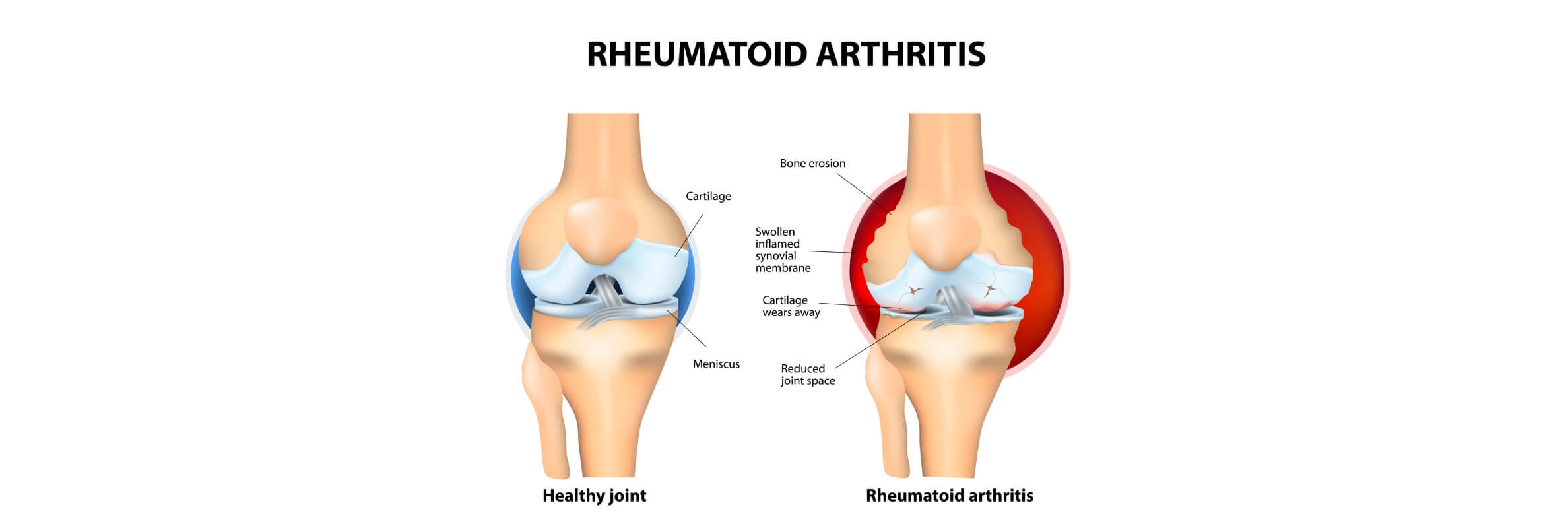
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic, systemic autoimmune disease that primarily targets synovial joints, leading to inflammation, swelling, pain, and eventual joint deformity if left untreated. It affects about 0.5% to 1% of the global population, with women being two to three times more likely to develop the disease than men [1]. The onset of rheumatoid arthritis commonly occurs between the ages of 40 and 60, and its impact goes beyond joints – it can also affect the cardiovascular, respiratory, and nervous systems, significantly impairing quality of life. [1, 2]
Conventional treatment of rheumatoid arthritis focuses on managing symptoms and slowing disease progression. Specifically, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and corticosteroids help relieve pain and inflammation. In turn, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) are used to delay joint damage [2, 3]. Biologic agents, such as TNF-α inhibitors, IL-6 receptor blockers, and JAK inhibitors, have further enhanced care by targeting specific components of the immune system [4]. However, not all patients with rheumatoid arthritis respond adequately to these therapies. Moreover, long-term use may lead to adverse effects and resistance.
Due to these limitations, researchers have been exploring innovative approaches that could offer more precise immune regulation with fewer side effects. One of the most promising approaches used in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) therapy involves the use of dendritic cells. Through genetic modification and antigen reprogramming, dendritic cells may restore immune balance, reduce inflammation, and prevent the immune system from attacking the body's own tissues. This form of therapy has the potential to transform RA management and offer hope to those living with this debilitating condition.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Chronic Autoimmune Condition
As noted above, rheumatoid arthritis is a disease that primarily affects the joints but can also impact other organs and tissues throughout the body. Unlike osteoarthritis, which is caused by mechanical wear and tear, rheumatoid arthritis results from an abnormal immune response, where the body mistakenly attacks its own healthy cells – particularly the synovium, the lining of the joints. [1, 2]
Once activated, the immune system produces pro-inflammatory cytokines that trigger continuous inflammation. This leads to joint pain, swelling, stiffness, and over time, erosion of cartilage and bone, as well as deformities in the affected joints. If left untreated, rheumatoid arthritis can cause severe disability and significantly reduce quality of life. [1, 2]
What Causes Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Although the exact cause remains unknown, research points to a combination of genetic, environmental, and hormonal factors. Known risk factors include:
- Genetic predisposition (e.g., presence of HLA-DR4 genes)
- Environmental exposures such as smoking and air pollution
- Hormonal influences, with RA being more common in women
- Infections that may trigger immune dysregulation
Once triggered, this autoimmune response causes chronic inflammation and ongoing tissue destruction, affecting not only the joints but also the skin, lungs, eyes, heart, and blood vessels in some patients. [1, 2]
Impact of Rheumatoid Arthritis on the Body
It is important to understand that rheumatoid arthritis is not just a joint disease. It is associated with systemic complications, including:
- Cardiovascular disease
- Lung involvement (e.g., interstitial lung disease)
- Osteoporosis
- Anemia and fatigue
- Depression and reduced mobility
The progressive nature of rheumatoid arthritis emphasizes the need for early diagnosis and effective long-term treatment strategies aimed at controlling inflammation, preventing damage, and preserving function. [1, 2]
However, as new therapies emerge – like dendritic cell-based immunotherapy – the goal is shifting from symptom management to immune system reprogramming, potentially changing the course of the disease altogether.
