Pulmonary malignancy remains one of the leading causes of oncological mortality in the world, and that is why a correct understanding of the level of disease progression is critically important for both doctors and patients. Determining the level of spread of the disease is not a formality, but a key aspect that directly affects the prognosis, choice of therapy, and the possibility of using modern treatment methods.
The lung cancer staging process is based on assessing the size of the primary tumor, the state of the lymph nodes, and the presence of distant metastases.
Today, knowing the extent of pulmonary disease opens up access for the patient not only to standard protocols, but also to personalized strategies, including targeted and immunotherapy. That is why more and more patients are considering lung cancer treatment abroad, where advanced diagnostic capabilities, molecular profiling of tumors, and a multidisciplinary approach to treatment are available.
Lung Cancer Stages and the Importance of Accurate Lung Cancer Staging
One of the most life-threatening oncological diseases is lung tumor. A clear understanding of lung cancer staging is therefore fundamental: staging explains how far the disease has progressed, whether cancer has spread beyond the airways, and which treatment plan can offer the best possible outcome.
According to histological structure, small cell lung cancer and non-small cell lung carcinoma (including adenocarcinoma, large-cell carcinoma, and squamous cell carcinoma) are distinguished.
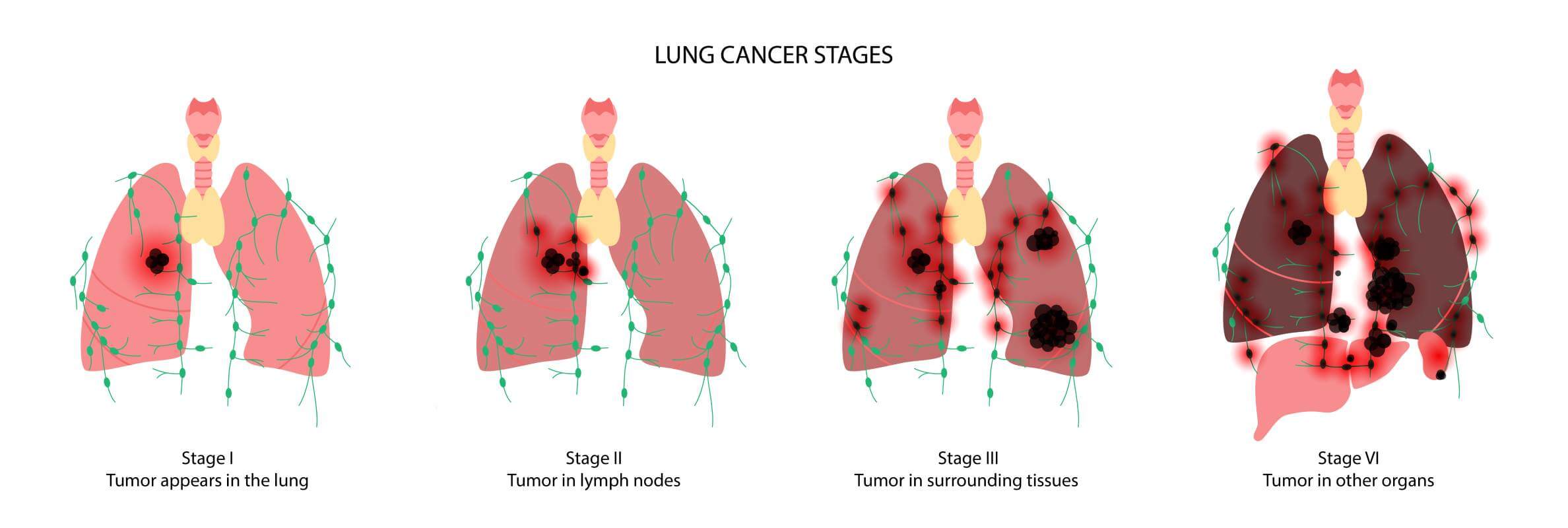
Each cancer stage reflects a specific level of disease spread – from early stage, when the tumor is localized, to advanced lung cancer, including metastatic lung cancer (stage 4), when distant organs are involved.
Why accurate staging is essential for treatment decisions
Correct lung cancer staging directly determines whether curative treatment is possible or whether therapy will focus on disease control. In the early stage of the disease, surgery and localized treatment may offer long-term survival. In contrast, when other lung structures or distant organs are involved (cancer has spread), systemic therapy becomes the cornerstone of care.
Importantly, precise lung cancer staging opens access to advanced diagnostics and innovative therapies. Many patients seek lung cancer treatment in Germany, where high-resolution imaging, molecular profiling, and multidisciplinary teams can accurately diagnose lung cancer and make an individualized decision on treatment.
