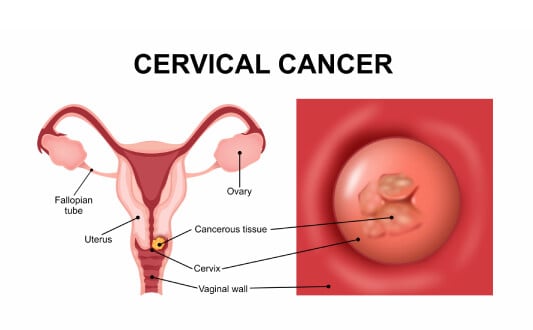
Cervical cancer is one of the most common malignancies among women worldwide, ranking as the fourth most frequent cancer with more than 660,000 new cases and over 350,000 deaths each year [1]. Despite these alarming numbers, progress in early diagnostics and treatment methods has significantly improved survival rates. When doctors diagnose cervical cancer at an early stage, the chances of achieving full recovery are very high. For many patients, the most effective strategy is surgical treatment for cervical cancer, which remains the primary method of therapy even in the era of advanced radiation and systemic therapies [3].
The importance of surgery lies in its ability to completely remove the tumor, prevent further spread, and, in some cases, preserve a woman's fertility. With timely intervention, women with early stage cervical cancer can benefit from procedures that save the uterus, allowing them to plan for future pregnancies. At more advanced stages, radical interventions may be required, but modern techniques ensure greater precision and safety than ever before [3].
Germany is widely recognized as a global leader in cervical cancer treatment, offering innovative surgical technologies, highly experienced surgeons, and comprehensive rehabilitation programs. German hospitals are known for combining minimally invasive approaches with excellent oncological outcomes, making them an attractive destination for women seeking world-class care.
Overview of Surgical Options for Cervical Cancer
Surgery has been used to treat cervical cancer since the mid-19th century, and over time, it has transformed from highly invasive operations into safer, precise, and often minimally traumatic procedures [4]. Today, cervical cancer surgery is considered the gold standard for treating early cancers, particularly when tumors are localized to the cervix and can be completely removed. This approach is guided by a number of general principles: remove as many cancer cells as possible, preserve surrounding healthy cervical tissue, and, whenever possible, maintain fertility and overall quality of life [5, 6].
Factors That Influence the Choice of Surgery for Cervical Cancer
Doctors decide which type of surgical procedures are most suitable based on:
- The size of the tumor
- How deeply the tumor has invaded the cervix (invasion depth)
- Whether lymph nodes are affected
- If the cancer has spread to nearby pelvic organs or distant sites
Each of these factors determines the stage of the disease and guides the surgical approach.
Surgical Options for Cervical Cancer by Stage
Stage 0 (Carcinoma in situ). At this stage, abnormal cells are found only on the surface of the cervix. Treatment usually involves removing or destroying these cells without removing the uterus. The aim is to completely remove all abnormal cervical tissue and ensure no cancer cells remain. Options include:
- Conization (removal of a cone-shaped piece of cervical tissue for diagnosis and treatment)
- Cryosurgery (freezing abnormal cells)
- Laser surgery (using high-energy light to vaporize cancer cells)
- Loop Electrosurgical Excision Procedure (LEEP)
Early cervical cancer (Stages IA-IIA1). If the tumor is still confined to the cervix, treatment may include:
- Cone biopsy (useful for very small tumors)
- Trachelectomy, a fertility-preserving surgery where the cervix is removed but the uterus is left in place
- Hysterectomy, which removes the uterus and cervix, sometimes with lymph nodes, to ensure complete tumor removal
Advanced cervical cancer (Stages IB2-IIA2). Surgery becomes more complex and usually involves:
- Radical hysterectomy with removal of pelvic lymph nodes
- At this stage, surgery is often combined with radiation therapy and chemotherapy for the best outcomes
When cancer has spread (Stage IIB-IV). If the tumor has grown into surrounding tissues or distant organs, surgery is usually not the primary option. In these cases, treatment often focuses on radiation therapy and systemic approaches.
Innovative Surgical Methods for Cervical Cancer
Modern progress in oncology has transformed the way doctors treat cervical cancer. Instead of relying solely on large incisions and long hospital stays, surgeons now use advanced technologies that make operations more precise, less traumatic, and often fertility-preserving [5, 6]. Below are the most important innovations shaping the future of cervical cancer treatment.
