- Local therapy for ovarian cancer
- Systemic therapy for ovarian cancer
- Additional treatments and follow-up care
- New treatment options for 4 stage ovarian cancer
- Specialized hospitals and cost of treatment for ovarian cancer
- Treatment of ovarian tumors abroad, with Booking Health
- Frequently asked questions of our patients
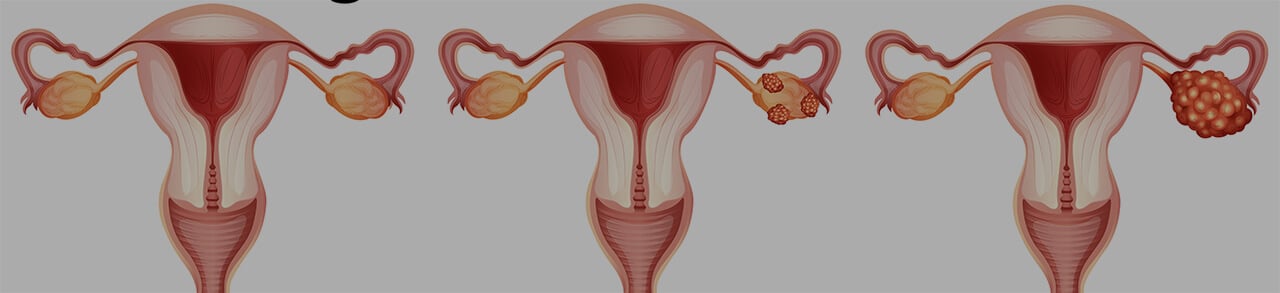
Ovarian cancer remains a significant global health challenge, affecting thousands of women annually and representing one of the most lethal gynecological malignancies. The disease's complexity and high mortality rate, particularly in advanced stages, underscore the critical need for proper treatment approaches. Ovarian cancer requires a precise histological diagnosis and a differentiated treatment approach. Depending on the characteristics of the tumor, oncologists and gynecologists perform sparing laparoscopic and open surgical procedures and photodynamic and radiation therapy. In addition to conventional chemotherapy and the administration of antiestrogens, doctors have started using personalized dendritic cell vaccines and drugs for targeted therapy in their clinical practice. Information about the methods of targeted delivery of chemotherapeutic drugs to a tumor with nanoparticles is also available. Stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment options are in the sphere of special attention, as they must be efficient and well tolerated at the same time.
Local therapy for ovarian cancer
Local therapy includes the surgical removal of the tumor, photodynamic therapy, and irradiation of the organs affected by metastases. These techniques can be aimed at curing cancer or alleviating its symptoms. A feature of local therapy is the targeted destruction of the primary tumor or metastases with minimal impact on healthy tissues. The treatment regimen includes one or more therapeutic methods and is developed according to the results of diagnostics. In a case of suspected ovarian cancer, the procedure of diagnosis making includes:
- CA 125, CA 19-9, HE 4, and CA 72-4 tumor marker testing;
- AFP and β-HCG testing in suspected germ cell tumors;
- inhibin test in suspected stromal tumors;
- abdominal and pelvic ultrasound examination;
- contrast-enhanced CT scanning of the chest, abdominal cavity, and pelvis;
- biopsy with histopathological examination (the gold standard for diagnosis making).
Surgical treatment is carried out when the tumor can be removed completely, or when the operation will alleviate the patient's condition significantly (eliminate pain, restore normal bowel function, or manage other symptoms). The following types of surgical procedures can be performed to treat ovarian cancer:
- Unilateral removal of the ovary. If a fallopian tube is affected, it will also be removed during the laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy.
- Bilateral removal of the ovaries.
- Combined removal of the ovaries and uterus.
- Surgery for advanced cancer.
The most precise and safe method of surgical treatment for ovarian cancer is surgery using the da Vinci robot. The da Vinci robotic system combines the advantages of laparoscopic procedures (small incisions of the anterior abdominal wall and minimal blood loss) with higher accuracy, due to the use of an advanced set of surgical instruments. In addition to the classic light source and high-resolution video camera, the da Vinci robot has 3 arms. The presence of an additional manipulator and a volume of movements compared to a human hand, allow surgeons to precisely remove even small ovarian tumors of any localization. The use of special microsurgical instruments eliminates the risk of complication development and makes negative postoperative symptoms less pronounced.
Photodynamic therapy can be performed during surgery or in the postoperative period. Prior to the procedure, a woman should take a phthalocyanine-based drug. Phthalocyanine is a pigment that accumulates in malignant cells and decomposes with the formation of oxygen-derived radicals under the influence of infrared light rays. Oxygen radicals oxidize the internal structures of cancer cells and destroy the tumor. Photodynamic therapy is completely safe and non-toxic for healthy tissues.
