The fast-growing stem cell biology has turned modern medicine upside down, providing new ways of thinking about how to cure the previously considered incurable diseases. The special property of stem cells to promote tissue regeneration and convert to different types of tissues has provided the basis for new stem cell-based solutions in the fields of cardiology, neurology, oncology, and orthopedics. Stem cell therapy is currently the most promising option in the field of regenerative medicine, and it gives hope for millions of patients around the globe.
The market size of stem cell treatments has reached US$297 million in 2022 and is projected to grow at an annual growth rate of 16.8% between 2022 and 2027 due to the encouraging outcomes of clinical trials, increased funding for stem cell research, emerging technologies of cell therapies, and the growing demand for advanced treatment methods [1].
Stem Cell Therapy: Mechanisms and Types
The area of stem cell physiology has progressed at an incredible rate in current biomedical science. It is now known that the stem cells serve as the natural system of repair in the body, and it is able to repair the tissues that are damaged and also keep almost all the organs intact. This regenerative potential forms the basis of clinical application of stem cell treatments since scientists can use it to repair the structure and function of diseased tissues. In contrast to the traditional medications that can only treat the symptoms, stem cell-based treatments induce tissue regeneration and long-term healing at the cellular level.
How Stem Cell Therapy Works
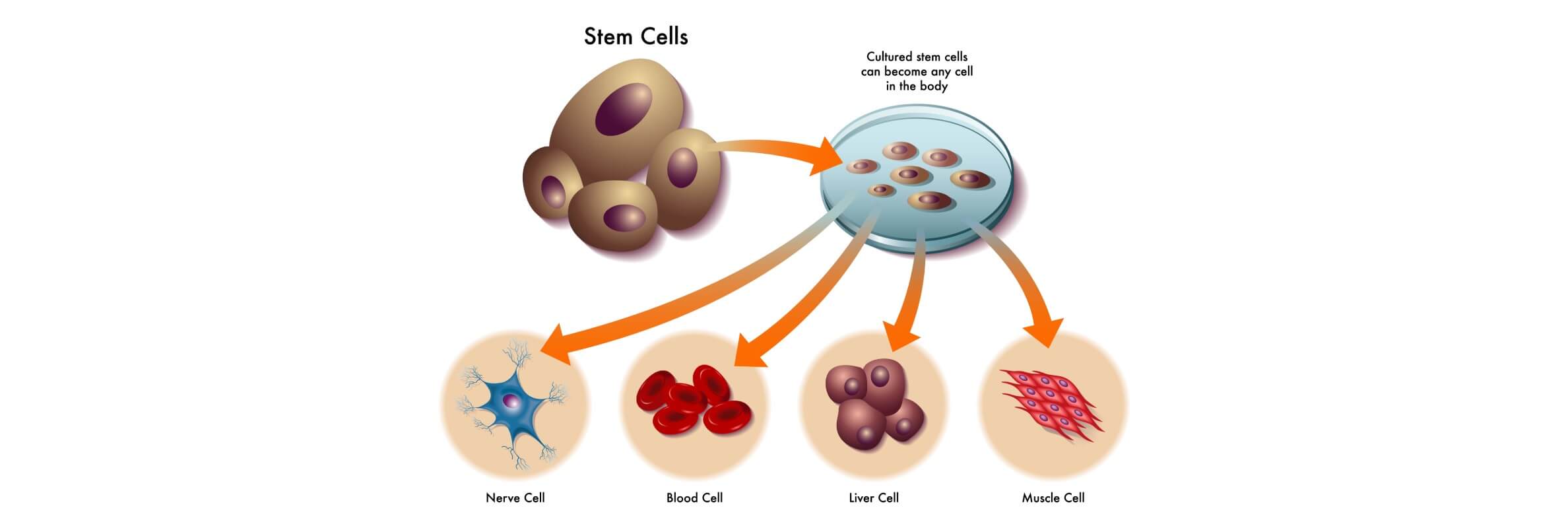
It has a single mechanism that depends on the differentiation of human stem cells into specialized cells. These are the nerve cells, muscle cells, bone, and blood-forming cells. When the stem cells are implanted into the body of the patient in the form of transplantation or injections, they travel to the sites of injury and initiate the process of tissue regeneration.
The doctors can apply cell-based therapy with autologous (patient's own) or allogeneic (donor) stem cells, depending on the condition. It is not merely aimed at substituting destroyed tissues but also to induce natural healing through the release of growth factors that stimulate the healing of tissues. Stem cell transplantation has gained popularity in the oncology, hematology, and neurology fields as a part of a multifaceted treatment approach aimed at treating the disease at its primary level.