Minimally Invasive Surgery for Cervical Cancer
One of the biggest advancements is the introduction of minimally invasive surgery, which includes both laparoscopic and robotic-assisted approaches. These methods allow surgeons to operate through tiny cuts in the abdomen rather than large incisions [7, 8].
Advantages include:
- Less trauma to healthy tissues
- Reduced blood loss during surgery
- Smaller scars and better cosmetic results
- Faster recovery and shorter hospital stays
Techniques:
- Laparoscopic hysterectomy – removal of the uterus and cervix using a camera and fine instruments inserted through small incisions
- Robotic-assisted hysterectomy – similar to laparoscopy, but the surgeon controls robotic arms for greater precision and dexterity
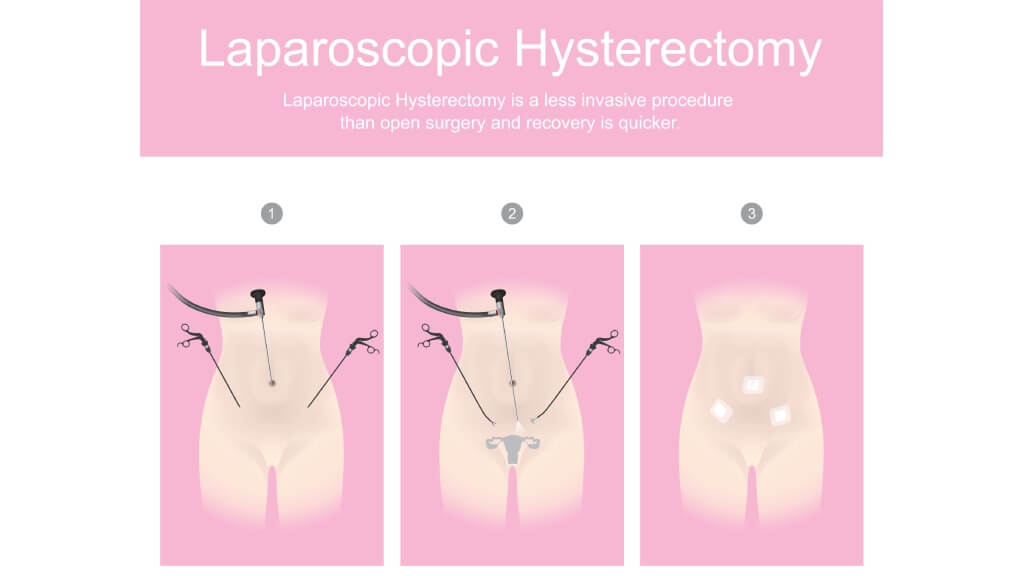
However, long-term results have reduced the initial excitement. For example, the 2018 LACC trial found that, at 4.5 years, disease‑free survival was significantly lower with minimally invasive approaches (86.0%) compared to open surgery (96.5%), a difference of 10.6 percentage points. Patients undergoing minimally invasive surgery were also at higher risk of recurrence and had worse overall survival (93.8% vs. 99.0%) [9].
Nevertheless, some more recent analyses suggest that when surgical teams avoid factors that may cause cancer cell spillage – such as using uterine manipulators too early or creating intra-abdominal openings – outcomes may be more comparable to open surgery [10].
In other words, minimally invasive approaches offer shorter recovery and better cosmetic results, but in early stage cervical cancer, open radical hysterectomy currently shows superior long-term oncologic outcomes and may be preferred to ensure safe removal of all cancer cells. Therefore, continued research is needed to optimize minimally invasive approaches and ensure patient safety [11].
Fertility Preservation Options in Cervical Cancer Treatment
For young women with early cervical cancer who wish to have children in the future, fertility preservation is an important goal. The main surgical option here is radical trachelectomy, a procedure where the cervix, surrounding tissues, and nearby lymph nodes are removed, but the uterus is preserved [12, 13].
Indications:
- Small tumors (usually <2 cm)
- No deep invasion into the cervical canal
- No signs of distant spread or lymph node involvement
Benefits and risks:
- Preserves the ability to conceive naturally
- Increases the risk of miscarriage due to changes in the cervix
- Delivery must usually be by cesarean section
What research shows:
- Oncologic safety: In some stage IB1 patients, radical trachelectomy shows oncologic outcomes comparable to radical hysterectomy [14].
