With more than 1.9 million new cases and 0.9 million deaths in 2020, rectal cancer (RC) was the third most common cancer and the second most common cause of cancer mortality worldwide [1, 2, 3]. Geographical disparities were reported in incidence and mortality rates, time trends, and the future burden of RC across different countries and regions [1, 2, 3]. There were also changes in the age pattern of CRC, with increasing incidence in the young patients, especially in developed countries [4].
These disparities may reflect differences in exposure to the risk factors for RC, including lifestyle and environmental factors [5, 6]. Identifying and avoiding modifiable risk factors, especially lifestyle factors (e.g., alcohol consumption, smoking, obesity, unhealthy diet) as well as increasing protective factors (e.g., physical activity, taking specific medications such as aspirin, healthy diet) [5, 6] have a pivotal role in the primary prevention of RC. RC screening (secondary prevention) for the detection and removal of premalignant lesions of the colorectum is also considered an effective preventive method in RC control programs [7, 8, 9]. However, there are still many cases where the disease is detected at advanced stages. At this point it is especially important to act quickly and choose the most effective approaches. This brings us to the question of modern methods of treating advanced rectal cancer which are currently offered by leading German cancer clinics.
Understanding Stage 4 Rectal Cancer
Stage 4 rectal cancer is thе form of the disease in which the tumor process goes beyond the local area and involves distant organs. Stage 4 rectal cancer often manifests itself as multiple foci in the liver, lungs or peritoneum, and the tumor cells are no longer limited to the primary focus. That is why patients begin to look for countries with wider possibilities of systemic therapy and innovative methods. In this context Germany is considered one of the leading destinations for colon cancer treatment.
Spread and Mechanisms of Metastasis
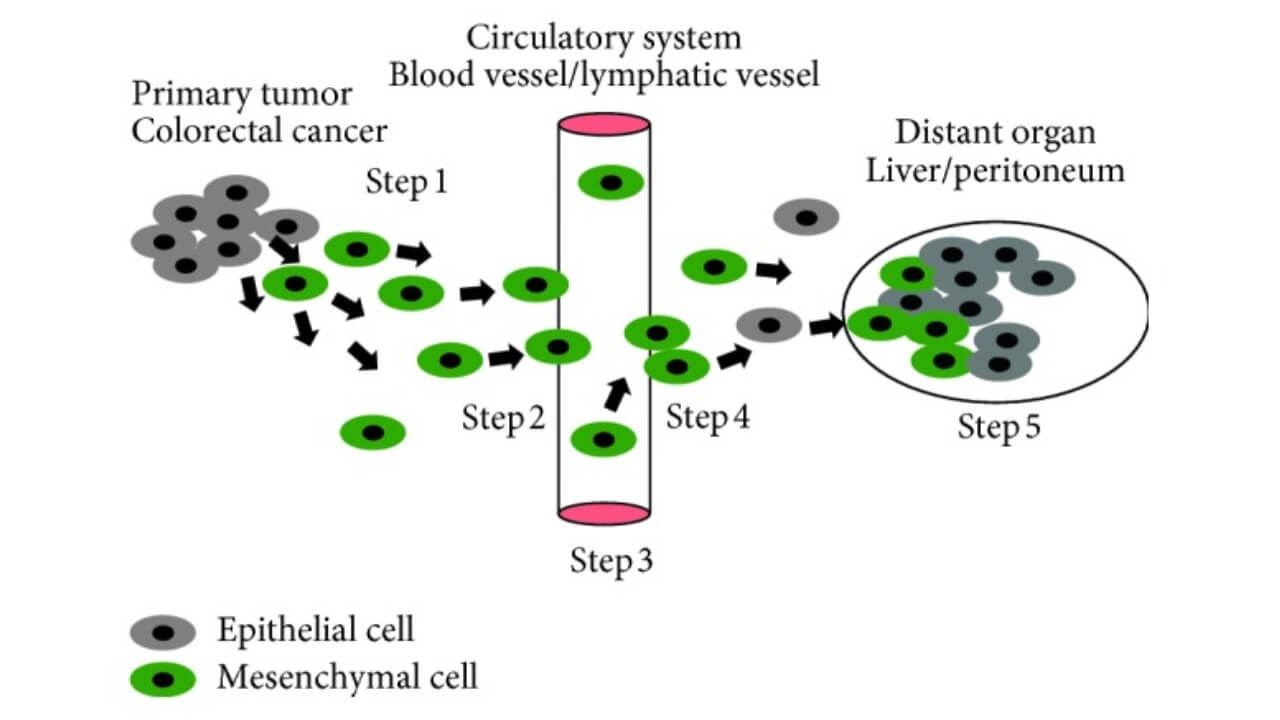
Metastasis at stage 4 is a complex multi-step process in which tumor cells gradually acquire the ability to break away from the primary tumor, penetrate blood or lymphatic vessels and overcome the body's protective barriers. The most important mechanisms are 一 disruption of intercellular contacts, activation of enzymes that destroy the intercellular matrix and modifying cell behavior that allows it to migrate over considerable distances [11].