The effectiveness of stem cell-based treatment relies on the knowledge of the biological behavior following transplantation, and how they engage with the microenvironment. The modern research in the field of stem cell physiology is focused on improving the efficiency of the engraftment process, regulation of differentiation, and elimination of undesired changes, including the development of cancer cells [2].
Main Types of Stem Cells
Stem cells exist in a number of varieties that have their own sources and abilities. Their potential to distinguish and the ethical issues of their utilization are the primary differences.
Embryonic Stem Cells
Embryonic stem cells are acquired at the embryonic stage, and they have the maximum level of pluripotency一in other words, they can form any type of cell in the human body. Such embryonic stem cells have played a crucial role in the development and modeling of diseases. Their application, however, is questionable in terms of both ethical and regulatory issues一this results in bans in most institutions. In spite of all these controversies, current research on these stem cells has continued to reveal crucial biology of stem cell mechanisms and regeneration abilities.
Adult Stem Cells
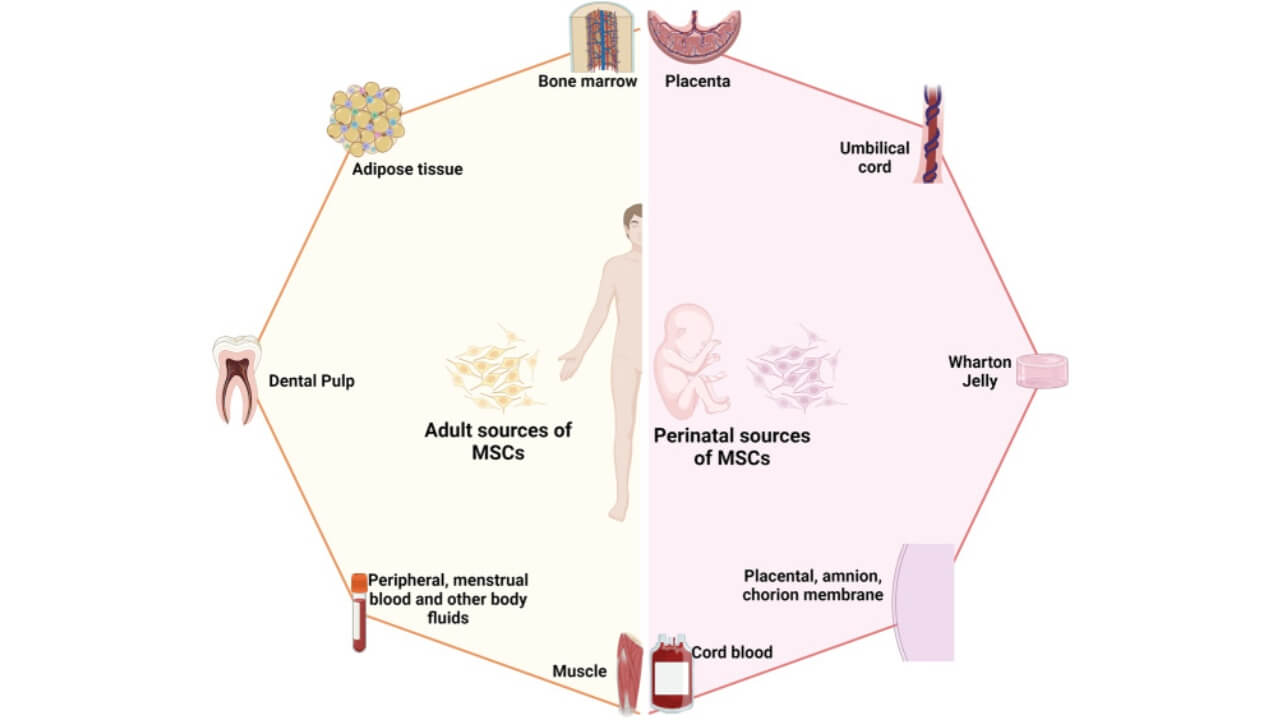
Adult cells exist in particular tissues, including bone marrow, skin, and the gastrointestinal tract. Natural repair and maintenance is the primary role of these tissue-specific stem cells. Bone marrow stem cells are the most frequently used for the treatment of leukemia and other blood-related cancers. Adult stem cells are also safer and morally acceptable, though they have a smaller range of differentiation than embryonic ones.
