Breast cancer (BC) is the most widespread type of cancer among women. According to international data, more than 2 million new breast cancer cases were diagnosed in 2020. This high incidence is linked to numerous breast cancer risk factors, including both genetic and lifestyle components. The risk of breast cancer grows with age, and about 80% of patients are older than 50 [1]. Survival strongly depends on the stage at the moment of breast cancer diagnosis and the identified breast cancer subtypes.
Although breast cancer can also affect men, it is rare. Still, when doctors detect breast cancer at an early stage, the chances to successfully treat breast cancer are high. Most breast cancers diagnosed at this point are localized and respond well to modern breast cancer treatment.
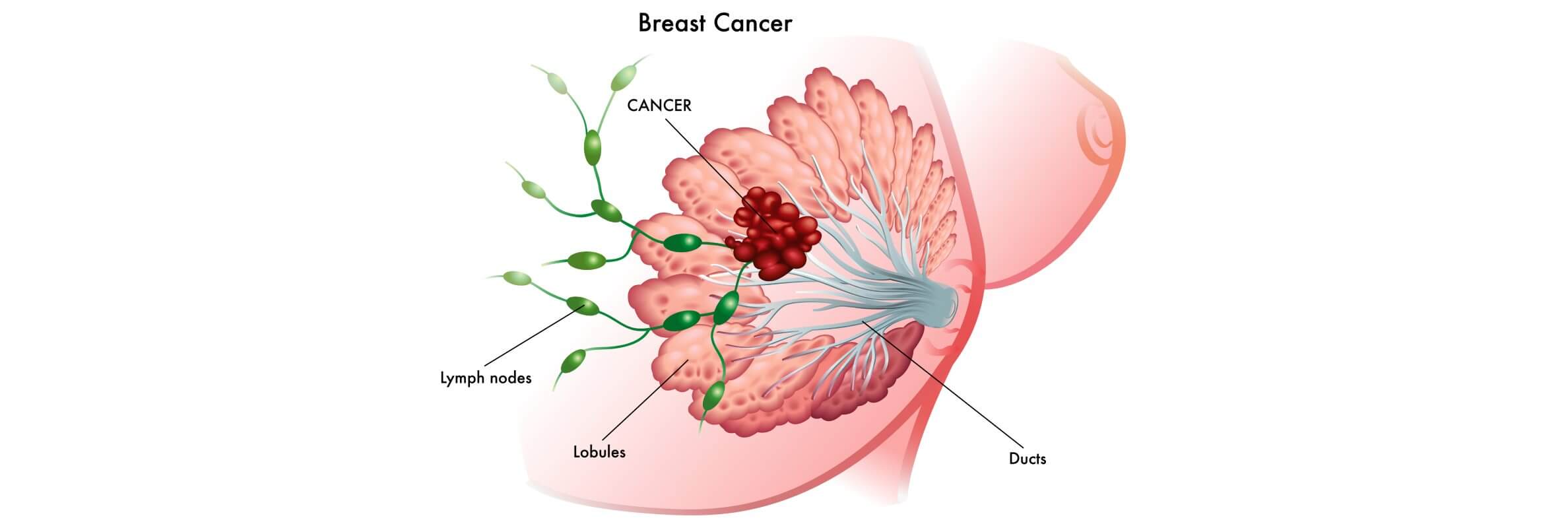
The stage of the disease at cancer diagnosis is one of the crucial elements for choosing a treatment plan and predicting outcomes. Early stages usually affect only breast tissue and breast cells, while stage IV breast cancer, or invasive breast cancer, means that breast cancer spreads to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs.
Accurate staging is achieved through modern diagnostic methods, including tests that analyze breast cancer genes and the biology of breast cancer cells. These help doctors tailor the treatment plan to the type of breast cancer, whether it is hormone therapy–sensitive or triple-negative breast cancer. Due to strong awareness programs, today doctors can detect breast cancer earlier.
How Is the Stage of Breast Cancer Determined?
After the first step – confirmation of breast cancer diagnosis, doctors proceed with the evaluation of the stage of breast cancer. This process requires additional tests and consultations with related specialists. The stage reflects how far breast cancer spreads within the body and directly influences the treatment plan. For instance, at the first stage of breast cancer, doctors usually recommend breast-conserving surgery, while advanced stages may require a combination of surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or other treatments. Information about the stage of breast cancer also defines prognosis and life expectancy. According to European statistics from 2017, the five-year survival rate is about 87% at stage I, 75% at stage II, 46% at stage III, and only 20% at stage IV breast cancer (metastatic disease).
