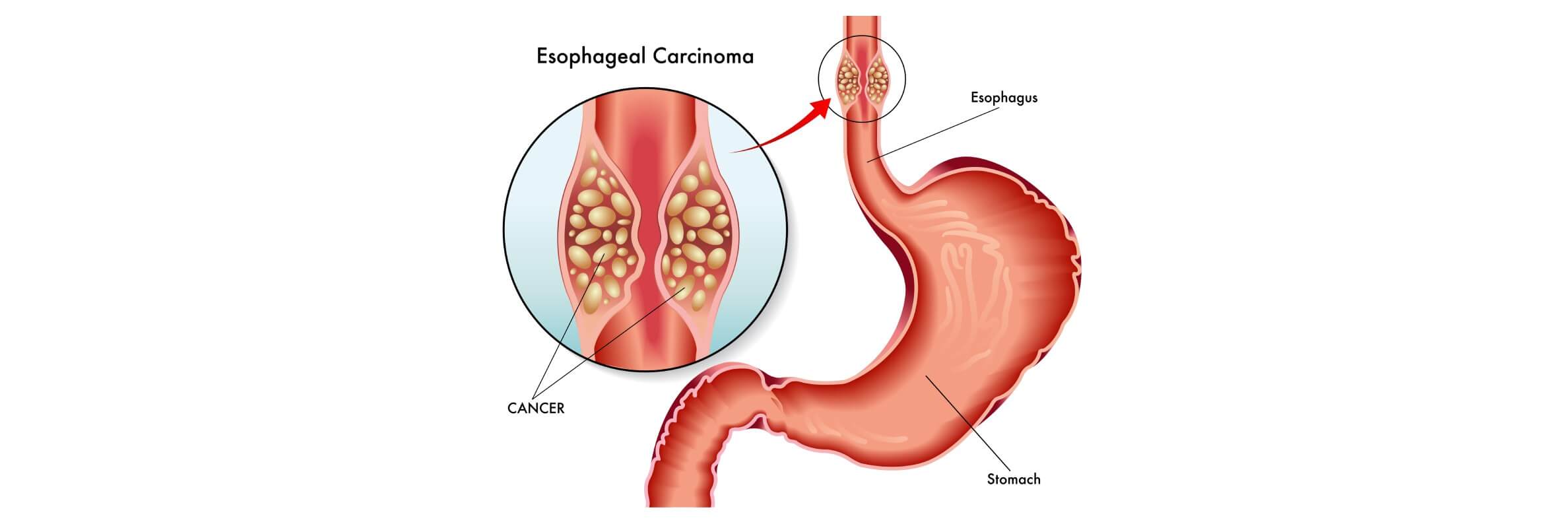
Esophageal cancer is still among the deadliest cancers of the digestive system, with about one out of every 20 cancer-related deaths worldwide. In 2022, over 500,000 new cases were diagnosed globally, and it is particularly high in East Asia and some parts of Africa.
In the US, the American Cancer Society (ACS) [1] projects over 22,000 new cases by 2025, and the overall five-year survival rate is under 25%, which is a sign of aggressive disease presentation and its prevalence. However, over the last few years, there have been positive changes, and esophageal cancer treatment has become more efficient due to the introduction of new approaches, such as targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and the implementation of precision techniques in surgical practice.
Understanding Esophageal Cancer and Its Stages
The esophageal cancer originates in the inner lining of the esophagus and is generally classified into two histological types, namely the adenocarcinoma, which is normally found in the lower esophagus, and the squamous cell carcinoma, which is commonly found in the upper and middle esophagus. According to the National Cancer Institute [2], some of the risk factors include chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), smoking, excessive alcohol use, and Barrett's esophagus.
The disease is staged using the TNM classification system; the system examines the size of the tumor (T), the involvement of lymph nodes (N), and the presence of distant metastases (M).
- Stage 0 (carcinoma in situ): abnormal cells are present, however, in the inner layer of the esophagus only.
- Stage I: the cancer has extended more deeply into the esophagus; however, it is still localized.
- Stage II-III: the cancer has already extended to the adjacent tissues and/or lymph nodes.
- Stage IV: the cancer has spread to other body areas, which are usually the liver, lungs, or bones.