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells
One of the major achievements in stem cell technology was the development of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These are normal adult cells which scientists reprogram to become pluripotent cells一or in other words, roll back the developmental clock. iPSCs can be used to form almost any tissue and allow personalized cell therapy without the ethical issues that have been raised by the use of embryo-derived cells. The discovery of the iPSC has transformed cell-based therapy, enabling researchers to model diseases, test drugs, and even investigate personalized strategies for transplantation.
Mesenchymal Stem Cells
Of all types of stem cells, the mesenchymal stem cell (MSC) has been the focus of the greatest clinical investigations. Isolated from bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord, and other sources, these multipotent cells have demonstrated great promise in stimulating tissue regeneration and decreasing inflammation [2]. They are closely related to mesenchymal stromal cells and are applied in orthopedic injuries, autoimmune diseases, and even cardiovascular diseases. Due to the easy harvestation of mesenchymal stem cells and their immune-modulatory properties, they have formed the basis of most stem cell therapies and are currently undergoing clinical trials.
Understanding Stem Cell Diversity
All the types of stem cells have their specific functions in the human body. Embryonic cells offer the most comprehensive range of differentiation and, therefore, are useful in genetic disease modeling and regenerative studies. Adult stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells, in their turn, have been the basis of the present stem cell therapies because of their availability and safety record.
The current developments in stem cell physiology continue to improve our knowledge of how cell-based therapy can be used to repair damaged organs, cure diseases, and recover better after an injury. The better we understand the processes involved in this therapy, the nearer we get to the point in the future when personalized stem cell-based medicine will be a routine part of clinical practice.
Medical Fields & Indications for Stem Cell Therapy
The treatment possibilities include almost all medical fields. With the force of stem cell physiology, clinicians have been able to learn how to repair damaged tissues, restore the functionality of the organs, and even reprogram the natural healing process of the body. Since the transplantation of stem cells in leukemia, these new treatments have demonstrated the fact that cell-based therapy is not a dream but a reality in present-day clinical practice.
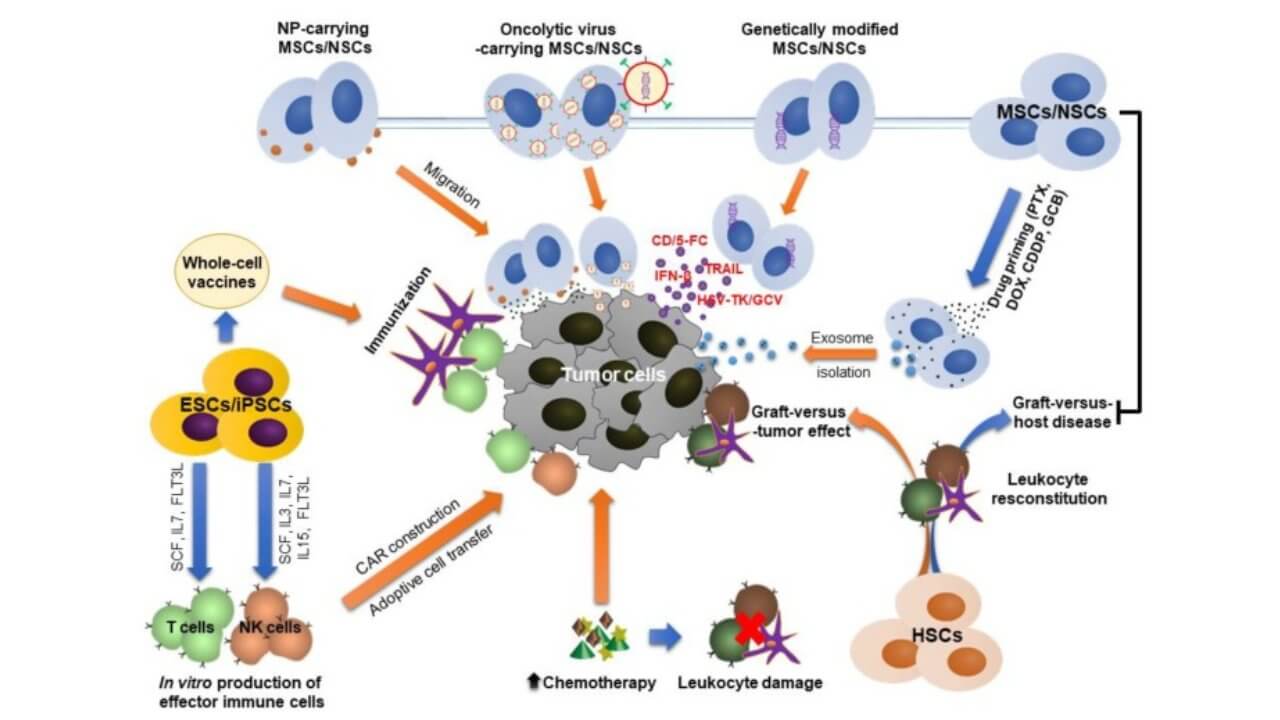
Stem Cell Therapy in Oncology and Hematology
Today, transplantation of stem cells has taken up a significant role in cancer medicine, especially in the treatment of leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma. Doctors are able to replace the bone marrow with healthy stem cells, and thus, they are able to restore normal blood formation following intensive chemotherapy or radiation. Such blood stem cell treatments not only cure diseases, but also assist in reconstructing the immune system [3].
