If you need information about innovative treatments for stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany, you can find it
Cervical cancer is one of the most common female oncological diseases. In most countries, it is second to breast cancer. However, in the coming years, the number of this type of cancer cases is expected to decrease. A vaccine was developed that protects women from the main cause of cervical cancer - papillomavirus infection. Let's discuss how to prevent cervical cancer.
Prevention of cervical cancer
Cervical cancer is one of the diseases that is diagnosed late in most cases. Therefore, its mortality is very high despite the fact that effective methods of preventing cervical cancer have been developed.
To prevent this disease, it is necessary:
- To avoid human papillomavirus infection . To do this, one should limit the number of sexual partners and use condoms, because the disease is transmitted through sexual contact.
- To undergo regular examinations by a gynaecologist. The tumor does not develop from nothing. It is preceded by many years of precancerous disease that can be easily detected. Unfortunately, most women do not go to the gynaecologist in the absence of symptoms and are not examined on time.
- To be treated timely. Against the background of predisposing and precancerous diseases of the cervix a woman needs to undergo treatment. In particular, surgical intervention may be required. Most often it is carried out through minimally invasive surgery. Foci of altered epithelium are "cauterized" with a laser. Cryodestruction or electrocoagulation are also used.
These are the main ways to prevent cervical cancer in adult women. However, in recent years, specific prevention methods have been actively used. Children are vaccinated against the papillomavirus infection. This eliminates the main risk factor of cervical cancer, because, as a rule, it is caused by papillomavirus of highly oncogenic types.
Cancer vaccination
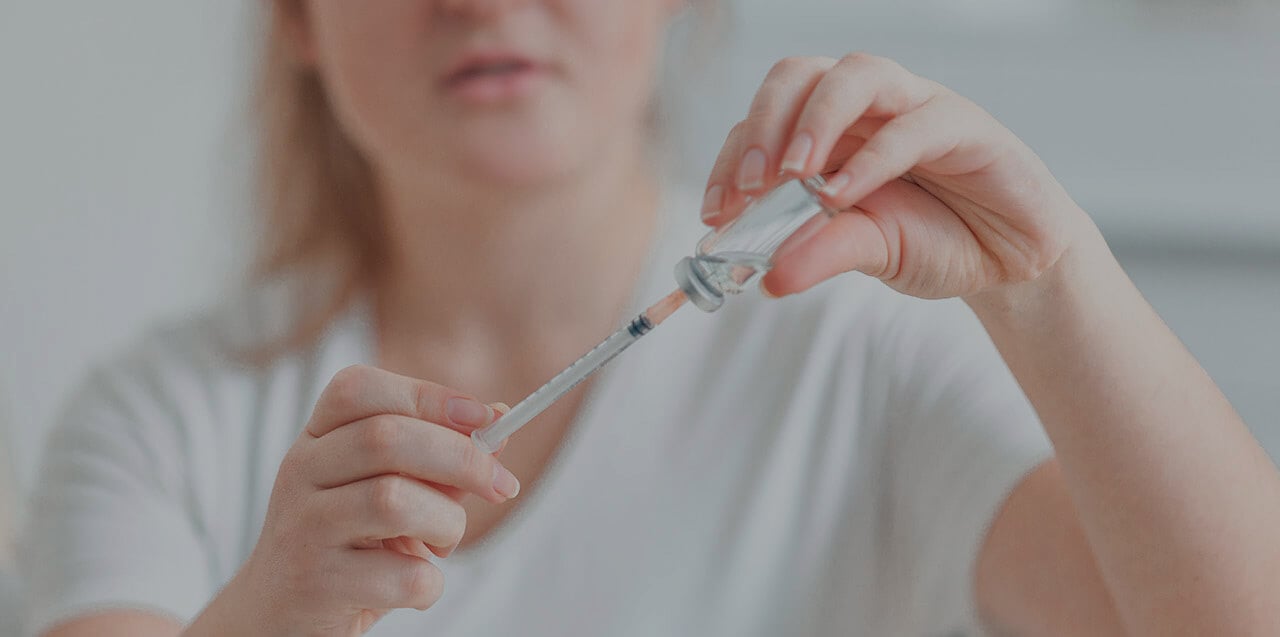
The simplest and most effective method of prevention is the cervical cancer vaccination. It does not guarantee a 100% proof against cancer in the future. However, this risk is reduced approximately by three times.
How does the vaccine work against cervical cancer? The principle of its action consists in infecting the person with papillomavirus for the subsequent development of immunity. HPV 16 and 18 types cause more than 2/3 of malignant tumors. Cervical cancer vaccination prevents the infection of these types of virus, which can prevent not only oncopathology, but also the development of anogenital warts and reduces the risk of cervical dysplasia by twice as much.
The cervical cancer vaccination makes it possible to prevent some other, less common oncological pathologies caused by papillomavirus.
