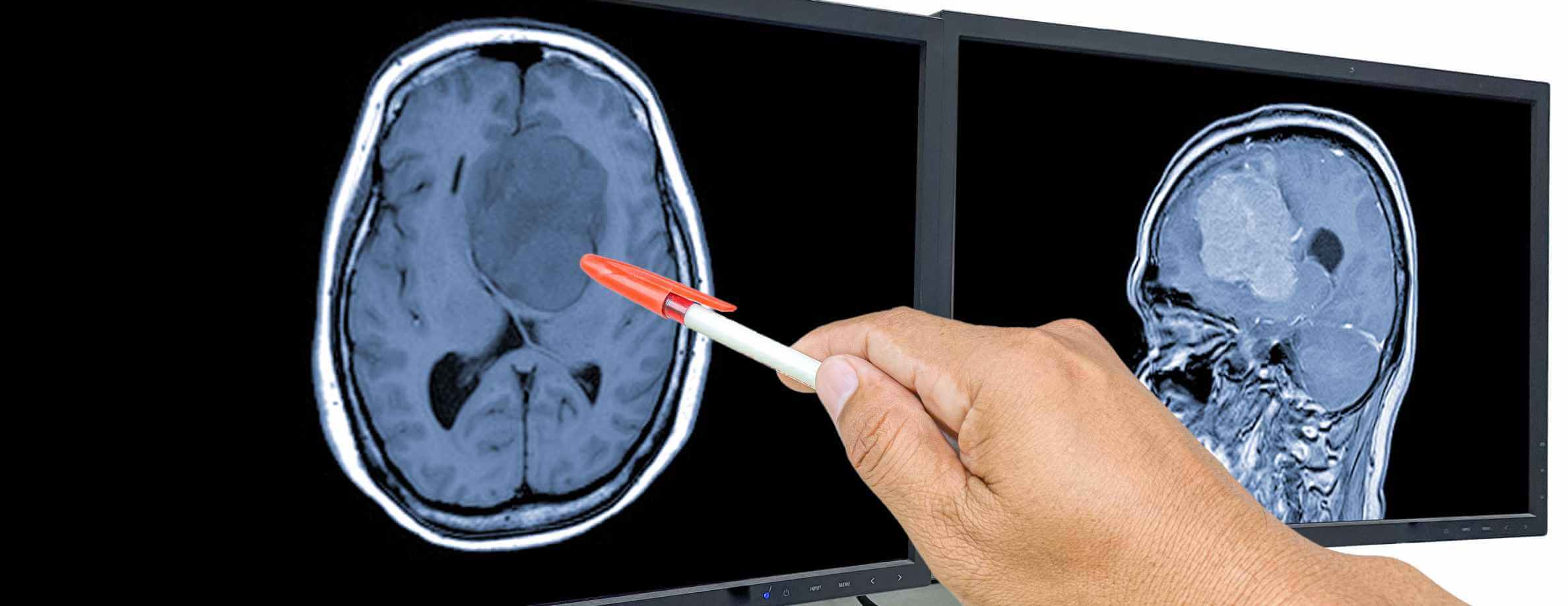
Glioblastoma (GBM or glioblastoma multiforme) is considered one of the most aggressive forms of brain cancer. Newly diagnosed GBM patients, according to global statistics, number approximately 3-5 per 100,000 population annually [1]. Specifically, in Germany, data from the 2022 national cancer registries show that about 3,130 women and 4,180 men were diagnosed with malignant central nervous system tumors that year. Many of those tumors represented high-grade gliomas (HGG), including GBM [2]. To be more exact, the incidence of glioblastoma in this country ranges within 1.6 to 4.3 cases per 100,000, depending on age, sex, and region.
When looking at these data, many might notice that GBM has relatively low incidence. However, brain tumors present a significant burden, as they are associated with very poor prognosis. Data demonstrate that median overall survival under current standard-of-care (surgery + radiation + chemotherapy) remains in the range of 10-15 months; 5-year survival rates linger below 5-10 %. To support these data with evidence, there was a large retrospective study conducted in Germany. It involved over 40,000 adult GBM cases (1999-2014), which showed a median OS of 10.0 months; modest improvements were noted in 2-year survival rates over time (from 16.6 % → 19.3 %) [3].
