Globally, brain and central nervous system (CNS) cancers are a significant health burden. In 2022, there were approximately 321,600 new cases and 248,400 deaths from brain and CNS cancers worldwide – a mortality-to-incidence ratio nearing 78% in adults ≥15 years old [1]. Meanwhile, research shows that global deaths from these cancers rose from approximately 136,200 to 258,600, driven largely by population growth and aging [2].
Even benign tumors, such as meningiomas, pose severe risks – not due to spread, but because they can compress vital brain centers, leading to neurological dysfunction or life-threatening complications [3]. That is why prompt detection and timely brain tumor diagnosis are essential to preventing irreversible damage to brain tissue and preserving function.
Germany, with its advanced medical infrastructure and high-precision diagnostics, is leading the way in brain cancer care. In this country, patients gain access to advanced imaging, personalized treatment planning, and innovative therapies – making early intervention more accessible and effective than ever.
Symptoms of Brain Tumor at Early Stages
Early symptoms of brain tumor are often subtle or even absent, which makes detection difficult. In the beginning, many patients do not experience any noticeable problems. Doctors typically divide all signs and symptoms into two groups: cerebral symptoms and focal symptoms.
- Cerebral symptoms occur because the tumor increases pressure inside the skull, blocks the flow of cerebrospinal fluid, or causes swelling of brain tissue. These symptoms are general and can resemble other conditions such as migraines or high blood pressure.
- Focal symptoms are linked to the tumor's location in the brain. Each area controls specific functions such as speech, movement, or vision. When a brain tumor develops in one of these regions, patients may notice very specific neurological changes.
Because the brain itself has no pain receptors, early complaints are often missing. Common signs usually appear only when the tumor grows large enough to press on surrounding structures. This delay is one of the main reasons why diagnosis is often made at a later stage [3].
Headaches and Seizures: First Alarming Signs of Brain Tumors
Among the earliest and most distressing brain tumor symptoms are headaches and seizures. While headaches are extremely common in the general population, those caused by brain cancer or a primary brain tumor often have distinctive patterns that make them different from ordinary tension headaches or migraines [3, 4].
What Brain Tumor Headaches Feel Like
Doctors describe three main types of brain tumor headaches.
Hypertension-type headaches:
- Caused by increased intracranial pressure
- Patients often describe a "bursting" or "pressing from the inside" sensation
- Typically worse in the morning, sometimes accompanied by nausea or vomiting
Hydrocephalic headaches:
- Result from the excess accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid inside the brain's ventricles
- Pain may improve or worsen depending on head position
- At first episodic, later becoming persistent
Vascular headaches:
- Triggered by compression or spasm of blood vessels
- Often pulsating and localized, sometimes resembling migraine attacks
The American Brain Tumor Association [3] shows that about 50-60% of patients with brain tumors report chronic headaches as an initial complaint.

Seizures: Another Key Warning Sign of Brain Tumor
Brain tumor seizures are another major red flag. They happen when abnormal electrical activity spreads from compressed or damaged brain cells. Seizures may:
- Start as twitching or numbness in one limb (focal seizure)
- Progress to generalized convulsions
- Be the very first sign that leads to tumor detection [4]
Pituitary Gland Brain Tumors and Endocrine Symptoms
When a tumor develops in the pituitary gland, headaches often combine with hormonal disturbances. Patients may experience:
- Irregular menstrual cycles or infertility
- Unexplained weight changes
- Vision problems due to pressure on the optic nerves [5]
It is important to recognize these patterns in brain tumor symptoms, as this can help patients and doctors distinguish them from more benign conditions, leading to faster diagnosis and treatment.
