Cervical cancer is one of the most frightening diagnoses to give to a woman. More than half a million new cases are reported every year worldwide, and half are diagnosed at late stages when the patient already shows signs of the disease. New technologies in screening and vaccines have enhanced early diagnosis, but problems remain, including how to work successfully within a complex staging system to select the best individual method of treatment. You might be recently diagnosed or just wanting to explore the options after a recurrence, but it is paramount to know what you will go through. This guide will show the main steps, describe new treatment types, and provide you with the knowledge to ask the correct questions and make the right decisions.
Understanding Cervical Cancer: The Main Challenges
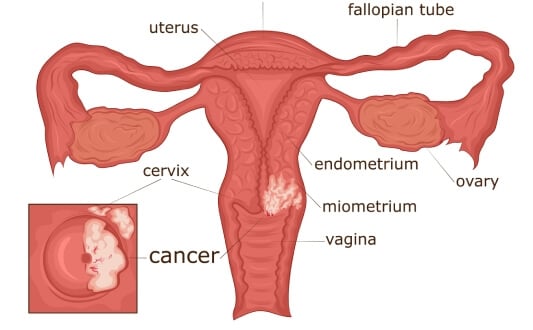
Persistent HPV infection is most commonly associated with a tumor in the cervix, especially the high-risk types of HPV infection, such as types 16 and 18. Such results support the significance of prevention and have made a tremendous contribution to the development of the HPV vaccine market globally. Cervical cancer is still a significant health problem worldwide, despite the efforts made to prevent it. By 2022, it had caused more than 660,000 new cases and around 350,000 deaths across the globe [1]. This constant burden highlights the necessity of further advancements in the areas of diagnosis and treatment for cervical cancer, particularly focusing on early diagnosis and successful management.
Development of the disease may follow a pattern, where, due to pre-cancerous changes, it may take years before the disease is detected and treated. Cervical cancer staging is very important in the procedure of choosing the most relevant treatment plan. The most common (and most used) is the FIGO staging system, the most recent update of which (used in ESGO/ESTRO/ESP 2023 guidelines [2]) includes clinical and radiologic data as well.
The stages range from localized tumors to advanced metastatic disease:
- Stage 0 cervical cancer: At this stage atypical cells are found only in the superficial layer of the cervical epithelium and have not yet penetrated deeper tissues. This condition is called carcinoma in situ (cancer in place). This is a pre-invasive form of the disease which has a very high chance of complete cure if treated promptly
- Stage 1 cervical cancer: The cancer is limited to the cervix. This covers very early tumors that can be seen only through a microscope (Stage 1A cervical cancer), and lesions that are visible and are restricted to the cervix (Stage 1B). Treatment for stage 1 cervical cancer at this point has a good prognosis
- Stage 2 cervical cancer: The cancer has spread past the cervix but is still contained in the pelvis. It can encompass the upper area of the vagina (Stage IIA) or extend into the tissue surrounding the vagina (Stage 2B), but not to the pelvic wall or lower vagina
- Stage 3 cervical cancer: The disease has spread more widely in the pelvis. It involves the lower third of the vagina (Stage IIIA), spread to the pelvic wall or kidney (Stage IIIB), and/or proven spread of the cancer to pelvic or para-aortic lymph nodes (Stage IIIC)
- Stage 4 cervical cancer: The cancer has either spread to adjacent tissues, including the bladder or rectum (Stage 4A), or is located in distant sites such as the lungs, liver, or bones (Stage 4B). This is the highest stage, associated with a much poorer prognosis
The less advanced stages of the disease can be treated through surgery only; however, in more severe cases, a combination of chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and, more recently, targeted therapy may be necessary. The 2023 ESGO/ESTRO/ESP guidelines recommend individualization of treatment based not only on the stage but also on patient-specific factors, with a primarily multidisciplinary and evidence-based approach. According to the latest ESGO recommendations [3], 2025 will become a tipping point in the history of cervical cancer practice, incorporating precision medicine, minimally invasive medical procedures, and holistic patient care.
Standard Treatment Options for Cervical Cancer
Germany adheres to internationally recognized standards for cervical cancer treatment by stage, particularly the ESGO/ESTRO/ESP guidelines. Therapy is provided in specialized oncology centers using advanced diagnostic tools and a multidisciplinary approach. Surgical intervention is normally employed during early stages (for stage 1 cervical cancer treatment or stage 2), which includes radical hysterectomy with removal of pelvic lymph nodes. In very few scenarios, fertility-sparing surgeries are carried out, such as conization or radical trachelectomy. While minimally invasive surgery is available, ESGO guidelines recommend caution in certain high-risk tumors.
