Germany is one of the most preferred destinations for stem cell therapy thanks to its strong scientific background, reliable healthcare system, and many clinics where this kind of therapy is carried out. Because of that, the country has become a place of choice for international patients looking for new medical solutions in regenerative medicine. Here, mesenchymal stem cells are used to repair damaged tissues, improve the immune system, and help in the treatment of different health conditions.
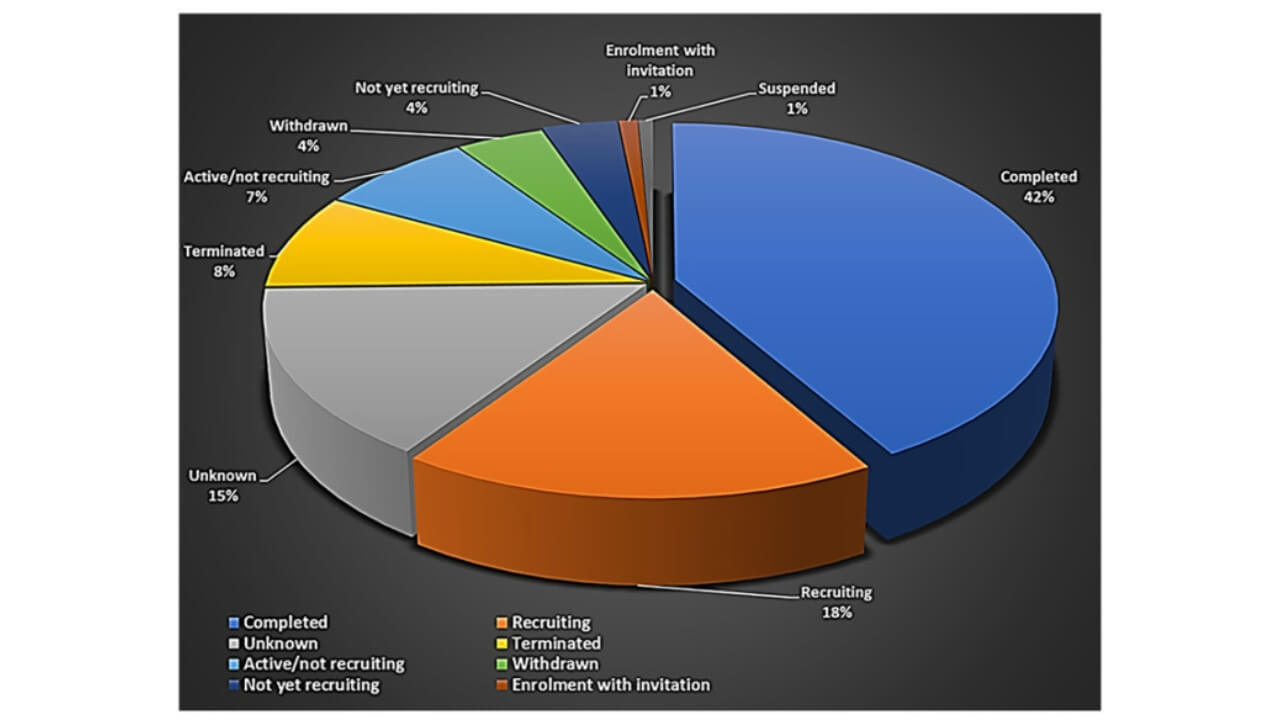
The number of companies working in regenerative medicine, including stem cell therapy, has been growing fast — from about 772 in 2016 to more than 1,550 in 2024 [1, 2]. By February 2023, over 8,000 clinical trials on stem cell products had been completed or were still running worldwide [3]. The global market for stem cell therapy grew by about 25.5% between 2015 and 2022, reaching almost US$297 billion by the end of 2022 [4].
All these numbers show how quickly the field is developing. Germany’s progress in stem cell therapy combines experience, safety, and innovation, which allows its doctors to offer advanced regenerative treatment to people from different countries.
