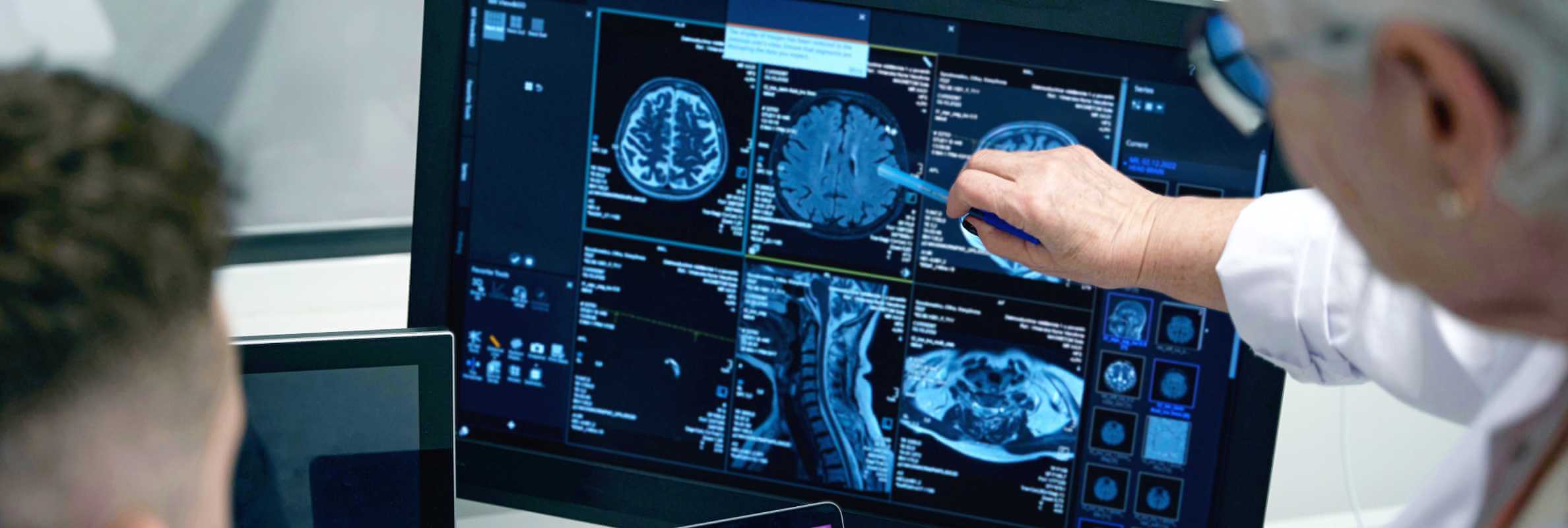
Brain cancer refers to a range of tumors originating in the brain. As the evidence suggests, the most aggressive and prevalent malignant form in adults is glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) [1]. In fact, recent data reports that this tumor accounts for ~14% of all primary brain tumors [2].
When taking a look at global statistics, the incidence of glioblastoma can vary: estimates range from 3.19 to 4.17 cases per 100,000 person-years [3, 4]. As for the median age at diagnosis, it is around 64 years; the disease is slightly more common in men than in women.
Unfortunately, we want to note that the prognosis for GBM is poor. The average survival time post-diagnosis is approximately 12 to 18 months. Only about 5% of patients survive beyond five years [5].
Nevertheless, despite these figures, personalized treatment plans and innovative technologies are offering hope for better outcomes and an improved quality of life. We would like to invite brain cancer patients and their families to read this article, so they can see that, with the right care and innovative approaches, they now have more options than ever before.
Standard Protocol-Based Treatments for Brain Cancer
Standard treatments for brain cancer can remove or destroy tumor cells while preserving neurological function. A combination of surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy is often used, customized to the individual patient's condition [6].
Surgical intervention is typically used as the first step in treating brain tumors, especially when the tumor is accessible and operable. Specifically, a craniotomy approach is used to remove a portion of the skull to access the brain and excise the tumor. As the evidence demonstrates, this treatment strategy can alleviate symptoms. Moreover, it can also improve the effectiveness of subsequent treatments. However, patients should understand that complete removal may not be feasible. Unfortunately, this can occur if the tumor is located near critical brain regions.
