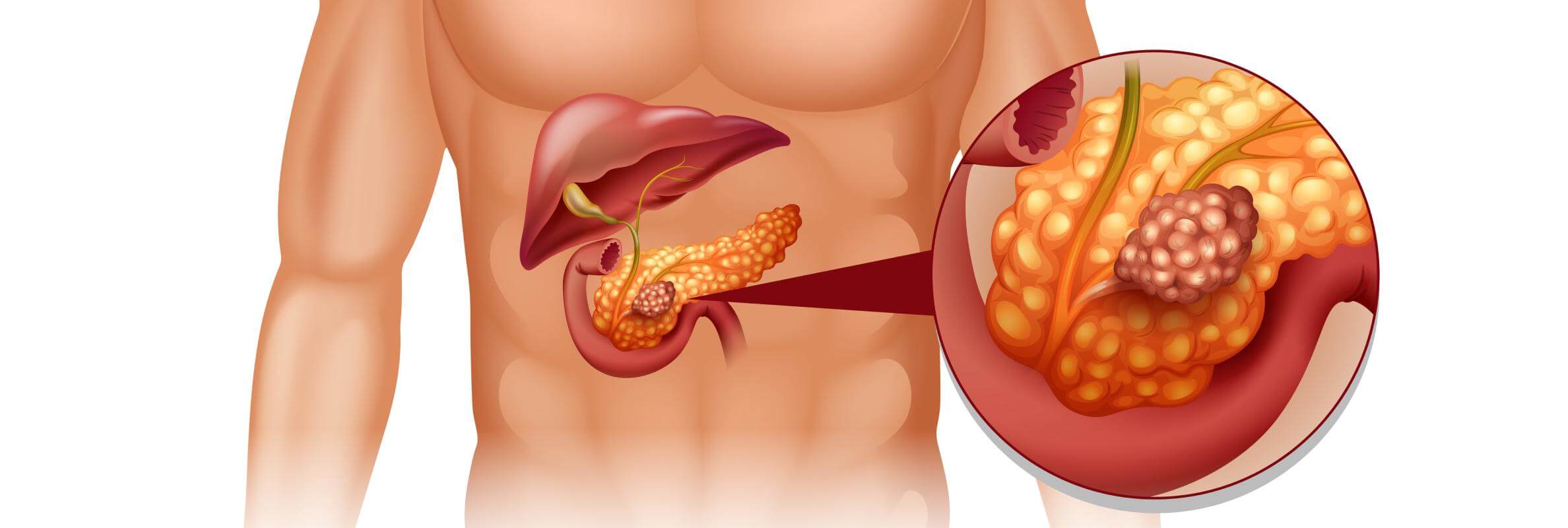
Pancreatic cancer (PC) remains one of the most aggressive forms of gastrointestinal carcinomas [1]. Just imagine that in 2022, approximately 467,000 deaths were attributed to this disease [2]; that places PC among the top six causes of cancer-related mortality worldwide [3].
The overall 5-year survival rate sits around 13% [4]. That is a horrific statistic. For localized cases, survival can improve to roughly 44%, but here's the problem: most patients don't get diagnosed until the disease has already metastasized, which drops the 5-year survival rate to about 3% [5].
Despite these statistics, we want to ask pancreatic cancer patients to not despair. Potential for earlier intervention and improved outcomes are connected with recent developments of new innovative diagnostic tools and treatment modalities.
Pancreatic cancer treatment continues evolving. We encourage patients and families to read this article – to explore treatment options available.
Conventional Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer: What Is Currently Available
Treatment approach for pancreatic cancer (PanCa) depends on tumor stage and location. Surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation therapy form the basis of pancreatic cancer treatment protocols [6].
Surgery is preferred when tumors are confined to the pancreas, without indistinctive borders or distant spread. The most common surgical procedure is the Whipple operation. It involves removing the head of the pancreas along with nearby structures – e.g., parts of the stomach, small intestine, bile duct, and gallbladder. As the available evidence suggests, it can offer the best chance for long-term survival in eligible patients. However, it is a complex and demanding procedure that requires a high level of skill – it must be performed only by the best specialists in this field.
Chemotherapy is usually used as a primary treatment for stage 3 pancreatic cancer, it is designed for the cases when the tumor is considered inoperable or has spread to nearby structures. It is also widely utilized in stage 4 pancreatic cancer. The response rates are often limited, although this approach can extend survival in both stages. In stage 3, chemo can help slow the disease progression and reduce tumor size, improve symptoms. In stage 4 it can help manage this metastatic disease by controlling tumor growth. Regardless of the stage of the disease, this treatment strategy can cause significant side effects that impact the overall well-being of pancreatic cancer patients.