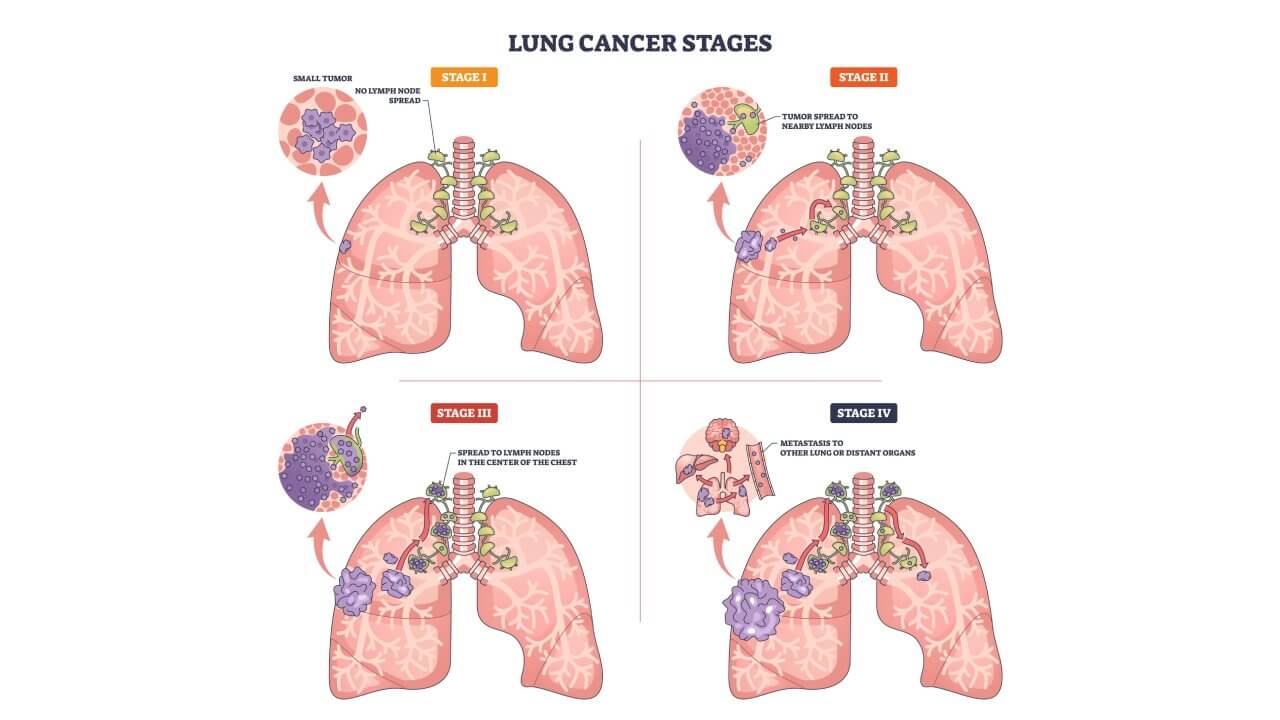
Lung Cancer Staging Systems: TNM Staging for Lung Cancer and SCLC Staging
The process of lung cancer diagnosis begins immediately after the morphological or cytological result of biopsy. It is from this moment that an understanding of the nature of the pathological process and its further behavior is formed. Proper staging allows you to accurately understand how lung cancer cells behave in a particular patient: whether the process is limited to the primary focus, involves lymphatic structures, or has signs of systemic spread. This is key for predicting the course of the disease and choosing the optimal treatment tactics.
Depending on the biological type of the disease, different approaches are used for this assessment. One is based on a detailed anatomical description of the extent of the process (TNM system), while the other, a simplified clinical approach (limited/extensive), is used for aggressive forms. Both systems have a common goal: to provide a clear picture of the extent of the disease and possible therapeutic options.
TNM for NSCLC
For non-small cell lung carcinoma, the international TNM system is used, which is the basis for determining the clinical extent of the disease. It is used after doctors can diagnose lung cancer and confirm the histological type of the tumor.
The TNM system assesses:
- T (Tumor) – size and local spread of the primary tumor.
It takes into account how large the tumor is, whether it is limited to pulmonary tissue, whether it has grown into the bronchi, pleura, or adjacent structures of the chest. As the T score increases, the local aggressiveness of the process increases.
- N (Nodes) – involvement of regional lymph nodes.
Not only is the fact of node involvement assessed, but also their location, from intrapulmonary to mediastinal. It is the N component that often determines whether surgical treatment is possible.
- M (Metastasis) – presence of distant metastases.
If metastases are detected, the disease automatically enters the metastatic one, regardless of the size of the primary tumor.
The combination of T + N + M scores forms the overall clinical stage (I–IV), which is used to plan treatment for NSCLC.
Staging for small cell lung cancer (SCLC)
Small cell lung cancer is characterized by rapid growth and early metastasis, so in addition to TNM, another simplified staging system is used for it. Once lung cancer is diagnosed, SCLC is divided into:
- limited stage - the tumor is limited to one half of the chest and can be covered by a single field of radiation therapy
- extensive stage – the process extends beyond one lung, which effectively corresponds to stage IV lung cancer in the clinical sense
This approach reflects the biology of the disease, where even at the time of the initial examination, lung cancer cells are often already circulating outside the primary tumor [1].
