Cervical cancer remains a significant global health concern. In 2022, approximately 660,000 new cases and 350,000 deaths were reported worldwide, making it the fourth most common cancer among women [1]. Almost all cases of cervical cancer are attributable to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection – particularly high-risk strains like 16 and 18 – which emphasizes the importance of preventative measures like vaccination and screening [1].
Early-stage diagnoses offer a significantly better outlook; for example, in high-income regions like the US or the UK, adolescent girls and women aged 15-44 diagnosed with cervical cancer have a 10‑year survival rate of nearly 90 %, whereas survival for those with stage IV – cancer that has metastasized – is often under 20 % [2].
For stage 4 cancer, traditional approaches, such as chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery, often yield limited efficacy and impose considerable burdens on the immune system. For this reason, selecting German hospitals equipped with advanced treatment methods can significantly improve patient outcomes.
German clinics are known for their integration of innovative techniques that aim to control tumor growth, minimize side effects, and preserve quality of life. Importantly, thanks to these innovations, many women with even advanced cervical cancer are now living longer, maintaining a good quality of life, and in some cases achieving long-term remission. This progress offers real hope that recovery is possible, even at later stages.
Understanding Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Stage 4 cervical cancer is the most advanced form of cervical cancer. In stage 4A, cancer spreads from the cervix to nearby pelvic structures such as the bladder or rectum. In stage 4B, the disease extends beyond the pelvis to distant organs like the lungs, liver, bones, or distant lymph nodes – commonly referred to as metastatic cancer [3].
Symptoms and Patient Challenges in Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Because advanced cervical cancer has spread extensively, symptoms can be widespread and serious. Patients may experience:
- Persistent fatigue or weakness
- Bone pain or fractures
- Difficulty breathing or coughing up blood (if the lungs are involved)
- Vaginal fistulas or abnormal bleeding
- Weight loss and anemia
These symptoms often significantly affect quality of life and demand comprehensive supportive care [4].
Early Stages vs. Advanced Cervical Cancer: Comparison
- Early-stage cervical cancer (stages IA to IB) often remains localized within the cervix and may present no symptoms or only mild ones. Treatment at this stage is typically highly effective.
- By contrast, advanced cervical cancer, particularly stage 4, involves broader spread and poses greater treatment challenges. [2, 3]
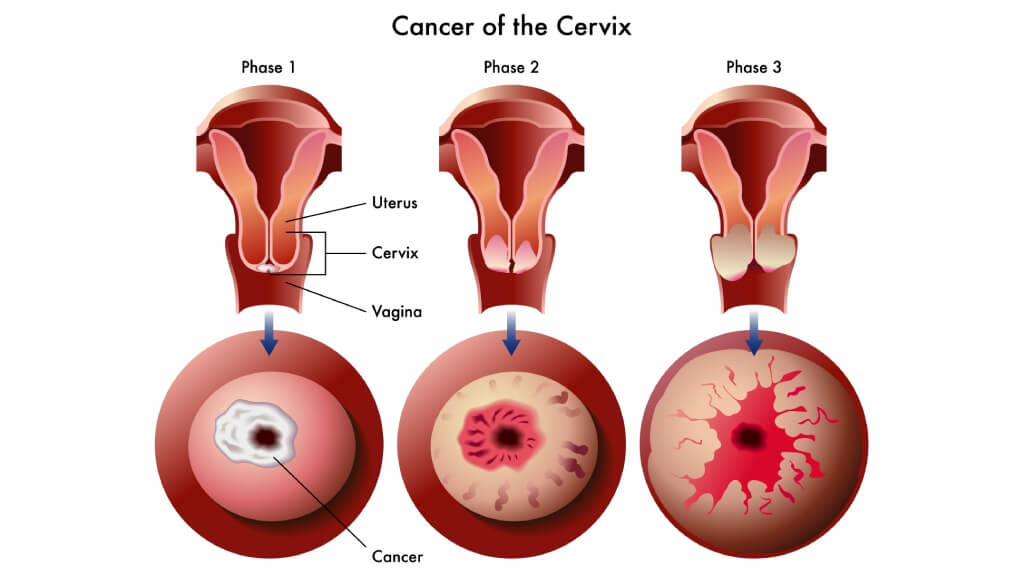
Diagnostic Steps in Stage 4 Cervical Cancer in German Clinics
German specialized cancer centers follow a thorough and multidisciplinary diagnostic protocol to assess the extent of disease accurately:
- Histological examination (biopsy) for a definitive diagnosis
- Imaging tests, including MRI for detailed views of the primary tumor and CT or PET-CT scans to detect lymph node and distant metastases
- Additional investigations may include cystoscopy (bladder imaging), sigmoidoscopy (rectal assessment), and chest X-ray or lung scans for lung involvement
These steps enable German oncologists to develop tailored cervical cancer treatment plans that consider both local tumor control and the patient's overall condition.
Standard Treatment Protocols for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer and Their Limitations
For decades, doctors relied on standard treatment protocols, such as chemotherapy, systemic therapy, classical radiation therapy, and open surgery, as the main approaches to managing advanced cervical cancer. While these methods remain important, they also come with drawbacks, especially for women diagnosed at later stages [5].