Radiation therapy is used as supportive treatment (alone or combined with chemotherapy). Recent studies suggest it may help relieve pain and shrink tumors in specific locations – it can also reduce risk of local recurrence. However, the overall benefit in terms of long-term survival is modest – similar to chemo.
If patients want to receive the best treatment for pancreatic cancer, overcoming high recurrence rates and limited survival, they should consider more modern and personalized options, sometimes beyond the borders of their homeland.
Innovative Therapies
Treatment strategies are changing thanks to discoveries in medical research and science – new pancreatic cancer treatments can improve the body's own ability to fight cancer or target tumors more effectively with fewer side effects. Dendritic cell therapy and transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) are considered 2 of the most promising innovations today.
Dendritic Cell Therapy
Dendritic cell therapy is advanced form of immunotherapy that works by utilizing the body's own immune system—this approach was recognized with a Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011 [7]. Dendritic cells are responsible for identifying threats and activating cancer-fighting T cells. In therapy, a patient's dendritic cells are collected and trained in a lab to recognize cancer-specific markers.
They are reinfused into the body to produce a targeted immune response against pancreatic tumor cells. Studies show that dendritic cell therapy can lead to tumor regression and slower disease progression; it can also lead to improved quality of life (all with minimal side effects) – these make it a suitable option even for frail/elderly patients with advanced pancreatic cancer. That is a crucial advantage when you consider how harsh conventional treatments can be on already weakened patients.
To better understand how dendritic cell therapy works and how it potentially offers long-term remission, we invite readers to watch a video interview with Professor Frank Gansauge—a leading immunologist in Germany with over two decades of experience. In this interview, he explains the science behind dendritic cells and shares success stories of his patients.
"Every Patient Deserves Individual Approach": Interview with Renowned German Immunologist Prof. Gansauge
Interventional Radiology
To manage pancreatic cancer in patients with advanced or unresectable disease, minimally invasive image-guided interventions are implemented more and more often. These techniques mean targeted elimination of tumor tissue with minimal injury to surrounding structures due to real-time guidance using ultrasound and computed tomography (CT).
Thermal ablation (radiofrequency ablation – RFA, microwave ablation – MWA) is used for locally advanced pancreatic adenocarcinoma (PAC). These methods work by applying intense heat directly into tumor to induce destruction. Thermal ablation isn't yet included in standard protocols of care, however research shows promise in selected cases where it improves symptom control. Recent prospective data demonstrated local control rates and radiological response of 60-75% at 6 to 12 months.
Cryoablation uses subzero temperatures. It destroys malignant cells through ice crystal formation—associated with minimal perioperative complications and low number of side effects (pain, indigestion). This approach is especially useful when lesions are close to critical structures like the portal vein. Cryoablation can be administered in cases of metastatic pancreatic ductal cancer or resectable tumors when patient is unwilling or unable to undergo surgery. Research is still ongoing, but cryoablation is efficient in dealing with locally advanced pancreatic cancer (LAPC): pilot studies showed progression-free survival of approximately 66% at 6 months in LAPC patients following cryoablation.
Electrochemotherapy (ECT) is an ablation technique which enhances chemotherapeutic uptake through electric current-mediated impact—currently under evaluation for chemotherapy-resistant or surgically inaccessible pancreatic tumors. Early-phase trials report pancreatic tumor responses of up to 65%, especially for borderline resectable or recurrent malignant lesions involving high vascularization. ECT can also induce an immunotherapeutic effect. As such, it offers potential advantage when combined with immunotherapy in advanced pancreatic disease scenarios.
Prof. Kovács: How Electrochemotherapy Became the Gold Standard for Hard-to-Reach Tumors
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is an advanced and new treatment for pancreatic cancer that is considered effective for inoperable tumors or those that have metastasized to the liver or lungs. As many know, traditional chemotherapy circulates throughout the body. In contrast, TACE can deliver treatment directly into the artery feeding the tumor while simultaneously blocking blood flow. This maximizes drug concentration at tumor site and starves cancer cells of oxygen and nutrients. As a result – this targeted approach helps shrink tumors and prolong survival. Patient comfort increases with fewer systemic side effects. Due to these advantages, TACE is often used as part of broader oncology plan, as it can be combined with other therapies (immunotherapy, for instance) for more personalized and effective treatment path.