What Are Dendritic Cells and How Do They Work in Rheumatoid Arthritis?
Dendritic cells are a specialized subset of immune cells that help regulate and initiate the body's immune response. They are often referred to as the "sentinels" of the immune system because of their unique ability to detect harmful agents – such as pathogens, toxins, and abnormal cells – and trigger a defense mechanism by activating other immune components, particularly T lymphocytes. [5-8]
Biological Role and Origin of Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells originate from bone marrow hematopoietic stem cells and differentiate from myeloid or lymphoid progenitors depending on their subtype. Once matured, they are distributed throughout various tissues, including the skin, lungs, gastrointestinal tract, and lymphoid organs, where they constantly patrol for signs of danger. [5]
There are two main types of dendritic cells in humans:
- Conventional (myeloid) dendritic cells (cDCs): Primarily responsible for antigen presentation and T cell activation
- Plasmacytoid dendritic cells (pDCs): Known for producing large amounts of type I interferons during viral infections and influencing immune tolerance
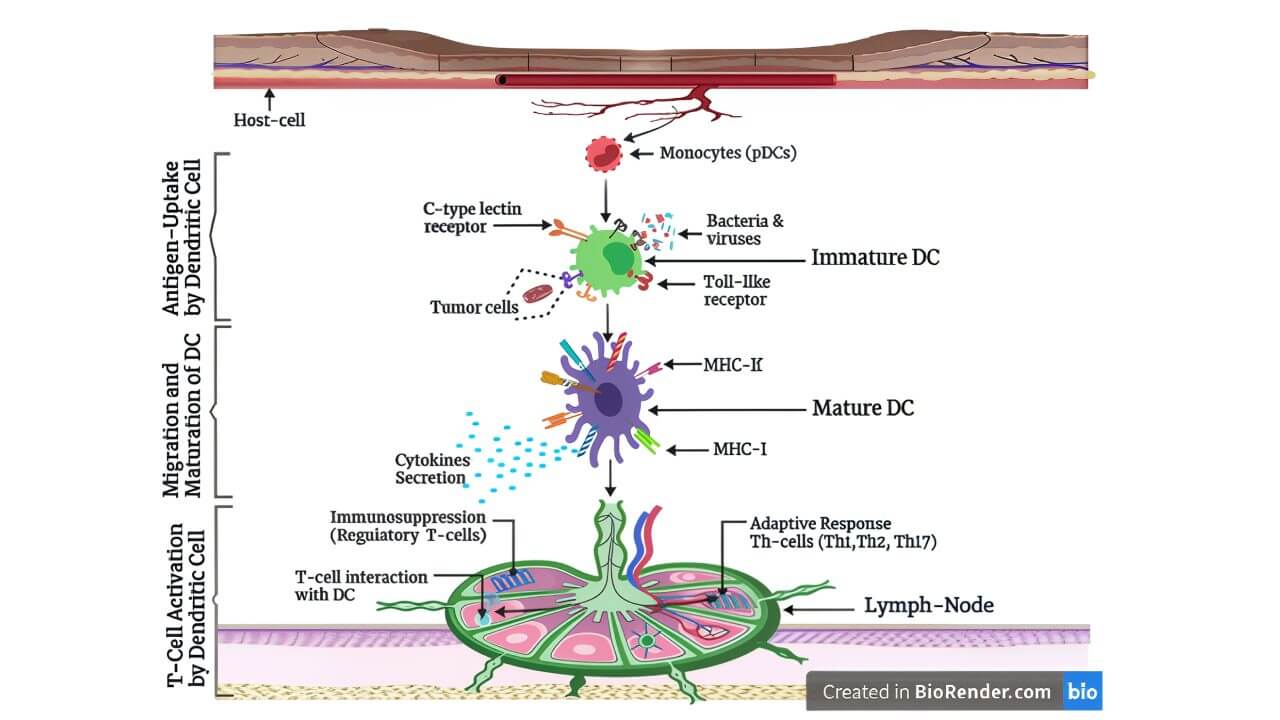
How Dendritic Cells Work in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Step-by-Step
- Antigen capture: Immature dendritic cells reside in peripheral tissues where they detect and ingest antigens through processes like phagocytosis, macropinocytosis, or receptor-mediated endocytosis.