Staging of breast cancer relies on several diagnostic methods:
- Mammography – an X-ray of breast tissue that detects tumors and abnormal breast cells. Depending on the facility, mammography can be traditional or digital.
- Ultrasound examination – this helps evaluate the condition of breast tissue, distinguishing between solid tumors (which may contain malignant breast cancer cells) and benign cysts.
- MRI – magnetic resonance imaging provides detailed visualization of the tumor’s invasion, involvement of the second breast, and spread to nearby organs. MRI is especially useful for invasive breast cancer and inflammatory breast cancer, and is often performed before planning breast cancer surgery, chemotherapy, or radiation therapy.
- Biopsy – the golden standard in breast cancer diagnosis. A biopsy allows microscopic study of breast cancer cells. Fine-needle aspiration, core biopsy, or surgical biopsy may be used. In many cases, the results determine whether hormone therapy, radiation therapy, or chemotherapy will be part of the treatment plan.
General tests also support accurate staging and safe breast cancer treatment:
- Complete blood count (to detect anemia)
- Biochemical blood test (to evaluate liver and kidney function before chemotherapy)
- Inflammatory markers
- Electrocardiogram (to check the heart before systemic cancer treatment)
Once all results are collected, doctors can accurately define the stage of breast cancer and select the most effective treatment for breast cancer. Naturally, stage IV breast cancer requires different strategies compared to early-stage breast cancer (EBC). That is why the choice of breast cancer treatment depends on staging systems and classifications, which will be discussed further.

Stage of Breast Cancer According to The TNM Staging System
The TNM staging system is widely used in oncology. This method is used to classify practically every solid tumor, including breast cancer (BC). The main advantage is universality: it allows physicians worldwide to follow unified guidelines for cancer treatment and create a precise treatment plan for every patient.
The TNM system answers three core questions:
- Where is the primary tumor located? What is its size? Is it localized within breast tissue?
- Are lymph nodes affected, and if so, how many and where?
- Is there metastatic breast cancer (MBC), and has the disease spread to distant organs?
There are two types of TNM staging in breast cancer. The first is the clinical stage of breast cancer, based on non-invasive tests and biopsy results before surgery. The second is the pathologic stage of breast cancer, determined after examining surgically removed breast tissue and lymph nodes. Pathologic staging is more accurate, since some breast cancer cells are invisible to imaging but detectable under a microscope.
"T" – Tumor
This describes the size of the initial tumor and its effect on surrounding structures.
- TX – tumor cannot be assessed.
- T0 – no signs of primary tumor.
- Tis – carcinoma in situ (stage 0). At this stage, minimally invasive options such as breast-conserving surgery or chemoembolization may replace extensive breast cancer surgery.
- T1 – tumor <2 cm. This stage of breast cancer is often managed with surgery plus radiation therapy; if needed, hormone therapy is added depending on the type of breast cancer.
- T2 – tumor 2–5 cm. Requires a combination of breast cancer surgery, radiation therapy, and systemic approaches.
- T3 – tumor >5 cm. Here, invasive breast cancer becomes a major concern, and multimodality therapy is usually required.
- T4 – tumor of any size invading skin or chest wall. T4d corresponds to inflammatory breast cancer, an aggressive variant associated with edema, pain, and redness.
"N" – Nodes
This refers to the spread of breast cancer cells to nearby lymph nodes. Micrometastases (<0.2 mm or <200 cells) may not affect prognosis, but macrometastases are clinically significant.
- N0 – no lymph node involvement.
- N1 – 1–3 lymph nodes affected.
- N2 – 4–9 lymph nodes involved.
- N3 – ≥10 lymph nodes, or spread above/below the clavicle.
"M" – Metastases
This describes the presence of distant disease.
- M0 – no metastases.
- M1 – confirmed stage IV breast cancer with distant lesions (bone, liver, lungs, brain, marrow). This requires systemic treatment for breast cancer, such as chemotherapy, targeted drugs, or hormone therapy. For some patients with advanced breast cancer, novel systemic regimens and other treatments help to relieve pain and extend survival.