Focal Symptoms by Brain Tumor Location
Unlike general cerebral symptoms, focal symptoms of a brain tumor depend directly on the tumor's location in the brain. Because different brain regions control different body functions, the first noticeable complaints often point to where the tumor is growing. As previously noted, even a benign tumor can press on brain cells, disrupt neural pathways, and damage otherwise healthy cells, leading to severe deficits [3-5].
| Brain Region (Tumor's Location) | Focal Symptoms |
|---|---|
| Central gyrus | Paralysis or weakness (paresis) in limbs; speech disorder (motor aphasia). |
| Frontal lobe | Seizures, loss of smell, mood and behavior changes, reduced motivation, or aggression. |
| Parietal lobe | Sensory loss, inability to recognize objects by touch (astereognosis), apraxia (cannot perform purposeful actions), difficulty with reading/writing, and amnestic aphasia. |
| Temporal lobe | Hallucinations (auditory, visual, or taste-related), tinnitus, partial blindness, and focal seizures. |
| Occipital lobe | Visual disturbances: flashing lights, shapes, a narrowed visual field, or complete blindness. |
| Corpus callosum | Memory and intelligence decline, difficulty coordinating the actions of both body halves. |
| Subcortical structures | Involuntary movements, muscle tone changes, paresis, headaches, vegetative (autonomic) disturbances. |
| Brain ventricles | Hydrocephalus (fluid buildup), endocrine disorders (e.g., weight changes, hormonal imbalance). |
| Chiasmosellar region | Pituitary adenomas → infertility, irregular cycles, erectile dysfunction, vision loss from optic nerve compression. |
| Pineal gland | Difficulty looking upward, impaired pupillary light reflex, hydrocephalic crises with sudden headache and vomiting. |
| Posterior cranial fossa/brainstem | Ataxia (poor coordination), nystagmus (rapid eye movement), balance problems, cranial nerve dysfunction, heart and breathing disturbances. |
Central Gyrus. The central gyrus governs voluntary movements and sensory input. Tumors here can cause spastic paralysis or paresis (muscle weakness), depending on which area is affected – legs, arms, or face. If the anterior section is damaged, motor control is lost; posterior involvement leads to sensory changes. Patients may also develop motor aphasia, a speech disorder caused by impaired coordination of muscles used in speaking.
Frontal Lobe. Frontal lobe tumors often present with seizures. As they grow, they can alter personality, decision-making, and emotional control. Family members may notice apathy, irritability, or aggression. Loss of smell is another common brain tumor sign.
Parietal Lobe. The parietal lobe is responsible for body awareness and higher cognitive functions. Patients may lose the ability to recognize familiar objects by touch (astereognosis), struggle with reading or arithmetic, or experience amnestic aphasia – recognizing an object but forgetting its name.
Temporal Lobe. Temporal lobe tumors frequently cause hallucinations (hearing voices, seeing shapes, or unusual tastes/smells). Patients may report tinnitus or partial blindness. These tumors also trigger localized seizures that can spread, producing generalized convulsions.
Occipital Lobe. Because the occipital lobe controls vision, tumors here produce distinctive brain tumor symptoms: flashing lights, colored spots, narrowing of visual fields, or even blindness in one or both eyes.
Corpus Callosum. The corpus callosum connects the brain's two hemispheres. Tumors here interfere with coordination between the body's left and right sides. Patients may also show progressive memory loss and reduced problem-solving ability.
Subcortical Structures. In the subcortical structures, tumors disrupt motor regulation, leading to involuntary movements, paresis, and abnormal muscle tone. Patients may complain of persistent headaches or vegetative disturbances (heart rate and blood pressure instability).
Brain Ventricles. Tumors of the ventricles often block cerebrospinal fluid flow, causing hydrocephalus. Patients may adopt a "forced head position" to ease pressure. Hormonal or metabolic changes – such as weight loss, obesity, or diabetes insipidus – can also occur.
Chiasmosellar Region. The chiasmosellar region includes the pituitary gland and optic nerve structures. Here, tumors like adenomas can cause infertility, erectile dysfunction, irregular menstrual cycles, or vision loss due to optic nerve compression.
Pineal Gland. Tumors in the pineal gland may lead to difficulty moving the eyes upward (Parinaud's syndrome) and loss of normal pupillary reflexes. Episodes of sudden increased intracranial pressure, called hydrocephalic crises, can bring intense headaches and vomiting.
Posterior Cranial Fossa/Brainstem. Tumors in the posterior fossa often cause early intracranial hypertension and ataxia (poor balance and coordination). Involvement of the brainstem is particularly dangerous: it can disturb breathing, heart rate, and consciousness – sometimes resulting in life-threatening outcomes.