More recent methods use stem cell therapies together with gene therapies, in which the human stem cells are genetically engineered to become resistant to chemotherapy. It has been demonstrated in clinical tests that adult stem cell treatments and mesenchymal stem cells may assist in decreasing the issues in treatment, decreasing inflammation, and assisting in quicker recovery after transplantation.
Stem Cell Therapy in Neurology
Regenerative cell therapy is a prospect for patients with conditions that were thought to be irreversible in neurology. Stem cell-based interventions are now being tested for diseases including Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, multiple sclerosis, and spinal cord injuries. Induced pluripotent stem cells and human embryonic stem cells are being used by scientists to replace damaged nerve cells, repair the synaptic connections, and promote the tissue regeneration of the central nervous system [4].
Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injuries
Stem cells have opened up a real possibility of restoring functions after spinal cord injuries. After injection, the cells reduce inflammation, stimulate the formation of new neuronal connections and create conditions for the regeneration of damaged tissues. Patients have recorded improvements in sensitivity, muscle strength and movement control depending on the level of damage.
The effectiveness of the method largely depends on the correct selection of cells and the time from the moment of injury. But even in difficult cases, the therapy shows excellent results. You can learn more about the application of the technology and practical results in the following video.
Stem Cell Therapy for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Stem cells have already proven their effectiveness in supporting the function of motor neurons in ALS. They secrete neurotrophic factors that nourish and protect nerve cells, reduce inflammation in the spinal cord and stimulate the formation of new neuronal connections.
Clinical experience shows that patients experience stabilization of muscle strength, reduced stiffness, improved coordination of movements and even an increase in the ability to independently perform household activities. The effect of the therapy is noticeable within a few weeks after the introduction of the cells and is maintained if the patient follows the recommended rehabilitation programs. Find out how the method really helps patients in the following video.
Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in Children
Stem cells are already showing significant results in supporting children with autism. The injected cells improve the functioning of neuronal networks and stimulate connections between neurons responsible for social interaction, speech and emotional regulation. Parents often notice a decrease in autism symptoms, better concentration and greater adaptability in everyday life.
The patient’s mother, Cindy Johnson, shared her experience of how the therapy has really affected her child’s life: improved interaction with the environment, expanded communication skills and general activity. Learn more about the results and approach to treatment in the video below.
Stem Cell Therapy in Orthopedics
The use of stem cell therapies in orthopedics has gained popularity because of their capability to repair bone, cartilage, and ligaments. Mesenchymal stem cells that have been harvested from bone marrow or adipose tissue are applied in procedures to ensure that tissue regeneration is achieved following fractures, osteoarthritis, and tendon injuries. Such cells specialize into osteoblasts and chondrocytes and speed up recovery and restore the functioning of the joints.
Stem Cell Therapy for Joint Diseases
Stem cells demonstrate great results in treating joint diseases. Mesenchymal cells, introduced into the affected area, trigger natural cartilage regeneration, reduce inflammation and restore mobility. Many patients have recorded a stable reduction in pain and restoration of joint function, which confirms the real clinical effect.
The therapy is best shown in osteoarthritis and chronic meniscus injuries, when the joint still has the potential to recover. If the protocol is correctly selected and the cells are precisely introduced, the results are excellent. You can learn more about the indications and results of many years of practice in the following video.
Stem Cell Therapy in Cardiology
This therapy in cardiology is used to repair the myocardium, which is already damaged due to a heart attack or chronic ischemia. Practices with mesenchymal stromal cells and tissue-specific stem cells have established the capacity to create new blood vessels, enhance heart output, as well as encourage the restoration of tissues in the heart muscle.