- Migration and maturation: After encountering a foreign antigen, dendritic cells undergo maturation and migrate to the nearest lymph node. During this transition, they increase expression of co-stimulatory molecules (e.g., CD80, CD86), major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, and cytokines.
- Antigen presentation and T cell activation: Mature dendritic cells present antigen fragments on MHC class I or II molecules to naive T cells, initiating T cell activation and determining whether the immune system will attack or tolerate the antigen.
Immune modulation: Depending on the context, dendritic cells can induce either an immune attack (as seen during infection) or immune tolerance (important for avoiding autoimmunity). This dendritic cell function helps maintain balance within the immune system.
Innate and Adaptive Immunity
Dendritic cells are unique in their capacity to provide a link between the innate and adaptive immune systems [5]:
- Innate immunity: Dendritic cells detect microbial patterns using receptors such as toll-like receptors (TLRs)
- Adaptive immunity: Dendritic cells activate antigen-specific T cells, influencing the outcome of the immune response (tolerance vs. activation)
This role makes dendritic cells ideal targets in immunotherapy, especially for autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis, where the immune system misfires and attacks the body's own tissues.
Therapeutic Role of Dendritic Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis
The therapeutic revolution in immunology began with the discovery of dendritic cells by Canadian immunologist Ralph M. Steinman in the 1970s. Steinman identified these rare immune cells as the key initiators of adaptive immunity. For his discovery, he was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011. [5]
In particular, Steinman's research demonstrated that dendritic cells are essential for processing and presenting antigens to T lymphocytes, thus triggering a tailored immune response. Before his work, the understanding of how the immune system distinguished threats and generated memory was incomplete.
Specifically, Steinman's discovery achieved the following [5]:
- Identified the central role of dendritic cells in organizing immune activation and tolerance
- Paved the way for dendritic cell based immunotherapy, now used in oncology, infectious diseases, and autoimmune disorders
- Inspired a generation of immunologists to explore how modifying dendritic cell function could restore immune balance in disease
From Immune Activation to Immune Regulation in Rheumatoid Arthritis
While initial interest focused on dendritic cells' ability to stimulate immunity, further research uncovered their potential in doing the opposite – suppressing harmful immune responses, especially in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis. [6]
This led to the development of tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs) – a subtype engineered or pharmacologically induced to [6]:
- Downregulate T cell activation
- Promote regulatory T cell (Treg) development
- Reduce the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines (e.g., TNF-α, IL-1)
- Foster long-term antigen-specific immune tolerance
Preclinical studies and early clinical trials have shown that tolDCs can dampen autoimmune responses and protect tissues from immune-mediated damage. This approach is especially helpful for patients with autoimmune diseases who have not responded well to conventional therapies or who experience intolerable side effects. [6]
As of today, dendritic cell based immunotherapy has shifted from experimental research to clinical reality, offering a personalized and targeted approach to restoring immune health and improving outcomes for people with chronic autoimmune conditions.
Dendritic Cells and the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
As discussed earlier, rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a prototypical autoimmune disease characterized by chronic inflammation that primarily targets the joints. What is interesting is that dendritic cells lie at the heart of this immune misfiring – immune sentinels that not only detect pathogens but can also mistakenly help initiate and sustain the body's attack on its own tissues. [1, 6]