The distinction between TNM for NSCLC and limited/extensive for SCLC determines:
- the possibility of surgical treatment,
- the appropriateness of radiation therapy,
- the choice of systemic therapy,
- the prognosis of the disease.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Stages: Stage 1 to Stage 4 Overview
When pulmonary malignancy is initially diagnosed, the first thing to understand is what level of the progression is in. This is what the stages of non-small cell lung cancer reflect: they show whether the process is limited to the pulmonary tissue, has become locally advanced, or has become metastatic with distant metastases.
Stage I lung cancer: early, localized tumor
Within stage I, the tumor is confined to the pulmonary tissue and has not spread to the lymph nodes. Therefore, stage 1 lung cancer is often associated with the highest chances of complete control of the process, since it has not yet acquired a systemic character.
The process is considered local: there are no signs of spread beyond the primary zone, which allows the use of treatment methods with a radical goal. The biological behavior at this level is significantly different from later forms, where additional anatomical structures are involved.
This level is divided into IA1, IA2, IA3, and IB. The main difference between them is usually associated with the size of the primary formation and minimal local features. At the same time, the general logic remains unchanged: the process remains local and does not yet show signs of systemic spread. [2].
Such a division allows you to more accurately assess the prognosis and choose the optimal treatment tactics, taking into account the individual characteristics of the disease.
Stage II lung cancer: larger tumor or early signs of lymph node involvement
When talking about stage 2 lung cancer, it usually means that the tumor has become larger or there are signs of involvement of nearby lymph nodes. At this level of the disease, the tumor can still potentially be controlled with local methods, but a combination of treatments is often needed.
The process gradually moves from a purely local to a locoregional one, which changes the approach to therapy. At this period, a single method of influence is often not enough, so combined strategies are preferred, which combine local treatment with additional systemic approaches to reduce the risk of relapse.
This period of the disease is not homogeneous and is divided into stage IIA and stage IIB. They differ in the degree of local spread of the process and the volume of structures involved. This division allows for a more accurate assessment of the prognosis and adaptation of treatment to the specific clinical situation.
Despite the greater complexity compared to the first level, at this phase, there is still the possibility of effective disease control provided that a timely and individualized approach is taken.
Stage III lung cancer: locally advanced disease
Stage III is already locally advanced cancer, when the process goes beyond the pulmonary tissue: it can involve the mediastinal lymph nodes or adjacent structures of the chest.
This period is characterized by locoregional spread, when the lesion is still confined to the chest, but requires more complex and coordinated treatment approaches. It is here that an accurate assessment of the extent of the process and its biological behavior plays a crucial role.
Within this level, it is important to understand the logic of the subcategories. For example, stage IIIA is sometimes considered a borderline variant, where surgery may be considered in some cases after prior treatment aimed at reducing the volume of the lesion. In contrast, IIIB usually indicates more extensive spread within the chest, where nonoperative methods become the mainstay of therapy, and treatment is based on a combination of radiation and systemic exposure.
Thus, the third level is a turning point where treatment moves from local solutions to a multimodal strategy, requiring careful planning and the participation of a multidisciplinary team.
Stage IV: advanced stage with distant metastases
Stage 4 lung cancer means that the disease has spread beyond the chest wall or has metastasized to distant sites – that is, it is already an advanced stage. There is also an important substages in this category:
- stage IVA often describes limited distant spread (for example, within the pleura or with isolated metastases);
- whereas stage IVB usually means multiple metastases to various organs.
Summarizing the levels of extent of non-small cell lung tumors from I to IV, it is important to remember that the stage determines not only the prognosis, but also the logic of treatment. To better understand what solutions are used at each period and how individual tactics are formed, we recommend going to the guide Treatment options for non-small-cell lung cancer, which describes in detail modern approaches to therapy depending on the extent of the disease [4].
Stage 1 Lung Cancer: Meaning and Typical Treatment Approach
Stage I lung cancer is an early stage of the disease, when the tumor is localized within one lung, without lymph node involvement, and without signs that the cancer has spread beyond the primary site. In the lung cancer staging system, this disease extent corresponds to a situation where cancer cells have not yet become systemic, which fundamentally affects the approach to treatment and prognosis.
After establishing a lung cancer diagnosis and determining the cancer stage, the first one indicates a localized process:
- the tumor is limited to the pulmonary tissue;
- no lymph nodes are involved;
- there are no distant metastases in the other lung or other organs.
At this period, the disease is clearly different from advanced lung cancer, where treatment is systemic in nature.
Surgery is the gold standard for the treatment of stage I non-small cell lung cancer. The goal of treatment is to completely remove the lung tumors with maximum preservation of pulmonary function. In such cases, the decision is based on an accurate definition of achieving a surgical stage. For patients in whom surgery is contraindicated, stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) may be an alternative. It allows local treatment of the tumor without surgical intervention and is considered an option for early disease control [5].
Stage 2 Lung Cancer: Meaning and Treatment Planning
Stage II lung cancer is a transitional stage between localized and stage when the tumor has spread widely. Once lung cancer is diagnosed and the extension of disease is determined using the modern staging system, it becomes clear that the tumor is no longer the earliest form, but the cancer has spread only locally, not widely throughout the body. This is what distinguishes stage II from the later ones.