What Is Stem Cell Therapy and How It Works
One of the most developed branches of regenerative medicine is stem cell therapy, where human cells are used to regenerate damaged organs and tissues. In Germany, the field has moved from experimental research to real clinical practice, giving international patients access to treatments that are backed by solid science. This treatment takes advantage of the fact that stem cells have a self-renewing capacity一they can differentiate into specific cell types and, as a result, they form a biological repair system that has the ability to regenerate tissues.
Types of Stem Cells and Their Characteristics
It is important to know the different types of stem cells to understand the mechanisms of cell therapy in Germany:
Embryonic Stem Cells (ESCs)
- These pluripotent cells, which are derived from the embryonic cells during their early stages, are capable of producing any type of cell in the body
- They possess enormous regenerative capabilities, which qualify them as an ideal resource for experimental therapies in neurology, cardiology, and rare degenerative disorders
- The main reason embryonic stem cells are used mainly in research is due to ethical concerns and strict regulations
Adult Stem Cells (ASCs)
- These multipotent cells are found in the bone marrow, adipose tissue, and several other organs. They can develop into a limited range of cell types related to the tissue they come from.
- The application of autologous cells in clinical practice is favorable due to their low tendency to be rejected by the immune system and also due to their non-controversial nature.
- They are also important in the healing of musculoskeletal injuries, in the rehabilitation of heart tissue following a heart attack, and in regulating immune reactions.
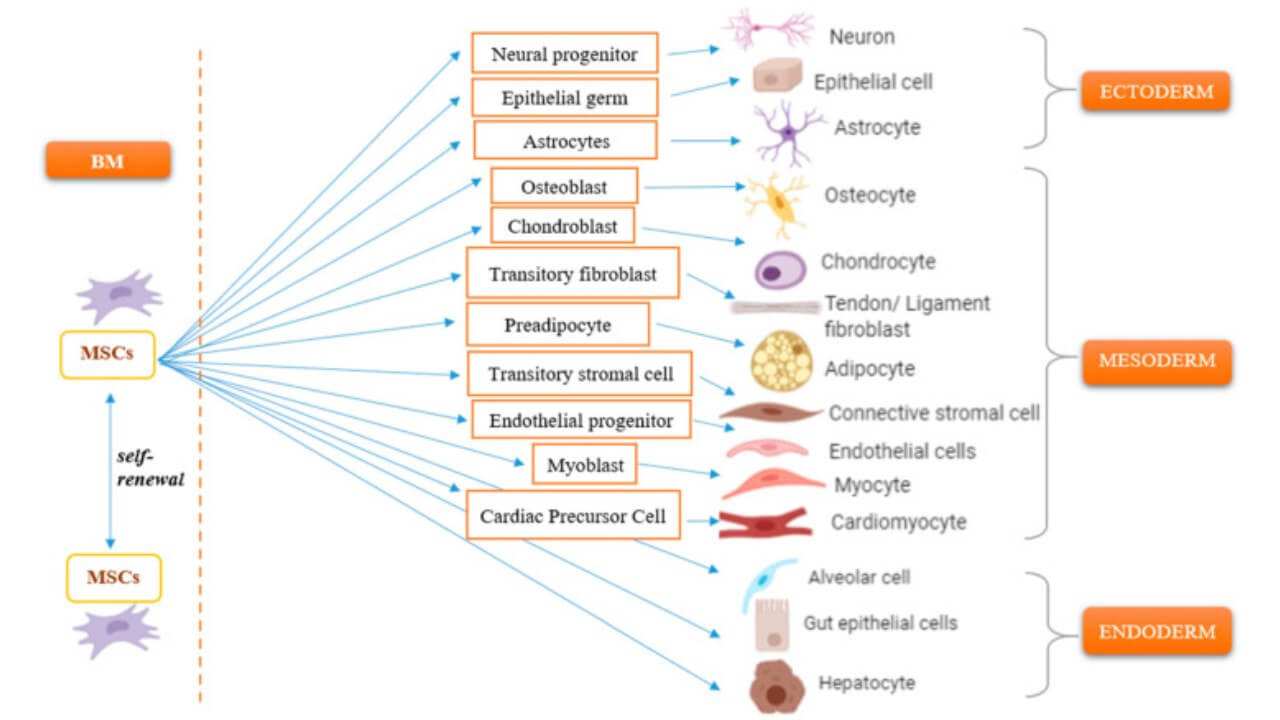
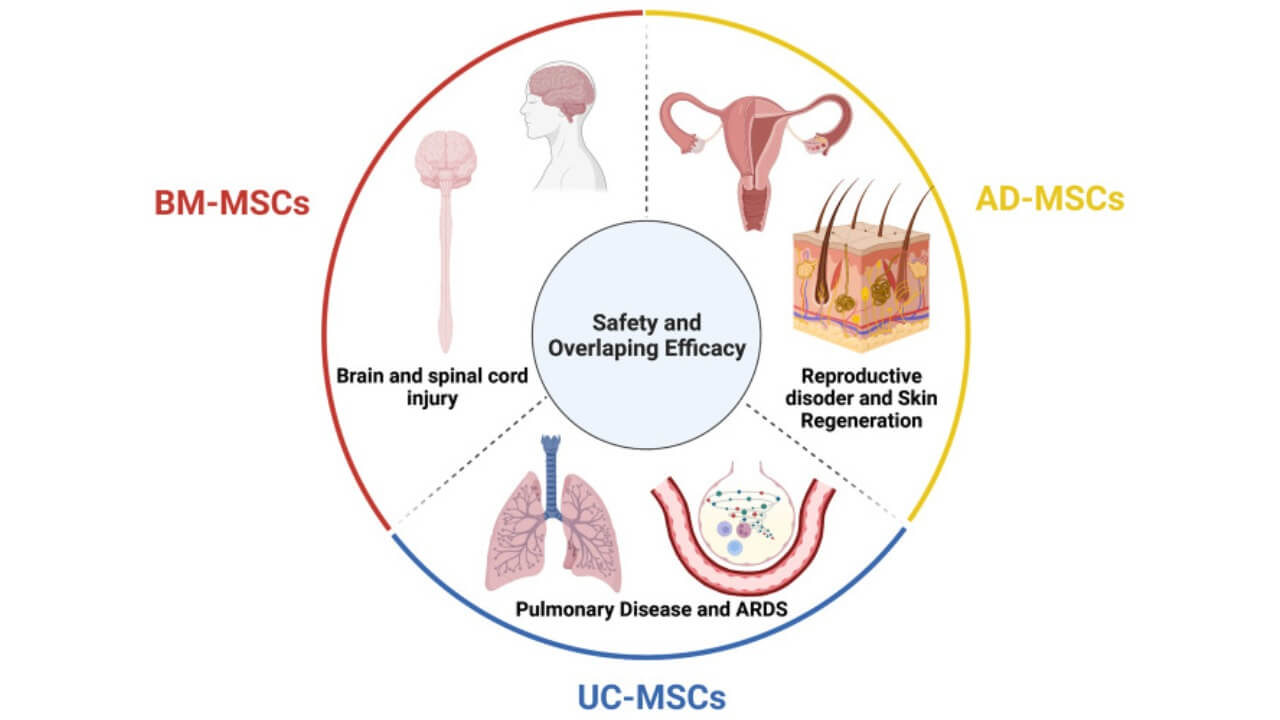
Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs)
- A high immunomodulatory subtype of adult stem cells.
- MSCs have the potential to inhibit hyperreactive immune system responses in autoimmune diseases, facilitate anti-inflammatory reactions, and release trophic factors that trigger local tissue healing.
- They are retrieved from bone marrow, fatty tissue, and umbilical cord blood and are commonly used for clinical purposes.