Among them are cancers of:
- Vulva and vagina
- Throat
- The male penis
- Rectum
Many patients are afraid that the vaccine used to prevent cervical cancer will infect them with the virus. They are afraid that the immunity may not develop and the papillomavirus will remain in their body forever. These fears are futile. Cervical cancer vaccination for prevention does not contain live virions. It is recombinant in its origin, meaning that this is a virus that can not actually infect humans. Cervical cancer vaccination causes an immune response, which develops as a result of the antigen penetration into the body. This antigen is characteristic of HPV oncogenic types, but not for the causative agent of the disease. Therefore, there is no need to refuse the cervical cancer vaccination.
The vaccine is effective in 99% of patients. This means that 99 people out of one hundred stimulate the formation of antibodies to papillomavirus infection. They remain in the blood for at least 54 months after the completion of the course of vaccination against cervical cancer.
Cervical cancer vaccination is not used for treatment purposes. It is ineffective for women who:
- Have developed cancer of the cervix, vulva or vagina
- Have precancerous diseases of the cervix
- Are infected with papillomavirus infection
Cervical cancer vaccination does not help prevent other sexually transmitted infections, apart from HPV. In addition, it does not form immunity against all types of papillomavirus infection without exception.
Cervical cancer vaccination helps prevent only 2, 4 or 9 of the most dangerous types of HPV - depending on which vaccine is used. But there are hundreds of types of viruses. Therefore, cervical cancer vaccination does not give 100% protection.
When to have cervical cancer vaccination?
Cervical cancer vaccination is done at the age of nine or ten for girls, based on which vaccine will be introduced. Often, parents ask by which age should their child be vaccinated against cervical cancer. Both boys and girls should be vaccinated against cervical cancer before the age of 15 - until their first sexual intercourse.
Why are there such limitations? Most women become sexually active from the age of 15 years of age. After that, they are likely to become infected with papillomavirus infection. It is extremely common among sexually active people. In addition, the risk of infection even after the first sexual intercourse is quite high. A single contact with the carrier of infection amounts to a 70% risk of infection.
Can cervical cancer vaccination be done later in life? Yes it is possible. But in order for the cervical cancer vaccination to be 100% effective in girls, it should be done before the first sexual activity. That is, the vaccination can be done 17 and 18 years before the first sexual experience. Papillomavirus infection is transmitted even during contact without penetration. Therefore, even an examination by a gynaecologist does not help establish the onset of sexual activity. Therefore, it is better to vaccinate a child under 15 years of age. Although vaccines were tested on patients under 45 years of age, vaccinations can be done at any age if the woman is not infected with HPV type 16 or type 18. However, the older the woman the lower the effectiveness of the vaccination.

Where is the cervical cancer vaccination injected?
Often women ask where is the vaccination against cervical cancer injected. The drug is usually injected either into the shoulder or into the thigh: to its outer surface at the level of the upper third. It is important to know where the vaccine is being given, because the vaccine is not allowed to be injected intravenously. It is also not injected subcutaneously or intradermally - this method was not tested in clinical studies, so the results cannot be predicted.
Let`s consider how the vaccination process is going on, using the Gardasil vaccine as an example. In total, three doses of 0.5 ml are required. The second dose is administered two months after the first one, and the third one - after another four months. Thus, the full course of vaccination takes six months.
It is possible to reduce the course or, on the contrary, increase it. You can compress the course for a maximum of three months. In this case, the second dose is administered one month after the first one, and the third one- after another 2 months.
Sometimes the vaccination has to be stretched over time. For example, if there are contraindications for the introduction of a regular dose of the drug. A course is considered completed in which all three injections were performed within 12 months.
Before administering the vaccine, doctors check the syringe. They shake the syringe or vial. Suspension should not contain foreign particles. One syringe is used, only once and only for one person. The location of the injection should be treated with alcohol, so as not to cause an infection.
Arguments For and Against
Some women think about whether they should get a shot against cervical cancer. They weigh the pros and cons of this procedure. Here are the main arguments for and against the cervical cancer vaccination to help in making a decision.
Vaccination is a good way to prevent a deadly disease. After the cervical cancer vaccination, dangerous side effects almost never develop. Protection from the virus is provided in the majority of cases.
The following cons can be identified:
- The vaccine does not protect the person against all types of papillomavirus infection
- Vaccination can not completely eliminate the risk cervical cancer (not only because it does not give protection against all infections, but also because cervical cancer can develop in some cases without HPV)
- Sometimes there are side effects
- Over time, immunity to HPV can weaken
Women who weigh the arguments for and against the vaccine cervical cancer vaccination often question its safety.
Possible side effects are:
- Swelling on the injection site
- Increased body temperature
- Headache
- Nausea
- Dizziness
According to research, 8% of cases of side effects require hospitalization. This happens in 0.003% of patients who received the vaccine. Is this a lot or a little? Severe side effects develop in approximately one in 30,000 patients.