After entering the bloodstream or lymphatic system, individual cells can settle in distant organs, where they form new foci and trigger cancer cell growth. In the case of rectal cancer, the liver and lungs are most often affected due to the peculiarities of venous outflow from the colon. If the circulation takes the cells to the abdominal cavity, they can attach to the peritoneum and give peritoneal metastases [11].
At this stage, the disease becomes systemic. Because of the complex biology of metastasis, colon cancer treatment requires a multidisciplinary approach (combination of systemic, surgical and locoregional methods).
Why Patients Choose Stage 4 Rectal Cancer Treatment in Germany
Germany is known for its cancer care system, multidisciplinary approach and access to new cancer treatment protocols. Here, patients with stage 4 rectal cancer are offered:
- Personalized systemic therapy programs using targeted therapies and immunotherapy
- Local techniques for controlling metastases in the abdominal cavity, in particular, hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy
- Modern endoscopic and surgical interventions aimed at reducing the volume of the tumor mass and controlling symptoms
- Access to innovative immune approaches that are actively used in leading German cancer centers
Thanks to this, patients receive not only standard colon cancer treatment but also expanded opportunities for controlling the disease, even when it comes to advanced stages.
Standard Treatment Options for Rectal Cancer Stage 4 in Germany
Stage 4 rectal cancer is diagnosed when the cancer has spread beyond the primary tumor and the patient has distant metastases. Classical methods of cancer treatment in Germany include: surgery, systemic therapy and radiation therapy. However, they have a number of limitations.
- Traditional surgery requires large incisions in the anterior abdominal wall, which increases the risk of bleeding and complications during surgery
- Classical systemic therapy, including chemotherapy, is administered intravenously, due to which the drugs enter the rectal tissue only partially, while negatively affecting healthy organs
- Conventional intensity-modulated radiation therapy can cover large areas of the body which increases the likelihood of complications after colon cancer treatment
- Recovery from such procedures takes a long time, and the patient's quality of life is significantly impacted
Increasing the effectiveness of colon cancer treatment is possible by increasing the doses of chemotherapy and radiation therapy or the volume of operations. However, due to the high risks, this is practically impossible in most cases.
Modern medicine offers innovative approaches (targeted therapies, CAR T cell therapy and dendritic cell vaccines) to fight cancer cells more effectively and minimize side effects. Unfortunately, in many countries with limited resources, such methods are not used due to insufficient equipment and a lack of experienced specialists.
Advanced Treatment Options for Stage 4 Rectal Cancer in Germany
German oncology hospitals use modern protocols, which include improved standard cancer treatment methods for rectal tumors, as well as for the elimination of metastases.
Surgical Treatment Options for Rectal Cancer Stage 4
Surgery is one of the treatment methods for stage 4 rectal cancer. When operating, surgeons can remove the rectum with a primary tumor, pelvic organs if a tumor has spread to them, as well as metastases in the lungs, liver, and abdominal cavity.
To perform surgical procedures as accurately as possible and without the risk of complications, doctors in Germany use the following methods:
- Laparoscopic resection is the surgical removal of a tumor using miniature endoscopic instruments. Such operations are performed through small skin incisions (usually up to 0.5-1.5 cm). During the intervention, doctors perform all the manipulations while looking at the screen, which allows them to zoom the image by 4 to 10 times.
- Resection with the da Vinci Surgical System is a technique for removing a tumor with metastases using a state-of-the-art robotic system. The manipulations are performed by a robot whose movements are controlled by a specially trained surgeon. Such an approach reduces the risk of major blood loss during surgery and damage to healthy rectal tissue.
A stage 4 tumor is often inoperable due to its large size. Therefore, cancer patients often require chemotherapy to reduce the size of the neoplasm and metastatic lesions.