Chemotherapy is predominantly used in combination with chemoradiation in cases of locally advanced stages of cervical cancer (≥IIB), or as systemic treatment in metastatic or recurrent disease. In more complex or severe cases, specific agents may be added to chemotherapy, such as an anti-VEGF agent, to increase overall survival.
Biomarker expression may be considered when choosing immunotherapy, including PD-1 inhibitors, based on emerging ESGO and EMA guidance.
Radiotherapy continues to be a mainstay of treatment for stage 3 cervical cancer and as an adjuvant in stage 4. German centers are widely adopting techniques such as IMRT, which is extremely accurate and has reduced side effects.
Innovative and Advanced Therapies for Cervical Cancer
New high-tech treatments have opened a new era in healthcare, providing more targeted, personalized, and effective ways to combat diseases. These innovative therapies continue to transform clinical practice and improve patient outcomes in a large number of conditions.
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) for Cervical Cancer
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a technologically advanced interventional mode of administering treatment to tumors with very high precision. This minimally invasive procedure involves both direct delivery of chemotherapy and embolization, selectively blocking the arteries supplying the tumor with blood, in order to not only localize the drug to the tumor site but also to starve the tumor of oxygen and nutrients.
In the case of locally advanced cervical cancer, TACE may be used as a neoadjuvant treatment to decrease tumor load prior to surgery or radiation, making it easier to treat. TACE provides good local control with symptom relief and a decrease in tumor mass, which may allow the use of other systemic agents, such as immunotherapy or targeted therapy.
This localized treatment not only enhances the control of local tumors and symptoms but also significantly contributes to multimodal treatment options. TACE has been demonstrated as an adjuvant (to improve the efficacy of systemic drugs, like immunotherapy) by releasing tumor-associated antigens, facilitating the immune response for cancer cell recognition and destruction.
The procedure is carried out under real-time fluoroscopy by inserting a catheter through the femoral artery to the vessels that feed the tumor. Once there, chemotherapeutic agents are injected, and then embolic materials are administered to block the blood flow to the tumor.
TACE is an easily tolerated procedure that is repeatable and can be adjusted to meet the needs of patients. It is especially useful in cases where surgical options are limited or systemic therapies require assistance. TACE has its niche in the overall management of cervical cancer, whether as a sole intervention, for downstaging the tumor, or as a component of a multidisciplinary regimen.
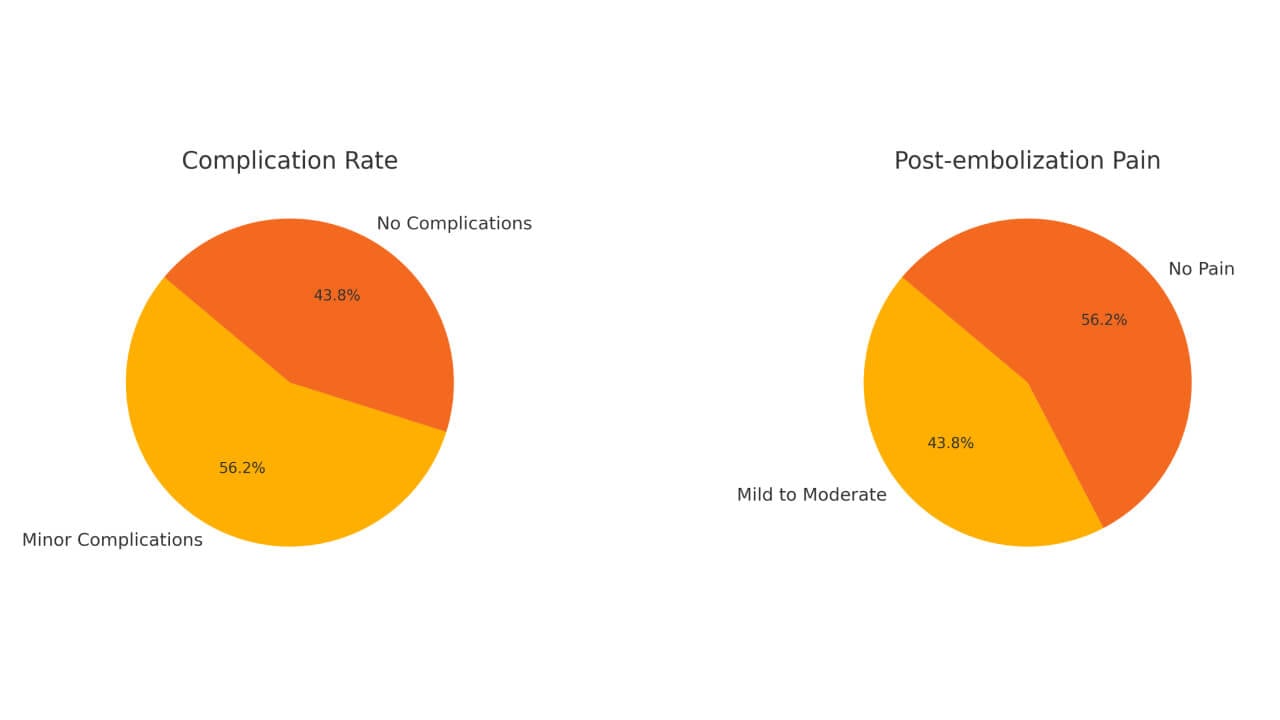
The clinical potential of TACE is reinforced by recent clinical results of uterine arterial chemoembolization in advanced-stage or recurrent cervical cancer [4]. TACE showed a very good safety and efficacy profile in a cohort of 16 women with cervical cancer.