- Recurrence and mortality: Large reviews report recurrence rates under 5% and mortality under 2% after trachelectomy for small tumors; risks increase when tumors are ≥2 cm [15].
- Fertility results: Among women trying to conceive after trachelectomy, about 54% achieved pregnancy and nearly 70% had live births [16]. Broader analyses show live-birth rates around 67%, with vaginal and abdominal trachelectomy achieving up to 76% live births, while laparoscopic approaches achieve ~57% [17].
- Obstetric risks: Pregnancies after trachelectomy carry higher risks of miscarriage and preterm birth. However, with expert perinatal care, many women successfully deliver healthy babies [18, 19].
In summary, radical trachelectomy offers an excellent balance between effective cancer control and preserving fertility. German hospitals are leaders in offering this option, with highly trained surgeons performing these operations successfully. As a result, women have the chance to both overcome cancer and pursue motherhood.
Advanced Multidisciplinary Care for Cervical Cancer
As previously mentioned, for patients with invasive cervical cancer or advanced cervical cancer, surgery is rarely used alone [5, 6]. Instead, treatment usually combines different methods:
- Radiation therapy to destroy hidden cancer cells
- Chemotherapy to target the disease that may have spread
- Surgery to remove localized tumors when appropriate
In this setting, teamwork is crucial. Specialists from oncology, radiology, surgery, and pathology collaborate to create a treatment plan tailored to each patient.
Another important factor is the role of the immune system. After major surgery or radiation therapy, the body's defenses can weaken, so doctors recommend immune support therapies, balanced nutrition, and regular monitoring [5, 6]. This holistic approach helps improve survival rates and reduces the chances of relapse.
Surgical Treatment of Recurrent Cervical Cancer
Sometimes, even after successful initial therapy, cervical cancer can return. This condition is called recurrent cervical cancer. The new tumor may appear in the cervix itself, nearby pelvic organs, or, in some cases, in distant parts of the body. When the recurrence is localized only in the pelvis and has not spread to distant organs, doctors may recommend an extensive operation known as pelvic exenteration [20, 21].
Pelvic Exenteration: A Radical Surgical Option in Cervical Cancer
This is one of the most complex forms of surgical treatment of cervical cancer. During the procedure, surgeons perform surgery to remove all areas affected by the disease, including:
- The uterus and cervix
- Parts of the vagina and surrounding tissues
- Pelvic lymph nodes
- In some cases, the bladder or rectum, if cancer cells are detected there
Although this operation is very demanding, it can offer a chance of cure when other methods are not effective [20]. International guidelines recommend exenteration for women with central pelvic recurrence or persistent disease, no distant metastases, and when a margin-negative (R0) resection is achievable – always after a multidisciplinary tumor board review [13].
Research evidence:
- Large clinical series show that, in some patients, pelvic exenteration achieves 5-year overall survival rates of ~38-51% [22, 23]
- The most important prognostic factors are achieving clear surgical margins and the absence of pelvic wall or nodal involvement, which significantly improve outcomes [23, 24]
- Survivors often report an acceptable quality of life, though challenges remain in role and social functioning, which is why psychological and rehabilitation support are essential [25, 26]
Reconstruction Options After Cervical Cancer Surgery
To improve the quality of life after such extensive surgery, reconstruction is usually performed in the same procedure:
- Neo-bladder creation from a segment of intestine to replace the removed bladder.
- Colostomy, in which stool passes through a new opening in the abdominal wall into a small external bag.
- Neo-vagina reconstruction using tissues from other body parts, allowing women to maintain sexual function.
Recovery After Cervical Cancer Surgery and Support
Recovery takes several months and requires close follow-up. Patients are supported by a multidisciplinary team that includes oncologists, surgeons, radiologists, psychologists, and rehabilitation specialists. These experts develop a personalized treatment plan, ensuring not only physical healing but also emotional and social adaptation.
Even though pelvic exenteration is a major operation, it provides hope for women whose cancer has spread locally but not beyond the pelvis, offering a possibility of long-term survival and even cure when performed in specialized centers.