Hematopoietic Stem Cells (HSCs)
- The one in charge of the production of all blood cells, including the red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets
- HSCs play a vital role in cancer therapy, particularly among those who are recipients of chemotherapy or bone marrow transplant
- They also aid in the recovery of the immune system and long-term hematologic stability
Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
- Adult cells that have been reprogrammed to a pluripotent cell state, which can be differentiated into various cell types
- iPSCs have the same potential as embryonic stem cells and the advantages of autologous adult cells, offering both ethical and immunological safety
- They are applied in research to model diseases, to test new therapies, and possibly create personalized regenerative therapies
Mechanism of Stem Cell Therapy
Stem cell therapy is based on a combination of regenerative and immunomodulatory processes. Upon their introduction into the body, stem cells travel to the place of injury or inflammation, differentiate into the required cell types, and become a natural part of the tissue structure [6]. They also release bioactive molecules, such as growth factors and cytokines, that can stimulate nearby injured tissues, induce angiogenesis, minimize fibrosis, and mobilize resident cells to engage in repair. Meanwhile, the immune system is regulated with the assistance of some stem cells, especially mesenchymal stem cells, which suppress the overactive immune response, protecting healthy tissues. This immunogenic-tissue regeneration combination is the basis of cell therapy in Germany and the reason why it is effective in multiple conditions.
Scientific Evidence and Ongoing Research
Multiple clinical trials conducted in many countries across the world have established that stem cells have the potential to enhance tissue healing, reduce disease symptoms, and quality of life in neurological, cardiovascular, orthopedic, and autoimmune diseases. Researchers are working on the best sources of various types of stem cells, dosage, and method of administration to enhance safety and efficacy. The studies investigate stem cell therapy application in combination with gene editing, bioengineered scaffolds, and targeted delivery to utilize most of the regenerative capabilities and come up with a personalized solution. Stem cell therapy in Germany is thus a highly advanced form of medicine, involving the regenerative and immunomodulatory potentials of the endogenous stem cells to repair the injured tissue and aid in long-term recovery.
Medical Indications and Applications in Germany
Germany stem cell therapy has shown remarkable success in treating a wide range of medical conditions that traditional medicine cannot fully heal. The combination of innovation and high clinical safety is used in German clinics where cell therapy is integrated into the multidisciplinary approach for neurological, autoimmune, orthopedic, and internal organ diseases. The leadership of Germany in regenerative medicine and biotechnology makes the country a world center for attracting international patients in need of effective stem cell treatment solutions.
Neurological and Neurodegenerative Diseases
One of the most studied fields where the German stem cell therapy can be applied is the neurodegenerative disorder. The stem cells can differentiate to form neurons and glial cell types, which are applicable in repairing the neural functions after injury or disease. Cell therapy is applied in the treatment of such conditions as Parkinson's disease, multiple sclerosis, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), and stroke.
Stem Cell Therapy for Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis
Stem cells today make it possible to actually support the functioning of motor neurons in ALS. They do not just protect nerve cells, but also restore connections between them, reduce inflammation and help restore signals in the spinal cord. Patients experience stabilization of muscle strength, improved motor functions and greater independence in daily life.
This method has already helped many people regain control over their own bodies and experience noticeable changes in daily activity. Learn more about the results of the therapy and its practical application in the following video.
Stem Cell Therapy for Spinal Cord Injuries
Spinal cord injuries no longer mean complete loss of motor or sensory functions. Stem cells restore neurons, improve connections between nerve fibers and stimulate regeneration of damaged areas. As a result patients regain control over their movements, experience improved sensitivity and can resume activities they previously thought were impossible.
Real patient stories confirm the effectiveness of this method and its life-changing ability. Learn how the treatment works and what results patients get in the thematic video.
Stem Cell Therapy for Autism in Children
Stem cells open up new possibilities in supporting children with autism. These cells help to improve the functioning of neuronal networks, stimulate the development of speech, social interaction and emotional regulation. The introduced cells help restore neuronal connections and improve the overall condition of the nervous system. Parents notice that children become more attentive, active and open to interaction. They also observe a reduction in behavioral symptoms of autism.
Real results are already available in practice: the patient's mother, Cindy Johnson, shares how the therapy helped her child improve communication skills and overall development. Learn about her experience and the effectiveness of the method in the video below.