Gene therapy is usually used to complement stem cell-based therapies to increase cell survival and functionality. By putting in more stem cells in the ischemic areas, physicians can stimulate the formation of functional myocardium and reduce the rate of heart failure. These findings of the clinical research studies indicate that cell therapy would be able to substitute invasive surgical procedures for a significant number of cardiac patients.
Stem Cell Therapy in Endocrinology
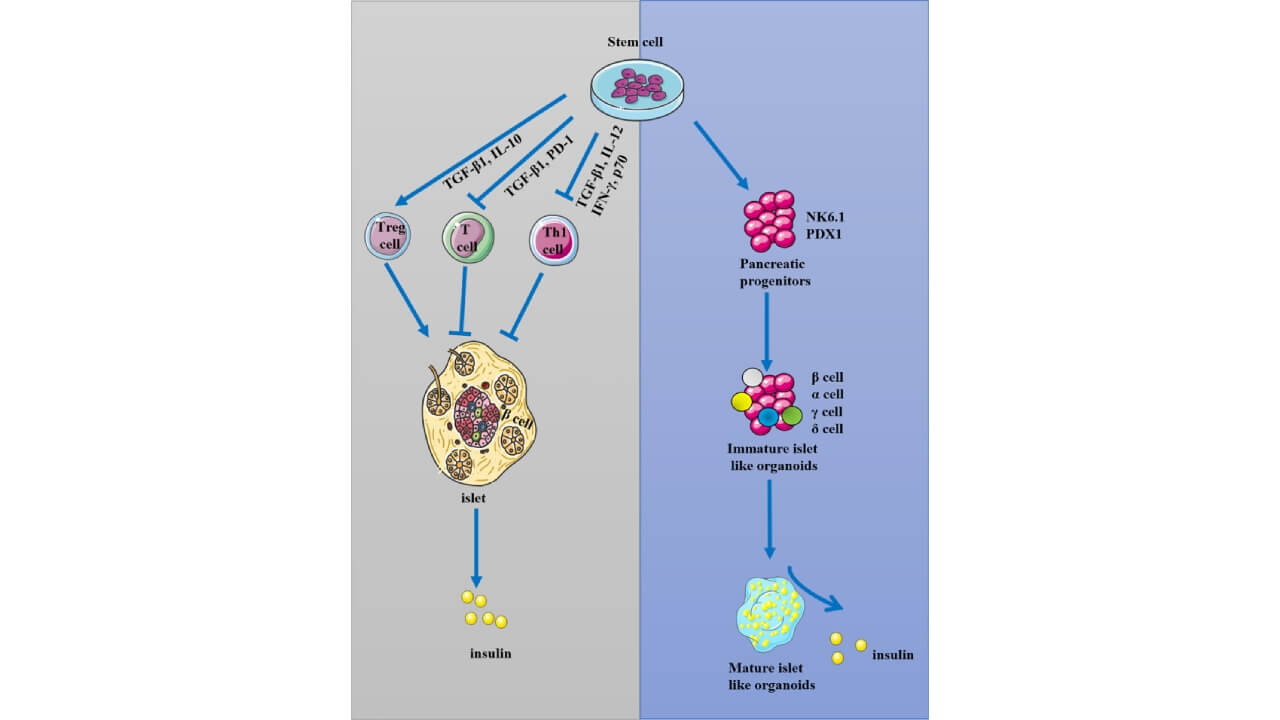
In endocrinology, this kind of therapy also has potential. Researchers are coming up with the use of stem cells to cure diabetes mellitus by restoring beta cells that produce insulin and also regenerating thyroid and adrenal glands [5]. Human embryonic stem cell research makes it possible to create specific endocrine cell lines to be transplanted.
With cell therapy coupled with specific molecular control, physicians can soon cure diseases such as type 1 diabetes not by injections of insulin but by replacing damaged natural activity. The enormous possibilities of stem cell physiology in hormone-producing organs are emphasized by such approaches.
Stem Cell Therapy in Ophthalmology
Ophthalmology is also undergoing a revolution with stem cell therapies, which provide an opportunity to heal corneal damage or retinal degeneration. Now, researchers can regenerate photoreceptors, retinal pigment epithelium, as well as corneal tissue.
Stem Cell Therapy for Optic Nerve Atrophy
Stem cells have opened up a completely new direction in ophthalmology一the ability to influence optic nerve atrophy, which was previously considered practically incurable. Unlike corneal correction or retinal regeneration, here the therapy is aimed at restoring the conductivity of the visual pathway一the ability of nerve fibers to transmit a signal from the eye to the brain.