These results support TACE as a safe, effective, and cost-effective alternative treatment for cervical cancer to augment outcomes in patients with limited options — a potent adjuvant to both radiation and systemic therapies.
Electrochemotherapy of cervical cancer
Electrochemotherapy (ECT) treatment for cervical cancer combines electrical pulses with chemotherapy drugs to dramatically increase treatment effectiveness. Electrochemotherapy of cervical cancer works by creating temporary pores in cancer cell membranes — allowing massive drug uptake that wouldn't occur otherwise. Professor Karl R. Aigner pioneered this technique for pelvic malignancies, demonstrating that tumor cells become dramatically more vulnerable after electroporation.
Electro-chemotherapy procedure: electrodes positioned around tumor at 2.5-3 centimeters apart create electrical fields. Pulses are delivered (patients under anesthesia), synchronized with ECG to avoid cardiac complications — computer controls everything automatically. Cancer cells become porous. When high-concentration chemotherapy is administered, drug penetration increases exponentially.
Electrochemotherapy for cervical cancer is particularly effective for recurrent cases or when radiation has already been used. Tumors can shrink 80% within a week in some cases — that is the power of this approach. Side effects are minimal because treatment is localized.
Electrochemotherapy cost vary by complexity. Booking Health provides cost of electrochemotherapy information — investment worthwhile when conventional options are exhausted.
Regional chemotherapy for cervical cancer
Regional chemotherapy for cervical cancer delivers concentrated drugs directly to pelvic region through arterial catheters — avoiding dilution that occurs with systemic chemotherapy. Professor Karl R. Aigner developed isolated pelvic perfusion techniques achieving complete remission in cervical cancer patients without radiation therapy, crucial advancement for women facing this diagnosis. You can see the interview with professor Karl R. Aigner at the end of this section.
Method works by isolating blood flow to pelvis. High-dose chemotherapy drugs administered directly to tumor site — concentrations 10-20 times higher than systemic therapy can safely deliver. That is why results are dramatic: some patients treated by Professor Aigner achieved complete remission without radiation, without severe side effects, without long-term complications radiation causes (scarring, sexual dysfunction, bowel problems).
Squamous cell carcinomas like cervical cancer respond particularly well. Blood supply to these pelvic tumors is good, drugs reach cancer cells efficiently when delivered through arteries. After treatment, special filtration procedures remove remaining drugs — patients walk around clinic by afternoon.
Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC) for Cervical Cancer
A recent advancement in the treatment of peritoneal metastases is Pressurized Intraperitoneal Aerosol Chemotherapy (PIPAC), a minimally invasive procedure designed for high local efficacy and low systemic toxicity. PIPAC is a potent solution in cases of peritoneally involved advanced cervical cancer, allowing management of disease progression, symptoms, and maintenance of a good quality of life.
This method is performed with aerosolized chemotherapy pressurized into the abdominal cavity during laparoscopy. This increases the depth of the drug penetration into tumor tissue and ensures uniform distribution over the peritoneal surfaces. PIPAC permits higher local concentrations of the drug with fewer side effects by avoiding systemic exposure.
PIPAC has also been an effective therapeutic intervention in patients with cervical cancer who show peritoneal dissemination or a poor response to systemic treatment. It can be used repeatedly, keeping the tumor under control continually, with an excellent safety profile. Multimodal treatment plans may also include PIPAC, which increases the efficacy of systemic chemotherapy or immunotherapy.