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams (e.g., X-rays or protons) to target and kill cancer cells. According to literature, the most common forms include external beam radiation and proton therapy. External beam radiation can be used post-surgery to eliminate any remaining cancer cells. However, it can also be implemented as a primary treatment, in cases when surgery is not an option. On the other hand, proton therapy can provide more accurate tumor targeting. In particular, it can be beneficial for treating tumors located near sensitive areas of the brain. In addition, this approach is associated with fewer side effects compared to traditional radiation therapy.
Chemotherapy uses certain medications that can destroy cancer cells. As many know, it can be combined with surgery and radiation therapy. The research notes that chemotherapy can be effective for brain cancer. However, patients should take into account that it may cause side effects (e.g., nausea, fatigue, and an increased susceptibility to infections).
Overall, we want our readers to understand that each of the brain cancer treatment options that we described above has its own advantages and limitations. Furthermore, the choice of therapy can depend on various factors (e.g., the type, size, location of the tumor, etc.) as well as the patient's overall health.
Innovative Brain Cancer Treatments
Dendritic Cell Therapy for Brain Cancer
Dendritic cell therapy is a new and advanced Nobel-prize winning brain cancer treatment. According to the research, this approach can utilize the body's own immune system to recognize and combat cancer cells [7]. Many may ask: how does this treatment work? In dendritic cell therapy, a patient's dendritic cells are harvested and exposed to tumor-specific antigens in a laboratory setting. Then, they are reintroduced into the patient's body, where they can stimulate T-cells to target and destroy the cancer cells.
Of course, we understand that brain cancer patients may wonder how effective this strategy is. We would like to share that patients receiving dendritic cell therapy in German brain cancer treatment centers have demonstrated a 60-70% increase in two-year survival rates compared to those receiving standard treatments. Moreover, ~30% of those patients managed to achieve complete remission. In addition, the evidence suggests that dendritic cell therapy is well tolerated and causes minimal side effects. Therefore, patients, when undergoing this treatment, can maintain their daily activities.
We would like to invite our readers to watch the video interview with Professor Frank Gansauge to help understand dendritic cell therapy better. He has over two decades of experience in this area. In the interview, he describes how dendritic cells can guide the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells. He also discusses how the combination of dendritic cell therapy with conventional treatments can enhance overall effectiveness and improve patient outcomes.
Professor Frank Gansauge on Dendritic Cell Therapy and Its Role in Cancer Treatment
Interventional Radiology for Brain Cancer
Interventional radiology can offer minimally invasive, targeted treatments for brain cancer. As literature reports, these treatments can deliver therapies directly to tumor sites while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Embolization can block blood flow to the tumor, effectively starving it of nutrients. According to studies, this technique can reduce tumor size and alleviate symptoms. In particular, in the treatment for brain cancer, embolization can be used to reduce vascular supply before surgical resection or to control bleeding in inoperable tumors. It can also help shrink highly vascular brain tumors. This can make them more manageable and less risky to treat with other modalities. For example, research shows that preoperative embolization has a technical success rate of 91-100%. In addition, it can reduce postsurgical complications in meningioma patients from 39.39% to 21.21%.
Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA) uses high-frequency electrical currents to generate heat, destroying cancer cells. In particular, it can be effective for tumors that are difficult to access surgically. As the evidence suggests, RFA may be considered for cases of advanced brain cancer treatment where conventional surgery cannot be applied due to tumor location. This approach can offer the targeted destruction of tumor tissue. At the same time, it can preserve the surrounding healthy brain structures. For example, a recent study demonstrated that stereotactic biopsy combined with RFA in patients with intra-axial brain tumors resulted in an estimated one-year survival rate of 86.6%.