Autoimmune and Inflammatory Disorders
Autoimmune diseases represent another important field of cell therapy in Germany, where the body’s immune system attacks its own cells. In this case, stem cell treatment is a regenerative and immune-modulating treatment. Adult cells and mesenchymal stem cells are being used in the treatment of conditions like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, Crohn’s disease, and type 1 diabetes. These stem cells are able to reprogram the immune response and prevent chronic inflammation in healthy tissues. Stem cell therapy in Germany, in such cases, assists the patients to reach long-term remission, which minimizes the reliance on steroids or immunosuppressants.
Musculoskeletal and Orthopedic Disorders
Regenerative medicine plays an important role in the management of injuries and degenerative disorders of bones, cartilage, and joints. Cell therapy is a regular practice in German clinics for the treatment of osteoarthritis, tendon rupture, and post-traumatic bone damage. The adult cells, which are usually derived from mesenchymal stem cells found in the adipose tissue or the bone marrow, are used in the creation of new cartilage and bone tissues, which result in faster healing and enhanced mobility.
The stem cell therapy in Germany can repair the integrity of joints and alleviate pain without involving any invasive operation that characterizes traditional surgeries or other methods of treatment. This will be particularly useful for professional athletes and international patients who are interested in finding alternatives to joint replacement surgeries. The application of stem cells as a way of repairing musculoskeletal structures underscores the ability of best stem cell therapy to change orthopedic care.
Learn more about how this therapy works and its benefits in the comprehensive interview with Prof. Stehling.
Organ Damage and Internal Medicine Applications
In addition to neurology and orthopedics, internal medicine is another area where stem cell therapy is used, particularly in cardiology, hepatology, and nephrology. Angiogenesis of the heart is promoted by the introduction of stem cells for patients with myocardial infarction, thus repairing the damaged tissue of the heart, enhancing its contractile ability. On the same note, cell therapy in Germany promotes the healing of the organ tissues in chronic cases of liver and kidney diseases, decreasing fibrosis and restoring normal functioning of the organ.
The role of stem cell treatment in oncological diseases is also being researched in German clinics, where it can be used to promote recovery following chemotherapy or for immune system regeneration. In most clinical trials, the use of stem cell therapy and other advanced medical technologies is providing fresh possibilities for patients who have tried other forms of treatment elsewhere.
Stem Cell Therapy for Erectile Dysfunction
Modern stem cell therapy opens up real chances to restore erectile function without the use of complex or invasive procedures. The cells activate the natural processes of tissue repair, restore the functioning of nerve endings and blood vessels, improve blood supply and reduce inflammatory processes. Thanks to this, erections become more stable, sensitivity is higher and sexual activity is natural and confident.
Patients note a noticeable improvement, and Thomas has already been able to fully restore erectile function and regain self-confidence. His story clearly demonstrates that the method works and gives tangible results. Learn more about his experience in the video below.
Stem Cell Therapy in Anti-aging Medicine
Stem cells are actively used in modern anti-aging medicine. They improve metabolism at the cellular level and stimulate the body's natural regeneration processes. They reduce inflammation, support the cardiovascular system, improve skin elasticity and normalize the body's energy balance. Patients note not only an improvement in the appearance of the skin and its elasticity, but also an overall feeling of vigor, increased endurance and tone.
The method demonstrates real results and noticeable changes in practice which makes it one of the most promising approaches in modern rejuvenation medicine. Learn more about the results of the therapy in the following video.
Stem Cell Therapy for Optic Nerve Atrophy
Modern stem cells open a new approach to the treatment of optic nerve atrophy一a condition that was previously considered almost incurable. This method not only supports vision, but also stimulates the regeneration of nerve fibers, improves blood supply and creates favorable conditions for the restoration of signal transmission from the eye to the brain.
The most common treatment is mesenchymal stem cells, which can be administered locally (parabulbar or retrobulbar) or systemically. Their strength lies not only in the ability to partially replace damaged cells, but primarily in the release of growth factors that protect neurons, reduce inflammation and support tissue nutrition. The results of many patients demonstrate a noticeable improvement in visual functions and stabilization of the process of vision loss.