The PIPAC procedure has proven to be a significant benefit in the treatment of cervical cancer. Some of its key features are listed below:
- Low systemic toxicity and high local drug concentration.
- Successful tumor volume reduction and management of symptoms.
- Maintaining quality of life, even in terminal stages.
- Least invasive, repeatable therapy.
- Can be used effectively with systemic therapies and palliative care plans.
PIPAC plays a vital role in broadening cervical cancer treatment options for patients with few alternatives and supports a more individualized approach to care.
PIPAC is a newer, effective, and patient-centered form of treatment as part of an overall approach to advanced cervical cancer, with the potential to enhance outcomes in cases where other forms of treatment might fail.
Dendritic Cell Therapy for Cervical Cancer
Dendritic cell (DC) therapy is a medical revolution within the context of cancer immunotherapy, using the body’s immune system to attack and destroy cancer cells. Special antigen-presenting cells called dendritic cells are key in the activation and control of immune responses. They capture and process antigens and present them to T-lymphocytes, thus mobilizing the adaptive immune system to identify and kill abnormal cells.
Scientific Background
Dendritic cell therapy is based on remarkable immunological discoveries. Dendritic cells are immune cells recognized for inducing adaptive immune responses and were discovered in 1973 by Dr. Ralph M. Steinman as a unique group of immune cells. For this discovery, he won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011.
Dendritic cell therapy is a relatively new, individualized method of immunotherapy intended to stimulate a patient’s immune system to destroy cancer cells. This therapy is particularly applicable to patients with recurrent, residual, or metastatic cervical cancer who have a limited response to conventional therapies.
Treatment Process
The treatment involves several precise steps, all conducted under GMP-certified laboratory conditions. First, a sample of the patient’s blood (approximately 200 ml) is taken to isolate monocytes—immune precursors that will later develop into dendritic cells. In the lab, these cells are matured and "trained" using tumor-specific antigens, either derived from tumor tissue or standardized HPV-associated proteins, which are commonly involved in cervical cancer.
After a 7-day cultivation and quality control process, the dendritic cells are prepared for reintroduction into the patient’s body. They are injected subcutaneously—typically in the groin area—to activate a natural and highly specific T-cell response. This immune activation aims to recognize and destroy cancer cells throughout the body, not only at the injection site, with the expectance of achieving a systemic therapeutic effect related to long-term tumor control.
Clinical Evidence
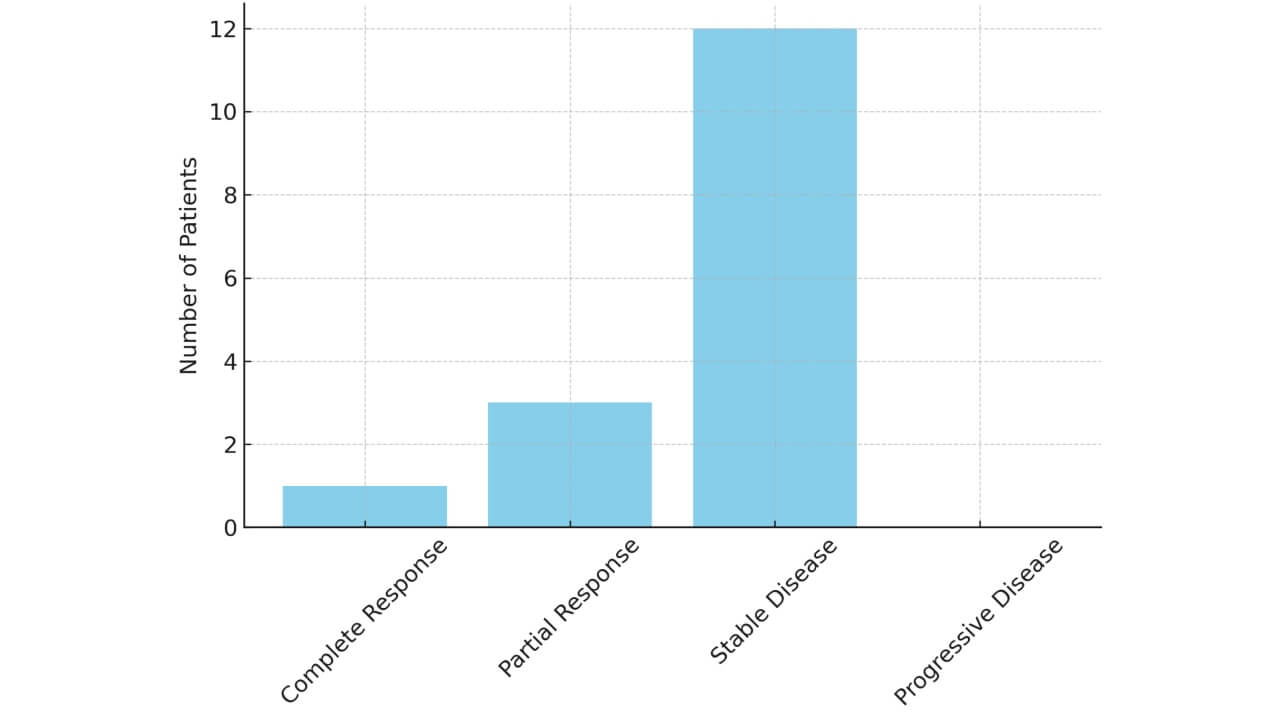
In a Phase I/II clinical trial involving 45 patients with recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer treated with dendritic cell vaccines, 44% of patients showed a positive immune response and experienced partial or complete tumor regression.