- Chemotherapy and systemic therapy: Uses cytotoxic drugs to destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells. In systemic therapy, these drugs circulate throughout the body via the bloodstream. While effective in shrinking the primary tumor or slowing disease spread, chemotherapy often harms healthy tissues as well, since it cannot always distinguish between cancerous and normal fast-growing cells. Common side effects include nausea, hair loss, and suppression of the immune system, leaving patients vulnerable to infections.
- Classical radiation therapy: External beam radiation uses high-energy beams to target tumors. It is often combined with chemotherapy for cervical cancer treatment. However, radiation may damage surrounding healthy organs like the bladder and rectum, requiring prolonged rehabilitation. Patients can experience fatigue, skin irritation, and long-term bowel or bladder issues.
- Open surgery: In some cases, radical hysterectomy (removal of the uterus and nearby structures) is performed. While this approach may control the disease locally, recovery is slow, and risks include infection, blood loss, and long-term changes in urinary or reproductive function.
Limitations of Traditional Approaches
- Do not significantly extend survival for stage IV disease compared to modern therapies
- Cause substantial damage to healthy tissues and the immune system
- Often result in reduced quality of life during and after treatment
- Require longer rehabilitation before patients can return to daily activities
These realities highlight the urgent need for modern, targeted options that can improve outcomes and reduce side effects for women undergoing cervical cancer treatment in advanced stages.
Advanced Treatment Methods in Germany for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Over the past decade, oncology has moved far beyond the limits of traditional chemotherapy and open surgery. Today, patients with cervical cancer at advanced stages can benefit from a wide spectrum of advanced treatment options that are safer, better tolerated, and more effective in improving quality of life.
German hospitals are internationally recognized for adopting advanced treatment methods early and integrating them into multidisciplinary care. These approaches are tailored to the individual condition of each patient, offering not only longer survival but also faster recovery compared with conventional protocols.
Categories of Advanced Therapies for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer in Germany
- Targeted therapy – drugs designed to identify and attack specific tumor markers, sparing healthy cells.
- Immunotherapy – checkpoint inhibitors and dendritic cell therapy that activate the patient's immune defense to destroy tumor cells.
- Embolization (TACE) – blockage of blood vessels supplying the tumor, sometimes combined with localized chemotherapy.
- Hyperthermia and HIPEC – heating tumor tissues or delivering heated chemotherapy directly into the abdominal cavity to enhance drug penetration.
- Modern radiation techniques – including image-guided external beam therapy and brachytherapy, which deliver high doses precisely to the tumor.
- Minimally invasive surgery – laparoscopic and robotic procedures that reduce trauma and shorten hospital stays.
Unlike standard therapies, these innovative therapies focus on local tumor control, personalization, and minimizing systemic side effects. Choosing cancer treatment in Germany gives patients access to these approaches, as well as world-leading expertise, modern equipment, and personalized medical programs. This combination of science and patient-centered care is why thousands of international patients travel every year for treatment in Germany.
| Aspect | Standard Treatments | Advanced Treatment Methods in Germany |
|---|---|---|
| Main approaches | Chemotherapy, systemic therapy, classical radiation, and open surgery | Targeted therapy, immunotherapy (incl. dendritic cells therapy), embolization (TACE), hyperthermia, HIPEC, brachytherapy, minimally invasive surgery |
| Effect on the body | Systemic impact on the whole body; damages healthy tissues and weakens the immune system | Localized or tumor-specific; aim to spare healthy organs and preserve the patient's immune system |
| Recovery | Long rehabilitation, higher risk of complications | Faster recovery, shorter hospital stays thanks to minimally invasive approaches |
| Personalization | Same drugs/protocols used for most patients | Personalized treatment plans based on tumor type, spread, genetic markers, and overall health |
| Expected outcomes | Limited survival improvement in stage 4 cervical cancer | Better tolerance, improved life expectancy, and enhanced quality of life |
Detailed Overview of Advanced Therapies for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Embolization and TACE for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Embolization is a minimally invasive technique used in cervical cancer treatment to cut off the blood supply feeding tumors. A catheter is inserted through a small incision in the groin and guided into the arteries supplying the cervix or metastatic sites. Tiny particles, called emboli, are then injected to block blood flow. Without oxygen and nutrients, cancer cells shrink or die.
One of the most advanced methods is TACE (transarterial chemoembolization). In this procedure, the emboli are microspheres saturated with chemotherapy drugs. This allows a very high drug concentration directly in the tumor, while minimizing systemic side effects. It is particularly valuable in advanced stages of cervical cancer when surgery is not possible. Clinical studies have reported disease control rates of up to 70% with TACE, offering patients a meaningful extension of survival and symptom relief.
Embolization is also used for patients with metastatic cancer affecting the liver, where it may be combined with radiofrequency ablation or microwave therapy. In addition, emergency embolization can control life-threatening uterine bleeding, which occurs in some patients with stage 4 disease. Research shows that uterine artery embolization successfully controls bleeding in more than 90% of cases, providing rapid stabilization and improving quality of life [6, 7].
Regional chemotherapy for stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany
Germany specializes in treating advanced cervical cancer through regional chemotherapy in Germany — specifically at Medias Klinikum Burghausen where Professor Karl R. Aigner performs isolated pelvic perfusion for stage IV disease. Regional chemotherapy for stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany achieves tumor control that systemic therapy cannot: concentrated drug delivery directly to cancer sites while protecting healthy organs from toxic exposure.