An example of success is the story of Sofia, who shared how the therapy helped her restore her vision and regain confidence in everyday life. Details of her experience and treatment results can be viewed in the video below.
Summary of Therapeutic Scope
Overall, there are over 80 disease categories for which German stem cell therapy is implemented. The unceasing study of scientists and medical professionals makes cell therapy in Germany evidence-based and constantly changing. A combination of adult cells, embryonic stem cells, and new types of cells that may be produced in laboratories enables clinicians to build personalized medical treatment with low risks and high clinical results.
Stem cell therapy in Germany is one of the most progressive areas of global medicine, providing not only treatment but also a path to recovery that will restore not only health but also quality of life for many international patients.
Treatment Options and Protocols in Germany
We can identify versatility and personalization in stem cell therapy in Germany. German clinics apply many different methods of cell therapy delivery depending on the disease and the personal requirements of the patient. This guarantees the highest level of therapeutic effect and safety.
Injection-Based Therapies
Local injection of adult stem cells or mesenchymal stem cells into the damaged tissues is one of the most widespread methods in Germany. Intra-articular injections enable local repair of cartilage, tendons, and ligaments when it comes to orthopedic or musculoskeletal diseases. In the same way, localized injections are employed in dermatology and wound healing.
This approach ensures that the therapeutic cells are delivered precisely to the site of injury, maximizing their regenerative potential while minimizing systemic risks. In Germany, cell therapy is usually combined with rehabilitation therapy and local injections to speed up recovery.
Intravenous Infusions
In cases of systemic disease, e.g., autoimmune or neurodegenerative conditions, intravenous stem cell therapy is commonly used. In this case, stem cells are transported in the blood and targeted at injured tissues or organs. This approach has the capability of regulating the immune system, lowering inflammation, and repairing various parts of the body at the same time. The efficacy and safety of intravenous administration of adult cells and embryonic stem cells under controlled hospital conditions have been proven by numerous clinical trials in Germany.
A combination of intravenous infusions with other therapies, such as immunotherapy, plasma therapy, or pharmacological regimens, is also a common procedure that leads to a synergistic effect, which improves tissue regeneration and patient outcomes.
Local and Organ-Specific Delivery
Other German procedures of stem cell therapy apply to organ-targeted therapy. For example, the injection of stem cells into the heart muscle can be used for myocardial infarction, promoting angiogenesis and recovery of contractile activity. In liver or kidney diseases, direct delivery to the affected organs enhances the effectiveness of stem cell-based therapy and minimizes the side effects.
Local delivery techniques are often used in conjunction with imaging guidance, such as ultrasound or MRI, to ensure accuracy and safety. German clinics focus on the fact that individualized patient assessment and proper diagnostics determine the choice of the delivery method.
Combination Therapies
In Germany, stem cell therapy is often combined with other treatments in order to maximize the results. For cancer patients, the therapy can be used to supplement chemotherapy and immunotherapy, as it stimulates faster recovery of the immune system and aids in repairing damaged tissues. In the case of musculoskeletal injuries, platelet-rich plasma, physiotherapy, or scaffold implants are used together with stem cells to promote tissue regeneration and functional recovery.
This multi-modal strategy shows the flexibility of German stem cell therapy programs and emphasizes the significance of an individual approach developed by medical specialists. This is because the combination of administration procedures with supportive therapies allows international patients to achieve maximum benefits safely and effectively.