Another study of 30 patients with advanced cervical cancer reported that 62% of patients demonstrated improved quality of life and immune activation, with a median overall survival of 12 months, showing excellent results compared to standard cervical cancer treatments by stage.
| Therapy Type | 2-Year Survival Rate | Response Rate | Duration | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatments | ~25% for advanced cancer | Less than 10% | Several weeks to months | Moderate to severe (fatigue, nausea, infertility, bowel/bladder issues) |
| Innovative Methods | ~60-75% in select advanced/refractory cases | 45-65% | Up to 4-6 sessions | Mild (fever, localized inflammation, flu-like symptoms) |
*Booking Health clinical analytics. Actual results may vary individually.
In terms of safety, dendritic cell therapy is well tolerated, and less than 5% of patients report mild to moderate adverse events, which occur primarily as local reactions to injections.
To discover more information on the price of cervical cancer treatment, including treatment packages, and our list of the best hospitals in the world, see our special page. It provides a clear cost for cervical cancer treatment and allows you to compare clinics in terms of services, location, and expertise.
You can learn more about dendritic cell therapy by watching the following interview with a pioneer in the area, Prof. Frank Gansauge. The specialist discusses the mechanisms of dendritic cell therapy, clinical uses, and the future of this promising treatment.
Expert Insights from Prof. Gansauge: The Power of Dendritic Cell Therapy in Cancer Treatment
Leading Сlinics for Сervical Сancer Treatment
Choosing a clinic is one of the key factors in the successful treatment of cervical cancer (especially in late or recurrent stages). Patients are increasingly turning to specialized cervical cancer treatment centers. They combine international clinical standards, a multidisciplinary approach and access to innovative therapy methods. The best cancer cervical hospital works on the principle of individualized treatment planning (taking into account the stage of the disease and tumor's molecular characteristics).
Germany is deservedly among the world leaders in terms of the level of medical services in cervical cancer clinics, as its university hospitals strictly adhere to the ESGO/ESTRO/ESP recommendations, use advanced surgical and radiotherapy technologies, and also actively implement innovative approaches. For many international patients a transparent cervical cancer treatment cost structure and the possibility of combining standard and experimental methods are also important factors. That is why German centers are consistently ranked among the world's top cervical cancer hospitals.
University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich (LMU Munich)
The LMU Munich clinic is widely recognized as one of the leading centers for gynecological oncology in Europe and is often considered by patients as the best cervical cancer hospital. It treats all stages of the disease – from early forms to metastatic processes. The center specializes in radical surgery, combined chemoradiotherapy and the integration of interventional and immunotherapeutic methods. LMU Munich is often called the best hospital in the world for cervical cancer among academic medical institutions – due to its strong scientific base and clinical research.
University Hospital Rechts der Isar, Technical University of Munich
The University Hospital Rechts der Isar is considered the best hospital for cervical cancer treatment in cases of locally advanced and recurrent cervical cancer. The gynecological oncology team works in close cooperation with departments of radiotherapy, interventional radiology and nuclear medicine. The clinic actively uses modern radiotherapy methods, targeted drugs and clinical protocols – making it one of the top oncology cervical cancer clinics in the world for patients with complex clinical cases.
University Hospital RWTH Aachen
RWTH Aachen University Hospital is a large referral center, that is consistently included in the list of cervical cancer hospitals offering both standard and innovative treatment approaches. The clinic has extensive experience in combining surgery, chemoradiotherapy and regional methods (including interventional technologies). For patients looking for the best hospital for treating cervical cancer with the optimal balance of effectiveness, safety and accessibility – RWTH Aachen is one of the best options in Europe.