Both of these stages may be considered as early stages, but unlike stage I, in stage II, the tumor is usually larger or nearby lymph nodes are involved. Lymph node involvement is a key distinction that lung cancer staging takes into account.
As mentioned earlier, this extent of the disease is divided into:
- stage IIA – less pronounced local spread;
- stage IIB – a larger tumor volume or clearer signs of node involvement.
Regardless of types of lung cancer, surgery remains the mainstay of treatment for stage II, if the patient is operable. At the same time, the role of neoadjuvant treatment is increasing here – systemic therapy, which is used before surgery to localize the process and reduce the risk of disease recurrence.
That is why the treatment plan for stage II lung cancer is almost always combined and is formed individually, taking into account the volume of the tumor, the state of the lymph nodes, and the general condition of the patient. Accurate lung cancer staging allows for the timely addition of surgery with systemic therapy and reduces the risk of relapse, without resorting to treatment typical of later stages [3].
Stage 3 Lung Cancer: Locally Advanced Lung Cancer and Treatment Strategy
Stage 3 is classified as locally advanced disease. In the current staging system, this means that the cancer has spread beyond the primary tumor and has involved the mediastinal lymph nodes or nearby structures, but has not yet spread to the other lung or distant organs. It is at this period that lung cancer staging becomes crucial for choosing treatment tactics.
During this period:
- The cancer cells remain within the chest.
- The process is complex but potentially controllable.
The basis of treatment is a combined approach, where chemoradiotherapy plays a leading role. For most patients, it is the standard. In selected cases – provided that the lymph nodes are limited and after careful evaluation – surgery may be included as part of a multimodality approach.
Therefore, accurate lung cancer staging, including assessment of mediastinal lymph nodes, determines whether treatment will be limited to chemo-RT or supplemented with surgery as part of a multimodal approach [6].
When a person is diagnosed with pulmonary malignancy, the most difficult thing is to understand where to start and how treatment decisions are usually made in modern clinical practice.
Booking Health has collected in this guide key information about available therapies, international treatment standards, innovative techniques, and opportunities for receiving help from leading oncology clinics. The goal of Booking Health is to give patients and their loved ones not only knowledge but also confidence in making important medical decisions.
Stage 4 Lung Cancer: Metastatic Lung Cancer Staging and Treatment Goals
Metastatic lung cancer stage 4 is determined during lung cancer staging, when the cancer has spread beyond the airways where the cancer started. At this cancer stage, abnormal cells are found in other organs, indicating the systemic nature of the disease. At this period treatment is not aimed at local control, but at prolonging life and improving its quality. The choice of tactics is made together with the patient, taking into account the benefits and possible side effects.
The mainstay of treatment is drug therapy. Depending on the biology of the tumor, chemotherapy, targeted drugs, and immunotherapy may be used [4]. Current regimens allow for effective disease control and are often well tolerated, so many patients can be treated on an outpatient basis.
When it comes to metastatic disease, patients need to see real paths and real stories. Booking Health tells how Germany approaches the treatment of stage IV lung cancer: from personalized systemic therapy to a focus on quality of life. A special place is occupied by patient stories that share their own experiences of treatment, decision-making, and what life with such disease looks like today.
Explore treatment approaches and patient experiences
Small Cell Lung Cancer Stages: Limited vs Extensive
For small cell carcinoma, the approach to staging and treatment is different, which once again emphasizes the importance of correctly determining the type of tumor. Small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) differs from other types of lung cancer in that it grows very quickly and spreads early. That is why it is not only staged in the same way as TNM staging for lung cancer. Instead, staging for SCLC is simplified and focuses on the main question: whether the process has stayed where the cancer started, or whether the cancer has spread further.
Below is a simple comparison table that explains the logic of staging [7].