How Dendritic Cells Contribute to Rheumatoid Arthritis
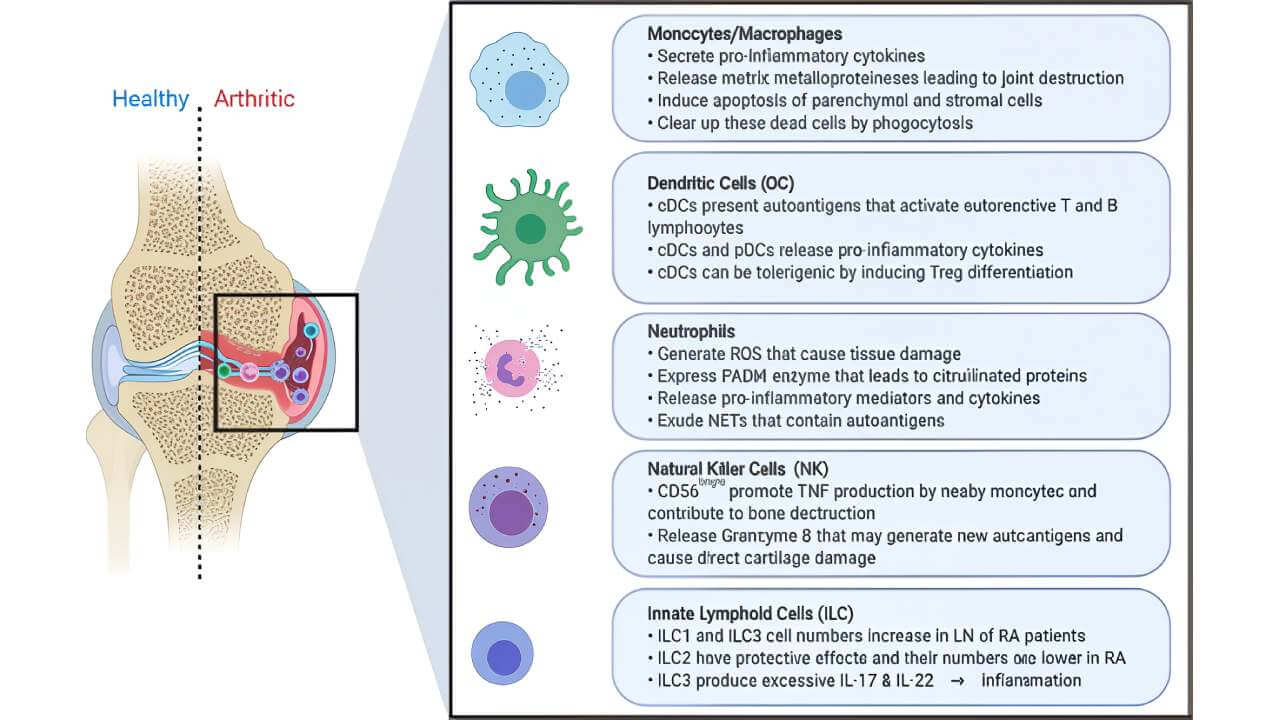
In patients with rheumatoid arthritis, dendritic cells are found in large numbers in the synovial fluid of inflamed joints. However, instead of maintaining immune tolerance, these dendritic cells present self-antigens to T cells, triggering pro-inflammatory cell responses that damage joint tissues. [7, 8]
Primary mechanisms include [7, 8]:
- Aberrant antigen presentation: Dendritic cells present autoantigens, such as type II collagen or citrullinated peptides, to naive CD4+ T cells. This leads to inappropriate T cell activation and expansion of pro-inflammatory Th1 and Th17 cell responses, which drive chronic inflammation and joint damage.
- Cytokine secretion: Dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis secrete high levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, and IL-12 – the cytokines that drive inflammation and joint destruction. TNF-α, in particular, promotes osteoclastogenesis, leading to bone erosion.
- Recruitment of other immune cells: By producing chemokines, dendritic cells recruit monocytes, macrophages, and neutrophils into the synovial tissue. These immune cells further intensify the inflammatory process and perpetuate tissue damage.
Resistance to apoptosis: Synovial dendritic cells in rheumatoid arthritis show prolonged survival, meaning they persist longer in inflamed joints and continue to fuel the autoimmune cycle.
Dendritic Cells: Friends or Foes?
Although dendritic cells are often recognized for their pro-inflammatory role in rheumatoid arthritis, they also possess the ability to regulate the immune response when exposed to the appropriate conditions. This paradox – being both drivers of disease and potential tools for therapy – makes dendritic cells promising candidates in modern rheumatoid arthritis therapy. [7, 8]
- Pathogenic role: In rheumatoid arthritis, dendritic cells act as amplifiers of chronic inflammation, leading to synovial hyperplasia, cartilage degradation, and bone erosion.
- Regulatory role: Under tolerogenic conditions, dendritic cells can promote regulatory T cells (Tregs) that dampen inflammation and help maintain immune balance.
This duality is what drives current research in dendritic cell immunotherapy, aiming to reprogram these cells into a tolerogenic state capable of reducing immune-related side effects and halting disease progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other autoimmune diseases.
Dendritic Cells Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
As research advances in immunology and personalized medicine, dendritic cell therapy has been recognized as an innovative solution for rheumatoid arthritis patients, particularly those who do not respond to conventional medications. By engineering tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs) to suppress rather than activate immune responses, scientists have developed a method that can induce immune tolerance, restore immune regulation, and alleviate inflammation in a targeted, lasting way.
What Are Tolerogenic Dendritic Cells?
As previously mentioned, tolerogenic dendritic cells are a genetically or pharmacologically modified form of dendritic cells that promote immune tolerance instead of initiating inflammation. In rheumatoid arthritis (RA), the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing pain and tissue destruction. However, TolDCs are programmed to "teach" the immune system to ignore self-antigens associated with joint tissue, reducing autoimmune responses without compromising the body's ability to fight infections. [7, 8]
Step-by-Step: How Dendritic Cells Are Genetically Modified and Prepared for Therapy
Here is a detailed overview of how cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is carried out, based on the clinical protocols and supported by EU GMP (Good Manufacturing Practice) standards:
- Blood collection and transport: 200 ml of the patient's blood is drawn and immediately transported under stable temperature conditions to a certified cleanroom laboratory.
- Cell separation and isolation: The blood undergoes centrifugation, separating it into layers. Then, the layer with lymphocytes, which includes dendritic cell precursors, is isolated. Red blood cells and granulocytes (non-specific immune cells) are discarded.