Cervical Cancer Treatment Cost Comparison
| Country | Surgery | Chemotherapy | Dendritic Cell Therapy | TACE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germany | €25,000 – €45,000 | €80,000 – €150,000 full course | €20,000 – €38,000 | €6,500 – €24,000 per session |
| United Kingdom | €35,000 – €55,000 | €90,000 – €165,000 full course | Not available | €25,000 – €45,000 |
| United States | €65,000 – €85,000 | €100,000 – €180,000 full course | €100,000 – €150,000 | €40,000 – €100,000 |
A Second Chance: Maria’s Battle Against Stage IV Cervical Cancer
It is a body blow, emotionally and physically, to be diagnosed with stage IV cervical cancer, especially when metastases have spread to the lungs, liver, and bones. Other debilitating symptoms, including chronic bleeding, fatigue, and severe abdominal pain, can rapidly develop without prompt and successful treatment. But the way cancer care is delivered has changed significantly in the past few years. Groundbreaking treatments and gaining control of the course of illness are becoming possible, thanks to innovative medical centers, paired with personalized international patient support services.
Today, innovative treatments, including dendritic cell therapy, immunotherapy, and targeted interventional therapy like chemoembolization, are bringing new hope. Patients who previously received a diagnosis with no alternatives are beginning to experience dramatic clinical responses.
Maria Gonzalez is a 47-year-old Spanish woman who was confronting the first signs of stage IV cervical cancer with metastasis. Her disease had spread to the liver and lungs. She was in persistent pain, and she barely had the energy to move. Local doctors were only able to provide palliative care, advising her to focus on comfort rather than cure.
But Maria was not willing to surrender. She and her daughter started searching across borders to find more sophisticated solutions. They found Booking Health, a reputable medical tourism organization that links international patients to the most well-known hospitals and oncologists across the globe. Booking Health connected Maria to a cancer center in Germany that has been successful in the medical treatment of advanced malignancies in gynecology through dendritic cell therapy and chemoembolization.
Henceforth, Booking Health has been an essential part of her journey. The team managed all the planning, including clinic selection, appointment scheduling, visa processing, translation services, and assistance after the treatment process. This all-inclusive support gave Maria time to concentrate on her recovery without having to navigate a foreign health system alone.
When Maria started her visit to the clinic, she underwent comprehensive diagnostics. Her medical staff created a customized therapy plan that integrated groundbreaking immunotherapy and selective chemoembolization to treat liver metastases. The response was swift. Within a few weeks, her symptoms began to improve, and imaging after three months showed a considerable reduction in tumor volume.
After six months, Maria reported phenomenal improvement in her quality of life. Her suffering was relieved, her strength restored, and she even returned to part-time employment. She says she never imagined she would feel like herself again.
Now Maria continues long-term immunotherapy maintenance and visits her medical team regularly. She is an eloquent example of how the availability of the latest treatment options and professional international organizations can radically shift the outlook, even for the most difficult diagnoses.
To patients such as Maria, Booking Health is not just a service provider, but a lifeline, an avenue to the best care in the world, and an ally in the struggle against cancer.
Advanced Cervical Cancer: There Is Always a Way Forward
The news of late-stage cervical cancer can be received as the end of the road, but it does not have to be. Even at stage 3 or 4, when the disease may have metastasized to other areas of the body, and the usual treatments may no longer seem effective, contemporary oncology offers a variety of innovative treatment plans that are constantly updated year after year.
This complex stage does not have a one-size-fits-all approach. The difference lies in the possibility of designing a treatment plan based on individual conditions, needs, and goals. This can be a well-considered mix of systemic therapy (such as chemotherapy or immunotherapy), interventional therapy (such as TACE), and advanced cell biotechnology (such as dendritic cell therapy). These multimodal strategies, in many instances, provide not only symptom control but also the potential to prolong life and improve its quality.
Here is where Booking Health comes in. We understand how desperate, frightened, and paralyzing the choices can be for patients with advanced cancer. We are dedicated to matching you with a world-class medical center, the best oncologist, and the latest treatment modalities — faster, safer, and with full logistic support. From medical document translation and visa services to direct scheduling and personal coaching throughout your treatment, we accompany you every step of the way.
For patients with stage 4 cervical cancer, we invite you to read our detailed review of 4 stage cervical treatment, in which you will find comprehensive information, options, and real patient outcomes demonstrating that all is not lost.
Regardless of the complexity of your diagnosis, you are not alone, and your case is not hopeless. Recovery is possible with the right strategy and the right support. It becomes a plan.