Intra-Arterial Chemotherapy, as a new treatment for brain cancer, can deliver high concentrations of chemotherapy drugs directly to the tumor via the bloodstream. By doing so, this approach can enhance the treatment's efficacy while limiting systemic exposure. As suggested in studies, intra-arterial delivery can provide more targeted drug penetration across the blood-brain barrier (a major obstacle in systemic chemotherapy). In particular, this method can be beneficial for patients with tumors resistant to conventional chemotherapy. It can even improve outcomes for aggressive brain tumors (e.g., glioblastoma). For example, studies have shown that intra-arterial chemotherapy can extend the median overall survival in glioblastoma patients from 14.6 months to 25 months.
Prof. Kovács: How Electrochemotherapy Became the Gold Standard for Hard-to-Reach Brain Cancers
Thermal Ablation Techniques for Brain Cancer
Laser Interstitial Thermal Therapy (LITT) can employ laser energy to heat and destroy tumor tissue. According to the research, this approach can be valuable for patients with deep-seated or inoperable brain tumors (e.g., recurrent glioblastomas). Its minimally invasive nature allows for shorter hospital stays and quicker recovery. This makes it a viable alternative when open surgery is too risky. Moreover, LITT also causes minimal disruption to surrounding brain tissue. Therefore, it may be repeated if new tumor growth occurs. For example, studies indicate that LITT can help achieve a median overall survival of approximately 9.7 months in newly diagnosed glioblastoma patients and about 9.0 months in recurrent cases.
Cryoablation freezes cancer cells, causing cell death. It can be useful for treating tumors near sensitive structures because the freezing process can be controlled to avoid damage to healthy tissue. In brain oncology, cryoablation may be considered for metastatic brain lesions or recurrent tumors. As the available evidence shows, the visualization of the ice ball during the procedure can provide patients with a sense of safety and control. In addition, cryoablation can help reduce inflammation and edema around the tumor site, thereby potentially improving patient comfort. For example, clinical studies have demonstrated that cryoablation can be a safe and effective option for brain tumors; complication rates are comparable to standard brain tumor surgery.
Electrochemotherapy is one of the alternative brain cancer treatments that combines chemotherapy with electrical pulses. For brain tumors, as the research suggests, this approach can potentially improve drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier. In other words, it can help treat resistant or recurrent brain malignancies with lower systemic toxicity. In particular, the technique may be used to target localized tumor clusters that have not responded to systemic chemotherapy. For example, preclinical studies have demonstrated that electrochemotherapy can achieve complete tumor elimination in ~69% of treated cases.
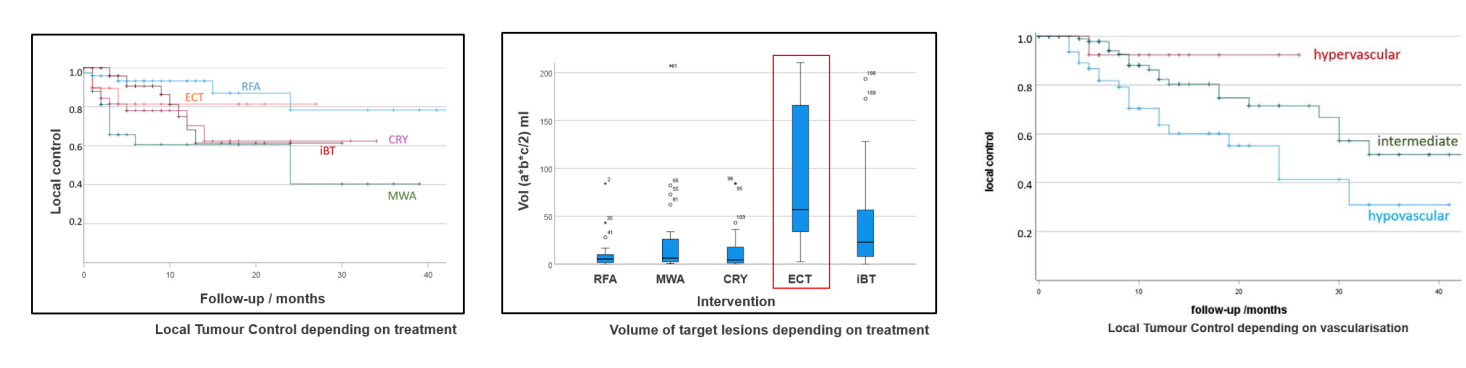
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) can deliver chemotherapy directly to the tumor's blood supply source, followed by embolization to trap the drug within the tumor. As a result, this approach can maximize tumor exposure to the drug. If we look at what the research data report, TACE is being explored for cases involving hypervascular brain tumors or metastatic lesions with a defined arterial supply. As suggested, this treatment strategy, by targeting the tumor locally, can help reduce tumor burden and control growth. Moreover, when combined with other treatments, it may enhance overall therapeutic effectiveness and extend progression-free survival.