- Cell culture and stimulation: The remaining cells are washed and suspended in a nutrient solution. Specific growth factors are added to stimulate the transformation of precursor cells into dendritic cells. Early in this process, autoantigens (e.g., antigens associated with inflamed joint tissue) derived from the patient's plasma are introduced to help train the tolDCs.
- Maturation phase: Over 7 days, the cells mature in an incubator, developing their characteristic branched (dendritic) morphology. Microscopic monitoring ensures quality and proper differentiation.
- Quality control: Before administration, the quantity, viability, and surface markers of the tolDCs are analyzed using flow cytometry. Only the highest-quality cells are selected for immunization.
- Administration to the patient: The prepared tolDCs are injected subcutaneously in the groin region. This is followed by high-dose vitamin infusions to support immune recovery. Patients typically return home the same day.
This approach ensures that each rheumatoid arthritis patient receives dendritic cells that are specifically trained to suppress the immune attack on their own joints. Studies confirm that dendritic cell therapy leads to a measurable improvement in joint mobility, decrease in pro-inflammatory cytokines, and increased regulatory T cell activity. [7, 8]
Safety Profile and Immune Regulation
Unlike systemic immunosuppressants, dendritic cell therapy does not compromise the body's global immune defense. Instead, it induces antigen-specific tolerance, significantly lowering the risk of immune-related side effects such as infections or malignancy.
Because the cells are autologous (derived from the patient's own blood), the risk of rejection or allergic reaction is virtually zero. This makes dendritic cell based immunotherapy one of the safest forms of experimental therapy currently in clinical use for autoimmune diseases like RA. [7, 8]
How Dendritic Cell Therapy Compares to Other RA Treatments
The treatment of rheumatoid arthritis has significantly evolved over the past two decades.
For example, standard therapies – such as DMARDs, biologics, and JAK inhibitors – aim to control inflammation and prevent joint damage. However, these therapies often involve broad immunosuppression, leading to systemic side effects and varied responses among patients.
In contrast, dendritic cell therapy (especially tolerogenic dendritic cells, or tolDCs) represents a RA treatment innovation that targets the disease at a much earlier stage in the immune response by restoring immune tolerance instead of suppressing it entirely. [7, 8]
Current Treatment Options for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Conventional synthetic DMARDs (csDMARDs)
- Mechanism: Reduce inflammation by inhibiting the rapid proliferation of immune cells.
- Limitations: Slow onset (can take weeks/months); gastrointestinal issues, liver toxicity, bone marrow suppression.
- Biologic DMARDs (bDMARDs)
- Mechanism: Target specific cytokines or immune cell surface markers involved in inflammation.
- Limitations: Increased risk of serious infections (e.g., tuberculosis, herpes zoster); costly and often requiring lifelong use.
- Targeted synthetic DMARDs (tsDMARDs/JAK inhibitors)
- Mechanism: Inhibit Janus kinases (JAKs), enzymes involved in the signaling of inflammatory cytokines.
- Limitations: Increased risk of blood clots, infections, and cardiovascular events; routine blood monitoring needed.
How Dendritic Cell Therapy Differs From Other Rheumatoid Arthritis Treatments
Dendritic cell therapy offers an innovative and personalized approach that differs fundamentally from conventional RA drugs:
| Feature | Standard Therapies | Dendritic Cell Therapy |
|---|---|---|
| Target | Cytokines/immune cells | Dendritic cells (immune initiators) |
| Mechanism | Broad immune suppression | Immune regulation and tolerance induction |