Prof. Kovács: Why TACE Doubled Cancer Survival – What Patients Need to Know
| Characteristics/Therapy type | 2-Year Survival Rate | Response Rate | Duration | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatment | ~25% for advanced cancer | Less than 10% | Several cycles | Severe (nausea, fatigue, hair loss, immunosuppression, skin irritation) |
| Innovative Methods | ~60% for advanced cancer | 45-65% | Up to 4 sessions | Mild (localized discomfort) |
Treatment costs for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
| Treatment Method | GERMANY* | GB | USA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatment | €80,000 - €150,000 full course | €90,000 - €165,000 full course | €100,000 - €180,000 full course |
| Innovative Methods | €25,000 - €60,000 full course | €70,000 - €120,000 full course | €100,000 - €150,000 full course |
* The cost of each treatment can vary significantly based on factors such as the country of treatment, the reputation of the hospital or clinic, the complexity of the case, the length of hospital stay, the follow-up care required, and whether the treatment is part of a broader combination therapy plan. Additional expenses, such as diagnostics, travel, accommodation, and supportive care, may also affect the total cost.
Success Stories
Robert Franklin Smith (USA) received a pancreatic cancer diagnosis and immediately began looking for the best treatment for pancreatic cancer in the world.
A short line first: he underwent liver-metastasis surgery. Then the longer one: after resection of metastatic lesions linked to the primary pancreatic tumour, Robert continued systemic chemotherapy, following a standard protocol that offered disease control but still felt limited in terms of long-term possibilities.
However, Robert's family was not satisfied with the limitations of standard treatment in the United States. During their search for more advanced solutions, they discovered the pancreatic cancer alternative treatment options available in Germany. In particular, they were interested in dendritic cell therapy offered by Dr. Frank Gansauge at LDG Laboratories in Berg.
The Smiths didn’t want to handle logistics alone, so they contacted Booking Health for support. Mrs Smith later mentioned how impressed they were by the organisation, the clarity of communication, and the genuinely warm attitude they experienced — small details that matter when stress levels are high. She described Dr Gansauge’s combination of medical accuracy and human approach as something that made them feel safe and properly understood.
Dendritic cell therapy stabilised Robert’s condition, lowered recurrence risk, and improved his general well-being – appetite, energy, day-to-day function.
For families like the Smiths, Germany may be considered the best country for pancreatic cancer treatment. Advanced medical care here can create real possibilities.

Why It Is Important to Choose the Best Place for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
Patients have to make many decisions. The first stage – and sometimes the hardest – is choosing the right hospital for treatment. As we discussed in this article, the best medical centers for treatment of pancreatic cancer offer patients greatest chance for positive outcome - they combine advanced technologies with experienced pancreatic cancer specialists.
Key advantages of best hospitals for pancreatic cancer treatment include: accurate diagnostics, access to minimally invasive surgical options, expertise in complex procedures like the Whipple procedure (pancreaticoduodenectomy), availability of advanced therapies (immunotherapy, targeted radiation oncology, interventional radiology), and a multidisciplinary team [3].
Patients can also refer to pancreatic cancer hospitals rankings and patient reviews. These help find the best pancreatic cancer hospitals in the world that offer best possible outcomes.
Overall, we want to emphasize: it is essential that pancreatic cancer patients select the best pancreatic cancer doctors and top pancreatic cancer treatment centers.
Best Treatment Centers for Pancreatic Cancer: Global Rankings
Below we want to offer our readers the list of some of the best pancreatic cancer treatment centers globally.
| Pancreatic Treatment Centers | Country | Specialty Highlights |
|---|---|---|
| Mayo Clinic | USA | Advanced diagnostic and therapeutic options – e.g., minimally invasive surgery, chemo, RT, palliative care |
| Johns Hopkins Hospital | USA | Expertise in Whipple procedure; availability of pancreatic cancer vaccines |
| University Hospital RWTH Aachen | Germany | Minimally invasive surgery; another advantage – advanced research |
| University Hospital Freiburg | Germany | Advanced surgical oncology (robotic and conventional); the hospital tends to personalized therapy |
| University Hospital Tuebingen | Germany | Multidisciplinary team; innovative clinical trials |
Mayo Clinic, USA is NCI-designated comprehensive cancer center. High survival rates set this institution apart. At this facility, highly individualized treatment plans are developed against background of approved protocols and advanced research—that is why it's often called the best hospital to treat pancreatic cancer.