Radiation therapy is rarely used as the first-line treatment for a primary tumor, but it is effective for local and distant metastases. In particular, radiation therapy is becoming the method of choice for inoperable metastases in the brain or spinal cord. Depending on the location of the malignant focus, oncologists and clinical radiologists use targeted external radiation therapy or internal irradiation – brachytherapy.
Systemic therapy for ovarian cancer
Conventional systemic therapy involves the intravenous or oral administration of drugs that enter the systemic circulation and reach the primary tumor and metastases. Systemic treatment is effective at advanced stages of cancer, when it is impossible to remove the whole primary tumor and micrometastases are present in the uterus, fallopian tubes, omentum, spleen, or liver.
Chemotherapy for ovarian cancer is carried out in a combined mode with the use of cytostatic preparations of platinum (for example, cisplatin or carboplatin) and taxanes (for example, paclitaxel and docetaxel). The drugs are administered intravenously every 3-4 weeks. In most cases, a course of chemotherapy includes 3 to 6 of these cycles.
Hormone therapy is most effective for stromal tumors. It includes three groups of drugs that block the action of estrogen:
- Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone agonists that directly inhibit estrogen synthesis in the ovaries
- Tamoxifen with antiestrogenic activity
- Aromatase inhibitors that inhibit the synthesis of estrogen from other steroid hormones
Targeted therapy currently includes 2 types of drugs:
- Angiogenesis inhibitors, which suppress vascular endothelial growth factors (VEGF) and contribute to a decrease in tumor size.
- Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARP), which deprive tumor cells of the ability to repair damaged DNA, which ultimately leads to their death. Thanks to the accelerated approval procedure, which the FDA conducts in exceptional cases, olaparib (Lynparza), a PARP inhibitor, entered clinical practice ahead of schedule.
Additional treatments and follow-up care
Additional methods can be used as part of an integrative therapeutic approach, along with the conventional medical interventions. Their goal is to enhance the effect of the main therapy and reduce its side effects, relieve stress, and improve the patient's quality of life. These methods include:
- acupuncture;
- massage;
- phytotherapy;
- aromatherapy;
- meditation;
- yoga and gymnastics qigong.
After the completion of active treatment and discharge from the clinic, the woman remains under the supervision of both a gynecologist and an oncologist. The list of mandatory medical examinations includes a gynecological examination, a CA 125 blood test, and abdominal ultrasound scanning. These are held every 3 months during the first 2 years, every 4 months during the third year, and every 6 months during the subsequent years.
When complaints, pathological changes on an ultrasound scan, or increased levels of CA 125 appear, a doctor will carry out an extended examination in order to receive additional information. This includes a CT scan of the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs, as well as a chest X-ray or CT scan. With the timely start of treatment, using modern surgical technologies and pharmaceuticals, the five-year survival rate at the first stage of ovarian cancer reaches 90%.
New treatment options for 4 stage ovarian cancer
Stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment options are aimed at restricting the growth and spreading of the primary tumor, destroying metastases or suppressing their growth, restoring function of the cancer affected organs (e.g. bowel function, urination), and improving the general condition of a woman. The treatment regimen is elaborated by the tumor board, which includes a gynecologist, oncologist, radiologist, and other related specialists. Only a multidisciplinary team is able to pay attention to all the peculiarities of a clinical situation and come to the optimal decision.
Surgery and cytoreduction
In women with stage 4 ovarian cancer, surgery is usually only part of a complex therapy. In most cases the surgical intervention is cytoreductive, i.e. the surgeon tries to remove all of the visible tumor and nearby affected tissues. In eligible patients, the surgical removal of metastases is also performed. Candidates for such an intervention are women with single metastatic foci in the liver or brain. If a woman is too weak to tolerate the intervention, performing interval cytoreductive surgery is possible.
HIPEC (Hyperthermic Intraperitoneal Chemotherapy)
Any type of surgery is always followed by chemotherapy. First, it is performed right after the surgical intervention, in the form of hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC). HIPEC is considered a surgical procedure, as it requires creating direct access to the abdominal cavity. The heated solution, with a chemotherapeutic agent, is administered through a large catheter to the abdominal cavity. This allows for the destruction of separate cancer cells and microscopic metastatic foci that remain there after the surgery.
The HIPEC procedure lasts for 60-90 minutes. After it, the chemotherapeutic solution is washed out and the surgical incisions are closed. HIPEC and surgery mutually enhance the efficacy of each other. Without cytoreductive surgery, HIPEC is unable to destroy the primary tumor and large metastatic foci. Without the HIPEC, surgery is unable to remove the microscopic metastases and cancer cells that have spread through the abdominal cavity.