In view of the information provided above, we want to suggest immuno-oncology (IO) as a promising approach for GBM patients. It works by utilizing the patient's immune system to selectively attack brain cancer cells while sparing normal cells. As an innovative treatment strategy, IO aims to train or reprogram immune cells to distinguish malignant from healthy tissue. Conventional treatments alone can rarely prevent relapse in patients with primary brain tumors. IO can potentially improve patient outcomes and survival. So, it is no wonder why it may seem especially appealing to those affected by GBM.
Why Immunotherapy Matters in GBM
Glioblastoma (GBM) is known for its aggressive biology. It can also demonstrate significant resistance to standard therapies. Therefore, before discussing "why" patients should consider immunotherapy (IT) for GBM, we would like to explain the unique challenges that glioblastoma cells can pose; the reasons why current GBM treatments often fail; and how utilizing the body's immune defenses can potentially increase survival of patients with brain tumors.
Peculiarities of GBM: Fast Tumor Growth, Infiltration, Resistance
First and foremost, patients should understand that GBM cells can proliferate very quickly, often doubling in weeks. Moreover, the tumor is highly heterogeneous: different subclones may carry distinct mutations. Due to this, the implementation of targeted approaches can be difficult.
Second, GBM cells, unlike a discrete tumor mass, can infiltrate adjacent brain parenchyma; they migrate along white matter tracts and blood vessels. Consequently, even the most aggressive surgical resection cannot remove all tumor cells without causing damage to critical normal cells.
Furthermore, surviving residual cells (including cancer stem-like GBM cells) can adapt under treatment pressure, leading to tumor recurrence. In addition, there are multiple escape mechanisms (e.g., DNA repair capacity, efflux pumps, hypoxic niches) that help shield GBM against chemo- and radiotherapy.
Why Standard Brain Cancer Treatment Often Fails
Surgical limitations. Typically, surgeons aim for "maximal safe resection." However, the infiltrative margin means that microscopic tumor cells always remain. As mentioned above, this makes it impossible to remove further tissue, as patients might suffer unacceptable neurological deficits.
Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) constraints. Many cytotoxic drugs and biologics can struggle to cross the BBB in sufficient concentrations. Delivery to peritumoral infiltrated zones can be suboptimal, even when systemic therapy is given.
Tumor recurrence and adaptation. After initial therapy, the residual tumor can repopulate. Unfortunately, recurrent GBM tends to be more resistant. In fact, cell clones that survive chemo/radiation can be more aggressive and less susceptible to further intervention.
Immunosuppressive microenvironment. One of the features of GBM is that it can manipulate the local brain environment to suppress immune activity: recruitment of regulatory T cells, myeloid-derived suppressor cells, and tumor-associated macrophages. These factors blunt any spontaneous immune attack on tumor cells.
Role of the Immune System and Immune Response
Simply put, the human immune system is designed to discriminate normal cells from abnormal ones (e.g., virus-infected or cancerous). T cells, antigen-presenting cells (APCs), dendritic cells, and innate immune effectors are considered major players. Specifically, in a healthy context, APCs process foreign or altered antigens and present them to T cells, which, then, produce an immune response targeting the abnormal cells.
However, in cancer, tumor cells can evolve to evade detection. They may reduce antigen presentation, produce immunosuppressive cytokines, or express inhibitory signals (immune checkpoints) to deactivate T cells. With this in mind, the idea behind immunotherapy becomes clearer: to reverse or bypass these evasion strategies, so that immune cells can once again attack cancer cells selectively.
When it comes to managing brain tumors, this can be especially challenging, given the BBB, the immunologically "cold" tumor microenvironment, and the limited infiltration of T cells under normal conditions.
Immune Checkpoint Blockade (ICB) and Why It Is Important
Among different immunotherapy strategies, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) or immune checkpoint blockade (ICB) are the most well-researched. These therapies can block inhibitory receptors on T cells (such as PD-1, PD-L1, CTLA-4, and newer targets like LAG-3, TIM-3, TIGIT) to unleash T cell activity against tumor cells.
ICB has significantly improved outcomes in patients with various types of cancer. However, we must note that the results have been more modest in GBM. Despite this, there are several interesting observations that we would like to share. They are evidence-based and support further development of this approach.
- In neoadjuvant (pre-surgery) ICB settings, anti-PD-1 therapy led to increased T cell infiltration in resected specimens and modest survival benefit versus adjuvant-only ICB. However, randomized trials of adjuvant PD-1 blockade in GBM have not shown clear survival advantage over standard-of-care alone. Moreover, the efficacy is limited by low mutational burden, paucity of tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs), and multiple redundant immunosuppressive pathways in GBM microenvironment.