| Effect on immune system | Systemic suppression | Antigen-specific modulation |
| Risk of infections | Moderate to high | Minimal (no systemic immunosuppression) |
| Personalization | Limited | Personalized immunotherapy using patient's own cells |
| Treatment frequency | Continuous/lifelong | Periodic tolDC injections |
By targeting dendritic cells, tolDC therapy modulates the immune response at its root. Instead of simply suppressing inflammation, it retrains the immune system to tolerate self-antigens, thereby preventing the activation of autoreactive T cells responsible for chronic inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis (RA). This helps reduce destructive cell responses that would otherwise lead to progressive joint damage. [7, 8]
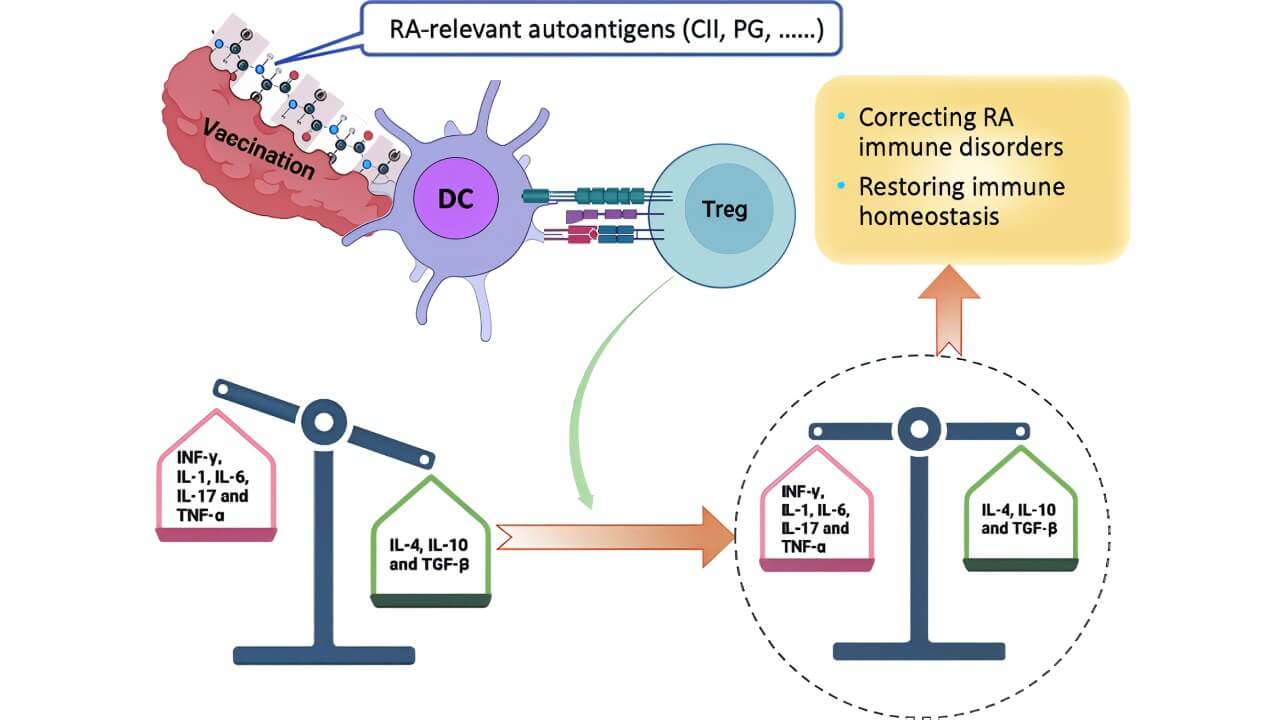
In other words, dendritic cell therapy addresses the cause rather than the consequence of RA. Instead of reacting to inflammation after it starts, tolDCs preemptively prevent the immune system from launching the attack in the first place.
Prof. Dr. Frank Gansauge: Dendritic Cells as Immune System "Officers"
To better understand the transformative role of dendritic cell therapy, we turn to one of Europe's leading experts in the field – Prof. Dr. Frank Gansauge, a famous immunologist and surgeon with over 22 years of experience in dendritic cell immunotherapy.
Prof. Gansauge describes dendritic cells as the "officers" of the immune system, trained to identify and report threats such as tumor cells or infections to the immune "soldiers" – T lymphocytes. These trained lymphocytes then carry out the targeted response, making dendritic cell therapy an intelligent, precise, and personalized form of immunotherapy.
From Science to Practice
In 2001, Prof. Gansauge founded one of the first private laboratories in Europe capable of producing dendritic cell vaccines under EU GMP-certified conditions. Today, his clinic specializes in creating highly individualized dendritic cell-based therapies for cancer and autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis.
He emphasizes:
- The therapy's dual potential: improving immune responses in cancer and inducing tolerance in autoimmune diseases.
- The use of fresh, non-frozen dendritic cells, which enhances their functionality and ensures maximum training capacity for immune cells.
- The fact that only one injection of dendritic cells, tailored to the patient's current disease state, can sometimes produce long-lasting effects, particularly when combined with standard treatments like chemotherapy or radiotherapy.
On Safety, Outcomes, and Future Use
- Prof. Gansauge confirms that side effects are minimal, and his clinic's work is supervised by the Paul Ehrlich Institute and other German regulatory authorities.
- In oncology, he has seen up to 50-65% response rates, with documented cases of no recurrence for 5+ years in diseases like colon cancer.
- Beyond cancer, dendritic cells show promise in anti-aging medicine, chronic infections, and potentially allergy treatment – areas where their immune-modulating properties can slow aging and increase resilience.
The Future of Immunotherapy: Prof. Gansauge on Dendritic Cells, Cancer, and Autoimmune Diseases
For those interested in a deeper, firsthand understanding of the science, process, and patient outcomes, we highly recommend watching the full interview with Prof. Dr. Frank Gansauge.
Availability of Dendritic Cell Therapy For Rheumatoid Arthritis in Germany
Germany has become a leading destination for dendritic cell therapy, offering this advanced treatment to select patients with rheumatoid arthritis at certified centers. The country emphasizes patient safety, scientific rigor, and individualized medicine, continuing to attract international patients seeking innovative solutions for autoimmune diseases.