Comparison: Stem Cell Therapy in Germany vs. Other Countries
| Criteria | Germany | Other Countries |
|---|---|---|
| Regulatory Standards | Strict EU and German medical regulations ensure patient safety and transparent quality control of all stem cell treatments. | Regulations vary; in some regions, stem cell therapy is still poorly standardized or lacks clinical oversight. |
| Clinical Experience | Over 20 years of expertise in cell therapy and regenerative medicine; thousands of successful treatments in certified German clinics. | Experience and infrastructure depend on location; some centers are still in the early clinical trials phase. |
| Cell Sources and Technology | Advanced processing of adult stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells; cutting-edge biotechnologies for damaged tissue repair. | Limited access to high-quality cell types or less advanced lab technologies. |
| Medical Supervision | Procedures performed by board-certified medical experts under strict hospital conditions. | Varies widely; sometimes performed in non-hospital environments. |
| Therapeutic Results | Proven improvement in neurological, autoimmune, orthopedic, and cardiac medical conditions; supported by European scientists. | Variable success rates; many programs lack long-term follow-up data. |
| Accessibility for International Patients | Germany's stem cell therapy programs are open to international patients with multilingual support and transparent coordination. | Some other countries have limited visa or communication assistance. |
Patient Journey: What to Expect
Going to Germany to receive the stem cell treatment is a well-organized process that strives to provide maximum safety, transparency, and positive clinical results for the patient. German clinics follow established protocols that integrate diagnosis, patient assessment, therapy preparation, and procedure execution.
Diagnosis and Initial Consultation
The first step is a comprehensive analysis of the patient’s medical condition. This involves a review of medical history, laboratory tests, imaging, and previous treatment. At this stage, medical professionals determine the most appropriate stem cell treatment and select the optimal types of cells to be used. In the case of an oncological disease or long-term damage to vital organs, consultations of multidisciplinary teams guarantee the choice of the most effective regenerative approaches.
Assessment of Suitability
After the diagnostics is done, patients will be assessed for eligibility. The potential to regenerate damaged tissue and regulate the immune system is what makes the adult stem cell therapies, or, in particular cases, embryonic stem cells, considered. The stem cell therapy Germany programs are very meticulous in considering factors like age, disease progression, and comorbidities to reduce the risk of harm and ensure that the therapeutic efficacy is high.
Preparation for Therapy
Preparation involves pre-treatment counseling, lab work, and, in some cases, other treatments. In Germany, preparation involves harvesting cells from adipose tissue or bone marrow, or growing them in certified laboratories. Patients are informed about the procedures, potential side effects, and post-treatment care, ensuring a transparent and comfortable experience.
Procedure and Administration
The procedure itself is done in hospitals, and its performance is strictly monitored. Stem cell therapy can also be done by means of local injections or intravenous delivery, depending on the protocol. The process is customized for the patient's needs, and in many cases, they have supportive regenerative medicine procedures to improve healing. German cell therapy focuses on evidence-based methods, accuracy, and safety.
Post-Treatment Follow-Up
Following the procedure, patients undergo follow-up care, which includes monitoring response, managing side effects, and incorporating rehabilitation or additional therapy. Regular assessments are usually done to monitor the improvement in functionality and tissue regeneration after stem cell-based therapies. For international patients, German clinics continue their care after discharge, providing additional guidance and support remotely.
Stem Cell Therapy for Children with Neurological Disorders
Samantha, USA: "Last year, our lives turned into real hell! Our child started having epilepsy seizures. He cried and hit his face with his hands without any obvious reason. Similar seizures occurred almost every day! They mostly happened in the morning, almost immediately after waking up. I learned about stem cell therapy in Germany, so we flew there to undergo the procedures. Improvement was seen immediately, and the child did not have a seizure the following morning. I can see that the child has started sleeping better and rarely shows any negative emotions now. I also notice a smile on his face more often! I hope that the results from the stem cells will last and continue to improve after the follow-up procedures."
Most doctors consider stem cells to be the most promising area of treatment for diseases of the central nervous system. So far, it is generally accepted that "nerve cells cannot be regenerated". However, the use of cell therapy in the past few years refutes this thesis. Many clinical trials test the effect of the patient's own adult stem cells and donor stem cells, including embryonic stem cells, on the body. The doctors usually get good results – in 60-70% of cases, parents note improvements in their child’s behavior.
It is assumed that the mechanism of stem cell therapy in autism is associated with the restoration of the damaged brain structures. Although the first results from therapy can be obtained immediately, they are expected to improve over the coming weeks and months due to the restructuring of the problematic parts of the central nervous system. The doctors mostly practice the introduction of autologous (the patient's own) stem cells, since this procedure is absolutely safe.