Comparison of Cervical Cancer Surgical Approaches by Country
When choosing where to undergo cervical cancer surgery, many patients look beyond their home country and explore leading destinations for oncology care. Germany, the United States, and the United Kingdom are often compared because they represent three leading healthcare systems with very different approaches. Looking at these countries side by side highlights important differences in access to innovative techniques, waiting times, costs, and overall quality of cervical cancer care.
Below is a comparison of the three countries:
| Aspect | Germany | United States | United Kingdom |
|---|---|---|---|
| Access to minimally invasive surgery | Widely available, including advanced robotic systems | Broadly available, but costs are high | Available in leading centers, less consistent across the NHS |
| Fertility sparing options | Radical trachelectomy and other fertility preservation procedures performed in specialized clinics | Available but not standard in all hospitals | Offered in select tertiary centers, longer referral times |
| Waiting times | Short, surgery can often be arranged within 1–3 weeks for international patients | Short in private sector, but depends on insurance | Long waiting lists in NHS; the private sector is faster but costly |
| Costs of cervical cancer surgery | €25,000-€45,000 | €65,000-€85,000 | €35,000-€55,000 |
| Availability of multidisciplinary care | Standard in all certified cancer centers, including gynecologic oncologists, radiologists, pathologists, and psychologists | Widely available in comprehensive cancer centers | Available, but access may be limited in smaller NHS hospitals |
As is evident, Germany stands out for combining reasonable costs with high-quality care in leading cervical cancer hospitals. Patients also benefit from advanced technology, highly experienced surgeons, and structured follow-up care. The emphasis on minimally invasive methods and fertility-preserving surgery makes Germany especially attractive for younger women.
In contrast, while the United States has excellent specialists and advanced technologies, the prices are significantly higher, and access is often determined by insurance coverage. The United Kingdom provides good care through the NHS, but patients may face long waiting times unless they turn to private clinics.
Overall, Germany offers a strong balance of advanced methods, affordable prices, and excellent surgical outcomes, making it one of the most popular choices for international patients seeking cervical cancer treatment.
Choosing the Right Hospital for Cervical Cancer Surgery
Selecting the right hospital is one of the most important steps in the journey of cervical cancer treatment. The outcome of surgery depends not only on the chosen technique but also on the surgeon's expertise and the hospital's overall experience. Research shows that hospitals with a high volume of oncological surgeries achieve better surgical outcomes, as their specialists perform these procedures regularly and collaborate within multidisciplinary teams.
Why Germany Is a Preferred Destination for Cervical Cancer Surgery
Germany has become one of the world's most sought-after destinations for women seeking advanced or invasive cervical cancer care. The country combines medical innovation with internationally recognized standards of safety and efficiency. Patients benefit from:
- Advanced technology: German centers use modern robotic systems and minimally invasive tools to ensure maximum precision during operations. These facilities also integrate surgery with radiation therapy and chemotherapy when needed, ensuring patients receive complete cancer care under one roof.
- Access to clinical trials: Many hospitals are involved in international research projects, giving patients the chance to access innovative therapies not widely available elsewhere.
- Shorter waiting times: Unlike in many countries where patients may wait months for surgery, German hospitals usually arrange treatment within just a few weeks – critical when you need to treat cervical cancer quickly.
- High surgical outcomes: Certified oncological departments, strict quality standards, and experienced specialists result in excellent recovery rates, fewer complications, and better long-term survival.
Leading Hospitals in Germany for Cervical Cancer Surgery
Several institutions exemplify these advantages and are recognized as leaders in gynecologic oncology and cervical cancer surgery:
- University Hospital Rechts der Isar (Munich) – Known for its high surgical volume and tradition in gynecologic oncology. Offers modern operating facilities and comprehensive cancer care.
- LMU Klinikum – University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian Munich – One of Germany's largest university hospitals, providing advanced surgical technology, interdisciplinary cancer teams, and international patient services.
- Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch – A multidisciplinary oncology center equipped with robotic systems and certified by the German Cancer Society for its consistently high-quality outcomes.
A Medical Journey with Booking Health
Finding the right path in the surgical treatment of cervical cancer can feel overwhelming. Many women consult several specialists, hear about different therapeutic strategies, and face uncertainty about the best choice for their health and future. In such situations, it is easy to follow standard protocols without realizing that advanced and individualized solutions may exist abroad.