The main goal of treatment is to stimulate the regeneration of damaged axons and improve microcirculation in the optic nerve area. Most protocols use mesenchymal stem cells, which are administered parabulbar, retrobulbar or systemically. Their action is based not only on the ability to transform into neuron-like cells, but primarily on a powerful trophic effect: they secrete neuroprotective growth factors, reduce inflammation, optimize tissue nutrition and create conditions for the restoration of nerve structures.
This direction of treatment shows excellent long-term results. The vision of many patients has been saved with the help of this type of treatment. One of these is Sofia, a patient with optic atrophy, who shared her experience, results, and path to therapy in the video below.
Stem Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction
Stem cells open up new possibilities for restoring erectile function. After injection, the cells stimulate the regeneration of blood vessels and nerve endings, improve blood supply to tissues and activate natural repair mechanisms. In addition, they reduce local inflammation and help restore tissue elasticity, which makes erections stable and reliable. Patients note increased sensitivity, stable erections and the return of confidence in sexual life.
The therapy has already proven its effectiveness in practice and allows you to restore a function that was previously considered impossible. Thomas has already restored normal erectile function and regained self-confidence - his story demonstrates how stem cells really work. Find out more in the video below.
Stem Cell Therapy in Anti-aging Medicine
Stem cells are already actively used in anti-aging medicine, helping to restore tissues, improve cell metabolism and stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. They reduce inflammation, support the cardiovascular system, strengthen the skin and improve the body's energy balance. Patients improved skin tone, improved skin appearance and an overall feeling of vigor and youth.
This method really works and gives noticeable results in practice. Learn more about this treatment method and the effectiveness of the therapy in the following video.
Treatment Options and Protocols of Stem Cell Therapy
The contemporary regenerative cell therapy is not a one-time treatment, but rather a set of well-thought-out medical strategies, which are developed according to the diagnosis of the patient, their age, and the general state. Since the biological behavior of human stem cells determines the type of various therapies, the differentiation potential, and delivery route, each therapy should be individually planned depending on thorough examination and lab analysis.
The primary aim of all stem cell-based protocols is to re-establish organ functionality, promote the regeneration of tissues, and treat diseases in a safe and effective way. The type of cell therapy is determined by the pathology一for example, in hematologic cancer, the type of cell therapy is cell transplantation, in musculoskeletal repair, the type of cell therapy is cell injection. It is necessary to learn about those differences to optimize patient outcomes.
Patient Evaluation and Stem Cell Therapy Planning
Specialists carry out a detailed medical examination before any stem cell treatments start, and choose the most appropriate type of stem cell to be used in the treatment. This involves evaluating the status of the patient, his or her immunity, and the risks of transplantation.
Biologists and clinicians work together to determine the best option related to adult stem cell treatments, mesenchymal stem cells, or tissue-specific stem cells. Laboratory tests are used to determine the quality and viability of stem cells, which are subjected to the highest clinical standards.
The planning of the treatment also includes the consideration of the use of autologous (patient-derived) versus allogeneic (donor-derived) stem cells. With autologous procedures, the risk of rejection is minimized, whereas transplantation using donor stem cells can be advocated with patients who have a genetic or bone marrow condition. The precise methodology will be based on the type of disease and the regenerative effect required.
Stem Cell Administration Methods
The mechanism of action of stem cell treatments is the path of delivery. The most prevalent methods are local stem cell injections, systemic infusion, and surgical transplantation of the stem cells.
- In orthopedics, dermatology, and neurology, stem cell injections are introduced into the tissue of the affected area. As an illustration, when the mesenchymal stem cells are injected into damaged muscles or joints, they migrate into the area, release growth factors, and facilitate tissue regeneration
- Infusion therapy is an intravenous administration of human stem cells一mostly in metabolic disorders as well as in autoimmune diseases. These circulating cells can migrate to inflammatory locations and trigger healing, and regulate physiological homeostasis
- Transplantation of stem cells is still necessary in hematology and cancer. This process is done by injecting transplanted cells into the bloodstream of the patient after undergoing high-dose chemotherapy or radiation. The transplantation of the stem cells replenishes the bone marrow activity and assists in the restoration of the immune system
All methods have their own advantages. Local administration offers focused repair effects, whereas systemic delivery has wider immunomodulatory effects. Clinicians should closely monitor patients to assess safety, cell survival, and clinical benefit.