Key Takeaway
Understanding these focal symptoms of a brain tumor helps clinicians suspect the exact tumor's location and guide further imaging and biopsy. Patients noticing unusual neurological changes – especially seizures, vision loss, or unexplained weakness – should seek immediate evaluation.
Secondary Brain Tumor Symptoms
In addition to the early and focal complaints, many patients later develop secondary brain tumor symptoms. These occur when a tumor grows large, blocks the circulation of blood or cerebrospinal fluid, or displaces surrounding brain tissue. Such complications are particularly dangerous in metastatic brain tumors, when cancer spreads from another organ (for example, lung or breast cancer) into the brain [3, 6].
Main Secondary Brain Tumor Symptoms
Impaired cerebral circulation:
- Large tumors or fast-growing cancerous brain tumors may compress blood vessels
- This can reduce oxygen supply to brain tissue, causing dizziness, memory problems, mood swings, or even fainting
- Severe disruption may result in stroke-like episodes
Brain edema:
- Tumor growth increases fluid in and around the brain, leading to swelling
- Symptoms may include headaches, nausea, blurred vision, and confusion
- Edema further compresses brain cells and worsens neurological deficits
Intracranial hypertension:
- Rising pressure inside the skull causes strong headaches, especially in the morning
- Patients may also notice double vision, reduced eye movement, or loss of vision
- If untreated, it can progress to loss of consciousness or coma
Dislocation and wedging of the brain:
- In advanced stages, the growing mass can physically push brain structures out of their normal position
- This "brain herniation" often leads to stiff neck, impaired breathing, abnormal heart rhythm, and rapid deterioration
- Without emergency treatment, this condition is often fatal
It is important to note that, while many secondary brain tumor symptoms may seem similar to those of migraines or high blood pressure, their progressive nature makes them especially dangerous. This is why it is critical to recognize them early – particularly in patients with metastatic brain tumors, where cancer spreads aggressively.
Diagnosis of Brain Tumors in Germany
Accurate and timely brain tumor diagnosis is essential for choosing the right treatment strategy. As discussed earlier, many symptoms caused by tumors – such as headaches or dizziness – can mimic other conditions. Therefore, high-precision imaging and biopsy are required to confirm the presence of abnormal growths in brain tissue [7, 8].
German hospitals are internationally recognized for their advanced diagnostic strategies and experienced specialists in neuro-oncology. From imaging to molecular tests, doctors can identify the exact tumor type, evaluate how deeply it infiltrates brain tissue, and confirm whether abnormal growths are cancer cells or benign tumors. This detailed workup ensures that each patient receives the most effective treatment plan from the very beginning.
| Diagnostic Method | Purpose | Typical Use |
|---|---|---|
| MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) | Produces detailed images of brain structures and soft tissues | First-line tool to detect tumors, assess size, and define relationship to healthy brain tissue |
| CT (Computed Tomography) | Provides cross-sectional images of the brain | Used in emergency cases (bleeding, swelling) or when an MRI is not possible |
| PET-CT (Positron Emission Tomography with CT) | Shows the metabolic activity of cancer cells | Differentiates between aggressive vs. slow-growing tumors, detects recurrence |
| Stereotactic biopsy | Extracts a small sample of tumor tissue for lab analysis | Confirms tumor type and guides treatment decisions |
| Functional MRI/Neuro-navigation | Maps active brain areas (speech, motor functions) | Helps surgeons plan safer operations, sparing vital functions |
Modern Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
Thanks to medical advances, patients today have access to a wide range of brain tumor treatment options. Therapy is selected individually, depending on whether the tumor is benign or malignant, its size, and its exact location. In German hospitals, treatment usually involves a multimodal treatment plan, meaning several methods are combined for the best outcome.
Surgery for Brain Tumors
Surgical removal remains the main method of treatment for many primary brain tumors. Whenever possible, neurosurgeons aim to remove the tumor completely, as this provides the best chance for long-term control and, in some cases, cure. The procedure is typically the first step in a broader treatment strategy, since reducing the tumor mass can make subsequent therapies – such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy – more effective [8].