| Criteria | Limited SCLC | Extensive SCLC |
|---|---|---|
| Definition and Spread | Cancer is confined to one lung, to the mediastinum, and nearby lymph nodes. | Cancer has spread beyond the affected side of the chest, involving the opposite lung, distant organs such as the brain, liver, or bones, or presenting with malignant pleural or pericardial effusions. |
| Incidence | Approximately 30% of patients are diagnosed with LS-SCLC | About 70% present with ES-SCLC. |
| Treatment Strategy | Standard treatment consists of concurrent chemotherapy combined with thoracic radiotherapy. Surgery may be considered. | Management is based on systemic therapy, most commonly chemotherapy combined with immunotherapy. |
| Staging Evaluation | Both types require comprehensive imaging, including CT scans of the chest and abdomen and a brain MRI to exclude metastases. PET/CT is increasingly used to improve staging accuracy. | |
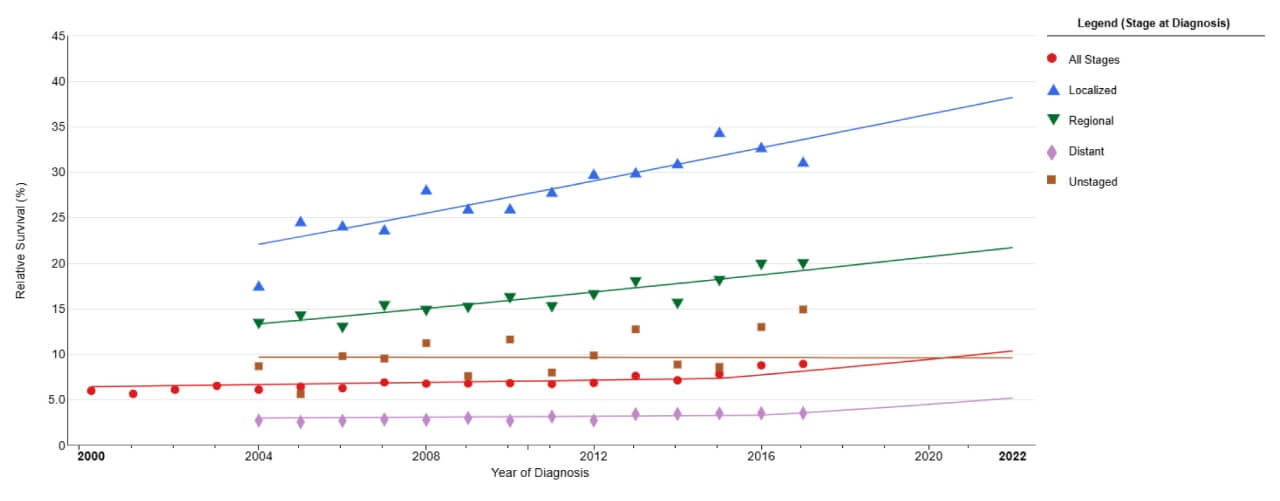
This graph shows how five-year survival rates decrease with increasing extent of the disease: from 31-63.8% in stage I to 0% in stage IV. However, these figures reflect generalized statistics and do not take into account individual factors, modern treatments, and a personalized approach.
Diagnostic Tests Used to Confirm Lung Cancer Stages
Once the diagnosis is made, accurate lung cancer staging is a key step, as it determines the further treatment tactics. This is done using a set of examinations, each of which answers its own clinical question.
Main diagnostic methods:
- CXR (chest X-ray) is the first diagnostic step in patients with suspected pulmonary tumors in many countries.
- CT (computed tomography) of the chest and abdomen – assessment of tumor size and regional spread.
- PET-CT (positron emission tomography CT) – detection of metabolically active foci and possible distant metastases.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging, most often of the brain) – clarification of central nervous system damage.
- Ultrasound-guided modalities (EBUS, EUS). EBUS – endobronchial ultrasound – is an endoscopic ultrasound through the bronchi, which allows you to see and take samples of the mediastinal lymph nodes without surgery. EUS – endoscopic ultrasound – is an endoscopic ultrasound through the esophagus to evaluate the lower mediastinal nodes and nearby structures.
- VATS (video-assisted thoracoscopy) biopsy uses fibre-optic cameras and is traditionally carried out through three to four triangulated incisions. Biopsy – morphological confirmation of tumor type (adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and others) [8].
Lung Cancer Stages and Prognosis: Key Factors That Influence Outcomes
The level of prevalence of malignant process is an important prognostic indicator, but it is not the only factor that determines the course of the disease and the effectiveness of treatment. In real clinical practice, the result is formed at the intersection of several components, and not only based on anatomical classification.
Biological features of tumor formation play a large role – growth rate, histological structure, and molecular characteristics. The presence of certain genetic changes or immunological markers can significantly affect the response to modern methods of therapy and the possibility of long-term control of the process.
No less important is the general condition of the patient. The functional reserves of the body, the work of the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, as well as concomitant diseases, often determine which treatment approaches are possible and how well they are tolerated. That is why two patients with a similar extent of the lesion can have completely different treatment results.
Access to modern diagnostics, multidisciplinary discussion, and personalized treatment strategies also has a significant impact. Taken together, these factors allow us to form a more accurate forecast and choose the optimal tactics for each specific person.
So, what influences prognosis?
- Tumor type (NSCLC or SCLC, histological subtype)
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and SCLC have different biology, growth rates, and sensitivity to treatment.
- Biomarkers (EGFR, ALK, PD-L1, etc.) that open up access to targeted and immunotherapy
The presence of mutations (EGFR, ALK, ROS1, BRAF, etc.) or PD-L1 levels can significantly improve the prognosis due to the possibility of using targeted therapy or immunotherapy – even in late phases.
- Patient's general condition and comorbidities
Physical condition, pulmonary and heart function, and the presence of comorbidities often determine what treatment is possible and how well it will be tolerated.
- Extent of disease spread within one stage
Even within the same stage (e.g., IIIA or IV), the prognosis can vary significantly depending on the number of affected lymph nodes or metastatic foci [10].