Cancer Treatment Abroad: Patient Experiences with Booking Health
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex cancer management programs in each individual case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized cervical cancer treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you on the way of pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods for cervical cancer with leading specialists in this field.
Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients About Cervical Cancer Treatment
Send request for treatmentTreatment of cervical cancer involves chemotherapy, surgery, or radiation. In more progressive stages, the treatment of cervical cancer can include immunotherapy, targeted therapy, dendritic cell therapy, and TACE.
Yes, cervical cancer is usually treatable, especially at the initial stage. Newer treatments can be used successfully in cervical cancer patients even at later stages of the disease or during recurrence cases to substantially prolong the survival and lower the chances of relapse.
Pap tests, HPV testing, and cervical biopsy are used in the diagnosis of cervical cancer. To evaluate the spread of the disease and the stage of cervical cancer treatment, it is better to use the imaging tools, such as MRI, CT, or PET scans.
The survival rates of cervical cancer depend on the stage of the cancer. Stage I cervical cancer shows a more than 90% survival rate in five years. Cervical cancer, particularly stage II-A cervical cancer, has a slightly low and yet optimistic prognosis.
The chemotherapy for cervical cancer is also necessary, particularly in the advanced stages. It is usually used together with radiation and helps in tumor reduction and in relieving the symptoms.
In some cases of early-stage cervical cancer, fertility preservation can be realized, particularly in fertility-sparing procedures such as radical trachelectomy or laser ablation. Nevertheless, certain treatments may affect fertility. Before patients begin therapy, they need to use private counseling to address concerns about future pregnancy.
The side effects of cervical cancer include fatigue, nausea, and problems with the immune system. Radiation treatment has the risk of affecting the bladder or bowel functioning, whereas surgery may cause pain or infection. Patients must talk to their physician about aspects associated with recovery.
Treatment of stage 0 cervical cancer and stage I cervical cancer often involves surgery, and it can be a possibility in some cases of stage II cervical cancer. At advanced stages, it may be used as a palliative treatment.
Radiation therapy destroys cancer cells in the cervix and area by the use of high-power beams. It is used as a routine treatment in case of inoperable or locally advanced disease.
Yes. One of the emerging treatments for recurrent or advanced cervical cancer is immunotherapy. These therapies provoke the immune system to fight cancer cells and are increasingly practiced for patients with PD-L1 expression or those who are unresponsive to other treatment methods.
The vaccination against HPV is not a cancer treatment. However, it protects patients from the HPV high-risk types that cause the majority of cases of cervical cancer. Preventive vaccination before exposure to HPV has been shown to play a significant role in the prevention of cervical cancer, especially in the future.
Yes, particularly in cervical cancer that is at advanced stages. Follow-up is important for the early identification of recurrence. Such symptoms as unusual bleeding or pain in the pelvis should also be examined as soon as possible.
The follow-up visits are usually done after every 3-6 months during the first two years, after which they will be done after every 6-12 months. Such visits might include physical examination, imaging, and laboratory tests to check for recurrence or late treatment effects.