University Hospital RWTH Aachen in Germany. European standards lead to excellence in pancreatic cancer surgery. Here, patients receive complex treatment with specialists from different departments and Euregional Comprehensive Cancer Center Aachen.
Johns Hopkins Hospital leads in pancreatic cancer research and performs intricate surgeries—it provides access to the Sol Goldman Pancreatic Cancer Research Center, one of world's leading research hubs for pancreatic malignancies. At this hospital, patients receive innovative and personalized care designed for complex cases (including borderline resectable tumors that other centers might consider inoperable). The surgical expertise here is exceptional, particularly for challenging anatomical presentations involving vascular involvement.
University Hospital Freiburg, Germany offers something different: truly integrated care where surgical oncologists, interventional radiologists, medical oncologists, gastroenterologists collaborate on every case – not just during occasional tumor board meetings but throughout entire treatment journey. Treatment options available here include robotic surgery for select patients, conventional open procedures when anatomy demands it, neoadjuvant chemotherapy tailored to tumor biology based on molecular profiling. That is why outcomes are consistently strong.
University Hospital Tuebingen, Germany, is focused on clinical trials to promote innovation in the treatment of pancreatic cancer. It has a highly integrated oncology team. This team offers patients access to innovative therapies and customized treatment plans – all aimed at maximizing outcomes. UniHospital Tuebingen emphasizes translational research. This approach allows the hospital to bring laboratory discoveries into clinical practice. By doing so, facility ensures patients benefit from latest advancements in cancer care before these treatments become widely available at other institutions.
Why German Clinics Are an Excellent Choice
Best hospitals in the world offer exceptional care to those struggling with pancreatic cancer. We hope readers see that now. However, we'd like to draw attention to top pancreatic cancer hospitals in Germany specifically – they're known for innovative technologies, high surgical success rates, affordable healthcare compared to many Western countries (particularly USA where costs can be 2-3 times higher for equivalent treatment).
Many clinics in Germany participate in international research collaborations. As such, they offer access to advanced clinical trials. German clinics assist patients through every step of treatment journey by providing navigation services—patients benefit from shorter waiting times and comprehensive support services including: appointment scheduling, translation support, visa assistance, accommodation arrangements, treatment coordination.
Advanced clinical trials available at German centers include dendritic cell therapy protocols, combination immunotherapy approaches, novel interventional radiology techniques like TACE and cryoablation, emerging targeted molecular therapies based on genetic tumor profiling.
Advanced Cancer Treatment: Patient Success Stories with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients with Pancreatic Cancer
Send request for treatmentTake a look at dendritic cell immunotherapy and TACE (transarterial chemoembolization) – these are the two that can have targeted effects with fewer side effects. You can check the full list of the available options of the Booking Health website.
Surgery (if possible) and interventional radiology techniques, chemo, and innovative therapies like immunotherapy are often combined – so the best result possible can be achieved after the course. And personalized medical plan is the most efficient option.
Very quickly due to aggressive nature of the disease. It is important to avoid postponing and start therapy ASAP, in the specialized healthcare facility; while you can always receive second opinion elsewhere and change your choice.
This is one of the essential methods used in pancreatic cancer treatment, particularly for inoperable or metastatic cases; regimens are numerous and are selected individually – among approved protocols. It can help shrink primary and metastatic neoplasms, manage disturbing cancer manifestations.
There is no a single one, and this is reasonable. Surgery, chemotherapy, dendritic cell therapy – all have their place and timing. Personalized strategies are important, as each clinical case has its peculiarities requiring action, sometimes beyond the standard protocol.
A patient may need action from invasive intervention to medication intake. This includes surgery (e.g., the Whipple procedure), chemotherapy, RT, immunotherapy, targeted therapy. Innovative treatments are expanding patient choices, you can read about them on the Booking Health website.
Early-stage detection and fast action offer better outcomes. Advanced stages often require more expertise, complex schemes and innovative approaches to prolong life. The prognosis is always individual; discuss it with your healthcare provider – and, if necessary, receive second opinion in specialized centers abroad.
Booking Health helps patients manage their expenses by providing transparent pricing and assistance with hospital negotiation, insurance issues. The costs can vary from €20,000 for immunotherapy to over €150,000 – for prolonged chemotherapy, etc.
Some patients live for several months to years. New therapies – dendritic cell immunotherapy and others – help extend life expectancy, even in advanced cases.