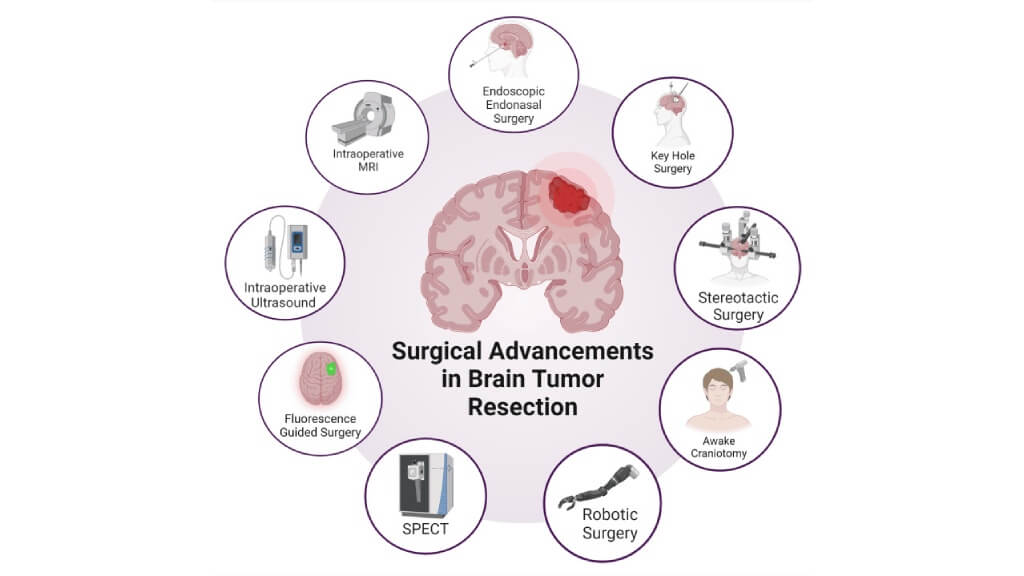
Modern neurosurgery in Germany employs advanced technologies, including neuronavigation systems, intraoperative MRI, awake craniotomy techniques (to preserve speech and motor functions), and fluorescence-guided surgery, which helps distinguish tumor tissue from normal brain cells during the operation. These innovations allow surgeons to maximize tumor removal while sparing as many healthy cells as possible.
- Goal: Maximal tumor removal, relieve pressure on the brain, and improve neurological function.
- Benefits: Can rapidly reduce symptoms such as headaches, seizures, or weakness caused by compression of surrounding brain tissue. Surgery also provides a tissue sample for pathology, which is essential for confirming the tumor type and guiding a personalized treatment plan.
- Limitations: Not always possible if the tumor is located deep within the brain or close to vital centers that control breathing, vision, or movement. In such cases, partial resection or minimally invasive approaches may be performed instead.
Studies show that patients who undergo maximal safe resection often experience better quality of life and longer progression-free survival compared to those treated with biopsy or partial removal alone [8].
Radiation Therapy for Brain Tumors
Radiation therapy is one of the most commonly used methods in brain tumor treatment, either as an additional step after surgery to kill remaining cancer cells or as a primary therapy when surgery is not feasible. Its goal is to stop tumor growth, shrink the tumor, and prevent recurrence, while preserving as much healthy brain tissue as possible.
- Goal: Eliminate remaining cancer cells, stabilize or shrink tumors.
- Benefits: Non-invasive, effective even for tumors not suitable for surgery, precise targeting reduces side effects.
- Limitations: May cause temporary fatigue, skin irritation, or cognitive changes; multiple sessions may be required.
In German hospitals, several advanced techniques are available:
- External beam therapy: The standard method, using high-energy X-rays directed at the tumor site.
- Stereotactic radiosurgery (Gamma Knife, CyberKnife): Delivers high-dose radiation precisely to small or hard-to-reach tumors in a single or few sessions. It is often used for benign tumors such as meningiomas, pituitary adenomas, or acoustic neuromas.
- Proton therapy: Uses charged particles that release their energy directly at the tumor site (Bragg peak effect), minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy cells. This makes it especially valuable for pediatric cases and tumors near critical brain structures.