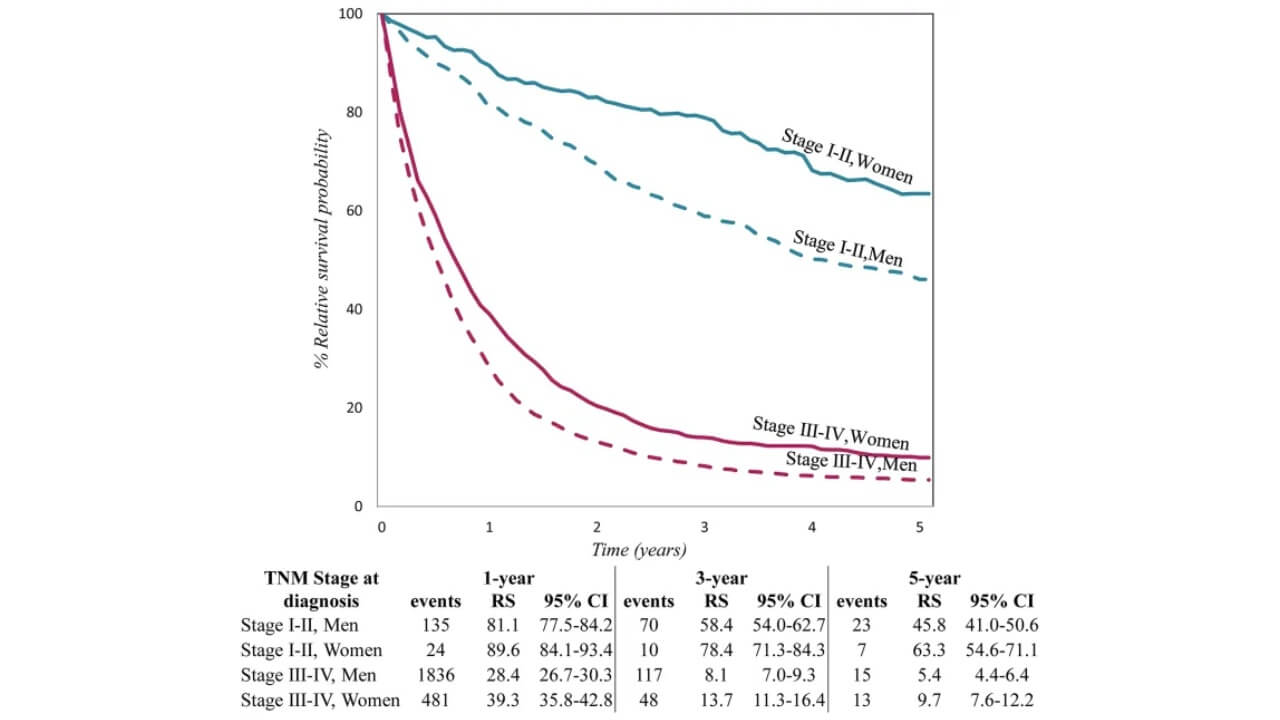
Why Patients Choose Lung Cancer Staging and Treatment Abroad
Many patients choose to have lung cancer treatment abroad not because of a lack of care at home, but because of the need for the most accurate decisions – staging and treatment planning.
One of the key reasons is access to modern imaging techniques, including PET-CT, which can detect even minimal signs of disease spread. Accurate staging data helps to avoid both undertreatment and overly aggressive approaches.
Equally important is the level of molecular diagnostics, which allows us to identify the biological features of the tumor and select personalized treatment. For many patients, these results open up access to targeted or immunotherapy.
In leading oncology centers, decisions are made collectively on multidisciplinary tumor (MDT) boards, where specialists from different fields review the clinical case. This approach reduces the risk of errors and ensures a coordinated treatment strategy.
Lung Cancer Diagnosis, Staging, and Treatment in Germany
Germany offers a full range of modern methods of treating pulmonary malignancy, which allows for the formation of individual tactics depending on the extent of the disease, biology of the tumor, and the patient's condition. It is the combination of different approaches that is the key advantage of German cancer centers.
Clinics in Germany use:
- Surgical treatment – from minimally invasive interventions to complex resections in specialized centers.
The scope of the intervention is selected individually – taking into account the prevalence of the process, respiratory function, and the general condition of the patient. The goal is to eliminate the lesion as radically as possible, while maintaining the quality of life.
- Chemotherapy according to modern international protocols.
It can be used alone or in combination with other methods – before surgery, after surgery, or as the main approach for advanced forms of the disease.
- Radiation therapy, including high-precision methods (EBRT, SBRT).
This allows for precise exposure to the pathological focus, minimizing the burden on healthy tissue. This approach is especially important in patients who cannot undergo surgery.
- Immunotherapy – a method that activates the body's own immune system to recognize and destroy tumor cells, often used alone or in combination with chemotherapy.
It can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy, especially in advanced forms of the disease. For many patients, this approach has become an option for long-term disease control.
- Targeted therapy selected based on the molecular profile of the tumor.
They target specific cellular abnormalities and are generally better tolerated than conventional chemotherapy, which is why precise molecular diagnostics are a key step in treatment in Germany.
- Dendritic cell therapy – an innovative immunotherapeutic approach based on the discovery of dendritic cells, for which the Nobel Prize was awarded, and which in Germany is implemented in specialized centers with a high level of expertise.
- Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) – a local method of affecting the tumor or metastases with minimal systemic load, which is performed in German clinics according to strict indications using a modern navigation system.
