Medical Blog About Treatment Abroad
Welcome to our medical blog – it is dedicated to empowering patients with knowledge about global healthcare! We created this platform with the intention to bridge the gap between patients and the medical innovations available globally.
What's Inside: Discover new and rare methods in oncology, immunology, heart surgery, neurosurgery, and other medical fields! Our health travel insights show how medical journeys open new possibilities with advanced treatments unavailable locally, including specialized cancer care abroad.
Who Benefits: This resource is for patients and their families who seek new treatment methods and explore options at leading international hospitals. Those who want to make informed healthcare decisions beyond borders.
Why Read: Booking Health experts provide verified information through patient-friendly articles – they translate complex medical advances into accessible info. Stay current with the latest developments in global healthcare and discover how international medicine can transform treatment outcomes!
Browse our latest articles and take the first step toward better health outcomes!
Diagnosis & treatment
 Understanding Brain Tumors
Understanding Brain Tumors
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of cells within the brain tissue that can be primary (originating in the brain) or metastatic (spreading from elsewhere). Approximately 26.3% of all brain and other central nervous system tumors were classified as malignant, whereas 73.7% were non-malignant. This indicates that non-malignant tumors are...
 Visualase™ System: Neurosurgical Laser Ablation
Visualase™ System: Neurosurgical Laser Ablation
Metastatic brain lesions occur approximately 10 times more frequently than primary tumors, accounting for approximately 200,000 of the 225,000 brain tumors diagnosed each year. The increasing incidence of brain metastases is associated with improved treatment of primary malignant tumors, which in turn leads to increased...
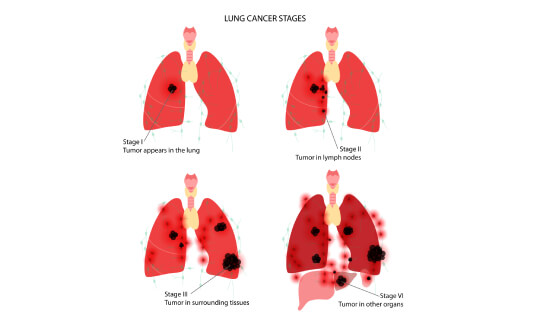 Lung Cancer Stages: A Clear Guide to Staging and TNM Classification
Lung Cancer Stages: A Clear Guide to Staging and TNM Classification
Pulmonary malignancy remains one of the leading causes of oncological mortality in the world, and that is why a correct understanding of the level of disease progression is critically important for both doctors and patients. Determining the level of spread of the disease is not a formality, but a key aspect that directly affects the prognosis, choice...
 Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Options: A Patient Guide to Modern Therapy
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Treatment Options: A Patient Guide to Modern Therapy
Lung cancer has been one of the most common causes of cancer death in the world for many decades. It is a serious global problem that affects millions of people. Non-small cell lung cancer is the most common type of cancer diagnosed, accounting for the majority of all cases. In the past, the prognosis for such patients was poor...
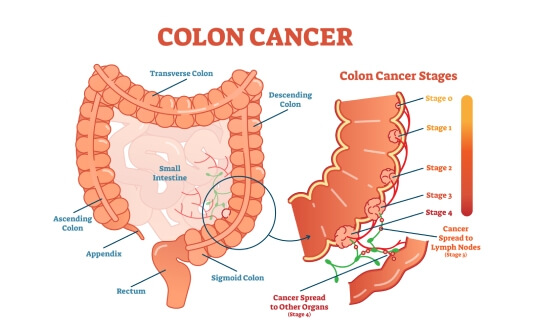 New Treatments for Stage 4 Colon Cancer in Germany
New Treatments for Stage 4 Colon Cancer in Germany
Colon cancer stage 4 is a form of colorectal cancer in which the cancer has spread beyond the colon and metastasized. The most common sites of involvement are the liver, lungs, peritoneum, ovaries, or distant lymph nodes. It is at this stage that the disease is no longer localized and requires a systemic, comprehensive approach to treatment.
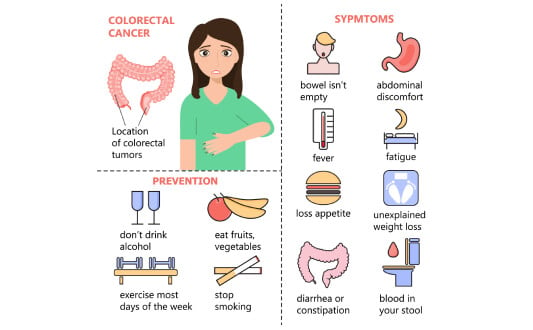 Bowel Cancer Symptoms: Early Warning Signs You Shouldnt Ignore
Bowel Cancer Symptoms: Early Warning Signs You Shouldnt Ignore
Bowel cancer is a malignant tumor that develops in the large bowel, including the colon and rectum. It represents about 7.6% of all new cases of cancer in the USA and is fourth most common type of cancer. It often begins with a benign polyp that transforms into malignancy over time. About 15% to 40% of colon tumors originate from colon polyps...
 Da Vinci Robot Surgery for Prostate Cancer
Da Vinci Robot Surgery for Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer (PCa) remains the 2nd most frequently diagnosed malignancy among men, with approximately 1.5 million new cases reported per year. Radical prostatectomy (RP) is the basic treatment for localized disease, as according to the International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading system, Gleason score, etc.
 Bowel Cancer Stages and Grading
Bowel Cancer Stages and Grading
Colorectal cancer (CRC), which comprises colon and/or rectum cancer, represents a significant health problem as the world’s third most commonly diagnosed and second most fatal cancer globally. Approximately 9.4% of cancer-related deaths were due to CRC in 2020. However, in light of the significant increase in the number of identified cases...