Research shows that stereotactic radiosurgery achieves local control rates of 80-90% for small benign tumors, with very low complication rates [9]. Proton therapy, meanwhile, has demonstrated up to 70% progression-free survival at 5 years in certain low-grade gliomas and other brain tumors [10].
Chemotherapy for Brain Tumors
Chemotherapy remains an important part of brain tumor treatment, especially for aggressive cancers such as glioblastoma. Unlike surgery or radiation, which target specific areas, chemotherapy works throughout the body to attack rapidly dividing cancer cells, including those that may have spread beyond the primary tumor. However, because it can also affect some healthy dividing cells (like those in the digestive tract or bone marrow), side effects are common.
- Goal: Destroy or slow the growth of tumor cells and prevent recurrence.
- Benefits: Effective against aggressive or metastatic forms of brain cancer; can reach tumor cells not removed surgically.
- Limitations: Side effects such as nausea, fatigue, low immunity, and hair loss; limited ability to cross the blood–brain barrier in some cases.
Chemotherapy can be administered in several ways:
- Orally (capsules or tablets, often taken at home).
- Intravenously (IV infusions), delivered directly into the bloodstream.
- Intrathecally, where drugs are introduced into the cerebrospinal fluid for better penetration into the brain.
It is necessary to mention that, when combined with surgery and radiation therapy, chemotherapy significantly improves survival rates and quality of life for many patients. For example, a study published in the New England Journal of Medicine showed that combining chemotherapy drugs with radiotherapy in glioblastoma patients extended median survival from 12 months with radiotherapy alone to 14.6 months [11].
Targeted Therapy for Brain Tumors
Targeted therapy represents a newer generation of brain tumor treatment, designed to act on specific molecules that help cancer cells grow and survive. Unlike traditional chemotherapy, which affects all rapidly dividing cells, targeted drugs selectively interfere with genetic mutations or signaling pathways present in the tumor. This precision means they usually cause fewer side effects and preserve more healthy cells.
- Goal: Block molecular drivers of tumor growth.
- Benefits: More precise, fewer side effects compared to chemotherapy, and protects surrounding brain tissue.
- Limitations: Only effective if the tumor carries the right mutations; resistance may develop over time.
Targeted therapy is often combined with other treatments in a personalized treatment plan, giving patients access to options tailored to their tumor's biology.
Examples of targeted therapies for brain cancer include:
- Anti-angiogenics: Block blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), essentially "starving" the tumor of oxygen and nutrients.
- EGFR inhibitors: Used for tumors with mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor gene.
- VEGF inhibitors: Disrupt tumor blood supply and growth.
Clinical studies have shown that anti-angiogenics can reduce swelling and improve quality of life in recurrent glioblastoma, with many patients experiencing symptom relief and slowed disease progression [12].
Immunotherapy: Dendritic Cell Therapy for Brain Tumors
Immunotherapy utilizes the body's own immune system to recognize and fight tumors. One of the most promising methods in brain cancer care is dendritic cell therapy, based on Nobel Prize-winning research by Ralph Steinman, who discovered dendritic cells and their critical role in immune defense.
In this approach, dendritic cells are collected from a patient's blood, "trained" in the laboratory to recognize tumor antigens, and then reintroduced into the patient's body. Once activated, they help direct the immune system to attack cancer cells more effectively.
- Goal: Stimulate the immune system to attack tumor cells.
- Benefits: Personalized, can help treat cancer resistant to conventional therapies, and has potential long-term immune memory.
- Limitations: Still under research, available only at specialized centers.
While not yet a universal standard, immunotherapy – including dendritic cell vaccines – represents one of the most exciting innovations in brain tumor treatment, offering hope for patients with few other options. For example, a 2022 study reported that patients with glioblastoma who received dendritic cell vaccines experienced an average overall survival increase of 3-8 months compared with standard therapy alone [13].