In other words, there are certain limitations. Yet, the concept of overcoming immune checkpoints remains central: by blocking these inhibitory signals, it is possible to tilt the balance so that T cells become capable of targeting the tumor.
| GBM Stage | Standard Therapy (surgery + RT + chemo) | Standard + Immunotherapy (experimental) |
|---|---|---|
| Stage III/lower grade gliomas | ~50 % response rate in selected trials* | Up to ~80 % in small cohorts (combination IT) |
| Stage IV/classical GBM | ~20 % response/modest survival | Up to ~60 % response in select reports (combination therapy) |
* "Response rate" here refers to measurable tumor shrinkage or control in trials, not guaranteed survival.
In summary, the incorporation of immunotherapy in the management of GBM can offer a different route for patients with brain cancer. This approach does not rely solely on cytotoxic approaches. Instead, it enables the body's immune cells to distinguish and eliminate malignant tumor cells. In view of this, IT can be viewed as an effective strategy for GBM, particularly given the limitations of standard therapy in addressing infiltrative tumor margins, as well as the tumor's recurrence and resistance.
Types of Immunotherapy for GBM in Germany
Monoclonal Antibodies and ICIs (Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors)
Monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) are the most clinically mature immunotherapies evaluated for GBM in Germany and worldwide. To explain broadly, mAbs either (a) bind tumor antigens or growth-factor pathways on GBM cells (e.g., EGFR, VEGF) to disrupt signaling, or (b) modulate T-cell activity by blocking inhibitory receptors (PD-1/PD-L1, CTLA-4). ICIs are mAbs by design. However, their goal is different: to release brakes on T cells rather than to directly bind a tumor receptor.
Strengths include:
- For subsets with pathway dependence (e.g., angiogenesis), mAbs can offer a rational cancer treatment lever.
- ICIs can restore T-cell function by interrupting PD-1/PD-L1 or CTLA-4 signaling; neoadjuvant dosing may prepare a systemic immune response detectable in the resected tumor and periphery.
- Large antibodies can traverse the blood-brain barrier (BBB) poorly under normal conditions. However, GBM-associated vascular leakiness and perivascular spaces permit some intratumoral exposure. It is important to note that ICIs can act peripherally to activate T cells that subsequently traffic to the brain.
Limitations and why results are variable:
- Not all GBM cells overexpress the same receptor (e.g., EGFR/EGFRvIII may be subclonal), so direct anti-EGFR strategies can miss large fractions of the tumor.
- GBM features sparse effector T-cell infiltration, multiple redundant suppressive pathways, and steroid use. These are factors that blunt ICI efficacy.
- Certain agents often improve imaging and symptoms (PFS, edema control) without extending survival. This can be useful clinically, but frustrating for overall survival endpoints.
Briefly said, for GBM, mAbs that target tumor pathways (EGFR/VEGF) and immune checkpoint inhibitors that release T-cell brakes can improve symptom control and advance neoadjuvant ICI strategies. Yet, due to blood-brain barrier (BBB) constraints, intratumoral heterogeneity, and immunosuppressive biology, durable survival gains remain inconsistent.