Stage 4 patients often have both pelvic disease and distant metastases. German approach treats each region individually: isolated perfusion for pelvic tumor, hepatic perfusion for liver metastases, pulmonary perfusion for lung involvement — sequential regional treatment controls disease throughout body without overwhelming patient with systemic toxicity. Results speak for themselves: patients who faced permanent colostomy or amputation achieve remission.
Professor Aigner's expertise is unmatched: 45 years performing regional chemotherapy, over 20,000 procedures completed, continuous refinement of techniques based on accumulated experience. A few cervical cancer patients achieved complete remission without radiation therapy — that demonstrates what's possible when treatment is delivered by surgeon who pioneered these methods. You can find more information in the interview with Prof. Aigner:
Electrochemotherapy (ECT) treatment for advanced cervical cancer
Advanced cervical cancer treatment in Germany: electrochemotherapy treatment option for cervical cancer stage 4 performed by Professor Karl R. Aigner at Medias Klinikum Burghausen. His electrochemotherapy (ECT) treatment for advanced cervical cancer combines electrical pulse technology with isolated pelvic perfusion — creating conditions where tumor cells cannot survive while healthy tissue remains protected.
How it works for stage IV disease: needles positioned around pelvic tumor deliver precisely calculated electrical pulses that open cancer cell membranes, then high-concentration chemotherapy administered through arterial catheters during perfusion session — drug uptake by tumor increases exponentially. For electrochemotherapy treatment for recurrent cervical cancer, this approach offers genuine hope when radiation has already been used and conventional chemotherapy failed.
Electro-chemotherapy performed by world's most experienced surgeon in this field: Professor Aigner has completed 20,000+ perfusion procedures, techniques refined over 45 years, outcomes other centers cannot match. Stage IV patients who traveled to Germany after being told "nothing more can be done" have achieved remission — not all, but enough to make the journey worthwhile for those facing limited options.
Booking Health provides detailed electrochemotherapy cost. The cost of electrochemotherapy represents access to specialized treatment unavailable in most countries.
Hyperthermia and HIPEC for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Hyperthermia therapy involves heating tumor tissues to temperatures of about 40-43 °C. This "fever-like" state makes cancer cells more vulnerable to chemotherapy and radiation, while healthy tissues are less affected. For example, clinical trials have shown that adding hyperthermia to radiotherapy doubles complete response rates (56% vs. 31%) in recurrent cervical cancer [8, 9].
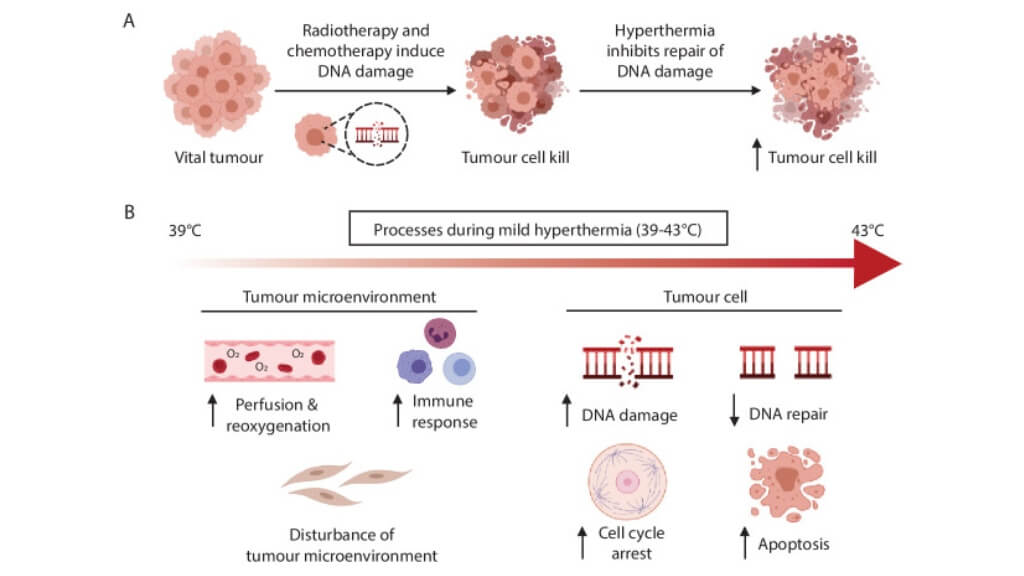
A more advanced approach, used in German oncology clinics, is HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy). This is performed during surgery for patients with peritoneal spread of cervical cancer. After visible tumor deposits are removed, the abdominal cavity is bathed with heated chemotherapy solution. The high temperature helps the drug penetrate deeper into tissues and destroy cancer cells that may be invisible to the surgeon's eye. Studies demonstrate that HIPEC can increase median overall survival to 30-45 months, compared to 12-18 months with systemic chemotherapy alone [10].