Prof. Kovács: Why TACE Doubled Cancer Survival – What Patients Need to Know
Comparative Table: Brain Cancer Treatments
| Therapy Type | 2-Year Survival Rate | Response Rate | Duration | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatment | ~25% for advanced cancer | Less than 10% | Several cycles | Severe (nausea, fatigue, hair loss, immunosuppression, skin irritation) |
| Innovative Methods | ~60% for advanced cancer | 45-65% | Up to 4 sessions | Mild (localized discomfort) |
* Booking Health data
Medical Procedures Costs Around the World for Brain Cancer
| Treatment Method | GERMANY* | Great Britain | USA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatment | €80,000 - €150,000 full course | €90,000 - €165,000 full course | €100,000 - €180,000 full course |
| Innovative Methods | €25,000 - €60,000 full course | €70,000 - €120,000 full course | €100,000 - €150,000 full course |
* Prices may vary depending on the course of treatment and tumor characteristics
Success Stories of Brain Cancer Patients
Daria Rogers is a 50-year-old glioblastoma multiforme patient from Ireland. She traveled to Germany for advanced care after experiencing a seizure in January 2024. Her tumor was successfully removed with surgery. Yet, despite this, Daria's medical team informed her that standard treatments usually can offer only 12-15 months of life expectancy.
However, Daria and her husband Maurice refused to accept that outcome. They started to search for alternative options. Soon, they discovered dendritic cell immunotherapy. Daria and Maurice reached out to Booking Health to help them arrange the treatment just three weeks after her surgery.
"In Germany, glioblastoma treatment was surprisingly straightforward. They took my blood, provided supportive care, and created a personalized vaccine in the lab. I didn't experience any side effects, so it was all very comfortable."
After returning to Ireland, Daria began radiation therapy and chemotherapy. She believes that the immunotherapy helped her tolerate the standard treatments much better.
She said: "Despite undergoing radiation five times a week, I had plenty of energy and experienced very few side effects."
Her follow-up MRI and CT scans were even more encouraging. They were performed three months later and again in October 2024. They showed no signs of tumor recurrence.
Now, the Rogers family believes that dendritic cell therapy can potentially be life-changing for treating aggressive brain cancer cases. Daria urges other glioblastoma patients to not give up and search for new brain cancer treatments to ensure the best possible outcomes.
Daria Rogers: How Modern Brain Cancer Treatment in Germany Changed My Glioblastoma Prognosis
Treatment for Brain Cancer Advanced Stages and Individualized Approach
Receiving a diagnosis of advanced or metastatic brain cancer can feel overwhelming, often leaving patients and families with a sense of hopelessness. It is not uncommon to hear phrases such as "there’s little we can do," even from medical professionals. However, it is not the end of the road. In fact, it may be the beginning of a new path, one shaped by innovation, determination, and the possibility of better outcomes.
Medical science is advancing rapidly, and neurology is at the forefront of that progress. Brain cancer treatment is no exception. Although traditional methods such as surgery, radiation therapy, and chemotherapy have helped many patients, they are not always enough, especially in aggressive or recurrent cases such as glioblastoma, glioma, or brainstem tumors. These standard treatments often come with significant side effects that can impact daily life and limit quality of living. Worse still, tumors may become resistant over time, making these approaches less effective.