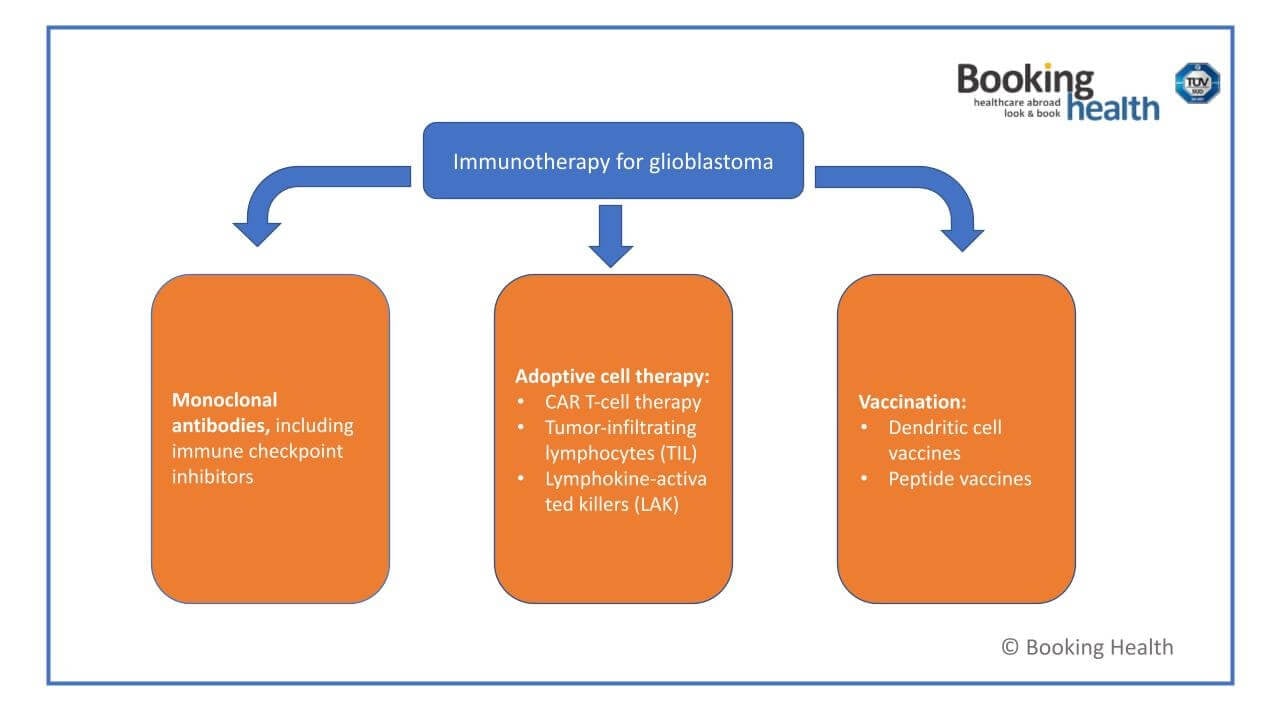
CAR-T Cell Therapy and ACT (Adoptive Cell Therapy)
CAR-T is a form of adoptive cell therapy. This approach requires that a patient's own T cells are collected, genetically engineered to recognize GBM-specific targets, expanded, and reinfused to produce a focused anti-tumor immune response. In GBM and other brain cancer entities, CAR-T remains investigational; related T cell therapies (e.g., TILs) are also actively studied. However, we would like to highlight that this treatment is available in selected university centers in Germany, where GBM patients can access the most innovative and effective therapies available.
How CAR-T therapy works:
- Leukapheresis – Peripheral blood mononuclear cells are collected; high-quality apheresis is critical to yield sufficient T cells for manufacturing.
- Genetic modification – Ex vivo insertion (often viral-vector–mediated) of a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) that endows T cells with tumor-recognition and activation domains.
- Cell expansion and quality control – Engineered T cells are expanded to therapeutic numbers and tested for identity, potency, and sterility before release.
- Lymphodepletion – Short course chemotherapy reduces competing lymphocytes, creating "space" for the infused immune cells to engraft.
- Reinfusion – The "living drug" is given back intravenously; CAR-T T cells can proliferate in vivo and persist, enabling ongoing surveillance to kill cancer cells if the antigen is present.
Related ACT approaches in GBM include:
- TIL therapy (tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes): harvest naturally tumor-reactive T cells from resected GBM tissue, expand ex vivo, then reinfuse (systemically or locoregionally). Modern protocols select CD137⁺ tumor-reactive TILs and show feasibility with evolving response signals.
- LAK cells (lymphokine-activated killers): earlier-generation ACT using peripheral lymphocytes expanded with IL-2.
Advantages of CAR-T (and ACT) for GBM are as follows:
- Engineered T cells can persist as immunologic memory, offering long-term surveillance against antigen-bearing tumor cells.
- Antigen-directed T cell therapies can spare surrounding healthy tissue.
- Trials increasingly test CAR-T with other modalities (e.g., multi-antigen CARs, ICIs, TTFields), aiming to overcome immune escape.
There are certain limitations associated with utilizing this approach. First, commercial CAR-T list prices reimbursed in Germany range ~€282,000-€420,000 per dose (hematologic indications). Total episode costs commonly reach €400,000-€500,000 when manufacturing, hospitalization, CRS/ICANS management, and follow-up are included. Solid-tumor programs can be even higher. Hence, patient-specific GBM programs often cite €450,000-€550,000.
Second, antigen heterogeneity, limited T cells within the tumor, and major immunosuppression produce transient responses in many studies. Consistent overall-survival gains over standard care have not yet been proven. In addition, cytokine release syndrome (CRS) and neurotoxicity (ICANS) require professional monitoring – this is another reason why care is centralized.