The decision on the best treatment for esophageal cancer is highly dependent on the stage of diagnosis, the general health of a patient, the type of tumor, and molecular features. An individualized approach to treatment, taking into account the stage of the disease, and interdisciplinary consultation is the key to achieving a positive outcome and providing each patient with the most appropriate therapy for esophageal cancer.
Standard Approaches to Esophageal Cancer Treatment
The optimal treatment for esophageal cancer generally follows established esophageal cancer treatment guidelines, combining both local and systemic therapies. The type of therapy is determined by the stage of the disease, the biology of the tumor itself, and the patient's state of health. The common treatment option in localized or locally advanced cases is typically neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy, which tries to shrink the tumor and mitigate the risk of metastasis. This is followed by an operation. This trimodal approach is suggested by both the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) [3] and the European Society of Medical Oncology (ESMO) [4], as it enhances resectability and survival in selected patients.
Surgery has continued to be used as one of the keys in the management of esophageal cancer, especially at stages I-III, where the cancer is limited to the digestive tract or the lymph nodes. Surgical operations are commonly conducted, and the most prevalent is esophagectomy, which is done to excise the tumor and also the lymph nodes that are located around the tumor. High-resolution endoscopy can permit endoscopic surgery (i.e., endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR) or submucosal dissection), particularly in selectively chosen early-stage patients, in cases of superficial invasion without nodal involvement. Surgery may be the initial management or a secondary intervention after a neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and the decision is based on the multidisciplinary assessment of the disease profile and the health status of the patient.
Innovative and Emerging Treatments for Esophageal Cancer
With recent developments in research, new approaches are reconstituting the treatment for esophageal cancer, particularly in advanced and treatment-resistant cases. One of the future esophageal cancer treatment options is dendritic cell therapy, as well as an expanding range of strategies in interventional radiology, such as transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) and electrochemotherapy (ECT). These approaches are more action-specific, less systemic, and provide new hope to patients with metastatic disease.
Dendritic Cell Therapy for Esophageal Cancer
The dendritic cells are central in the coordination of the immune response. Their capability to capture, process, and present tumor antigens to T-cells has been exploited to come up with personalized cancer vaccines. This method became known internationally when Ralph Steinman won the 2011 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for the discovery of dendritic cells and their essential contribution to adaptive immunity [5].
One of the approaches in oncology is to isolate dendritic cells from the patient and load them with tumor-specific antigens and reintroduce them into the patient to induce a specific immune response. This technique has demonstrated encouraging outcomes in esophageal cancer, especially in individuals who have previously been treated with other cancer therapies without success.
Image-Guided Innovation in Advanced Esophageal Cancer Care
As esophageal cancer increasingly requires advanced treatments beyond conventional medications, new and emerging methods are providing additional therapeutic options. These techniques aim to manage localized tumors, improve drug delivery, and prolong life while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues.
Electrochemotherapy for Esophageal Cancer: A Game-Changer in Local Tumor Control
Electrochemotherapy (ECT) is a promising development in local tumor therapy, especially in patients with metastatic esophageal cancer with involvement of the liver and other visceral organs. Electro-chemotherapy is a combination of low-dose chemotherapy and targeted electrical pulses, which cause temporary cell membrane permeability, permitting chemotherapy agents to enter tumor cells more effectively. Such a specific cytotoxic effect increases the drug concentration in tumor tissue and minimizes systemic side effects, which is why ECT is especially effective in patients who have already used all the systemic therapies or cannot tolerate further treatment.
Recent studies have shown great results when using ECT for esophageal cancer metastases. It offers prolonged local tumor control, decreasing the size and progression of tumors. ECT is particularly useful in lesions that are poorly vascularized or otherwise inaccessible to conventional treatments. Additionally, it has a good safety profile, which means that it can be used repeatedly, which allows controlling metastatic sites without deteriorating the quality of life of the patient.
The efficacy of ECT is also confirmed by the fact that it has been reported to have better local tumor control as compared to other treatments of esophageal cancer and the fact that tumor size has been shown to reduce with time. Its accuracy and influence on the vascularization of tumors underscore its ability to overcome biological resistance in cancer cells.
The cost of electrochemotherapy ranges from €7,500 to €12,000, which is often less than the for repeated chemotherapy cycles. The cost of electrochemotherapy is worthwhile given its results and reduced side effects.