Why Germany Leads in Dendritic Cell-Based Therapy For Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Strict regulation and quality assurance: Germany's Paul-Ehrlich-Institut oversees all cell-based immunotherapies, ensuring that dendritic cell therapy complies with EU GMP guidelines. This strict oversight guarantees the safety, consistency, and efficacy of each cell product.
- GMP-certified laboratories: Clinics offering dendritic cell therapy work with specialized labs equipped with modern clean rooms and advanced biotechnological platforms. World-famous experts like Prof. Dr. Frank Gansauge have more than two decades of experience producing and applying dendritic cell vaccines with precision and patient-specific customization.
- Experienced clinical teams: Treatment is delivered by highly trained teams of immunologists and rheumatologists, many of whom are involved in ongoing clinical research. These centers are often affiliated with leading German universities or cancer immunotherapy institutes, contributing to continuous innovation and best practices.
Advantages for Advanced RA Patients
Germany offers a unique opportunity for advanced RA patients who have exhausted standard treatment options, including biologics and DMARDs.
In this country, certified centers provide integrated care models that include comprehensive immune monitoring, tailored dosing, and real-time clinical evaluation, significantly reducing the risk of immune-related side effects. Many clinics combine dendritic cell therapy with supportive treatments such as high-dose vitamin protocols and lifestyle guidance, promoting both immune resilience and overall wellness.
Moreover, patients benefit from short wait times, with therapy typically initiated within 2-3 weeks of consultation – crucial for those with rapidly progressing disease.
Overall, by choosing Germany, rheumatoid arthritis patients gain access to world-class clinical expertise and an environment where immune system balance is restored using the most advanced therapeutic approaches available today.
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
Finding the most suitable treatment of rheumatoid arthritis can be overwhelming, especially for patients who have already endured numerous therapy sessions, visited multiple specialists, and struggled to find relief from chronic pain and joint damage. The abundance of clinical recommendations and the complexity of autoimmune disease management often lead patients to accept conventional treatments that may offer only partial relief – or carry long-term side effects.
Booking Health is here to help you make an informed, personalized choice. With more than 12 years of experience in international medical coordination and access to certified centers offering advanced treatments like dendritic cell therapy, we are among the leaders of immune system innovation and individualized patient care.
Whether you are newly diagnosed or an advanced rheumatoid arthritis patient seeking innovative therapies, Booking Health ensures that your care plan is tailored to your needs. We assist at every stage of the medical journey:
- Comprehensive analysis of medical documentation
- Coordination with leading specialists in immunology and autoimmune diseases
- Selection of the most suitable certified treatment center in Germany
- Preparation and submission of all required medical documents
- Remote consultations with physicians to build a personalized care plan
- Organization of travel, visa support, and accommodation
- 24/7 support from a personal medical coordinator and interpreter
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
- Ongoing follow-up care and guidance after treatment
At Booking Health, we understand that health is a priceless asset. That is why we collaborate only with clinics certified to provide EU GMP-compliant therapies, ensuring safety, efficacy, and the most modern approach to dendritic cell-based immunotherapy.
Take control of your health journey with a partner who truly understands your needs. Contact a Booking Health consultant today to explore your options for personalized rheumatoid arthritis therapy with the world's leading specialists in immune system modulation and innovative cell-based treatment.
Dendritic Cell Therapy: Patient Stories with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions About Dendritic Cell-Based Immunotherapy In Rheumatoid Arthritis
Send request for treatmentDendritic cell immunotherapy for autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, is a RA treatment innovation that involves harvesting a patient's own immune precursor cells and modifying them in a lab to become tolerogenic dendritic cells (tolDCs). Once reintroduced into the body, these cells help reprogram the immune system by inducing tolerance in the immune system and restoring immune regulation, ultimately aiming to halt disease progression by stopping the immune attack on joint tissue.
Under normal conditions, dendritic cells activate immune responses. However, in dendritic cell immunotherapy, they are re-engineered into tolDCs that guide the immune system toward tolerance instead of inflammation. This helps suppress autoreactive T cells, reducing inflammation and modulating the immune response to prevent further joint damage in RA.
Yes. The safety of DC therapy is well-documented, especially since it uses autologous (patient-derived) cells, which virtually eliminates the risk of rejection. Unlike conventional drugs, it does not cause systemic immunosuppression, thereby significantly lowering the risk of immune-related side effects such as infections or organ damage.
Criteria for treatment include:
- Diagnosed with RA and experiencing active symptoms
- Failure to respond or intolerance to conventional DMARDs or biologics
- Interest in personalized immunotherapy based on immune system profiling
- Classified as advanced RA patients seeking innovative solutions
Eligibility is determined after review by immunology experts at certified centers.
Clinical outcomes from early trials and real-world applications show promising results, including:
- Noticeable symptom reduction
- Improvement in joint mobility and physical function
- Decreased dependence on steroids and biologics
- Long-term modulation of immune response and disease stability
While more large-scale studies are underway, current evidence supports its value as a safe and effective option.
This personalized immunotherapy is offered by leading German clinics that are EU GMP-certified. These certified centers specialize in advanced immunomodulatory treatments for autoimmune diseases, including RA.