However, the risks to which you are exposed without having cervical cancer vaccination are much higher:
- Risk of developing cervical cancer in a woman during her lifetime is about 3.5%. This risk is 1000 times higher than the probability of getting serious complications after the introduction of the vaccine
- Approximately 1.8% of all women die from cervical cancer
- On average, this cancer reduces the patient's life by 24 years
The side effect from cervical cancer vaccination in the form of a slight swelling at the injection site look much more preferable than the risk of a deadly disease.
Another argument against cervical cancer vaccination may be the price. Vaccination against cervical cancer costs differently in different countries. The types of vaccines differ. One dose on average costs 100-200 euros. However, the total price of vaccination against cervical cancer is even higher. After all, the body needs three doses for a full immunization.
Many residents of developing countries with low incomes refuse to receive vaccination after learning about the cost of vaccination against cervical cancer. However, we must understand that by abandoning this means of preventing HPV, we thereby refuse to have protection from a dangerous oncological disease. And even if we consider the issue solely from a financial point of view, the cost of a vaccine against cervical cancer is nothing compared to the costs that are spent on treating this disease. It costs tens of thousands of euros. Therefore, the price of a vaccine can not be a fully-fledged argument against getting the vaccination.
Contraindications to the cervical cancer vaccination
The vaccination has contraindications, as with any other procedure. They are divided into absolute and relative.
There is only one absolute contraindication - it is an individual intolerance. If the allergic reaction develops after the first dose, the person is provided with the necessary help. For this, the necessary preparations are available in the office where the vaccination is carried out. However, subsequent doses are not administered.
Relative contraindications to cervical cancer vaccination include disorders of blood clotting:
- Hemophilia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Reception of anticoagulants
In this case, you should consider the risks that the injection carries. If a decision is made in favor of vaccination, measures must be taken to prevent the formation of a hematoma at the site of the injection.
In case of severe infectious disease or a significant increase in body temperature, vaccination should be postponed until recovery. However, minor hyperthermia or non-dangerous infections do not require the cancellation of another vaccine administration.
Where can I get cervical cancer vaccination?
Find the location where vaccination against cervical cancer is carried out, it is not difficult. The vaccine can be administered at any private or public clinic.
The price of a cervical cancer vaccine is the same. However, you do not need to pay for the introduction of the vaccine in the state clinic. The vaccine itself may have to be bought at the pharmacy.
The cost of cervical cancer vaccination in a private clinic may be higher because you will need pay for the services of a specialist who injects the vaccine. You may need to pay for the examination before vaccination, but you do not have to buy the vaccine yourself. The procedure will be faster, more comfortable and more convenient for a girl and her parents, because the conditions in private clinics are better, and the queues are smaller.
The effectiveness of cervical cancer vaccination does not depend on where the vaccine is given because the same vaccines are used in all clinics. However, the choice of the drug depends on how much the vaccination will cost.
Usually one of two vaccines is used: Cervarix or Gardasil. The first one is cheaper. Gardasil is about 50% more expensive. However, this vaccine is better, because Cervarix protects only 18 and 16 types of HPV whereas Gardasil also prevents infection with papillomavirus 6 and 11 types. These are viruses with low oncogenic risk, but they are most common. These types of HPV cause the formation of genital warts.
Thus, the cost of vaccination depends more on the vaccine administered than on the clinic. When choosing a drug, you need to consider how much the vaccine costs and what types of papillomavirus it protects. The more types of virus the vaccine resists, the better you will be protected. Today, the most effective vaccine is Gardasil 9. It protects against 9 types of HPV. However, this vaccine is much more expensive, so in most countries the drug is not registered and is not applied.
Examination and Treatment in Germany
One of the measures to prevent cervical cancer is regular examination. You can have preventive diagnostics in Germany . This country has a much lower incidence of cervical cancer than in developing countries. One of the reasons for this phenomenon is the timely detection and treatment of precancerous diseases.
In Germany, it is also possible to undergo cervical cancer treatment if this disease has already been detected. Whatever the purpose of your visit to one of the clinics in Germany is, we are ready to help you by solving all organizational issues.
With Booking Health you get:
- The choice of the best clinic, whose doctors specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of cervical cancer.
- Saving up to 70% of the amount you would have spent while organizing a trip to Germany by yourself.
- Reduced waiting time for the examination and treatment.
- Insurance against unforeseen medical events.
- Full transparency of financial relationships and return of unused funds.
- Free consultations with the doctor within 3 months after the end of the course of treatment.
We also provide the following services: booking tickets, issuing a visa, working with medical records. We will provide an interpreter, meet you in Germany and take you to the clinic. Thanks to Booking Health you can fully concentrate on the treatment, delegating all organizational issues to us.
Choose treatment abroad and you will be sure to get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
National Center for Biotechnology
Read:
Treatment of stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany
Article menu:
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health