An important advantage is not only the treatment itself, but also the aftercare: structured follow-up after therapy, control of side effects, rehabilitation, and long-term monitoring of the patient's condition.
To help you navigate the cost of different approaches, below is a comparative table of prices for lung cancer treatment in Germany, which allows you to evaluate the available options and plan your treatment more transparently.
| Treatment type | Cost Germany | Cost USA | Cost GB | Cost Australia |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Surgery | €15,000 – €25,000 | €65,000 – €85,000 | €35,000 – €55,000 | €20,000 – €50,000 |
| Chemotherapy | €80,300 – €150,000 full course | €100,000 – €180,000 full course | €90,000 – €165,000 full course | €5,000 – €250,000 for one cycle |
| Radiotherapy | €28,000 – €42,000 | €40,000 – €80,000 | €35,000 – €65,000 | €17,000 – €22,000 |
| DC therapy | €20,000 – €38,000 | €40,000 – €100,000 | not available | not available |
| TACE (transarterial chemoembolization) | €6,500 – €24,000 per session | €37,000 – €150,000 | €30,000 – €118,000 | €30,000 – €80,000 |
| Targeted therapy | €375,500 – €420,000 full course | €600,000 – €1,000,000 full course | €400,000 – €500,000 full course | not available |
| Immunotherapy | €20,000 – €38,000 for 1 cycle | €35,000 – €60,000 for 1 cycle | €25,000 – €45,000 for 1 cycle | €50,000 – €120,000 for 1 cycle |
For patients with metastatic disease, it is important to understand that the approach to treatment at this level is significantly different from local forms. Here, the main emphasis is shifted from a radical effect on disease control to preservation of functional status and quality of life.
That is why it is worth reading the separate guide Treatment of stage 4 lung cancer in Germany, which describes in detail modern approaches to treatment at the stage IV of this disease. It considers both standard systemic methods and innovative technologies, in particular dendritic cell therapy, transarterial techniques (TACE), hyperthermia, and other approaches used for long-term control of the process. For a broader understanding of the possibilities of modern medicine, it can be helpful to explore the newest and most effective treatment methods currently available in German clinics. Such an overview allows patients to better navigate contemporary therapeutic strategies and understand how different approaches may be applied depending on the extent of the disease.
How Booking Health Helps Patients Arrange Lung Cancer Care in Germany
When it comes to lung cancer treatment abroad, the most difficult thing is to put everything together: medical opinions, treatment options, clinics, and logistics. Booking Health helps you go through this journey calmly and consistently – from the first analysis of documents to returning home after treatment.
The Booking Health team starts with a detailed analysis of your medical information and the formation of a personalized treatment plan adapted to your specific clinical situation. Then, a suitable clinic in Germany is selected, and direct contact with doctors is organized so that decisions are considered and transparent.
During preparation and treatment, the patient receives full support: paperwork, preliminary consultations, coordination of hospitalization, support from a personal coordinator and translator 24/7. It is important that budgeting is clear and without hidden costs, and after the program is completed, aftercare and communication with doctors are provided.
Booking Health does not impose decisions – the goal of the service is different: to help you understand the possibilities, reduce the organizational burden, and give a sense of control at a time when it is especially important. If you need a clear path to lung cancer treatment in Germany, support is at your fingertips.
Cancer Treatment Abroad: Patient Experiences with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions About Lung Cancer Stages
Send request for treatmentThe main lung cancer stages include I-IV, which reflect how far the disease has progressed; these stages of lung cancer are determined by examination data and indicate the localization or spread of the tumor.
TNM staging of lung cancer is based on the principle of tumor, node metastasis, that is, an assessment of the size of the tumor, the status of the lymph nodes, and the presence of distant metastases within the lung cancer staging system.
NSCLC stages are divided into detailed TNM stages, while SCLC stages are also classified by so-called "limited vs extensive stage lung cancer" classification, due to the more aggressive biology of the tumor.
Stage 1 lung cancer (you can also say lung cancer stage 1) means early-stage lung cancer, when the tumor is localized only in the airways and does not affect the lymph nodes.
Stage 2 lung cancer means a larger tumor or initial lymph node involvement. Stage 2 lung cancer treatment planning usually includes surgery followed by systemic therapy.
Stage 3 lung cancer is locally advanced lung cancer, when the process has spread to the mediastinal lymph nodes, and requires a combined approach according to the stage 3 lung cancer treatment strategy.
Stage 4 lung cancer is a metastatic lung cancer stage, when the tumor has distant metastases, and therapy is focused on advanced lung cancer treatment goals: disease control and quality of life.
Tests for lung cancer staging include CT, PET-CT lung cancer staging, MRI, biopsy for lung cancer staging, and other imaging for lung cancer staging (EBUS, EUS).
Yes, restaging lung cancer is possible after surgery, when pathological staging of lung cancer data refines the real phase and increases lung cancer staging accuracy.
It directly determines the available treatment options by lung cancer stage, forming a personalized lung cancer treatment plan.
Patients choose lung cancer treatment in Germany because of the highly accurate diagnostics, innovative approaches, and experience of German oncology centers for lung cancer, which often exceeds the capabilities of local treatment.