Combined and Advanced Protocols of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell treatments are commonly employed as a component of a holistic treatment approach in most modern clinics along with gene therapy, physiotherapy, pharmacologic support, or biologically active compounds that promote regeneration. By incorporating cell therapy with the targeted molecular therapies, the physicians can enhance cell engraftment, differentiation control, and inhibit immune rejection.
More complex stem cell-based therapies are usually based on stem cells that are grown in rigorous laboratory conditions. These improved preparations are better at the efficiency of tissue repair, especially in cardiac and neurological uses. As an example, mesenchymal stromal cells can be used in conjunction with tissue-specific stem cells as a hybrid protocol to produce synergies in complex diseases.
Individualized stem cell therapies are also coming up. The examination of the genetic and epigenetic markers will allow doctors to choose the most suitable type of stem cells according to the biology of each patient. This is a precision medicine strategy that ensures maximum success in therapy and few side effects.
Stem Cell Therapy Safety and Monitoring
The safety control is a part of every stem cell treatments protocol. The application of stem cells must be under constant monitoring. Cell-based therapy carried out in hospitals should be subject to International Good Manufacturing Practice (GMP), to guarantee the purity and functionality of the administered cells [6].
Follow-up monitoring is the evaluation of the effectiveness of stem cell treatments and patient survival. Most of the time, positive results are realized within a few months, particularly when the use of stem cell-based treatment is considered in combination with multidisciplinary approaches.
With such protocols, physicians can carefully regulate the mechanism of treatment in the human body一be it the localized injection of stem cells or the entire transplantation. The investigation of stem cell physiology and clinical science is still growing and opening up possibilities, allowing doctors to cure diseases at their source and recreate damaged structures naturally.
What to Expect from Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy presents opportunities never seen before, but it has not come without difficulties. It is essential to get to know the potential and the limitations.
Benefits of Stem Cell Therapy
The primary benefits of stem cell-based therapies as a mode of treatment are that they can induce tissue regeneration and restore the functionality of damaged organs. Adult cells therapy and mesenchymal stem cells are able to reduce inflammation, enhance injury repair, and aid in the recovery for orthopedic, cardiac, and neurological disorders. Stem cell-based therapies have now gone a step further and provide pluripotent cells that can be differentiated to almost any cell type, including nerve cells and cardiac muscle cells [7].
Moreover, the regenerative cell therapy can replace damaged cells and also release bioactive factors that boost the repair process of the body itself. Stem cells can balance the immune system, inhibit fibrosis, and enhance long-term disease outcomes in chronic disease.
Limitations of Stem Cell Therapy
In spite of these advantages, there are also some limitations. The behavior of transplanted cells is not predictable一not every adult cell or pluripotent stem cell survives and engrafts as planned and desired. Methods involving the utilization of human embryonic stem cells must be controlled in terms of ethics and regulations. Certain stem cell-based treatments remain experimental, and long-term safety information is unavailable. Treatment options for stem cell therapies may not be available in all regions, and many patients still can not afford them.
Risks of Stem Cell Therapy
Some of the potential risks are immune rejection and unwanted differentiation. As an example, the induced pluripotent stem cells have a low probability of developing cancerous cells unless managed carefully. Patients undergoing transplantation of stem cells have to be closely monitored in order to identify adverse reactions at an early stage.
Appropriate laboratory guidelines and compliance with stem cell physiology requirements are necessary to reduce the risk levels. With the right choice of the type of stem cells, ensuring quality control of blood-based stem cells or mesenchymal stem cells, and proper planning of their administration, the clinician can optimize therapeutic effects and minimize complications.
Future Directions and Innovations in Stem Cell Therapy
The future lies in individualized therapy and innovative developments. Clinicians can now choose the best stem cell types depending on the profile of the particular patient, in order to stimulate tissue regeneration and cure an illness. The complex protocols integrate injection, infusion, and transplantation of stem cells with the enhancement of genetic modification or cell-based therapy, and improve survival and integration of transplanted cells. Human embryonic stem cells and blood stem cells are designed to restore hematopoiesis in blood cancer, and patient-specific nerve cells provide a new solution to the spinal cord and neurodegenerative diseases in neurology. Modern stem cell technology, supported by these innovations, now makes it possible to produce scalable, healthy cells. It is a new environment in which individualized, biologically precise stem cell-based therapies can become a clinical reality.
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex management programs in each individual case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you in pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods and with leading specialists in this field.