Scientists are still obtaining further evidence of the effectiveness of cell therapy. A 2015 study by Michael Chez demonstrated the restoration of the ability to initiate social interactions and form relations after stem cell therapy in more than 50% of patients. A study at Duke University (USA) showed alleviated autism symptoms (according to a survey) in 60% of patients.
Thus, the use of stem cells for autism is a promising area of treatment. It may be used as a standard treatment method in the future. But so far, this treatment method is not available to all patients, since it is expensive and only available in a limited number of clinics. Many parents go with their children to Germany for treatment.
Stem Cell Therapy: Patient Stories with Booking Health
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex management programs in each individual case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you in pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods and with leading specialists in this field.
FAQ: Stem Cell Therapy in Germany
Send request for treatmentYes, in Germany, stem cell treatment is available in qualified German clinics. Advanced protocols with adult stem cells and mesenchymal stem cells are used for regenerative and immune-modulating applications in cases of autoimmune, neurological, musculoskeletal, and organ-specific conditions.
Germany is regarded as a pioneer in the area of stem cell treatment, where the safety standards and number of medical professionals are high, and the laboratory equipment is well-developed. It is one of the best treatments for patients across the globe due to its combination of regenerative medicine and the evidence-based mechanism of stem cell therapy.
Stem cell therapy in Germany is used in a wide range of diseases, such as neurodegenerative, autoimmune, orthopedic, cardiovascular, and certain types of oncological diseases. Ongoing clinical trials are also exploring new indications that expand the potential uses of stem cells.
Some of the approaches to stem cell treatment in Germany are local injections, intravenous infusion, organ-targeted delivery, and combination with other treatment methods like immunotherapy or physiotherapy. Individualized protocols guarantee that cells arrive at the injured tissue in a safe and effective way.
Booking Health support assists in choosing the appropriate clinics in Germany, arranging the appointment, making diagnostics, and planning the travel for international patients. They provide therapy prescriptions, insurance support, and after-care services, making access to stem cell therapy in Germany easy.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Dong-Sook Kim, SeungJin Bae. Impact and challenges of enactment for advanced regenerative medicine in South Korea. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Oct 12:10:972865. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.972865. eCollection 2022. [DOI] [PubMed]
[2] BioInformant. Global Regenerative Medicine Industry Database – Featuring 1,920+ Companies. https://bioinformant.com/product/regenerative-medicine-companies/
[3] Clinical trial.gov. https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/search?cond=Stem%20Cells
[4] Mahshid Bahari, Hossein Mokhtari, Farshid Yeganeh. Stem Cell Therapy, the Market, the Opportunities and the Threat. Int J Mol Cell Med. 2023;12(3):310–319. doi: 10.22088/IJMCM.BUMS.12.3.310. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[5] Mohammad Mousaei Ghasroldasht, Jin Seok, Hang-Soo Park, Farzana Begum Liakath Ali, Ayman Al-Hendy. Stem Cell Therapy: From Idea to Clinical Practice. Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 5;23(5):2850. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052850. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[6] Lina N Zaripova, Angela Midgley, Stephen E Christmas et al. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in the Pathogenesis and Therapy of Autoimmune and Autoinflammatory Diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 7;24(22):16040. doi: 10.3390/ijms242216040. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[7] Duc M Hoang, Phuong T Pham, Trung Q Bach et al. Stem cell-based therapy for human diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022 Aug 6;7:272. doi: 10.1038/s41392-022-01134-4. [DOI] [PMC free article]
Read:
A Comprehensive Guide to Stem Cell Therapy
Article menu:
- What Is Stem Cell Therapy and How It Works
- Medical Indications and Applications in Germany
- Treatment Options and Protocols in Germany
- Comparison: Stem Cell Therapy in Germany vs. Other Countries
- Patient Journey: What to Expect
- Stem Cell Therapy for Children with Neurological Disorders
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
- FAQ: Stem Cell Therapy in Germany
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health