What is recommended and supported by clinical trials data, is diet balancing carefully, staying physically active, managing stress; it is also great to receive emotional support. Feel free to contact support groups and patient communities, this can be of great use.
First, take a look at Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins Hospital (USA), University Hospital RWTH Aachen, University Hospital Freiburg, and University Hospital Tuebingen – all are located in Germany. Booking Health will help you with selection.
Top hospitals in rankings have highest survival rates. Mayo Clinic, Johns Hopkins Hospital , UniHospital RWTH Aachen, University Hospital Freiburg, and UniHospital Tuebingen report better outcomes compared to general hospitals.
Access to multidisciplinary teams, experience with complex surgeries, personalized treatment plans – all an individual patient needs.
Booking Health can help arrange a second opinion cancer diagnosis from top-ranked pancreatic cancer centers worldwide. Any suspicion must be excluded before therapy starts.
Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins Hospital (USA), University Hospital RWTH Aachen, University Hospital Freiburg, and University Hospital Tuebingen – all are located in Germany – deserve patients’ attention. Don’t be afraid because of the location, they are open for people from all countries.
Absolutely. Best centers provide highly personalized care approach. Patients can be certain that each treatment plan will be customized.
Yes. University Hospital RWTH Aachen, University Hospital Freiburg, and University Hospital Tuebingen; Mayo Clinic and Johns Hopkins Hospital (USA). Booking Health will arrange an appointment in any of them.
Yes. Many of the best pancreatic cancer hospitals offer access to immunotherapy. These treatments are typically part of advanced programs – that aims to improve outcomes for patients with pancreatic cancer.
For stage 4 pancreatic cancer, the 2-year survival rate with standard chemotherapy is around 25%. On the other hand, innovative methods (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, TACE, or ablation) can extend survival to approximately 60%.
What response rates are achieved in stage 4 pancreatic cancer with innovative treatments (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, TACE, ablation)?
In stage 4 pancreatic cancer, standard chemotherapy achieves a response rate below 10%. In contrast, innovative approaches like dendritic cell therapy, electrochemotherapy, and thermal ablation can reach 45-65%.
Standard chemotherapy for stage 4 pancreatic cancer often requires several treatment cycles over many months. In turn, innovative treatments (e.g., TACE, ablation, or dendritic cell therapy) are usually completed in up to four sessions.
Standard treatments for stage 4 pancreatic cancer often cause severe side effects, including fatigue, nausea, and immune suppression. However, innovative therapies (e.g., TACE, cryoablation, or dendritic cell therapy) typically cause only mild, localized discomfort.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Science Direct. Pancreatic cancer. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0140673625002612
[2] ASCJournals. Global cancer statistics 2022: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. https://acsjournals.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.3322/caac.21834
[3] BMC Cancer, Springer Nature. The global, regional burden of pancreatic cancer and its attributable risk factors from 1990 to 2021. https://bmccancer.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12885-025-13471-y
[4] Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. Pancreatic Cancer Diagnoses and Mortality Rates Climb; Five-Year Survival Rate for Pancreatic Cancer Stalls at 13%. https://pancan.org/press-releases/pancreatic-cancer-diagnoses-and-mortality-rates-climb-five-year-survival-rate-for-pancreatic-cancer-stalls-at-13/
[5] Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. Pancreatic Cancer Survival Rates. https://pancan.org/facing-pancreatic-cancer/about-pancreatic-cancer/survival-rate/
[6] Medscape. Pancreatic Cancer Treatment Protocols. https://emedicine.medscape.com/article/2007067-overview?form=fpf
[7] Roman Volchenkov, Florian Sprater, Petra Vogelsang, Silke Appel. The 2011 Nobel Prize in physiology or medicine. Scand J Immunol. 2012 Jan;75(1):1-4. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.2011.02663.x. [DOI] [PubMed]
Read:
Evolving Standards of Care for Pancreatic Cancer in Germany
Germany offers dendritic cell-based immunotherapy for pancreatic cancer
Top 10 Leading Oncology Hospitals for Cancer Treatment in Germany
Article menu:
- Conventional Therapies for Pancreatic Cancer: What Is Currently Available
- Innovative Therapies
- Success Stories
- Why It Is Important to Choose the Best Place for Pancreatic Cancer Treatment
- Best Treatment Centers for Pancreatic Cancer: Global Rankings
- Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients with Pancreatic Cancer
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health