The new treatments of cervical cancer are immunotherapy, dendritic cell therapy, TACE, and biologic agents. These are the alternative treatments for cervical cancer, especially in cases of metastasis or recurrence where standard treatment methods are ineffective.
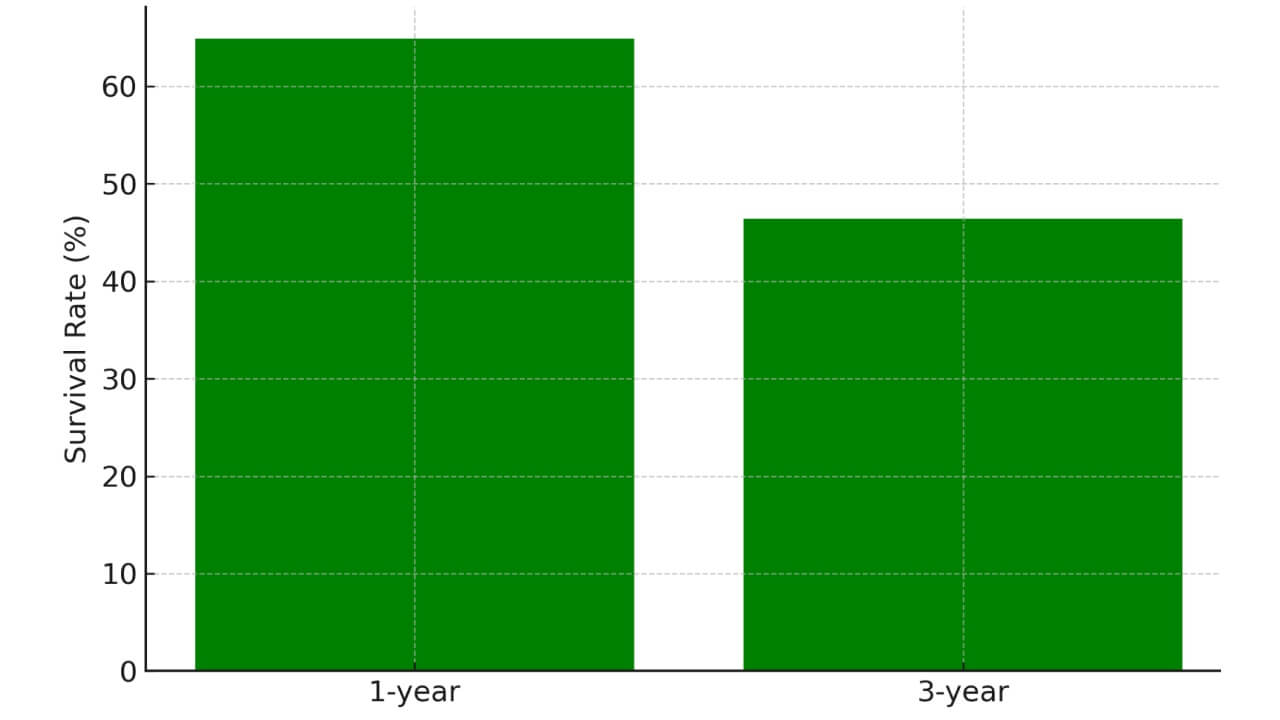
The two-year survival rate for advanced or stage IV cervical cancer averages around 25% with conventional therapy. However, it can reach up to 60-75% in patients receiving innovative treatments (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, PIPAC, or TACE) at specialized oncology centers.
In cervical cancer, traditional chemoradiation achieves a tumor response rate below 10%. On the other hand, advanced approaches like electrochemotherapy, dendritic cell therapy, and targeted interventional radiology have demonstrated 45-65% response rates in some patients.
Standard cervical cancer therapy courses often last several weeks to months, depending on the regimen. In contrast, innovative treatments (e.g., TACE, PIPAC, or dendritic cell therapy) may be completed within four to six short sessions.
In Germany, full-course treatment ranges from €25,000-€60,000 for innovative therapies and €80,000-€150,000 for conventional options. Costs are higher in the UK and USA, where prices may exceed €120,000-€180,000. Access in Australia remains limited, and when available, it tends to be considerably more expensive.
Management of cervical cancer is individualized and based on stage, tumor spread and patient condition. Alongside standard oncologic approaches patients may benefit from locoregional techniques, immune-based strategies or intraperitoneal treatment – when conventional options are limited.
The best results are achieved in centers, that treat cervical cancer regularly and work within dedicated gynecologic oncology programs. Experience with complex pelvic tumors, access to multidisciplinary decision-making and the ability to adapt treatment (when disease behavior changes) are critical.
Patients often choose countries with structured cancer care systems, transparent clinical protocols and strict quality control. Germany is a perfect example – here treatment decisions are evidence-based, closely monitored and adjusted promptly.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] International Agency for Research on Cancer (IARC). Cervical cancer. https://www.iarc.who.int/cancer-type/cervical-cancer
[2] ScienceDirect. ESGO/ESTRO/ESP Guidelines for the management of patients with cervical cancer – Update 2023*. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1048891X24024241
[3] The European Society of Gynaecological Oncology (ESGO). CERVICAL CANCER POCKET GUIDELINES. https://www.esgo.org/media/2019/03/Pocket-Guidelines_Cervical-cancer_June2023.pdf
[4] Yonghua Bi, Yanli Wang, Jianhao Zhang et al. Clinical outcomes of uterine arterial chemoembolization with drug-eluting beads for advanced-stage or recurrent cervical cancer. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021 Dec;46(12):5715-5722. doi: 10.1007/s00261-021-03267-6. Epub 2021 Sep 2. [DOI] [PubMed]
Read:
Treatment of stage 4 cervical cancer in Germany
Article menu:
- Understanding Cervical Cancer: The Main Challenges
- Standard Treatment Options for Cervical Cancer
- Innovative and Advanced Therapies for Cervical Cancer
- Leading Сlinics for Сervical Сancer Treatment
- A Second Chance: Maria’s Battle Against Stage IV Cervical Cancer
- Advanced Cervical Cancer: There Is Always a Way Forward
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
- Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients About Cervical Cancer Treatment
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health