Booking Health assistance ensures a stress-free experience, offering:
- Professional clinic and treatment coordination
- Translation of medical documentation
- Full visa, travel, and accommodation support
- 24/7 access to a personal coordinator throughout your journey
With Booking Health assistance, advanced RA patients can access innovative treatments in world-class medical facilities, supported by excellence in care and innovation.
Standard rheumatoid arthritis treatments suppress the activity of immune cells or cytokines to reduce inflammation. Dendritic cell therapy works differently—it reprograms dendritic cells restoring immune tolerance to the body’s own tissues.
How does the mechanism of action of dendritic cell therapy in rheumatoid arthritis differ from traditional drugs?
Conventional rheumatoid arthritis treatments block immune activity systemically, which often causes side effects. Dendritic cell therapy works locally—modulating the immune response, teaching the body not to attack its own joints while preserving its natural immune defenses.
During rheumatoid arthritis treatment, standard drugs suppress the entire immune system, which increases the risk of infections. Dendritic cell therapy does not block the immune system as a whole—it only regulates pathological reactions helping to restore the natural balance of the immune response.
With standard treatment for rheumatoid arthritis, the risk of infections is high due to systemic immunosuppression. Dendritic cell therapy is safer because it does not suppress the immune system completely, but only corrects autoimmune reactions reducing inflammation without compromising protective functions.
Conventional rheumatoid arthritis treatment regimens provide standard doses of drugs for all patients. In contrast dendritic cell therapy is created from the patient’s own cells, which allows for fine-tuning the immune response and providing a personalized approach to treatment.
Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are usually on medication continuously, sometimes for life. Dendritic cell therapy is administered periodically as injections of tolerogenic cells which provide a long-lasting effect, reducing inflammation and the need for ongoing medication.
Dendritic cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis costs around 20,000€–38,000€. The price may vary depending on the treatment duration, the number of injections and whether it is combined with other therapies.
In Germany dendritic cell therapy for rheumatoid arthritis is provided only after thorough evaluation. Treatments are individualized and performed in specialized centers under close supervision. Also dendritic cells are integrated with standard care to modulate immune response.
Choose treatment abroad and you will be sure to get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Scientific Reports. Global, Regional, and National Epidemiology of Rheumatoid Arthritis among People Aged 20-54 years from 1990 to 2021. https://www.nature.com/articles/s41598-025-92150-1
[2] The Lancet Rheumatology. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis, 1990-2020, and Projections to 2050: A Systematic Analysis of the Global Burden of Disease Study 2021. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanrhe/article/PIIS2665-9913(23)00211-4/fulltext
[3] Arthritis Research & Therapy. Use of NSAIDs in Treating Patients with Arthritis. https://arthritis-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/ar4174
[4] Kim Lauper, Michele Iudici, Denis Mongin et al. Effectiveness of TNF-inhibitors, abatacept, IL6-inhibitors and JAK-inhibitors in 31 846 patients with rheumatoid arthritis in 19 registers from the ‘JAK-pot’ collaboration. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022 Jun 15;81(10):1358–1366. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2022-222586. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[5] Mohammed Yusuf Zanna, Abd Rahaman Yasmin, Abdul Rahman Omar et al. Review of Dendritic Cells, Their Role in Clinical Immunology, and Distribution in Various Animal Species. Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 28;22(15):8044. doi: 10.3390/ijms22158044. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[6] International Journal of Molecular Sciences. Tolerogenic Dendritic Cell-Based Approaches in Autoimmunity. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/22/16/8415
[7] Arthritis Research & Therapy. The Mechanism of Dendritic Cell-T Cell Crosstalk in Rheumatoid Arthritis. https://arthritis-research.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13075-023-03159-8
[8] P Wehr, H Purvis, S‐C Law, R Thomas. Dendritic cells, T cells and their interaction in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 2019 Jan 21;196(1):12–27. doi: 10.1111/cei.13256. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[9] Biomedical Journal. Innate Immunity Drives Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2319417020300986
[10] Frontiers in Immunology. Reestablish Immune Tolerance in Rheumatoid Arthritis. https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/immunology/articles/10.3389/fimmu.2022.1012868/full
Read:
Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis in Germany
Arthritis - Accurate diagnosis and effective therapy at reputable German hospitals
Article menu:
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Chronic Autoimmune Condition
- What Are Dendritic Cells and How Do They Work in Rheumatoid Arthritis?
- Therapeutic Role of Dendritic Cells in Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Dendritic Cells and the Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Dendritic Cells Therapy for Rheumatoid Arthritis
- How Dendritic Cell Therapy Compares to Other RA Treatments
- Prof. Dr. Frank Gansauge: Dendritic Cells as Immune System "Officers"
- Availability of Dendritic Cell Therapy For Rheumatoid Arthritis in Germany
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way with Booking Health
- Frequently Asked Questions About Dendritic Cell-Based Immunotherapy In Rheumatoid Arthritis
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health