Costs of Brain Tumor Treatment in Germany
The cost of brain tumor treatment in Germany varies depending on the method, tumor type, and patient's condition. Compared with many other countries, such as the US or the UK, German hospitals are known for transparent pricing and the use of advanced equipment, making high-quality care more accessible.
| Treatment Method | Germany | UK | USA | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | €25,000-€45,000 | €35,000-€55,000 | €65,000-€85,000 | Standard approach for removing a primary brain tumor. |
| Radiation therapy | €28,000-€42,000 | €35,000-€65,000 | €40,000-€80,000 | Includes external beam therapy, used after surgery or as a stand-alone. |
| Chemotherapy | €80,000-€150,000 (full course) | €90,000-€165,000 (full course) | €100,000-€180,000 (full course) | Systemic treatment, often combined with radiotherapy in aggressive brain cancer. |
| Targeted therapy | €375,000-€420,000 (full course) | €400,000-€500,000 (full course) | €600,000-€1,000,000 (full course) | Precision medicine that blocks tumor growth pathways, protects healthy cells. |
| Dendritic cell therapy | €20,000-€38,000 | Not available | €100,000-€150,000 | Personalized immunotherapy, activates the immune system to attack cancer cells. |
Why Choose Germany for Brain Tumor Treatment?
Germany is one of the world's leading destinations for brain tumor treatment. Patients choose the country not only for its strict medical standards but also for access to highly specialized hospitals that combine advanced technology, innovative methods, and expert neurosurgeons. Survival rates for brain cancer are higher than in many other countries because German hospitals use multimodal approaches – surgery, advanced radiation therapy, chemotherapy, targeted therapy, and immunotherapy – tailored to each patient's needs.
Some of the world-famous hospitals offering advanced neuro-oncological care include:
- University Hospital Freiburg – Expertise in complex neurosurgery and minimally invasive interventions
- University Hospital Tübingen – Strong neuro-oncology programs and advanced imaging for accurate brain tumor diagnosis
- University Hospital Erlangen – Active in clinical research and innovative therapies, including immunotherapy
- University Hospital Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE) – Known for its multidisciplinary tumor boards and participation in international trials
- LMU Klinikum Munich – Offers specialized treatment plans, including proton therapy and advanced surgical techniques
A major benefit of receiving treatment in Germany is access to innovative therapies such as proton beam therapy and dendritic cell vaccines. Many hospitals also participate in international clinical trials, providing patients with innovative options that go beyond conventional therapy.
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
Finding the best strategy for brain tumor treatment can be overwhelming. Patients often face conflicting advice, multiple consultations, and a long list of therapies – each with different side effects and success rates. In such a situation, it is easy to feel lost and simply follow the first option presented, rather than receiving a truly personalized treatment plan.
This is where Booking Health makes the difference. For more than 12 years, the company has been guiding international patients through their healthcare journey in Germany and worldwide. Our mission is to ensure that every individual with brain cancer has access to the most advanced methods of care, while avoiding unnecessary expenses and delays.
When you choose Booking Health, you receive:
- Expert coordination of diagnostics and therapy from start to finish.
- A personalized treatment plan, developed with leading German specialists.
- Assistance with all organizational matters: medical reports, documentation, visa arrangements, and transfers.
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs, saving patients up to 70% compared to booking directly.
- A personal interpreter and coordinator available 24/7 during your hospital stay.
- Post-treatment follow-up care once you return home.
Germany is known for its innovation in neurosurgery, radiation therapy, proton therapy, immunotherapy, and advanced supportive care. With Booking Health, you not only gain access to these technologies but also the reassurance that you are being guided by experts with a proven track record of success in helping patients treat cancer effectively and safely.
Health is the most valuable resource we have. Entrusting it to professionals with global experience ensures peace of mind and the best possible outcomes.
Contact Booking Health today to explore your options for advanced brain tumor treatment in Germany and take the first step toward recovery.
International Cancer Care: Patient Stories with Booking Health
Frequently asked Questions of Our Patients About Brain tumor symptoms
Send request for treatmentThe most frequent brain tumor symptoms in the early stages include persistent headaches, unexplained seizures, and subtle cognitive changes such as memory problems or difficulty concentrating. These signs and symptoms are often mistaken for less serious conditions, which is why medical evaluation is so important.
The complaints depend heavily on the tumor's location. For example, focal symptoms of a brain tumor in the frontal lobe may involve mood or behavior changes, while parietal lobe tumors affect sensation and coordination. Temporal lobe growths can trigger hallucinations, and occipital lobe tumors often cause vision problems.