Dendritic Cell Vaccines and Tumor Vaccines
Dendritic cell (DC) vaccination is a form of cancer vaccines designed to teach the patient's immune system to recognize and attack brain cancer cells. In a way, DCs can be considered professional antigen-presenting cells (APCs). They ingest, process, and display tumor antigens to T cells. Then, they initiate a coordinated immune response that can persist beyond the treatment window. It is this persistence that makes this approach so attractive for GBM, where microscopic disease and tumor recurrence are common after surgery and chemoradiation.
Dendritic cells and their role in adaptive immunity were discovered by Ralph M. Steinman, a Canadian immunologist, who was awarded the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for this work.
How DC vaccines work (mechanism). First, tumor tissue (resected) or tumor lysate is prepared to provide an antigen "catalogue." Antigens can also be collected from a patient’s blood – this is called "liquid biopsy". Then, monocytes from the patient's blood are matured into dendritic cells ex vivo and loaded with patient-specific antigens (lysate, peptides, or mRNA). The personalized vaccine is administered (often intradermally), enabling DCs to prepare CD4⁺/CD8⁺ T cells against GBM-specific targets. Once prepared, T cells can surveil for months, potentially restraining regrowth of tumor cells.
When it comes to evidence base and German/European experience, the externally controlled phase 3 study of autologous tumor-lysate–loaded DC vaccine (DCVax-L) should be mentioned. It associated vaccine use with statistically significant overall-survival extension for both newly diagnosed and recurrent GBM versus matched external controls. This research was published in JAMA Oncology and covered in German oncology media. To date, it remains the largest late-phase DC evidence, despite the fact that it was nonrandomized and, as such, remains subject to methodological debate. [4]
Beyond lysate-loaded DCs, peptide-based cancer vaccines pursue specific neoantigens or overexpressed targets. Specifically, IDH1 (R132H) peptide vaccines (often in lower-grade gliomas and IDH-mutant GBM) aim to exploit a truly tumor-specific mutation with encouraging immunogenicity and early safety results. In turn, EGFRvIII peptide vaccines demonstrated good antigen-specific immune responses. However, outcomes have been mixed across trials and combinations.
| Feature | Peptide Vaccines (e.g., IDH1 R132H, EGFRvIII) | Dendritic Cell Vaccines (e.g., tumor-lysate-loaded DCVax-L) |
|---|---|---|
| Antigen source | Defined synthetic epitope(s) | Patient-specific tumor lysate/peptides/mRNA |
| Personalization | Semi-personalized (mutation- or target-restricted) | Highly personalized (broad antigen repertoire) |
| Rationale | Focused immunity against a single dominant target | Poly-antigen response to mitigate antigen escape |
| Administration | Repeated subcutaneous/intradermal injections | Repeated intradermal (often outpatient) |
| Evidence snapshot | Strong immunogenicity; mixed clinical endpoints across trials (some signals in subsets) | Phase 3 external-control study reports OS benefit. |
| Costs (Germany) | Variable; often part of trials/compassionate pathways | €20,000-€38,000 baseline program costs (can rise with add-ons) |
Oncolytic Viruses
Oncolytic viruses (OVs) are genetically engineered or naturally occurring viruses modified to attack cancer cells selectively but in a way that allows to avoid causing damage to healthy tissue. In the management of GBM and other brain tumors, this action – direct lysis plus immune stimulation – makes OVs a strategy worth considering to be able to fight against the disease.
- As noted above, OVs replicate selectively in cancer cells (often due to defective antiviral defenses or tumor-specific promoters), causing cell lysis and release of tumor antigens.
- Viral infection triggers innate immunity – dendritic cells, NK cells, macrophages – and can convert an immunologically "cold" tumor into a "hot" one by releasing danger signals (e.g. GM-CSF, viral RNA) and attracting T cells. Hence, OVs act as in situ cancer vaccines.
This strategy can amplify the body's immune system to target residual or infiltrative tumor cells that evade surgery or chemotherapy. However, we would like to add that oncolytic viruses are rarely used in isolation, as they are most effective when used in combination immunotherapy. For example:
- OV + ICIs: OVs may upregulate PD-L1 or other checkpoints, making a tumor more sensitive to ICIs.
- OV + CAR-T/TIL/ACT: OVs can prepare the microenvironment, breaking down barriers to T-cell trafficking.