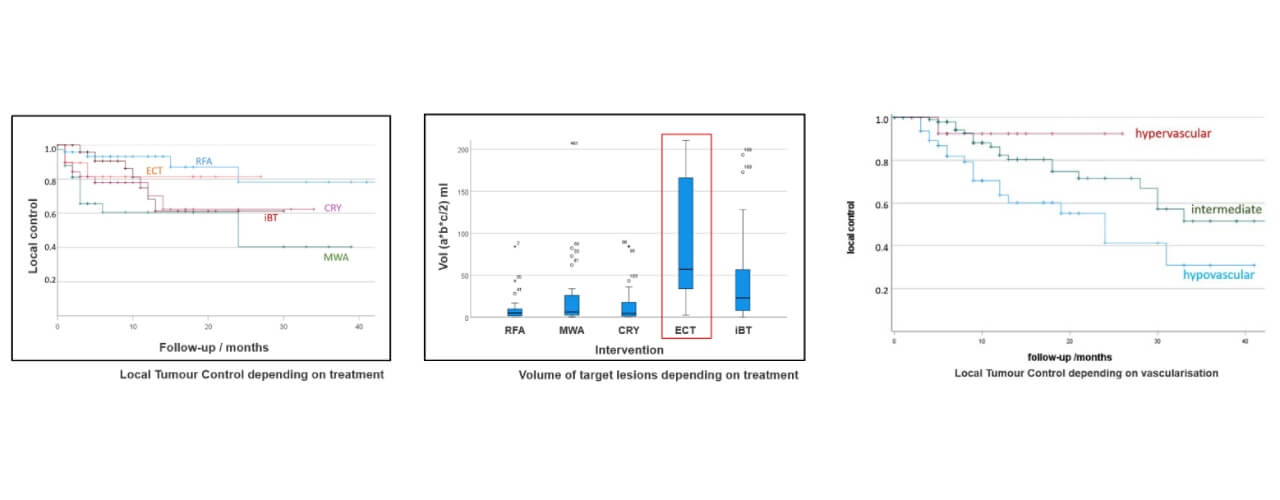
*Kovács A et al. Long-Term Comparative Study on the Local Tumour Control of Different Ablation Technologies in Primary and Secondary Liver Malignancies. J Pers Med. 2022 Mar 9;12(3):430
These visualizations reinforce the growing recognition of ECT as a highly effective, minimally invasive option for controlling metastatic esophageal cancer, offering new hope where conventional approaches have fallen short.
Electrochemotherapy (ECT): A Cancer Treatment That Doesn't Use Heat, Cold, or Radiation
Targeting the Esophageal Tumor with TACE
Transarterial chemoembolization (TACE) is a proven method of liver cancer treatment and is now being modified to treat esophageal cancer with liver or nodal metastases. The process requires administration of high-dose chemotherapy into the arteries feeding the tumor through a catheter, after which embolic agents are introduced to prevent blood flow, which helps to keep the drug in the tumor. This localized method achieves the maximum cytotoxicity with the minimum systemic exposure.
TACE is especially effective in the treatment esophageal cancer patients who have metastases located in the liver or para-aortic lymph nodes only. It can shrink the tumor, control symptoms, and in certain instances, downgrade the disease to enable re-evaluation of curative therapy. TACE is commonly used in combination with other modalities in multimodal treatment approaches for advanced-stage patients.
TACE has been clinically shown to have practical advantages in the treatment of esophageal cancer. The rates of tumor response in the short term have been positive, as reported in comparative outcome studies, such as a 2024 study in the World Journal of Surgical Oncology [6], which reported significant variations in objective response rates based on disease burden and treatment sequence.
These results indicate that TACE is a safe and effective local treatment modality in carefully selected patients and support its application in individualized interventional oncology for esophageal cancer.
Regional Chemotherapy for Esophageal Cancer
When esophageal cancer spreads beyond local control, conventional systemic chemotherapy often fails – not from wrong drug selection, but from inadequate tumor penetration. Regional chemotherapy transforms this equation by isolating specific anatomical regions and flooding them with concentrated cytotoxic agents at levels impossible through standard intravenous routes.