To gain deeper insights into new advances in ovarian cancer treatment through HIPEC, we spoke with Dr. Michael Lipp, a distinguished surgeon at Asklepios Hospital Barmbek Hamburg. With over a decade of experience in cytoreductive surgery and HIPEC procedures, Dr. Lipp has been at the forefront of implementing ovarian cancer new treatments. His expertise in performing complex HIPEC procedures weekly has contributed significantly to improving patient outcomes. In this comprehensive interview, Dr. Lipp shares valuable insights about the innovative HIPEC approach, its implementation, and its role in modern cancer treatment.
Dr. Michael Lipp on Precision Cancer Care: Transforming Treatment with HIPEC
Transarterial chemoembolization
Another form of administering chemotherapy is transarterial chemoembolization for ovarian cancer metastases. The technique is usually used in women with metastases outside the abdomen, i.e. in the liver, lungs, etc. However, transarterial chemoembolization for ovarian cancer metastases in the bowel is also possible. Before carrying out the procedure, the physician carefully explores the vascular system of the patient and finds the artery that provides the tumor with its blood supply.
After that, a high dose of chemotherapy drug is injected directly into this artery through an endovascular catheter. To prevent the drug from entering the systemic circulation and spreading throughout the organism, a solution with lipid emboli is introduced into the same artery. In addition, emboli block the tumor’s blood supply. Thus, transarterial chemoembolization for ovarian cancer metastases has two mechanisms of action: local administration of high doses of chemotherapeutic agents and depriving a tumor from nutrients.
Prof. Kovács: Why Interventional Oncology Should Be the Fourth Pillar of Cancer Care
Minimally Invasive Cancer Treatment: Prof. Dr. Atilla Kovács on TACE, Ablation & Future Innovations
Immunotherapy with DC vaccination
The field of dendritic cell therapy traces its roots to a revolutionary scientific breakthrough that fundamentally transformed our understanding of the immune system. In 2011, American immunologist Ralph Steinman was posthumously awarded the Nobel Prize in Medicine for his groundbreaking discovery of dendritic cells, a pivotal moment that laid the foundation for modern immunotherapeutic approaches.
Dendritic cell (DC) vaccination represents a groundbreaking advancement in cancer immunotherapy. Steinman's seminal research unveiled the crucial role of dendritic cells as key orchestrators of immune responses, providing the scientific rationale for developing personalized cancer vaccines that harness the body's own immune mechanisms. This innovative approach offers several significant advantages: it can be implemented at any stage of cancer, demonstrates excellent tolerability with minimal side effects, provides personalized treatment tailored to each patient's unique cancer profile, and establishes long-lasting anti-cancer immunity.
The treatment includes:
- Comprehensive medical assessment and laboratory testing
- Collection of blood samples or tumor fragments for individual vaccine manufacturing
- One-week waiting period for vaccine preparation
- Administration of the personalized dendritic cell vaccine
- Supportive medications and specialist consultations as needed
- Full outpatient care with minimal disruption to daily life
To understand the transformative potential of dendritic cell therapy as one of the newest treatments for ovarian cancer, we spoke with Prof. Frank Gansauge, a pioneer in cellular immunotherapy. With decades of experience in developing and implementing DC vaccination protocols, Prof. Gansauge has helped establish dendritic cell therapy as a cornerstone of modern cancer treatment. In this conversation, he explains how this personalized immunotherapy approach is revolutionizing cancer care through targeted immune system activation.
Prof. Frank Gansauge: How Dendritic Cell Therapy is Transforming Modern Cancer Treatment
Chemotherapy and Molecular Targeting
Systemic chemotherapy may also be a part of the treatment scheme, e.g. as neoadjuvant or adjuvant chemotherapy. The administration of systemic drugs, allows the malignant cells throughout the body to be targeted, but the healthy tissues, including liver and kidneys, suffer at the same time.
Another systemic therapy is targeted therapy. The term "targeted" means that the medication recognizes the specific target on the surface of the tumor cells and kills cells with such targets. PARP inhibitors are used for advanced ovarian cancer treatment. PARP inhibitors suppress the ability of tumor cells to repair damaged DNA and multiply successfully. Thus, the effect of chemotherapy is enhanced, as tumor cells are not able to recover after it. A combination of systemic chemotherapy and targeted therapy is often used for the treatment of stage 4 ovarian cancer.
What about the effectiveness of treatment?
| Treatment | 2-Year Survival Rate* | Response Rate** | Cost of treatment, €*** |
| Classical chemotherapy | up to 30% | up to 20% | 80,000 - 150,000 for the full course |
| Dendritic cell immunotherapy | up to 85% | up to 90% | 20,000 - 38,000 |
| CAR T-cell therapy | up to 50% | up to 40% | 450,000 - 550,000 |
| Chemoembolization | up to 50% | up to 80% | 6,500 - 24,000 |
*Booking Health data. Survival rates vary widely depending on the type of cancer, the patient's condition, and specific circumstances.