- OV + vaccine/DC therapy: Viral lysis provides fresh antigen substrate; vaccines supply defined epitopes.
- OV + standard therapy (chemo/radiation): Radiation or certain chemotherapeutics may increase viral replication or antigen release, enhancing OV efficacy.
Similarly to other methods discussed in this article, there are certain considerations and challenges associated with the implementation of OVs.
First, intratumoral injection is often necessary; systemic routes risk neutralization or off-target effects. Second, neurotoxicity, inflammation, viral recombination, and viral shedding must be managed, especially in the CNS.
Moreover, preexisting immunity (e.g. to HSV, adenovirus) may blunt OV replication and effectiveness. Lastly, single-virus targeting may miss antigen-negative clones, demanding polyvalent or engineered approaches.
Prof. Frank Gansauge on Dendritic Cell Therapy
To help our readers see the incredible potential of dendritic cell therapy, we would like to invite you to watch this video interview with Professor Frank Gansauge, head of LDG Laboratories in Germany. He has been working with dendritic cell therapy since 2001, when his clinic became one of the first private laboratories to apply this innovative method. Professor Gansauge describes dendritic cells as the "officers" of the immune system, capable of training effector lymphocytes to attack malignant cells.
In his practice, DC therapy is often combined with chemotherapy or radiation. He reports that this approach can significantly reduce relapse rates and improve survival in cancers (e.g., colon, pancreatic, and more recently glioblastoma).
According to Professor Gansauge, clinical results show that dendritic cell therapy can prolong life expectancy with minimal side effects. In fact, in some cases, this strategy can even prevent tumor recurrence for more than five years. Yet, he emphasizes that this approach is not a replacement for standard therapies, rather it is a great complementary tool.
Please watch this video interview with Professor Gansauge to learn more about his experience with dendritic cell therapy. We hope you might find answers to your questions related to the use of this treatment strategy to manage various cancers, including GBM.
Benefits and Limitations of IT in Germany
Overall, immunotherapy (IT) has become an important investigational and clinical option for brain cancer, particularly glioblastoma (GBM). No single modality has yet become a universally adopted standard. However, the research evidence from trials and programs in Germany highlights that it is necessary to consider both the strengths and the challenges of this approach.
Benefits of Immunotherapy in GBM
First, as we discussed, early-phase and phase III DC vaccine studies suggest that IT can extend the interval before tumor recurrence. In particular, this can be observed in patients who begin therapy shortly after maximal surgical resection and standard chemoradiation.
Second, IT (e.g., dendritic cell vaccines or CAR-T) is customized to the individual's tumor profile. By targeting patient-specific GBM cells or neoantigens (e.g., IDH1 mutations, EGFRvIII), these therapies account for GBM's heterogeneity better than "one-size-fits-all" chemotherapy.
Third, many know that cytotoxic chemotherapy causes significant systemic side effects. In contrast, many immunotherapies have relatively favorable tolerability profiles. For example, DC vaccination is usually associated only with mild local or flu-like reactions. This allows patients to maintain quality of life during treatment.
Last but not least, IT can be layered onto standard modalities without overlapping toxicity. For example, CAR-T and ICIs are being combined with radiotherapy or tumor-treating fields (TTFields) to enhance efficacy while maintaining tolerability.
Limitations of Immunotherapy in Germany
Regarding the limitations of immunotherapy approaches, we should note that these remain among the most expensive treatments in oncology. In Germany, dendritic cell vaccination typically costs €20,000-€38,000. On the other hand, CAR-T programs for solid tumors are estimated at €450,000-€550,000 per patient episode.
Moreover, IT is currently offered primarily at major university hospitals and specialized research centers (e.g., Freiburg, Ulm, Mannheim). The reason is: complex cell therapy manufacturing or trial enrollment requires advanced infrastructure. However, unfortunately, smaller regional clinics generally do not have it.
Furthermore, not every patient can develop a strong immune response to vaccination or CAR-T infusion. As we discussed in detail, GBM's immunosuppressive microenvironment, use of steroids, and heterogeneous antigen expression mean that therapeutic efficacy can vary among patients depending on their unique factors. Some patients can achieve long survival. However, others might show only transient responses.
Finally, although signals of benefit exist, phase III evidence remains limited. In other words, more randomized trials are needed before even such effective modalities like DC vaccines can be included in treatment guidelines.
Who Benefits Most?
- Newly diagnosed GBM patients who undergo gross total resection and start IT soon after standard chemoradiation appear to benefit most.