Yes. Both brain tumor seizures and brain tumor headaches are among the most common warning signs. Headaches related to tumors are often stronger in the morning and may worsen with coughing or bending. Seizures may begin locally – such as twitching in one limb – and sometimes progress to full convulsions.
When tumors grow larger, patients may develop secondary brain tumor symptoms such as brain swelling (edema), rising intracranial pressure, and displacement (herniation) of brain structures. These conditions are medical emergencies that require urgent treatment.
Yes. Tumors in the temporal lobe can affect hearing, while those in the occipital lobe often impact vision. Patients may experience ringing in the ears, partial blindness, or flashing lights. These brain tumor signs should always be checked by a neurologist.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Journal of Neuro-Oncology. Global burden of brain and central nervous system cancer in 185 countries, and projections up to 2050: a population-based systematic analysis of GLOBOCAN 2022. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s11060-025-05164-0
[2] Scientific Reports. 2025;15:19228. The global, regional, and national brain and CNS cancers burden and trends from 1990 to 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-04636-7
[3] American Brain Tumor Association. Signs & Symptoms. https://www.abta.org/about-brain-tumors/brain-tumor-diagnosis/brain-tumor-signs-symptoms/
[4] Cyrille D Dantio, Deborah Oluwatosin Fasoranti, Chubei Teng, Xuejun Li. Seizures in brain tumors: pathogenesis, risk factors and management (Review). Int J Mol Med. 2025 Mar 21;55(5):82. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2025.5523. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[5] American Cancer Society. Signs and Symptoms of Pituitary Tumors. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/pituitary-tumors/detection-diagnosis-staging/signs-and-symptoms.html
See more
[6] Cancer Research UK. What Is Secondary Brain Cancer? https://www.cancerresearchuk.org/about-cancer/secondary-cancer/secondary-brain-cancer/about
[7] Yihan Yang, Mike Z He, Tao Li, Xuejun Yang. MRI combined with PET-CT of different tracers to improve the accuracy of glioma diagnosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurosurg Rev. 2017 Sep 16;42(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/s10143-017-0906-0. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[8] Nidhi H Vadhavekar, Tara Sabzvari, Simone Laguardia et al. Advancements in Imaging and Neurosurgical Techniques for Brain Tumor Resection: A Comprehensive Review. Cureus. 2024 Oct 31;16(10):e72745. doi: 10.7759/cureus.72745. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[9] Radiation Oncology. 2011;6:48. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases: analysis of outcome and risk of brain radionecrosis. https://ro-journal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1748-717X-6-48
[10] Erik Thurin, Petra W Nyström, Anja Smits et al. Proton therapy for low-grade gliomas in adults: A systematic review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2018 Nov:174:233-238. doi: 10.1016/j.clineuro.2018.08.003. [DOI] [PubMed]
[11] New England Journal of Medicine. 2005;352(10):987-996. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. https://www.nejm.org/doi/full/10.1056/NEJMoa043330
[12] Seema Nagpal, Griffith Harsh, Lawrence Recht. Bevacizumab Improves Quality of Life in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Chemother Res Pract. 2011 Oct 2;2011:602812. doi: 10.1155/2011/602812. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[13] Linda M Liau, Keyoumars Ashkan, Steven Brem et al. Association of Autologous Tumor Lysate-Loaded Dendritic Cell Vaccination With Extension of Survival Among Patients With Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Glioblastoma. JAMA Oncol. 2022 Nov 17;9(1):112–121. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2022.5370. [DOI] [PMC free article]
Read:
Brain cancer treatments in Germany
Article menu:
- Symptoms of Brain Tumor at Early Stages
- Headaches and Seizures: First Alarming Signs of Brain Tumors
- Focal Symptoms by Brain Tumor Location
- Secondary Brain Tumor Symptoms
- Diagnosis of Brain Tumors in Germany
- Modern Treatment Options for Brain Tumors
- Costs of Brain Tumor Treatment in Germany
- Why Choose Germany for Brain Tumor Treatment?
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
- Frequently asked Questions of Our Patients About Brain tumor symptoms
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health