Three primary techniques are used. Isolated thoracic perfusion targets the mediastinum, lungs, and cervical lymph nodes – the most common sites of esophageal spread. Upper abdominal perfusion concentrates treatment on hepatic and abdominal metastases. Intraarterial infusion delivers continuous high-dose chemotherapy through tumor-feeding vessels. Each employs balloon catheters positioned under fluoroscopic guidance to isolate the perfusion bed, followed by blood filtration within 45 minutes to eliminate systemic toxicity.
Clinical validation comes, for instance, from 14 metastatic esophageal cancer patients who had exhausted first-line options: median overall survival reached 38 months, with regional therapy-specific survival of 13 months from treatment initiation. Response rates achieved 41% partial response and 27% stable disease. Squamous cell carcinoma patients demonstrated particularly strong responses, achieving 51-month median survival. [7]
Professor Karl Reinhard Aigner pioneered these techniques through decades of clinical innovation. His interview explores how regional perfusion may be used for advanced esophageal cancer patients.
Heat-Based Precision: RFA for Local Esophageal Tumor Destruction
Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) involves the utilization of high-frequency electrical currents to produce heat and ablate cancerous tissue. While it is primarily used for Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia, its use has recently expanded to include the treatment of localized metastatic lesions, especially in the liver. RFA provides a minimally invasive alternative to surgery, which gives the possibility to control local tumors and prolong the survival.
The intervention is typically done percutaneously under imaging guidance. It is most appropriate for small-to-moderate lesions and can be repeated in case of necessity. RFA can also be applied in conjunction with systemic therapy or as an alternative treatment option for patients who cannot undergo surgery. Thus, RFA is an important tool in interventional oncology.
Cold Precision: Cryoablation for Local Control in Esophageal Cancer
Cryoablation involves the use of extreme cold to ablate tumor cells with rapid freezing and thawing in order to induce irreversible cellular injury and vascular closure. Cryoablation is traditionally applied in dermatologic and urologic cancers, but is being used in treating esophageal cancer for localized lesions.
In patients with superficial tumors, cryoablation is a non-thermal alternative to RFA, which minimizes the risk of perforation or injury of surrounding tissues. It is especially applicable in cases where other forms of intervention, including radiation or surgery, are no longer available. Cryotherapy may also be used in the treatment of advanced cases to reduce dysphagia or bleeding and maintain esophageal functioning. Newer experience is in favor of its safety, repeatability, and as a component of a multimodal treatment approach – either as monomodal palliative therapy or in combination with systemic therapy.
| Therapy Type | 2-Year Survival Rate | Response Rate | Duration | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatments | ~55-70% for early stages ~30% for advanced stages | ~40-60% | Several weeks to months | Moderate to severe (fatigue, nausea, infertility, bowel/bladder issues) |
| Innovative Methods | ~60-75% in select advanced/refractory cases | 45-65% | Up to 4-6 sessions | Mild (fever, localized inflammation, flu-like symptoms) |
*Booking Health data
A New Chance in Esophageal Cancer: Harmohan’s Journey Beyond Standard Treatment
The case of Harmohan Kaur from the UK, who was diagnosed with esophageal cancer, not only came as a shock, but also presented the challenging aspect of choosing the best possible treatment. When she found out that traditional treatments did not provide much hope, she started to research innovative treatment methods in other countries. This took her to Germany and specifically to LDG laboratories, which is one of the centers of esophageal cancer treatment. She was treated by Dr. Gansauge, who developed a personalized approach according to her specific medical needs.
Booking Health helped to bring Harmohan in touch with a multidisciplinary medical team, which, in addition to offering high-quality clinical care, also gave her a feeling of stability. She remembers the individual attention that she was given: "They really care about their customers and go the extra mile to make the experience stress-free and easy. The hospitals they represent are of high quality."
Her treatment regimen was well planned, and it involved accurate diagnostics and a tailor-made treatment plan that was not restricted to standard procedures. The experience of Harmohan is a potent demonstration of the fact that alternative and advanced treatment for esophageal cancer can provide a new perspective, in particular, when it is carried out with professionalism and care.
International Cancer Care: Patient Stories with Booking Health
Hope Beyond the Diagnosis: Support for Advanced and Stage 4 Esophageal Cancer Cases
The diagnosis of stage 4 esophageal cancer is devastating and confusing, frightening. Nevertheless, treatment at advanced stages is not about giving up, but about modifying the therapeutic approach according to the patient’s condition.