- Recurrent GBM cases may also be considered, especially for experimental IT such as CAR-T or oncolytic viruses.
- Patients with good performance status, minimal steroid dependence, and adequate organ function are generally prioritized for IT programs.
Patient Story: Daria (Ireland) – "We Found Real Hope in Germany"
In January 2024, Daria was diagnosed with glioblastoma (GBM) Type IV after emergency surgery for a seizure. She was told that the disease would almost certainly recur. However, her family decided not to give up and started researching options beyond Ireland. They found Booking Health and were connected with Professor Frank Gansauge's team (LDG Laboratories) in Germany.
The reason why Daria and her family decided to try DC therapy is because the concept of this approach felt logical to them – to use dendritic cells to "teach" the immune system to recognize tumor cells. Within 3-4 weeks post-op, Daria traveled to Germany, where she received a personalized dendritic cell vaccine. She then completed standard chemoradiation at home.
Daria experienced no notable side effects from the vaccine. On the contrary, she sustained her energy during chemoradiation. However, what she and her family found the most incredible is that her MRI scans at ~3 and ~9 months post-surgery (2024) were clear.
The family believes that early timing and the combined approach (standard care plus DC therapy) were essential. "Don't lose hope. Go early and quickly. Combine standard treatment with dendritic cells if you're eligible."
We invite you to watch this video interview to hear Daria and her husband describe the decision, the procedure, and life after treatment.
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Choosing the right therapy for glioblastoma is one of the most difficult decisions a patient and their family will ever face. Standard treatments can prolong survival but rarely cure the disease, and innovative modalities like immunotherapy may seem promising but complex, costly, and available only in specialized centers. This is where professional guidance becomes indispensable.
Patients navigating immunotherapy options for glioblastoma in Germany often encounter fragmented information, language barriers, and difficulty distinguishing between experimental trials and established therapies.
Booking Health provides a comprehensive solution by connecting patients with specialized neuro-oncology centers across Germany, where immunotherapies such as dendritic cell vaccines, CAR-T cell therapy, immune checkpoint inhibitors, and combination strategies are available.
With over a decade of expertise, the company offers full organizational and medical support – from the first consultation to long-term follow-up – ensuring that patients receive safe, transparent, and individualized care. This is what we call Booking Health glioblastoma immunotherapy support.
Booking Health assists patients step by step, providing a seamless "medical journey":
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports to evaluate suitability for immunotherapy.
- Development of a medical care program, adapted to each patient's clinical condition, cancer stage, and previous therapies.
- Selection of the best treatment location, focusing on centers with strong experience in brain cancer immunotherapy.
- Preparation and forwarding of medical documentation directly to the chosen clinic.
- Preliminary consultations with treating clinicians before travel, clarifying protocols and expectations.
- Clinic booking and coordination of the hospital stay, including special services like ICU availability if needed.
- Visa and travel assistance, including flight booking and airport transfers.
- Interpreter and personal coordinator available 24/7, ensuring smooth communication with the medical team.
- On-site support during hospitalization, including visits from Booking Health doctors who monitor the quality of care.
- Follow-up services after discharge, including translation of medical records and guidance on continuing care in the home country.
- Medication support, helping patients obtain and transport drugs safely for ongoing treatment.
Health is the most precious asset. For patients and families facing glioblastoma, it is fragile, but it can also be safeguarded through professional choices and timely access to the best therapies. By offering comprehensive coordination and deep expertise, Booking Health enables patients to make informed decisions and pursue therapies that may not be available elsewhere.
Take control of your brain cancer journey today. Contact Booking Health to explore the most advanced immunotherapy options for glioblastoma in Germany with full support at every step.
Every Patient Has a Story: Booking Health Treatment Journeys that Inspire
Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients
Send request for treatmentIn Germany, immunotherapy options for glioblastoma include monoclonal antibodies, immune checkpoint inhibitors, dendritic cell and peptide cancer vaccines, CAR T and other T cell therapies, plus oncolytic viruses in trials. These approaches can activate immune cells to fight brain cancer.
CAR T cell therapy can modify a patient's T cells to target GBM antigens. It is considered one of the most advanced T cell therapies. The typical CAR T glioblastoma cost in Germany ranges from €450,000-€550,000.
Yes. Immunotherapy can be combined with standard treatment for GBM (e.g., DC vaccines after surgery and chemoradiation). This can strengthen the immune response and delay tumor recurrence. In addition, this can also potentially slow progression compared with standalone therapy.