Stem Cell Therapy: Patient Stories with Booking Health
FAQ: Comprehensive Guide to Stem Cell Therapy
Send request for treatmentStem cell therapy involves the exploitation of the regenerative capability of stem cells to heal damaged tissues, regenerate organ functions, and treat diseases. It is used in various spheres of medicine, such as neurology, orthopedics, cardiology, oncology, and endocrinology.
Costs of stem cell therapy differ depending on the type of cells, the treatment that the patient requires, and the location of the clinic. Complex regimens are usually more costly than localized infusion or stem cell injections.
There may be some side effects, such as inflammation, immune response, or some minor procedural complications. Clinics focus on mechanism-based protocols and monitoring to reduce risks and maximize the regenerative capability of the therapy.
This is true because stem cell therapy utilizes cell regenerative capacity. In regenerative medicine, clinical results indicate positive changes in tissue repair, organ functioning, and disease control in various conditions.
Some of these include adult stem cells, mesenchymal stem cells, tissue-specific stem cells and others. Depending on the patient’s needs and the type of disease, stem cell therapy may involve injections, transplants, or infusions.
Stem cell therapeutic intervention has the potential to treat various diseases, such as neurodegenerative diseases, orthopedic injuries, cardiac damage, hematologic disorders, endocrine disorders, as well as ophthalmologic problems.
Stem cell therapy can be done through localized injections of stem cells, systemic infusions, cell transplantation, and a combination of the regenerative medicine strategies. The decision will be based on the state of a patient, the type of cell used, and the regenerative potential the patient wants.
The advantages are repair of tissues, regeneration of organs, and enhancement of functioning, whereas the disadvantages are inflammatory responses or abnormal proliferation of the cells. It is not only a careful choice of the cell type, but also adherence to the mechanism of therapy, which is a guarantee of safe and effective results.
Yes, several studies prove that stem cell therapy is able to enhance organ functioning, decrease complications, and promote recovery. It has been proven to be beneficial in regenerative medicine with positive results recorded in the field of neurology, orthopedics, cardiology, and hematology.
Yes, medical tourism programs provide therapies for international patients. Booking Health support assists in clinics selection, organizing treatment programs, and legal matters, which helps foreign patients to get access to treatment abroad.
Germany offers some of the most advanced methods of stem cell therapy. German hospitals provide specialized regenerative medicine programs – ensuring treatments are safe, personalized and closely monitored.
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Mahshid Bahari, Hossein Mokhtari, Farshid Yeganeh. Stem Cell Therapy, the Market, the Opportunities and the Threat. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2023;12(3):310–319. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.12.3.310. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[2] Duc M Hoang, Phuong T Pham, Trung Q Bach et al. Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 6;7:272. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01134-4. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[3] Dinh-Toi Chu, Tiep Tien Nguyen, Nguyen Le Bao Tien et al. Recent Progress of Stem Cell Therapy in Cancer Treatment: Molecular Mechanisms and Potential Applications. Cells. 2020 Feb 28;9(3):563. doi: 10.3390/cells9030563. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[4] Ramyar Rahimi Darehbagh, Seyedeh Asrin Seyedoshohadaei, Rojin Ramezani, Nima Rezaei. Stem cell therapies for neurological disorders: current progress, challenges, and future perspectives. Eur J Med Res. 2024 Jul 25;29:386. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01987-1. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[5] Xin-Xing Wan, Dan-Yi Zhang, Md Asaduzzaman Khan et al. Stem Cell Transplantation in the Treatment of Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: From Insulin Replacement to Beta-Cell Replacement. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 18;13:859638. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.859638. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[6] Ammar Aljabri, Alhussain Halawani, Ghassan Bin Lajdam et al. The Safety and Efficacy of Stem Cell Therapy as an Emerging Therapy for ALS: A Systematic Review of Controlled Clinical Trials. Front Neurol. 2021 Dec 1;12:783122. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.783122. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[7] A Leventhal, G Chen, A Negro, M Boehm. The benefits and risks of stem cell technology. Oral Dis. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2013 Aug 27. Published in final edited form as: Oral Dis. 2011 Nov 18;18(3):217–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2011.01870.x. [DOI]
Read:
Article menu:
- Stem Cell Therapy: Mechanisms and Types
- Medical Fields & Indications for Stem Cell Therapy
- Treatment Options and Protocols of Stem Cell Therapy
- What to Expect from Stem Cell Therapy
- Future Directions and Innovations in Stem Cell Therapy
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
- FAQ: Comprehensive Guide to Stem Cell Therapy
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health