One-on-one treatment plans are currently adopted in special clinics, which integrate palliative surgery, immunotherapy, endoscopic procedures, interventional radiology, and supportive care. These techniques are chosen according to the behavior of the tumor, the spread level, and the general physical status of the patient. Instead of using a universal guideline, patients are assessed case-by-case to come up with a realistic and effective care plan.
Although curative treatment may no longer be possible, a combination of these methods can help reduce symptoms, improve quality of life, and, in some cases, prolong life. With the help of the international coordination services and access to the best medical centers, a lot of patients find their clarity, hope, and confidence in the treatment process.
The article about treatment for stage 4 esophageal cancer may provide a better image of the existing possibilities, as it describes the available treatments and how they can be applied to each patient.
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex cancer management programs in each individual case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized esophageal cancer treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you on the way of pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods for esophageal cancer with leading specialists in this field.
FAQ: Esophageal Cancer Treatment
Send request for treatmentEsophageal cancer is a cancerous lesion that arises in the lining of the esophagus. It is either adenocarcinoma or squamous cell carcinoma. It needs to be staged to combine treatment methods to control the disease.
The typical initial symptoms are the inability to swallow, chest pain, persistent cough, hoarseness, and unexplained weight loss. These symptoms closely resemble gastroesophageal problems, and, therefore, the early endoscopic diagnosis is essential to identify the problem and improve the results.
Diagnosis starts with an endoscopy and biopsy to detect cancer. Additional imaging is used to determine the size, spread of tumors, and stage. These guides the decision of whether to undergo surgery, neoadjuvant therapy, or palliative care, based on the extent of the cancer spread.
Surgery, chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and immunotherapy are the possible options. Endoscopic resection or minimally invasive esophagectomy can be applied in the initial stages. The disease could be treated by using combined targeted, ablative therapy or dendritic cell vaccination to manage the disease.
Esophageal cancer at an early stage is usually curable. In the more developed stages, the objective is to get remission and prolong survival.
At stages I-III, tumors are usually recommended to be removed. It can be used as a follow-up to neoadjuvant chemotherapy or radiation to make the tumor smaller. The type of surgery will depend on the location, extent of disease, and the general health of the patient.
The esophagectomy is the removal of the entire esophagus. The recovery process may last weeks or months and involve nutrition and lifestyle adjustments as well as rehabilitation.
Yes, chemotherapy is extensively employed either in the neoadjuvant or adjuvant, or palliative context. It is usually used with radiotherapy or surgery to reduce the size of tumors, stop recurrence, or cure metastatic disease in advanced cases.
Radiation therapy may be administered pre-operatively (as neoadjuvant), post-operatively, or as a palliative measure to relieve such symptoms as pain or obstruction. It is frequently used as a form of combined therapy, particularly when surgical options are limited by invasive cancer.
Electrochemotherapy (ECT), transarterial chemoembolization (TACE), dendritic cell therapy, and endoscopic procedures, e.g., stent placement, are some of the recent developments. The advantages of these new treatments are their high specificity of action and minimal side effects, which are particularly beneficial in patients with inoperable esophageal cancer.
Immunotherapy involves the activation of the immune system to target cancer cells. The dendritic cell vaccination is promising in metastatic and advanced esophageal cancer, particularly when the standard treatment is not effective. It can be included in a broader clinical plan to increase survival and delay relapse.
Yes, targeted therapy is aimed at the mutations or markers that are present in the tumor. It can be administered alone or together with chemotherapy, particularly in adenocarcinoma. This individual therapy can enhance the results and decrease toxicity.
Staging is very important for the prognosis. At an early stage, disease survival and curative potential are higher, whereas at stage IV, they are lower. Even in cases when this is not possible to attain long-term remission, new therapies are aimed at enhancing the quality of life.
Yes, esophageal carcinoma frequently metastasizes to the lymph nodes, liver, lungs, and bones. This metastatic dissemination impacts treatment choices and prognosis, yet local management in the form of ablation, radiation, or palliative care can be used.
Side effects are not uniform and can include fatigue, nausea, difficulty in swallowing, or weight loss. Digestion and nutrition may also be influenced by chemotherapy, radiation, and surgery. Care and lifestyle modifications can be used to address symptoms and enhance recovery.