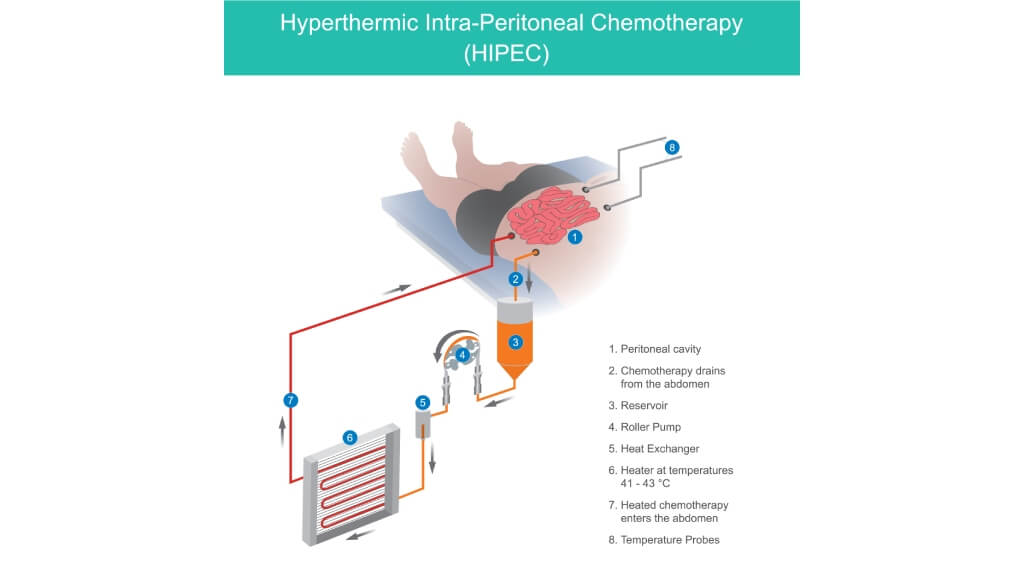
Both methods are considered advanced treatment options for patients with recurrent or metastatic disease, especially when conventional systemic therapy alone is insufficient. HIPEC, in particular, has shown promising results in improving local disease control and extending survival in selected patients with abdominal metastases.
| Method | How It Works | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hyperthermia | Local or regional heating of tumor tissue to ~42 °C | Increases tumor sensitivity to chemo and radiation; spares healthy tissues |
| HIPEC | Heated chemotherapy circulated in the abdominal cavity after surgery | Directly targets microscopic disease; can reduce recurrence and prolong life |
Targeted Therapy for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Unlike conventional chemotherapy, which affects all rapidly dividing cells, targeted therapy focuses on specific molecules that help tumors grow and spread. By acting directly on these molecular pathways, targeted drugs can target cancer cells more precisely, leaving most normal cells unharmed. This means fewer side effects compared with traditional systemic chemotherapy [11, 12].
For cervical cancer patients, two main classes of targeted agents are widely used:
- Angiogenesis inhibitors block the formation of new blood vessels, starving the tumor of oxygen and nutrients. Clinical trials have shown that adding these drugs to chemotherapy improves overall survival in advanced cervical cancer.
- EGFR inhibitors interfere with growth factor signaling pathways that drive cell division. While not as commonly applied as angiogenesis inhibitors, they represent a promising targeted treatment option.
The biggest advantage of targeted therapy is that it can be tailored to the biology of each tumor. Before prescribing, doctors in Germany often perform molecular testing to identify whether a patient's tumor expresses the target molecules. This makes cervical cancer treatment highly individualized and contributes to better tolerance and outcomes.
Immunotherapy for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
In recent years, immunotherapy has changed cancer care by enabling the body's own defenses to recognize and attack tumors. Many cervical cancers express molecules known as PD-L1, which help them "hide" from the immune system. Checkpoint inhibitors block this pathway, allowing the patient's immune system to detect and destroy malignant cells. For example, the KEYNOTE-158 trial reported that 14% of women with PD-L1-positive advanced cervical cancer experienced durable responses, with some lasting beyond two years [13].
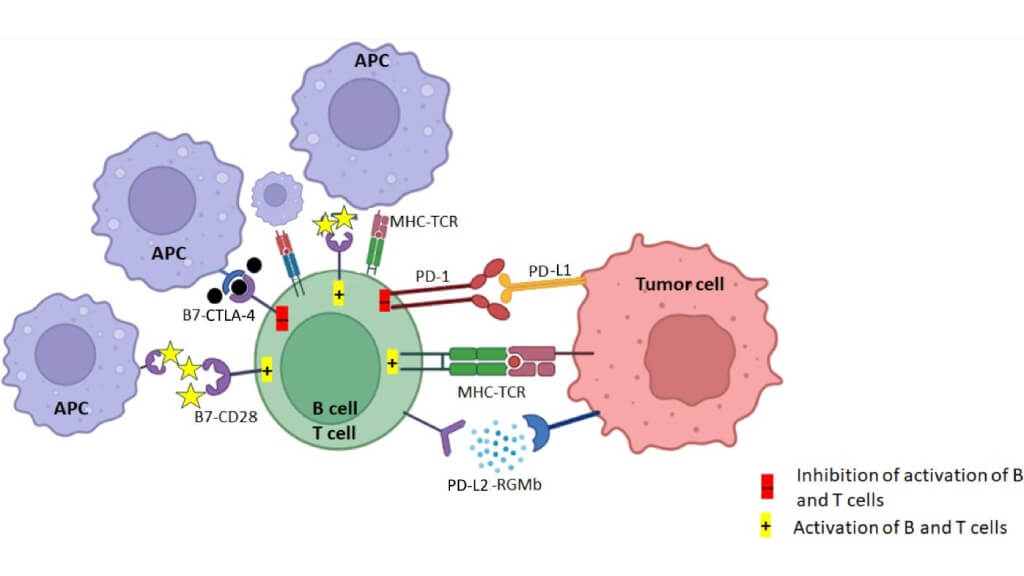
Note: The TCR of CD8+ T cell activates upon recognizing the tumor antigen presented on MHC class I and consequently induces the expression of PD-L1 on tumor cells.