**Booking Health data. Response rate is the number of patients who show improvement after treatment.
***The cost of treatment depends on the type of tumor, stage of cancer, and other factors.
Specialized hospitals and cost of treatment for ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is treated at large university hospitals and multidisciplinary healthcare facilities. This makes it possible to involve not only oncologists and gynecologists into the therapeutic process, but also specialists of other medical specialties. This is especially important when choosing stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment options, as many organs may be affected by the cancer.
Among the hospitals that accept foreign patients for treatment and also offer stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment options, it is worth noting the following ones:
- University Hospital Tuebingen, Department of Adult and Pediatric Gynecology, Mammalogy, and Obstetrics
- Asklepios Hospital Barmbek Hamburg, Department of Gynecology
- University Hospital Ulm, Department of Obstetrics, and Adult and Pediatric Gynecology
- University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich, Department of Gynecology, Mammalogy, Obstetrics, and Perinatal Medicine
- University Hospital Frankfurt am Main, Department of Adult and Pediatric Gynecology, Obstetrics, and Mammalogy
Prices for treatment depend on the country and the chosen hospital, as well as on the chosen treatment method. The cost of treatment for ovarian cancer stage 4 may include prices for a few therapeutic options. The average prices are as follows:
- Diagnosis of ovarian cancer – €3,470
- Surgical treatment of ovarian cancer by laparoscopic salpingo-oophorectomy, including the cost of treatment for stage 4 cancer – €11,540
- Treatment of ovarian cancer with spread to the pelvic organs and lymph nodes by hysterectomy, salpingo-oophorectomy, lymphadenectomy, including the cost of treatment for stage 4 cancer – €58,600
- Treatment of ovarian cancer with spread to the pelvic organs and lymph nodes by hysterectomy, salpingo-oophorectomy and hyperthermia, including the cost of treatment for stage 4 cancer – €34,765
- Cytoreductive surgery and hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC), including the cost of treatment for stage 4 cancer – €66,000
- Transarterial chemoembolization for ovarian cancer or transarterial chemoembolization for ovarian cancer metastases, including the cost of treatment for stage 4 ovarian cancer – €33,000
- Chemoembolization for ovarian cancer metastases – €33,000
- Chemotherapy for ovarian cancer, including the cost of treatment for stage 4 ovarian cancer – €5,480
- Dendritic cell treatment with a personalized vaccine – €20,000 - 38,000
Depending on the clinical situation, the doctor can offer monotherapy, using one of the methods, or a combination of different methods. The second option is always used for stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment.
Treatment of ovarian tumors abroad, with Booking Health
Booking Health is an online portal where patients can investigate information about medical facilities and current treatment methods, as well as book a medical program at leading clinics around the world.
Booking Health specialists help with the following important issues:
- selection of a hospital specializing in oncology and gynecology, including stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment;
- direct communication with your attending physician;
- preliminary preparation of a medical program, including stage 4 ovarian cancer treatment options;
- control of the cost of medical services, excluding overpricing and additional coefficients for foreigners (total savings of up to 50% of the initial price);
- making an appointment with a doctor on your desired date;
- monitoring of the implementation of all stages of the medical program;
- insurance against the cost of treatment increases, in case of complications (а coverage of €200,000, valid for 4 years);
- assistance in buying and forwarding medicines;
- communication with the hospital after the treatment’s completion, organization of additional medical examinations and distance consultations;
- control of invoices and return of unspent funds;
- interpreting and medical coordinator services;
- top-class service: booking hotels, airline tickets, and transfers.
If you want to know the treatment prices, including the cost of treatment for stage 4 ovarian cancer, or start your treatment right now, please leave your request on the Booking Health website.
Modern Cancer Treatment: Patient Journeys with Booking Health
Frequently asked questions of our patients
Significant breakthrough in ovarian cancer treatment is the development of dendritic cell vaccines, which help stimulate the immune system to fight cancer cells. Additionally, targeted therapies like PARP inhibitors prevent cancer cells from repairing their damaged DNA. These treatments are particularly effective when combined with traditional chemotherapy.
The da Vinci robotic surgical system represents the most advanced approach, combining laparoscopic precision with enhanced 3D visualization for superior tumor removal through minimal incisions. When paired with HIPEC therapy, it provides optimal treatment outcomes.
Innovative treatments include dendritic cell vaccines that boost immune response, hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) that delivers heated chemotherapy directly to cancer cells, and transarterial chemoembolization that targets tumors while blocking their blood supply.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
Read:
Why Booking Health - questions and answers
How to make right decision when choosing the clinic and specialist
7 reasons to trust to the rating of clinics on the Booking Health portal
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health