Yes, minimally invasive esophagectomy is often performed in Germany. It results in less trauma, faster healing, and decreased complication rates over open surgery.
Prices differ depending on the country of the treatment and the type of treatment. In Germany, the cost of modern treatment varies between €25,000-€60,000, and the complex surgeries or combined therapy can cost €70,000-€120,000. Final costs are based on the stage of the disease and the approach applied.
What is the 2-year survival rate for esophageal cancer with standard treatments and innovative methods?
The 2-year survival rate for esophageal cancer is ~30% for advanced stages, when managed with standard therapies (e.g., chemotherapy and radiation). However, innovative treatments (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, TACE, electrochemotherapy, etc.) can improve survival to ~60-75%.
What response rates can be expected in esophageal cancer using standard versus innovative therapies?
Standard treatments for esophageal cancer can show response rates of ~40-60%. In turn, innovative methods (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, TACE, or electrochemotherapy) can achieve ~45-65%.
Traditional treatment courses for esophageal cancer (e.g., chemotherapy, radiation therapy, etc.) can extend over several weeks or even months. On the other hand, innovative treatments (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, TACE, etc.) can be completed in 4-6 targeted sessions.
How do treatment costs for esophageal cancer differ across countries, and what is the situation in Australia?
The cost of treatment for esophageal cancer can vary. In Germany, innovative procedures typically range between €25,000-€60,000; in Great Britain and the USA, costs can exceed €100,000. In contrast, in Australia, access to innovative therapies (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, interventional radiology, etc.) remains limited; it is also considerably more expensive.
There is no single "best" therapy for esophageal cancer as treatment is defined by tumor depth, lymph node involvement and resectability. Interventional radiology is used to locally control tumor growth or complications while dendritic cell therapy represents an immune-based option aimed at systemic disease control (where standard protocols are insufficient).
The best hospital is one that can manage esophageal cancer beyond standard surgery or chemoradiation. German centers with experience in interventional oncology and immunotherapy can integrate image-guided procedures and dendritic cell therapy into individualized treatment plans ㄧ especially for advanced or recurrent disease (where conventional options are limited).
Choose treatment abroad and you will be sure to get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Esophageal Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/esophagus-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
[2] National Cancer Institute. Esophageal Cancer Treatment. https://www.cancer.gov/types/esophageal/patient/esophageal-treatment-pdq
[3] National Comprehensive Cancer Network. Esophageal and Esophagogastric Junction Cancers. https://www.nccn.org/guidelines/guidelines-detail?category=1&id=1433
[4] ESMO: European Society For Medical Oncology. Oesophageal cancer: ESMO Clinical Practice Guideline for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. https://www.annalsofoncology.org/article/S0923-7534(22)01850-6/fulltext
[5] Nobel Prize. Ralph Steinman and the discovery of dendritic cells. https://www.nobelprize.org/prizes/medicine/2011/steinman/facts/
[6] World Journal of Surgical Oncology. Clinical evaluation of oxaliplatin-loaded drug-eluting callispheres beads transarterial chemoembolization for unresectable or recurrent esophageal carcinoma. https://wjso.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s12957-024-03546-8
[7] Vashist Y, Aigner K, Dam M, Gailhofer S, Aigner KR. Regional Chemotherapy Is a Valuable Second-Line Approach in Metastatic Esophageal Cancer after Failure to First-Line Palliative Treatment. Curr Oncol. 2022;29(7):4868-4878. https://doi.org/10.3390/curroncol29070386 [DOI]
Read:
Esophageal Cancer: Treatment in Germany
Robot-assisted treatment of esophageal diseases: Da Vinci system
Stage 4 Esophageal Cancer: Comprehensive Guide and Treatment Options
Article menu:
- Understanding Esophageal Cancer and Its Stages
- Standard Approaches to Esophageal Cancer Treatment
- Innovative and Emerging Treatments for Esophageal Cancer
- Comparative Table: Esophageal Cancer Treatments
- A New Chance in Esophageal Cancer: Harmohan’s Journey Beyond Standard Treatment
- Hope Beyond the Diagnosis: Support for Advanced and Stage 4 Esophageal Cancer Cases
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
- FAQ: Esophageal Cancer Treatment
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health