For women with advanced disease, including stage 4 cervical cancer, checkpoint blockade has shown durable responses, even when other treatments failed. Typical treatment involves intravenous infusions every 3 weeks [13].
Moreover, compared with chemotherapy, immunotherapy usually causes fewer severe side effects. Some patients may experience immune-related reactions, such as skin rash or thyroid inflammation, but these are manageable with proper monitoring [13].
Clinical programs offering immunotherapy for stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany are often combined with other advanced modalities, such as radiation or targeted therapy, to achieve maximum benefit. The goal is not only to slow tumor progression but also to extend survival while maintaining a good quality of life.
Dendritic Cell Therapy for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
One of the most exciting advances in oncology is dendritic cell therapy, an approach that uses the body's natural "sentinel" cells to fight tumors. Dendritic cells act as messengers between the innate and adaptive immune systems. They capture tumor antigens and "teach" T-cells to recognize and destroy malignant cells [14].
This discovery earned Canadian immunologist Ralph Steinman the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011, opening the door to a new era of cancer immunotherapy. Since then, several clinics in Germany have implemented dendritic cell immunotherapy, tailoring it to each patient's tumor.
The process involves:
- Collecting the patient's white blood cells through a simple blood draw
- Culturing and "training" dendritic cells in the lab using tumor-specific antigens
- Re-injecting these activated cells back into the patient, where they stimulate the patient's immune system to mount a targeted attack
For women with metastatic cancer or recurrent disease, this therapy can be used as part of personalized treatment plans. In Germany, it is sometimes combined with other immunotherapies, chemotherapy, or even hyperthermia to enhance effectiveness. Clinical reports indicate response rates of 60-80% in advanced cancer, with improved survival compared to chemotherapy alone [14, 15].
Emerging data also highlight the role of therapeutic vaccines. For example, a therapeutic vaccine for cervical cancer in Germany may be designed to target HPV antigens, since almost all cervical tumors are linked to high-risk HPV infections. Such vaccines, when combined with dendritic cell therapy, offer a promising option for long-term disease control [15].
Radiation Therapy – Brachytherapy for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer in Germany
Radiation therapy remains one of the most important approaches in cervical cancer treatment, especially for women with advanced or metastatic disease [5]. Modern German oncology centers use advanced linear accelerators and image-guided technologies to maximize precision while minimizing harm to surrounding organs like the bladder and rectum.
A key innovation is brachytherapy in Germany. Unlike external radiation, where beams are directed from outside the body, brachytherapy places a small radioactive source directly inside or next to the tumor. This allows physicians to deliver higher doses of radiation exactly where they are needed, while protecting healthy tissues. It is particularly effective for controlling the primary cervical tumor and for relieving symptoms such as bleeding or pelvic pain [16].
In many cases, brachytherapy is combined with external beam radiation and chemotherapy to achieve a stronger effect. According to multicenter studies, image-guided brachytherapy combined with external beam therapy yields local control rates of 85-90% in advanced cervical cancer, with fewer complications. German oncologists carefully plan each course using MRI and CT scans, ensuring that the tumor receives the full therapeutic dose while side effects remain limited.
| Method | How It Works | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| External Beam Therapy | High-energy beams aimed from outside the body | Treats large tumor areas; often combined with chemotherapy |
| Brachytherapy | Radioactive source placed inside/next to the cervix | Delivers high local dose; spares surrounding healthy tissues |
Minimally Invasive Surgery for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
Surgery can play an important role in the management of cervical cancer, even at advanced stages. In Germany, doctors increasingly use minimally invasive surgery rather than traditional open procedures. These techniques involve small incisions and advanced instruments such as laparoscopes or surgical lasers, which allow precise tumor removal with less trauma to the body [5, 17].
Common approaches include:
- Laser surgery – uses high-energy beams to vaporize or cut away abnormal tissue
- Cryosurgery – destroys tumors by freezing them
- Laparoscopic trachelectomy – removal of the cervix and upper part of the vagina through small skin incisions. This procedure may preserve the uterus, offering fertility-sparing possibilities in some patients
When larger tumors are present, surgeons may still need to remove the uterus and nearby lymph nodes, but minimally invasive methods shorten hospital stays and speed up recovery. Specifically, studies report shorter hospital stays (2-4 days vs. 7-10 days with open surgery) and reduced complication rates [17].
German oncologists emphasize tailoring each operation to the extent of the disease and the patient's general health. These carefully planned surgical procedures are often combined with chemotherapy, radiation, or immunotherapy to ensure comprehensive care.