To create a truly personalized treatment plan, it is crucial to work with experts who understand both the medical and organizational aspects of cancer care. This is where Booking Health becomes your trusted partner. With over 12 years of experience in international medical coordination, the company helps patients access innovative surgical techniques and the best outcomes in leading hospitals.
Booking Health coordination includes:
- Careful analysis of your medical reports.
- Selection of the most suitable hospital and surgeon for your case.
- Preparation and translation of documents, ensuring nothing is overlooked.
- Scheduling surgery and hospital stay without delays.
- Support with visas, tickets, and transfers.
- A personal interpreter and medical coordinator available 24/7.
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs.
Germany is home to some of the world's best centers for cervical cancer care, offering modern minimally invasive techniques, fertility-preserving procedures, and advanced follow-up care, protecting the immune system and promoting recovery. With Booking Health, you can access these opportunities confidently, knowing that every detail is handled professionally.
Health is priceless, and entrusting your journey to experienced specialists ensures safety and peace of mind. Contact Booking Health today to learn more about surgical options for cervical cancer and start your journey toward recovery.
Cancer Treatment Abroad: Patient Experiences with Booking Health
Frequently asked Questions of Our Patients About Surgical Treatment for Cervical Cancer
Send request for treatmentThe main surgical treatment of cervical cancer depends on the stage of disease. Early stages may be managed with conization, which removes a small cone-shaped portion of the cervix. More advanced cases may require a hysterectomy, where the uterus and cervix are removed. In young women, trachelectomy can preserve fertility. Today, many of these surgical procedures are performed as cervical cancer surgery using minimally invasive techniques.
Yes. German hospitals offer fertility sparing surgery such as radical trachelectomy, which removes the cervix but preserves the uterus. This allows women to attempt pregnancy later. Outcomes are carefully monitored, and most centers report excellent surgical outcomes in terms of both cancer control and fertility preservation.
Minimally invasive surgery (laparoscopic or robotic) requires only small incisions, leading to faster recovery, less pain, and better cosmetic results. In contrast, open surgery involves larger cuts and longer healing times. Both approaches provide strong surgical outcomes, and the choice depends on tumor size, stage, and the surgeon's expertise.
Several leading cervical cancer hospitals in Germany, including the University Hospital Rechts der Isar in Munich, LMU Klinikum Munich, and Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch, are internationally recognized for their expertise, modern equipment, and innovative techniques. With proper surgical care coordination, patients can access specialized centers with multidisciplinary teams. Booking Health support helps you select the most suitable clinic for your needs.
Through Booking Health coordination, patients receive step-by-step support. This includes preparing documents, arranging consultations, booking surgery, and ensuring smooth surgical care coordination. Booking Health support also provides interpreters, transfer services, and 24/7 assistance.
Thanks to strong partnerships with German hospitals, Booking Health support ensures that international patients bypass long waiting lists. In most cases, surgical treatment of cervical cancer can be scheduled within 1-3 weeks. A tailored treatment plan is created to match each patient's needs.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] World Health Organization. Cervical Cancer. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cervical-cancer
[2] Journal of the National Cancer Center. Global burden of cervical cancer: current estimates, temporal trend and future projections based on the GLOBOCAN 2022. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2667005425000134?via%3Dihub
[3] National Cancer Institute. Cervical Cancer Treatment. https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical/treatment
[4] American Cancer Society. History of Cancer Treatments: Surgery. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/understanding-cancer/history-of-cancer/cancer-treatment-surgery.html
[5] National Cancer Institute. Cervical Cancer Treatment by Stage. https://www.cancer.gov/types/cervical/treatment/by-stage
See more
[6] American Cancer Society. Treatment Options for Cervical Cancer, by Stage. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/cervical-cancer/treating/by-stage.html
[7] Current Oncology. Minimally Invasive Surgery for Cervical Cancer in Light of the LACC Trial: What Have We Learned? https://www.mdpi.com/1718-7729/29/2/93
[8] Facts Views Vis Obgyn, 2019, 11 (2): 103-110. Surgical Steps of Total Laparoscopic Hysterectomy. https://fvvo.eu/pdf/58770459-5a06-4076-a747-5b73e24cd7c0/articles/deneme.14.3.050/103-110.pdf
[9] New England Journal of Medicine. Minimally Invasive versus Abdominal Radical Hysterectomy for Cervical Cancer. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa1806395
[10] Journal of Gynecologic Oncology. Minimally Invasive Radical Hysterectomy and the Importance of Avoiding Cancer Cell Spillage for Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: A Narrative Review. https://ejgo.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3802/jgo.2023.34.e5
[11] American Journal of Clinical Oncology. Laparoscopic Versus Abdominal Radical Hysterectomy for Cervical Cancer.