After successful operations according to R0 (no residual tumor) classification, the five-year survival rate of cancer patients reaches 50%.
Cytoreductive Surgery and Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy (HIPEC) for Stage 4 Rectal Cancer
Cancer treatment in Germany includes cytoreductive surgery and follow-up hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) for stage 4 rectal cancer with spread to the abdominal cavity. The essence of the method is that doctors remove all visible tumor cells and then the abdominal cavity is washed with a solution of chemotherapy drugs heated to 40-44 °C within 1 hour [12].
This method has the following advantages:
- Chemotherapy after surgery can destroy cancer cells, which can provoke the development of a recurrence in the future.
- The high temperature of chemotherapy drugs improves the penetration of active substances into pathological tumor cells and enhances the antitumor drug's properties.
- Due to its local action, HIPEC allows the use of higher concentrations of chemotherapy drugs. It reduces the risk of damage to healthy tissues and the development of systemic therapy complications.
- Drugs accumulate in tissues and continue to act for several weeks after the procedure.
- Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy is carried out immediately after surgery. As a rule, it shows excellent results just after a single application, so repeated procedures are not required.
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE)
Embolization is a cancer treatment method that involves the use of chemicals to block the arteries supplying the tumor cells. The specialists began to use it for liver metastatic cancer treatment at the end of the twentieth century. Nowadays, various techniques can be used for many other cancers, including malignant rectal cancer tumors.
Doctors in Germany are increasingly using TACE (transarterial chemoembolization). It is a type of embolization that is combined with regional chemotherapy. This method involves blocking the arteries with special microspheres saturated with chemotherapeutic agents. Such a therapeutic approach has the following advantages:
- Reduction of tumor growth 一 blockage of vessels supplying the tumor cells leads to oxygen starvation of cancer cells and their rapid death
- An additional effect of chemotherapy 一 anticancer drugs influence pathological foci, preventing tumor growth and metastatic colon cancer spreading
- The procedure is safe since the arteries are accessed through accurate incisions, which reduces the risk of bleeding and other complications
- Rehabilitation is not required 一 the patient must stay in bed for 24 hours after embolization
The embolization procedure is widely used before the surgical removal of the primary tumor. If surgery is not planned, the method can be used for such complications in cancer care as rectal bleeding. For rectal cancer treatment in Germany, chemoembolization can be used as an independent method for local control of the tumor cells. This example highlights the role of minimally invasive cancer treatments in Germany, a topic Professor Kovács discusses in detail in the video below.
Dendritic Cell Therapy
Modern therapy for stage 4 rectal cancer involves the use of dendritic cells to activate the patient's immune system. Dendritic cells are key antigen-presenting cells that recognize tumor cells and stimulate other immune cells to destroy them. Their biological significance was highlighted when research on dendritic cells was awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011.
The main advantages of Germany dendritic cell therapy:
- It strengthens the immune system's ability to fight tumor cells
- Allows for combination with surgery, systemic therapy and targeted methods
- Minimal impact on healthy tissues compared to classical chemotherapy
- Control of tumor cell growth even in the case of metastatic cancer
Clinical data show that the use of dendritic cell vaccines in patients with stage 4 rectal cancer significantly increases the duration of disease control and reduces the risk of relapse of metastatic colon cancer. Real-world insights on how this method works and when it is most effective are presented in the interview.
Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
Another effective direction for stage 4 rectal cancer treatment is the use of checkpoint inhibitors (ICI). These drugs block signals that inhibit the immune system allowing it to more effectively target cancer cells [13].
The use of checkpoint inhibitors is particularly indicated in metastatic rectal cancer (MRC), where standard methods have limited effectiveness. In combination with CAR T-cell therapy or dendritic cell vaccines, colorectal cancer patients receive treatment programs that allow significantly improved control of tumor cell growth and reduce metastatic spread [13].
Advantages of using checkpoint inhibitors:
- Activates the immune system for a long-term fight against tumor cells
- Promotes effective destruction of cancer cells without significant damage to healthy tissues
- The possibility of combination with other advanced rectal cancer therapies for patients with stage 4 rectal cancer
Thanks to this method, even at advanced stages, patients get real chances to control tumor growth, increase survival and improve quality of life.
CAR T-cell Therapy
CAR T-cell therapy is an advanced method of treating stage 4 rectal cancer Germany. The essence of the method is to genetically modify the patient's T-cells so that they can accurately recognize and destroy tumor cells.