Complementary and Supportive Therapies for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
While advanced medical interventions are central to managing cervical cancer, patients also benefit from a wide range of complementary therapies and supportive care programs. These measures do not replace conventional treatments, but they significantly improve the quality of life and help patients cope with the side effects of intensive therapies [5].
Key supportive approaches include:
- Nutritional support – tailored diets rich in protein and vitamins strengthen the body during and after therapy.
- Physiotherapy and exercise programs – maintain mobility, prevent muscle weakness, and support recovery.
- Psychological counseling – helps patients and families manage stress, anxiety, or depression linked to diagnosis and cervical cancer treatment.
- Pain management and palliative care – ensure comfort for those with advanced disease.
German clinics place strong emphasis on rehabilitation and holistic care. Patients undergoing cervical cancer treatment often receive integrative services as part of their personalized medical program. Research shows that structured rehabilitation programs reduce fatigue by up to 40% and improve emotional resilience in cancer survivors [5].
These complementary therapies are especially important for metastatic cancer patients after long hospital stays, as they help restore strength, independence, and emotional balance. Combined with advanced medical interventions, they provide a truly comprehensive approach to cancer treatment in Germany.
Benefits of Stage 4 Cervical Cancer Treatment in Germany
Choosing cancer treatment in Germany offers patients significant advantages compared with many other countries. Germany is known for strict government regulation of healthcare, ensuring that treatment standards and medical programs are monitored at the legislative level. All hospitals are regularly audited for quality, and only certified German oncologists with advanced training can lead cancer care programs.
Why patients choose cervical cancer treatment in Germany:
- Access to innovative options – including targeted therapy, immunotherapy, dendritic cell vaccines, TACE, hyperthermia, and HIPEC
- Personalized treatment plans – diagnostic programs determine the tumor type, stage, and molecular profile, allowing doctors to select the most effective therapy for each patient
- Effective treatment methods – advanced radiation (EBRT, brachytherapy) and minimally invasive surgery offer high precision with fewer side effects
- Comprehensive rehabilitation – recovery and supportive care are integrated into every treatment plan, ensuring physical and emotional well-being
- International patients benefit from multilingual medical teams, efficient logistics, and treatment coordination services
For women with cervical cancer in Germany, these advantages translate into higher survival rates and improved quality of life. According to statistics, survival for localized disease exceeds 85-90%, and even patients with stage IV disease can achieve meaningful life extension when treated in specialized cancer centers with advanced modalities [2].
| Treatment | Stage 4 Response Rate | Survival Rate | Germany (€) | UK (€) | USA (€) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | Not performed in Stage 4 | ~70-80% (early stages only) | 25,000-45,000 | 35,000-55,000 | 65,000-85,000 | Radical hysterectomy, lymph node removal |
| Chemotherapy | <10% | ~20% for advanced cancer | 80,000-150,000 (course) | 90,000-165,000 | 100,000-180,000 | Systemic side effects; limited benefit in stage 4 |
| Radiation therapy | <15% | ~20% (localized) | 28,000-42,000 | 35,000-65,000 | 40,000-80,000 | Includes external beam; often combined with chemo |
| Targeted therapy | 35-45% | ~50% with biomarkers | 375,000-420,000 (course) | 400,000-500,000 | 600,000-1,000,000 | Includes angiogenesis inhibitors |
| Standard immunotherapy | 35-45% | 30-50% | 20,000-38,000/cycle | 25,000-45,000/cycle | 35,000- 60,000/cycle | Checkpoint inhibitors |
| Dendritic cell therapy | 60-80% | ~80% (advanced cancer) | 20,000-38,000 | Not available | 100,000-150,000 | Personalized immunotherapy: Nobel Prize breakthrough |
| TACE (chemoembolization) | 30-40% (localized mets) | Improves survival when combined with ablation | 6,500-24,000 | Not widely published | Not widely published | Blocks tumor blood supply, delivers localized chemo |
| Hyperthermia | 25-35% | ~40% | 5,000-16,000 | 9,500-24,000 | 14,000-37,000 | Enhances chemo/radiation sensitivity |
| HIPEC | 40-55% | 30-50% | 55,000-75,000 | 83,000-118,000 | 112,000-150,000 | Heated chemotherapy during surgery for peritoneal spread |
| Modern radiation (brachytherapy) | ~30-40% | Improves local control | 25,000-40,000 (est.) | 30,000-50,000 (est.) | 40,000-70,000 (est.) | MRI-guided precision delivery of high-dose radiation |
| Minimally invasive surgery | 20-30% (when operable) | Higher quality of life post-op | 25,000-45,000 | 35,000-55,000 | 40,000-80,000 | Includes laparoscopic trachelectomy, robotic surgery |
As is evident, Germany not only offers advanced cancer treatment at lower costs than the US and the UK but also ensures broader access to innovative therapies earlier than many other countries.
Best Cervical Cancer Stage 4 Hospitals in Germany
Treatment of cervical cancer stage 4 requires a comprehensive approach that combines modern treatment methods and quality of life support. In Germany, patients have access to a wide range of advanced technologies: targeted therapy, immunotherapy, regional chemotherapy, hyperthermia, minimally invasive procedures and integrated palliative care. That is why many women choose cervical cancer stage 4 clinics Germany offers. Here multidisciplinary teams of doctors work with each case individually and use the latest international standards.