This is where innovative therapies offer new hope. Modern treatments, such as dendritic cell immunotherapy and interventional radiology methods, are now being used to treat brain cancer, including meningioma and metastasis to the brain, more precisely and with fewer side effects. These approaches do not require long hospital stays or constant medication. Often administered as outpatient procedures, they are designed to strengthen the body's own defenses while controlling tumor growth.
Immunotherapy, particularly dendritic cell therapy, is being used to treat both primary and metastatic brain tumors by helping the immune system recognize and attack cancer cells. Similarly, techniques such as TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization) and ECT (Electrochemotherapy) can slow tumor progression and reduce recurrence, even when other treatments have failed.
These advanced options can improve both survival and quality of life for those dealing with aggressive forms of cancer or requiring palliative care. They help patients reclaim a sense of control, which is critical when managing the challenges of a serious diagnosis.
If you or a loved one is seeking the best place for brain cancer treatment, do not settle for outdated approaches. Whether you are confronting a glioma, a brainstem lesion, or a meningioma, there are experts and doctors around the world who specialize in leading-edge, personalized treatments.
While these methods are not a guaranteed cure, they represent powerful tools in the fight against brain cancer. They can extend life, improve its quality, and bring hope to patients and families.
If you or someone close to you is facing a difficult diagnosis, remember this: there are more options than ever before. Stay hopeful, ask questions, and seek out the most advanced care available. It might change everything.
Leading Hospitals for Brain Cancer Treatment in Germany
Germany is considered one of the world leaders in neuro-oncology. Here patients have access not only to classical protocols – but also to innovative brain treatment methods (dendritic cell therapy and interventional radiology). That is why many patients choose this country as the best place for brain cancer treatment, because it combines high-tech interventions, experienced brain cancer treatment doctors and a multidisciplinary approach. German brain cancer treatment centers actively participate in international clinical trials – which allows the use of innovative treatment protocols in complex cases.
Best brain cancer treatment centers in Germany
| Hospital | City | Key Strengths |
|---|---|---|
| University Hospital Rechts der Isar | Munich | High-precision neurosurgery, intraoperative MRI, multidisciplinary approach, access to innovative treatment protocols |
| University Hospital of LMU Munich | Munich | Personalized neuro-oncology, molecular diagnostics, clinical trials, access to advanced treatment methods |
| Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch | Berlin | Stereotactic radiosurgery, high surgical volume, interdisciplinary team, participation in modern protocols |
| Schön Klinik Rendsburg | Rendsburg | Complex neurosurgery, postoperative rehabilitation, individualized care, access to advanced treatment approaches |
| Universitätsklinikum Regensburg | Regensburg | Precision neurosurgery and radiotherapy, involvement in clinical research, access to cutting-edge treatment protocols |
University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich
This university center in Munich is known for its high-precision neurosurgical interventions (using intraoperative MRI and awake surgery). Here patients can receive comprehensive treatment, that includes both standard and innovative methods. The high level of personalization and an experienced team make the clinic one of the best hospitals for brain cancer treatment in Southern Germany.
University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich
LMU Munich specializes in personalized neuro-oncology and molecular diagnostics of brain tumors. It actively uses innovative protocols (including LITT and cryoablation) which allow the safe treatment of deep or recurrent tumors. Each patient is accompanied by a personal brain cancer treatment doctor. Also clinic participates in international research – that is why, here, patients can receive the best brain cancer treatment in the world.
Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch
This high-tech center in Berlin is known for its large volume of neurosurgical interventions and precise radiotherapy methods. Helios Hospital actively uses interventional radiology (TACE and electrochemotherapy) for patients with inoperable or hypervascular tumors. The center also provides access to clinical trials which confirms its status among the top brain tumor centers in Germany.
Schön Klinik Rendsburg
Schön Klinik Rendsburg specializes in advanced neurosurgery and postoperative rehabilitation. Here patients can receive innovative methods (such as LITT and RFA) to treat complex or recurrent tumors with minimal impact on healthy tissue. An individual approach to each patient and attention to restoring function make the clinic one of the best hospitals for treatment of brain cancer.