Booking Health glioblastoma immunotherapy support covers medical review, program design, clinic booking, visas, interpretation, and follow-up, among other needs of GBM patients. It ensures transparent costs and efficient access to innovative cancer treatment in leading German centers.
Stage 4 glioblastoma uses a combination of approaches: surgical removal of the tumor, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and immunotherapy methods一monoclonal antibodies, CAR T-cell therapy and dendritic cell vaccination. They increase life expectancy and reduce the risk of relapse after surgery.
Stage 4 glioblastoma is characterized by headache, nausea, impaired vision, speech, coordination, personality changes and seizures. Symptoms appear due to rapid tumor growth, pressure on neighboring areas of the brain and swelling of tissues.
The cost of treatment depends on the method. Monoclonal antibodies cost an average of €375,000–420,000, CAR T-cell therapy costs €450,000–550,000 and dendritic cell vaccines cost €20,000–38,000. Prices are generally higher in the UK and US while access to these treatments is still limited in Australia.
Stage 4 glioblastoma has a response rate of around 20% with standard treatment while the response rate is up to 60% when immunotherapy is added. This approach significantly prolongs disease-free survival and improves overall survival.
Monoclonal antibody therapy provides high specificity of action — drugs recognize tumor cells by unique targets (EGFR, VEGF-A, PD-1/PD-L1) and destroy them. This method is well tolerated and is often combined with chemotherapy or radiation therapy to achieve better results.
CAR T-cell therapy activates the patient’s own immune system allowing modified cells to recognize and destroy the tumor. Treatment is carried out only in highly specialized clinics and shows a stable long-term immune effect even in aggressive forms of glioblastoma.
Dendritic cell therapy stimulates natural anti-cancer immunity, prevents relapses and helps control tumor process. Its effectiveness is confirmed by clinical observations—patients demonstrate long-term remission and better recovery after basic treatment.
The cost of treatment depends on the chosen method: monoclonal antibody therapy costs from 375,000€ to 420,000€, CAR T-cell therapy costs 450,000€–550,000€ and dendritic vaccine costs 20,000€–38,000€. The price is determined individually.
There is no single best treatment for glioblastoma. But for many patients immunotherapy gives hope. This includes immune checkpoint inhibitors, cellular therapies, dendritic vaccines or oncolytic viruses – depending on molecular profile and prior treatment response.
Hospitals experienced in glioblastoma immunotherapy are those involved in neuro-oncology research. Such centers can assess eligibility for immune-based treatments, manage risks and adjust therapy (based on clinical and radiological follow-up).
Germany offers structured access to glioblastoma immunotherapy within specialized centers – patients benefit from regulated protocols and experienced neuro-oncology teams. Also advanced immune-based treatments are available (used under strict clinical supervision).
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Stefaan W Van Gool, Jennifer Makalowski, Linde F C Kampers et al. Dendritic cell vaccination for glioblastoma multiforme patients: has a new milestone been reached? Transl Cancer Res. 2023 Jul 28;12(8):2224–2228. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-603. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[2] Robert Koch Institut. Cancer in the Central Nervous System. Accessed September 30, 2025. https://www.krebsdaten.de/Krebs/EN/Content/Cancer_sites/Central_nervous_system_cancer/central_nervous_system_cancer_node.html
[3] Ljupcho Efremov, Semaw Ferede Abera, Ahmed Bedir, Dirk Vordermark, Daniel Medenwald. Patterns of glioblastoma treatment and survival over a 16-years period: pooled data from the German Cancer Registries. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2021 Mar 20;147(11):3381–3390. doi: 10.1007/s00432-021-03596-5. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[4] Linda M Liau, Keyoumars Ashkan, Steven Brem et al. Association of Autologous Tumor Lysate-Loaded Dendritic Cell Vaccination With Extension of Survival Among Patients With Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Glioblastoma. JAMA Oncol. 2022 Nov 17;9(1):112–121. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.5370. [DOI] [PMC free article]
Read:
Dendritic cell therapy in cancer treatment in Germany - Vaccination against cancer
Article menu:
- Why Immunotherapy Matters in GBM
- Types of Immunotherapy for GBM in Germany
- Prof. Frank Gansauge on Dendritic Cell Therapy
- Benefits and Limitations of IT in Germany
- Patient Story: Daria (Ireland) – "We Found Real Hope in Germany"
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
- Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health