Modern cervical cancer stage 4 hospitals in Germany are distinguished not only by the presence of highly qualified oncologists, but also by state-of-the-art diagnostics (MRI, PET-CT and specialized laboratory tests). This allows for the development of personalized treatment plans that take into account not only local tumor control, but also concomitant organ damage.
A key aspect of an effective strategy is the combination of symptomatic support and the most effective tumor control – it is important not only to prolong life, but also to improve its quality. Patients work with a whole range of specialists: oncologists, radiotherapists, surgeons, palliative care and rehabilitation specialists. Such methods are commonly applied at cervical cancer stage 4 treatment centers Germany recognizes as top institutions.
Top Clinics for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer Treatment in Germany
| Rank | Clinic | City | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian | Munich | Advanced oncology care, immunotherapy, regional chemotherapy |
| 2 | University Hospital Rechts der Isar | Munich | Multimodal treatment, modern radiation oncology, complex case management |
| 3 | University Hospital RWTH | Aachen | Regional chemotherapy, interventional radiology, individualized treatment strategies |
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
Finding the right hospital and the most effective therapy for advanced cervical cancer can feel overwhelming. Many patients have already undergone multiple treatments, consulted different specialists, and faced conflicting recommendations. In such circumstances, it is easy to choose the first available option or to follow standard treatment protocols that may not offer the best outcomes.
This is where Booking Health's support in Germany becomes invaluable. For more than a decade, our company has been helping patients worldwide gain access to highly specialized cancer centers, innovative therapies, and personalized medical programs. By relying on our expertise, you can be confident that your chosen strategy for cancer treatment in Germany will be tailored to your individual case.
What we offer:
- Comprehensive treatment coordination – from medical document review to the development of a personalized treatment plan.
- Selection of the best hospital and experienced German oncologists for your condition.
- Administrative support – visas, tickets, and preparation of medical paperwork.
- Travel logistics – booking flights, arranging transfers, and organizing accommodation.
- Interpreter and personal coordinator available 24/7 during your stay.
- Cost savings of up to 50% by avoiding surcharges for international patients.
- Full transparency – no hidden fees or unexpected expenses.
Health is priceless, and choosing the right partner to guide you through your treatment in Germany can make all the difference. Booking Health combines medical expertise with patient-focused care to ensure that every aspect of your journey is safe, efficient, and comfortable.
Contact Booking Health today to learn more about advanced stage 4 cervical cancer treatments in Germany and begin your medical journey to healing.
International Cancer Care: Patient Stories with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients About Treatment of stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany
Send request for treatmentStage 4 cervical cancer treatment in Germany often begins with standard treatment protocols such as chemotherapy, external beam radiation, and palliative surgery. These approaches aim to shrink tumors, relieve symptoms, and control disease progression. While effective to some extent, they also affect healthy tissues and require longer recovery, which is why modern German hospitals increasingly combine them with advanced therapies for better outcomes.
Patients can access a wide range of advanced therapies in Germany, including targeted therapy, immunotherapy, dendritic cell vaccines, embolization (TACE), hyperthermia, HIPEC, brachytherapy, and minimally invasive surgery. These advanced treatment options improve tumor control, extend survival, and reduce side effects compared with conventional methods. German clinics design individualized treatment programs, ensuring each patient receives the most effective and tolerable combination.
Specialized oncology centers use image-guided techniques and brachytherapy in Germany to deliver radiation precisely to the tumor while sparing healthy organs. These innovative treatments reduce complications, improve quality of life, and allow higher doses to be applied locally. When combined with chemotherapy or hyperthermia, modern radiation therapy provides effective control of metastatic lesions in the pelvis or distant sites such as bones.
Yes. Immunotherapy for stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany has shown significant promise. Checkpoint inhibitors reactivate the patient's immune system by blocking PD-L1 pathways that help cancer cells hide. For some patients, this leads to durable responses and improved survival, even after standard treatments fail. German hospitals often combine immunotherapy with targeted or radiation therapy to maximize benefits.
Yes. Dendritic cell immunotherapy in Germany uses a patient's own immune cells to train T-cells to recognize and kill tumors. In addition, a therapeutic vaccine in Germany may target HPV antigens, since almost all cervical cancers are linked to high-risk HPV strains. These methods can be integrated into comprehensive care, offering patients hope for long-term disease control.
German hospitals integrate complementary therapies into recovery programs, including nutrition, physiotherapy, psychological support, and pain management. Such care is essential in comprehensive cancer care, helping patients rebuild strength, restore emotional balance, and return to daily life. Rehabilitation is always personalized, ensuring physical and mental well-being after demanding treatment.
Germany offers some of the most advanced stage 4 cervical cancer treatments in the world, delivered by expert oncologists in top German hospitals. Patients benefit from modern technologies, strict quality standards, and effective therapies that may not be available elsewhere. Lower costs compared with the US and the UK, plus specialized rehabilitation programs, make Germany a leading destination for international cancer care.
Booking Health support in Germany ensures efficient treatment coordination for patients worldwide. Services include hospital selection, medical translations, travel logistics, and cost savings of up to 50% for international patients. A personal coordinator assists at every step – from preparing medical documents to follow-up care – so patients can focus fully on healing while receiving world-class oncology services and cutting-edge treatments in Germany.