Universitätsklinikum Regensburg
This center combines high-precision neurosurgery, precision radiotherapy and modern systemic treatment methods. Patients with glioblastomas or metastatic lesions can undergo comprehensive therapy here (dendritic cell therapy, electrochemotherapy and cryoablation). Active participation in international research allows the institution to remain the best hospital for brain cancer treatment – providing innovative and safe solutions even in the most complex cases.
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for brain cancer can be challenging, especially in advanced or complex cases. After undergoing multiple treatments, consulting various specialists, and navigating conflicting medical opinions, you may find yourself exhausted and unsure of the next step. In such moments, it is easy to settle for the first available option or to follow standard protocols that often come with harsh side effects and limited long-term benefits. However, for conditions as serious as brain tumors, especially aggressive types such as glioblastoma, a more individualized, innovative approach may offer improved outcomes.
To make a well-informed decision and receive a treatment plan tailored specifically to your diagnosis, it is essential to consult with professionals in advanced cancer care. For over 12 years, Booking Health has been at the forefront of coordinating access to innovative brain cancer treatments across the top medical centers in Germany and beyond. We specialize in creating highly personalized treatment programs for each patient, ensuring that every aspect of care, medical and logistical, is handled with professionalism and compassion.
With Booking Health, you gain access to:
- In-depth analysis of your medical history and imaging
- Development of a personalized care plan with innovative treatment options
- Selection of the most suitable clinic and specialist
- Preparation and submission of medical documents
- Pre-treatment consultations with world-class neurologists, neurosurgeons, and oncologists
- Ongoing support during your hospital stay
- Coordination of follow-up care in your home country
- Full assistance with travel, visas, and accommodation
- A dedicated interpreter and coordinator available 24/7
- Transparent pricing with no hidden fees
Your health is your most valuable asset, and entrusting your treatment journey to experienced professionals is one of the most important decisions you can make. Booking Health is a trusted partner in navigating this path, offering clarity, support, and access to the best brain cancer treatment in the world available today.
Contact our medical consultants to learn how we can help you begin a personalized, hope-driven approach to brain cancer treatment in Germany or any other country of your choice with some of the world's leading specialists.
Hope in Cancer Treatment: Patient Success with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions About Brain Cancer
Send request for treatmentSome low-grade brain tumors can be treated successfully and managed long-term. However, unfortunately, high-grade tumors (e.g., glioblastoma) are difficult to cure. Despite this, current brain cancer treatments can help patients extend their survival and improve their quality of life.
Symptoms of brain cancer can vary based on the tumor's size and location. Typically, patients experience persistent headaches, seizures, nausea or vomiting, vision problems, difficulty speaking or understanding language, personality or behavioral changes, memory loss, and issues with balance or coordination.
Diagnosis of brain cancer usually involves a neurological examination, followed by imaging tests (e.g., MRI or CT scans). A biopsy is also often required. It can confirm the diagnosis and determine the tumor's type and grade.
Not all brain tumors are cancerous. Some are benign and may grow slowly or not at all. However, even benign tumors can cause serious symptoms if they press on vital areas of the brain.
Brain cancer treatment options may include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy. These approaches can be combined with immunotherapy and interventional radiology methods (e.g., electrochemotherapy (ECT), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), and thermal ablation) to increase effectiveness.
Radiation therapy for brain tumors uses high-energy beams to destroy or damage cancer cells. This approach can reduce harm to surrounding healthy brain tissue and improve treatment outcomes.
Side effects of brain cancer treatments can depend on the type and duration of treatment. These may include fatigue, nausea, vomiting, hair loss, cognitive changes, mood swings, headaches, and memory problems.
Recovery after brain surgery can vary based on the complexity of the surgery and the patient's overall health. Usually, hospital stays range from 3 to 10 days; full recovery at home can take 6 to 12 weeks.
Alternatives to brain cancer surgery include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and interventional radiology techniques (e.g., TACE, laser therapy, and ECT). These options can be used when surgery cannot be performed due to tumor location or patient condition.