[12] Obstetrics & Gynecology. Radical Trachelectomy for the Treatment of Early-Stage Cervical Cancer. https://journals.lww.com/greenjournal/abstract/2020/09000/radical_trachelectomy_for_the_treatment_of.13.aspx
[13] International Journal of Gynecological Cancer. ESGO/ESTRO/ESP Guidelines for the Management of Patients with Cervical Cancer – Update 2023. https://www.international-journal-of-gynecological-cancer.com/article/S1048-891X(24)02424-1/fulltext
[14] Gynecologic Oncology. Oncologic Outcome of Fertility-Sparing Radical Trachelectomy versus Radical Hysterectomy for Stage IB1 Cervical Carcinoma. https://www.gynecologiconcology-online.net/article/S0090-8258(08)00532-5/abstract
[15] Gynecologic Oncology Research and Practice. Fertility-Sparing Management in Cervical Cancer: Balancing Oncologic Outcomes with Reproductive Success. https://gynoncrp.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s40661-016-0030-9
[16] Journal of Gynecologic Oncology. Reproductive Counseling and Pregnancy Outcomes after Radical Trachelectomy for Early Stage Cervical Cancer. https://ejgo.org/DOIx.php?id=10.3802/jgo.2019.30.e45
[17] Evan S Smith, Ashley S Moon, Robin O’Hanlon et al. Radical Trachelectomy for the Treatment of Early-Stage Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review. Obstet Gynecol. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2021 Sep 1. Published in final edited form as: Obstet Gynecol. 2020 Sep;136(3):533–542. doi: 10.1097/AOG.0000000000003952. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[18] Journal of Medical Cases. Obstetric Outcomes and Complications After Vaginal Radical Trachelectomy: A Case Report.
[19] Gynecologic Oncology. Management of Pregnancy after Radical Trachelectomy. https://www.gynecologiconcology-online.net/article/S0090-8258(21)00343-7/fulltext
[20] Cancers. The Role of Pelvic Exenteration in Cervical Cancer: A Review of the Literature. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/4/817
[21] Journal of Clinical Medicine. Robotic-Assisted Pelvic Exenteration for Cervical Cancer: A Systematic Review and Novel Insights into Compartment-Based Imaging. https://www.mdpi.com/2077-0383/13/13/3673
[22] Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology of India. Survival After Pelvic Exenteration for Cervical Cancer. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s13224-021-01502-0
[23] International Journal of Gynecological Cancer. Survival After Curative Pelvic Exenteration for Primary or Recurrent Cervical Cancer: A Retrospective Multicentric Study of 167 Patients. https://www.international-journal-of-gynecological-cancer.com/article/S1048-891X(24)03091-3/fulltext
[24] International Journal of Gynecological Cancer. Evaluation of Survival and Mortality in Pelvic Exenteration for Gynecologic Malignancies: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analyses, and Meta-Regression Study. https://www.international-journal-of-gynecological-cancer.com/article/S1048-891X(25)00948-X/fulltext
[25] Gynecologic Oncology. Quality of Life after Extended Pelvic Exenterations. https://www.gynecologiconcology-online.net/article/S0090-8258(22)00276-1/abstract
[26] Cancers. Long-Term Survival, Prognostic Factors, and Quality of Life of Patients Undergoing Pelvic Exenteration for Cervical Cancer. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/14/9/2346
Read:
Article menu:
- Overview of Surgical Options for Cervical Cancer
- Innovative Surgical Methods for Cervical Cancer
- Surgical Treatment of Recurrent Cervical Cancer
- Comparison of Cervical Cancer Surgical Approaches by Country
- Choosing the Right Hospital for Cervical Cancer Surgery
- A Medical Journey with Booking Health
- Frequently asked Questions of Our Patients About Surgical Treatment for Cervical Cancer
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health