Mechanism of action of CAR T-cell therapy:
- T-cells are taken from the blood and modified so that a special receptor (CAR) appears on their surface, capable of recognizing tumor cells
- After returning to the patient's body these CAR T-cells actively attack cancer cells in the primary tumor and in distant metastases
- The method allows doctors to kill cancer cells pointwise (without damaging healthy tissues)
Advantages of CAR T-cell therapy for patients with stage 4 rectal cancer:
- Powerful and specific immune response against tumor cells
- Possibility of controlling metastatic cancer in the liver, lungs and abdomen
- Combination with other methods (dendritic cell therapy, checkpoint inhibitors or targeted therapies) increases the effectiveness of the treatment
- Reduced systemic complications compared to classical systemic therapy
Clinical studies in leading German oncology clinics demonstrate that CAR T-cell therapy can significantly improve the control of tumor cell growth and reduce the risk of metastatic spread.
When choosing a primary treatment method, patients often consider both the expected effectiveness and the treatment cost rectal cancer Germany, which depends on the individual therapy plan, hospital and combination of methods.
| Treatment method | Mechanism of action | Advantages | Cost of treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cytoreductive surgery + HIPEC | Surgical removal of all visible tumor cells followed by hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy | Destroys residual tumor cells; local action allows higher drug concentration | €55,000 - €75,000 in Germany €83,000 - €118,000 in Great Britain €112,000 - €150,000 in the USA |
| Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) | Blocking the arteries supplying the tumor with local chemotherapy | Reduces tumor size; minimal impact on healthy tissues | €6,500 - €24,000 in Germany €25,000 - €45,000 in Great Britain €40,000 - €100,000 in the USA |
| Dendritic cell therapy | Dendritic cells stimulate the immune system to recognize and attack cancer cells | Dendritic cell therapy has minimal systemic side effects; can be combined with other treatments | €20,000 - €38,000 in Germany Not available in Great Britain €100,000 - €150,000 in the USA |
| Checkpoint inhibitors | Block immune checkpoint signals to activate T-cells | Enhances immune response against tumor cells, reduces relapse risk | €375,000 - €420,000 in Germany €400,000 - €500,000 in Great Britain €600,000 - €1,000,000 in the USA. |
| CAR T-cell therapy | Genetic modification of T-cells to directly recognize and kill cancer cells | Highly specific attack; controls metastatic cancer | €450,000 - €550,000 in Germany |
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex management programs in each individual case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you in pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods and with leading specialists in this field.
International Cancer Care: Patient Stories with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions About Stage 4 Rectal Cancer Treatment in Germany
Send request for treatmentStage 4 rectal cancer treatment in Germany involves a comprehensive approach: surgery, systemic therapy, targeted therapies and immune methods and local procedures (HIPEC, TACE). The treatment is selected individually for each patient.
Treatment options for rectal cancer in Germany include advanced technologies, highly qualified surgeons and multidisciplinary teams that provide patients with access to modern treatment methods and international protocols.
The prognosis depends on the stage and spread of metastatic cancer, the patient's general condition and the use of innovative methods. Modern treatment in German leading clinics can significantly prolong disease control and improve quality of life.
Advanced treatment options for stage 4 rectal cancer in Germany include surgical removal of the tumor and metastases, HIPEC, TACE, targeted therapies, dendritic cell therapy and CAR T-cell therapy, which provides comprehensive tumor control.
The treatment cost of rectal cancer in Germany varies depending on the scope of procedures and therapies included. The cost of advanced rectal cancer therapy can differ based on the combination of surgery, systemic therapy, local interventional methods like TACE or HIPEC, and innovative immune treatments. Individual assessment by a German cancer clinic provides a precise estimate.
Symptoms of stage 4 rectal cancer include abdominal pain, blood in the stool, weight loss, anemia, constant fatigue and changes in bowel habits. Metastatic rectal cancer symptoms may occur as additional manifestations in the liver, lungs, and other organs.
Immunotherapy for rectal cancer and interventional therapies in Germany can more effectively fight tumor cells, reduce the risk of recurrence and control metastatic cancer when combined with classical treatment methods.
An international patient with stage 4 rectal cancer in Germany can start treatment via the Booking Health company. The Booking Health team provides all necessary services for organizing treatment abroad for rectal cancer (medical coordination, online consultations and treatment planning).