Targeted therapy for brain cancer uses medications designed to block specific molecules involved in cancer cell growth and survival. When compared to traditional chemotherapy, this approach can provide treatment with fewer side effects.
Immunotherapy can be used for brain cancer treatment. This approach can help the body's immune system recognize and fight the disease, especially in patients with brain tumors that are resistant to standard treatments.
Surgery is often the first and most effective step in treating brain tumors. This approach can help reduce tumor mass and relieve pressure on the brain. It can also improve the efficacy of additional therapies (e.g., radiation or chemotherapy).
Several new treatments are available at the best hospitals for brain cancer treatment. These include advanced immunotherapies and next-generation targeted drugs, as well as minimally invasive interventional procedures. These strategies can offer hope for patients with both primary and recurrent brain tumors.
In brain cancer, especially glioblastoma, the 2-year survival rate is around 25% with standard treatments. On the other hand, innovative methods (e.g., dendritic cell therapy and interventional radiology techniques) can increase survival to up to 60%.
Standard brain cancer therapy typically requires several treatment cycles over months. In turn, innovative options (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, TACE, ablation, etc.) can be completed in up to four sessions.
The response rate for conventional brain cancer treatments is usually below 10%. In contrast, innovative approaches can show 45-65% response rates.
Standard brain cancer therapies can often lead to severe side effects such as nausea, fatigue, and immune suppression. However, innovative brain cancer treatments generally cause only mild, localized discomfort.
Patients with brain tumors often face risks of neurological damage. Interventional radiology allows precise removal or reduction of tumor tissue (with minimal impact on surrounding brain structures); dendritic cell therapy strengthens the immune system to recognize tumor cells. These methods provide a personalized approach.
The best hospitals focus on patient experience during complex brain procedures. In Germany specialized centers guide patients step by step ㄧ from imaging and minimally invasive interventions to immune therapy ㄧ ensuring coordination between radiologists, neurosurgeons and oncologists.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Ashkan Pouyan, Masoud Ghorbanlo, Masoud Eslami et al. Glioblastoma multiforme: insights into pathogenesis, key signaling pathways, and therapeutic strategies. Mol Cancer. 2025 Feb 26;24(1):58. doi: 10.1186/s12943-025-02267-0. [DOI]
[2] Szymon Grochans, Anna Maria Cybulska, Donata Simińska et al. Epidemiology of Glioblastoma Multiforme–Literature Review. Cancers (Basel). 2022 May 13;14(10):2412. doi: 10.3390/cancers14102412. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[3] Marcin Jezierzański, Natalia Nafalska, Małgorzata Stopyra et al. TMZ in the Treatment of Glioblastoma Multiforme—A Literature Review and Clinical Outcomes. Curr Oncol. 2024 Jul 12;31(7):3994-4002. doi: 10.3390/curroncol31070296. [DOI]
[4] National Foundation for Cancer Research. WHAT IS GBM. https://www.nfcr.org/gbm-agile-what-is-gbm/
[5] The Brain Tumor Charity. Glioblastoma prognosis. https://www.thebraintumourcharity.org/brain-tumour-diagnosis-treatment/types-of-brain-tumour-adult/glioblastoma/glioblastoma-prognosis/
[6] Medscape. Glioblastoma Treatment & Management. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/283252-treatment?form=fpf
[7] Roman Volchenkov, Florian Sprater, Petra Vogelsang, Silke Appel. The 2011 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine. Scand J Immunol. 2012 Jan;75(1):1-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02663.x. [DOI] [PubMed]
Read:
Innovative Treatment for Glioblastoma in Germany: Dendritic Cell Therapy for Cancer
Article menu:
- Standard Protocol-Based Treatments for Brain Cancer
- Innovative Brain Cancer Treatments
- Interventional Radiology for Brain Cancer
- Comparative Table: Brain Cancer Treatments
- Success Stories of Brain Cancer Patients
- Treatment for Brain Cancer Advanced Stages and Individualized Approach
- Leading Hospitals for Brain Cancer Treatment in Germany
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
- Frequently Asked Questions About Brain Cancer
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health