Persistent fatigue or weakness, bone pain or fractures, difficulty breathing or coughing up blood (if the lungs are involved), vaginal fistulas or abnormal bleeding, weight loss and anemia.
In Germany, chemotherapy course costs around €80,000‑€150,000. In the UK, similar courses are about €90,000‑€165,000. In the USA, the cost ranges around €100,000‑€180,000.
Dendritic cell therapy demonstrates a 60‑80% response rate even in stage 4 cancer, TACE (chemoembolization) – up to 30‑40%, HIPEC – 40‑55%.
Dendritic cell vaccination – due to personalized mechanism of action – has survival rates up to around 80%. With HIPEC, median overall survival is 30‑45 months compared to 12‑18 months with systemic chemotherapy alone.
External beam therapy affects large areas from outside the body. Brachytherapy places a radioactive source inside or next to the cervix – that delivers a high local dose and spares surrounding healthy tissues.
Hyperthermia heats tumour tissue to about 42°C, increasing sensitivity to chemo‑ and radiotherapy. HIPEC delivers heated chemotherapy into the abdominal cavity after tumor removal, directly targeting microscopic disease and reducing recurrence.
Standard treatments have systemic impact, damage healthy tissues, weaken the immune system – all these often result in long rehabilitation. Advanced methods are localized or tumor‑specific, spare healthy organs and immune function, and enable faster recovery.
Standard treatments use the same drugs/protocols for most patients, offering limited survival improvement in stage 4 cases. Advanced methods are personalized based on tumor type – this leads to better tolerance and improved life expectancy.
In Germany stage 4 cervical cancer is treated using advanced methods – immunotherapy, targeted therapy, regional chemo and others.
The best hospitals for stage 4 cervical cancer treatment are specialized oncology centers with experience in advanced gynecologic cancers.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] World Health Organization. Cervical Cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer
[2] American Cancer Society. Survival Rates for Cervical Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/cervical-cancer/detection-diagnosis-staging/survival.html
[3] National Cancer Institute. Cervical Cancer Stages. https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical/stages
[4] Cancer Research UK. What Is Advanced Cervical Cancer? https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/cervical-cancer/advanced/about
[5] Cancer Research UK. Treatment for Cervical Cancer. https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/cervical-cancer/treatment
See more
[6] Albu S, Grigoriu C, Vasiliu C, et al. The Role of Uterine Artery Embolization in Cervical Cancer – Single Case Report. Maedica (Bucur). 2011 Apr;6(2):137–140. [PMC free article]
[7] Medicina. Therapy Response and Survival among Patients with Gynecologic Tumors Treated with Transarterial Chemoperfusion and Transarterial Chemoembolization. https://www.mdpi.com/1648-9144/60/10/1585
[8] Reports of Practical Oncology & Radiotherapy. 2018;23(6):595-603. Accessed August 27, 2025. Hyperthermia in cervical cancer – current status. [DOI]
[9] International Journal of Gynecological Cancer. 2022;32(3):288-296. The role of hyperthermia in the treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer: a comprehensive review. https://www.international-journal-of-gynecological-cancer.com/article/S1048-891X(24)00597-8/fulltext
[10] Gynecologic Oncology Reports. 2022;39:100909. Management of recurrent cervical cancer with peritoneal carcinomatosis with HIPEC. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352578921002137?via%3Dihub
[11] Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023;12(18):5992. Advances in Targeted Therapy for the Treatment of Cervical Cancer. https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/12/18/5992
[12] ESMO Open. 2019;3(1):e000462. Targeted therapy in cervical cancer. https://www.esmoopen.com/article/S2059-7029(20)32270-5/fulltext
[13] Exploration of Targeted Anti-tumor Therapy. 2025;6:1002296. Immunotherapy in cervical cancer: an innovative approach for better treatment outcomes. https://www.explorationpub.com/Journals/etat/Article/1002296
[14] Journal of Cancer. 2019;10(25):6364-6373. MTBHsp70-exFPR1-pulsed Dendritic Cells Enhance the Immune Response against Cervical Cancer. https://www.jcancer.org/v10p6364.html
[15] Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology. 2003;129(9):511-520. Dendritic cell-based tumor vaccine for cervical cancer I: in vitro stimulation with recombinant protein-pulsed dendritic cells induces specific T cells to HPV16 E7 or HPV18 E7. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00432-003-0462-6
[16] Frontiers in Oncology. 2024;14:1442712. Brachytherapy for cervical cancer: from intracavitary to interstitial technique. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/oncology/articles/10.3389/fonc.2024.1442712/full
[17] Current Oncology. 2022;29(2):1093-1106. Minimally Invasive Surgery for Cervical Cancer in Light of the LACC Trial: What Have We Learned?. https://www.mdpi.com/1718-7729/29/2/93
Read:
Cervical cancer treatment with dendritic cell therapy
Article menu:
- Understanding Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
- Standard Treatment Protocols for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer and Their Limitations
- Advanced Treatment Methods in Germany for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
- Detailed Overview of Advanced Therapies for Stage 4 Cervical Cancer
- Benefits of Stage 4 Cervical Cancer Treatment in Germany
- Best Cervical Cancer Stage 4 Hospitals in Germany
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
- Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients About Treatment of stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health