International patients can organize lung cancer treatment in Germany through Booking Health, which provides treatment coordination in Germany and the opportunity to get a second opinion on lung cancer.
Life expectancy depends on the lung cancer treatment by stage, tumor type, and response to treatment; early phases have a much better prognosis than advanced forms.
Worsening may be manifested by increased shortness of breath, pain, weakness, or new symptoms associated with metastases.
Late variants of stage 4 lung cancer are considered final when the disease is systemic in nature.
With modern treatment, many patients live for years, especially with access to targeted therapy and immunotherapy within lung cancer treatment abroad.
Treatment of stage 4 lung cancer is based on systemic therapy according to advanced lung cancer treatment goals, with a focus on disease control and quality of life.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Daria Sukhoruchenko. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Charles M Rudin, Elisabeth Brambilla, Corinne Faivre-Finn, Julien Sage. Small-cell lung cancer. Nat Rev Dis Primers. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2021 Jun 4. Published in final edited form as: Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2021 Jan 14;7(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41572-020-00235-0. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[2] Wanyin Lim, Carole A Ridge, Andrew G Nicholson, Saeed Mirsadraee. The 8th lung cancer TNM classification and clinical staging system: review of the changes and clinical implications. Quant Imaging Med Surg. 2018 Aug;8(7):709–718. doi: 10.21037/qims.2018.08.02. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[3] Amalia Constantinescu, Radu-Nicolae Căprariu, Emil-Robert Stoicescu et al. From TNM 8 to TNM 9: Stage Migration and Histology-Specific Patterns in Lung Cancer. Journals Cancers. Volume 17. Issue 20. doi: 10.3390/cancers17203290. [DOI]
[4] Mark A Socinski, Tracey Evans, Scott Gettinger et al. Treatment of Stage IV Non-small Cell Lung Cancer. Chest. 2013 May;143(5 Suppl):e341S–e368S. doi: 10.1378/chest.12-2361. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[5] Joe Y Chang, Reza J Mehran, Lei Feng et al. Stereotactic Ablative Radiotherapy for Operable Stage I Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Long-Term Results of the Single-Arm STARS Prospective Trial. Lancet Oncol. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2022 Oct 1. Published in final edited form as: Lancet Oncol. 2021 Sep 13;22(10):1448–1457. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(21)00401-0. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[6] Francesco Petrella, Stefania Rizzo, Ilaria Attili et al. Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: An Overview of Treatment Options. Curr Oncol. 2023 Mar 7;30(3):3160–3175. doi: 10.3390/curroncol30030239. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[7] Gregory P Kalemkerian. Staging and imaging of small cell lung cancer. Cancer Imaging. 2012 Jan 12;11(1):253-8. doi: 10.1102/1470-7330.2011.0036. [DOI] [PubMed]
[8] Bejoy Philip, Anchal Jain, Milosz Wojtowicz et al. Current investigative modalities for detecting and staging lung cancers: a comprehensive summary. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Dec 1;39(1):42–52. doi: 10.1007/s12055-022-01430-2. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[9] Matthew B Schabath, Michele L Cote. Cancer Progress and Priorities: Lung Cancer. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2019 Oct;28(10):1563–1579. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-19-0221. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[10] Bejoy Philip, Anchal Jain, Milosz Wojtowicz et al. Current investigative modalities for detecting and staging lung cancers: a comprehensive summary. Indian J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2022 Dec 1;39(1):42–52. doi: 10.1007/s12055-022-01430-2. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[11] Milena Sant, Caterina Daidone, Kaire Innos et al. Patterns of care and survival for lung cancer: Results of the European population-based high-resolution study. Front. Epidemiol. Sec. Clinical Epidemiology. Volume 3 - 2023. doi: 10.3389/fepid.2023.1109853. [DOI]
Read:
Comprehensive Guide to Lung Cancer: New and Standard Treatment Options
Lung Cancer Treatment in Germany: All New and Most Effective Treatment Options
Comprehensive Guide to 4 Stage Lung Cancer Treatment Options
Article menu:
- Lung Cancer Stages and the Importance of Accurate Lung Cancer Staging
- Lung Cancer Staging Systems: TNM Staging for Lung Cancer and SCLC Staging
- Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Stages: Stage 1 to Stage 4 Overview
- Stage 1 Lung Cancer: Meaning and Typical Treatment Approach
- Stage 2 Lung Cancer: Meaning and Treatment Planning
- Stage 3 Lung Cancer: Locally Advanced Lung Cancer and Treatment Strategy
- Stage 4 Lung Cancer: Metastatic Lung Cancer Staging and Treatment Goals
- Small Cell Lung Cancer Stages: Limited vs Extensive
- Diagnostic Tests Used to Confirm Lung Cancer Stages
- Lung Cancer Stages and Prognosis: Key Factors That Influence Outcomes
- Why Patients Choose Lung Cancer Staging and Treatment Abroad
- How Booking Health Helps Patients Arrange Lung Cancer Care in Germany
- Frequently Asked Questions About Lung Cancer Stages
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health