Cytoreductive surgery with hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy removes all visible tumor cells and locally applies heated chemotherapy drugs. This effectively destroys residual tumor cells and controls metastatic cancer.
TACE blocks the arteries that feed the tumor and delivers chemotherapy drugs directly to the affected area. The method reduces the size of the tumor, deprives the tumor cells of oxygen and limits damage to healthy tissue.
Dendritic cell therapy activates the immune system, stimulating it to attack tumor cells, which increases the body's natural defenses. The method can be combined with other treatments, has minimal impact on healthy tissue and improves control of tumor cells in stage 4 rectal cancer.
CAR T-cell therapy genetically modifies a patient’s T-cells to precisely recognize and destroy tumor cells. It provides highly precise tumor control and helps fight metastatic cancer. It can be combined with other treatments.
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Brenda K Edwards, Elizabeth Ward, Betsy A Kohler et al. Annual Report to the Nation on the Status of Cancer, 1975–2006, Featuring Colorectal Trends and Impact of Interventions (Risk Factors, Screening, and Treatment) to Reduce Future Rates. Cancer. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2013 Apr 8. Published in final edited form as: Cancer. 2010 Feb 1;116(3):544–573. doi: 10.1002/cncr.24760. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[2] Mercedes Navarro, Andrea Nicolas, Angel Ferrandez, Angel Lanas. Colorectal cancer population screening programs worldwide in 2016: An update. World J Gastroenterol. 2017 May 28;23(20):3632–3642. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v23.i20.3632. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[3] S J Winawer, R H Fletcher, L Miller, F Godlee et al. Colorectal cancer screening: clinical guidelines and rationale. Gastroenterology. 1997 Feb;112(2):594-642. doi: 10.1053/gast.1997.v112.agast970594. [DOI] [PubMed]
[4] Cathy Eng, Howard Hochster. Early-Onset Colorectal Cancer: The Mystery Remains. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2021 Aug 18;113(12):1608–1610. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djab127. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[5] Rebecca L Siegel, Nikita Sandeep Wagle, Andrea Cercek et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2023. CA Cancer J Clin. 2023 May-Jun;73(3):233-254. doi: 10.3322/caac.21772. Epub 2023 Mar 1. [DOI] [PubMed]
[6] Rebecca L Siegel, Kimberly D Miller, Ann Goding Saueret et al. Colorectal cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020 May;70(3):145-164. doi: 10.3322/caac.21601. Epub 2020 Mar 5. [DOI] [PubMed]
[7] Douglas K Rex, C Richard Boland, Jason A Dominitz et al. Colorectal cancer screening: Recommendations for physicians and patients from the U.S. Multi-Society Task Force on Colorectal Cancer. Gastrointest Endosc. 2017 Jul;86(1):18-33. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.04.003. Epub 2017 Jun 6. [DOI] [PubMed]
[8] Amir Qaseem, Carolyn J Crandall, Reem A Mustafa et al. Screening for Colorectal Cancer in Asymptomatic Average-Risk Adults: A Guidance Statement From the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2021 May 26. Published in final edited form as: Ann Intern Med. 2019 Nov 5;171(9):643–654. doi: 10.7326/M19-0642. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[9] Aasma Shaukat, Charles J Kahi, Carol A Burke et al. ACG Clinical Guidelines: Colorectal Cancer Screening 2021. Am J Gastroenterol. 2021 Mar 1;116(3):458-479. doi: 10.14309/ajg.0000000000001122. [DOI] [PubMed]
[10] Gholamreza Roshandel, Fatemeh Ghasemi-Kebria, Reza Malekzadeh. Colorectal Cancer: Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention. Cancers (Basel). 2024 Apr 17;16(8):1530. doi: 10.3390/cancers16081530. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[11] E Pretzsch, F Bösch, J Neumann et al. Mechanisms of Metastasis in Colorectal Cancer and Metastatic Organotropism: Hematogenous versus Peritoneal Spread. J Oncol. 2019 Sep 19;2019:7407190. doi: 10.1155/2019/7407190. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[12] Wim Ceelen, Jesse Demuytere, Ignace de Hingh. Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy: A Critical Review. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 22;13(13):3114. doi: 10.3390/cancers13133114. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[13] Suying Yan, Wanting Wang, Zhiqiang Feng et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors in colorectal cancer: limitation and challenges. Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 11;15:1403533. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1403533. [DOI] [PMC free article]
Read:
Rectal Cancer Treatment: Full Treatment Options Guideline
Article menu:
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health