Additional Factors of Breast Cancer Staging: Hormone Receptor Status
Tissue samples taken during biopsy or surgery are always analyzed with histological and immunohistochemical techniques. Histological examination defines the tumor type and degree of malignancy, while immunohistochemical methods provide insight into important biochemical and molecular markers of breast cancer.
For breast cancer diagnosis, immunohistochemical testing usually includes checking for hormone receptors. The growth of breast tissue is regulated by female hormones – estrogen and progesterone. These hormones act by binding to specific proteins on the cell surface called receptors. Estrogen receptors (ER) recognize only estrogen, while progesterone receptors (PR) recognize only progesterone. Once activated, they stimulate the growth and division of breast cells. Unfortunately, cancer cells may also carry these receptors, which allows normal hormone levels to fuel the progression of breast cancer.
That is why receptor testing plays a crucial role in developing an individual breast cancer treatment plan and ensuring personalized therapy. Tumors that contain estrogen and/or progesterone receptors are classified as ER-positive or PR-positive. Such types respond well to hormone therapy for breast cancer, as blocking the receptors or lowering hormone levels prevents tumor progression and reduces the risk of developing metastatic breast cancer (MBC).
If no receptors are found, the cancer is considered hormone receptor–negative and does not benefit from hormone-based treatment. In general, hormone receptor–positive cancers grow more slowly and respond better to therapy, although they may still relapse years after the completion of breast cancer treatment.
Additional Factors of Breast Cancer Staging: HER2/neu Status, Score 0–3+
Another important aspect of immunohistochemical testing in breast cancer diagnosis is the determination of HER2 (human epidermal growth factor receptor 2) status. HER2/neu is a protein located on the surface of breast cancer cells, regulating their growth and division. While HER2 is normally present in all tissues, its overexpression leads to uncontrolled proliferation and more aggressive forms of breast cancer.
Two laboratory techniques are commonly used for HER2 assessment: immunohistochemical (IHC) staining and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH). Both are performed in vitro on biopsy or surgical tissue samples. The IHC test is typically the first step, as it provides results quickly.
The results are classified into several categories:
- Score 0 or 1+: HER2-negative. These tumors do not require targeted therapy.
- Score 2+: equivocal. In such cases, FISH testing is recommended for a more precise conclusion.
- Score 3+: HER2-positive. These tumors tend to be more aggressive, but effective breast cancer treatment is available with HER2-targeted drugs.
Modern targeted therapy includes monoclonal antibodies and kinase inhibitors. These medications can be used alone or in combination with chemotherapy and radiation therapy for early-stage breast cancer or even in advanced cases, helping to prevent the development of metastatic breast cancer (MBC) and improving survival rates for many breast cancer survivors.
Additional Factors of Breast Cancer Staging: Determining Grade, Grade 1–3
Tumor grade mainly characterizes the structure of breast cancer cells and the degree of their abnormality. Accurate grade determination is essential for assessing the risk of breast cancer progression and the potential for developing metastatic breast cancer. Usually, three biopsy samples or tissue removed during breast cancer surgery are analyzed.
According to the Bloom–Richardson Grade (Nottingham modification), the grades are:
- Grade 1 (score 3–5): well-differentiated tumor, similar to normal breast tissue. The likelihood of breast cancer spreading or developing metastatic breast cancer (MBC) is low.
- Grade 2 (score 6–7): moderately differentiated tumor, an intermediate state between grades 1 and 3, when pathologists may be unsure about the exact type of breast cancer.
- Grade 3 (score 8–9): poorly differentiated tumor. These tumors have highly abnormal breast cancer cells, grow rapidly, and have a high probability of developing breast cancer in distant organs.
Another feature visible under the microscope is the ploidy of breast cancer cells. Normal breast cells are diploid (46 chromosomes), but breast cancer cells may become aneuploid with abnormal chromosome numbers. Aneuploid tumors are more aggressive and may require early treatment for breast cancer, including chemotherapy for breast cancer or other treatments. Correct assessment of tumor grade also helps doctors develop an effective treatment plan and choose whether hormone therapy is appropriate, depending on receptor status.
Comprehensive Breast Cancer Stage Grouping, Stages 0-4
When the results of all investigations are ready and grades are established, doctors proceed to "stage grouping." This comprehensive assessment helps assign the overall clinical and pathologic breast cancer diagnosis, which precedes the start of treatment for breast cancer.
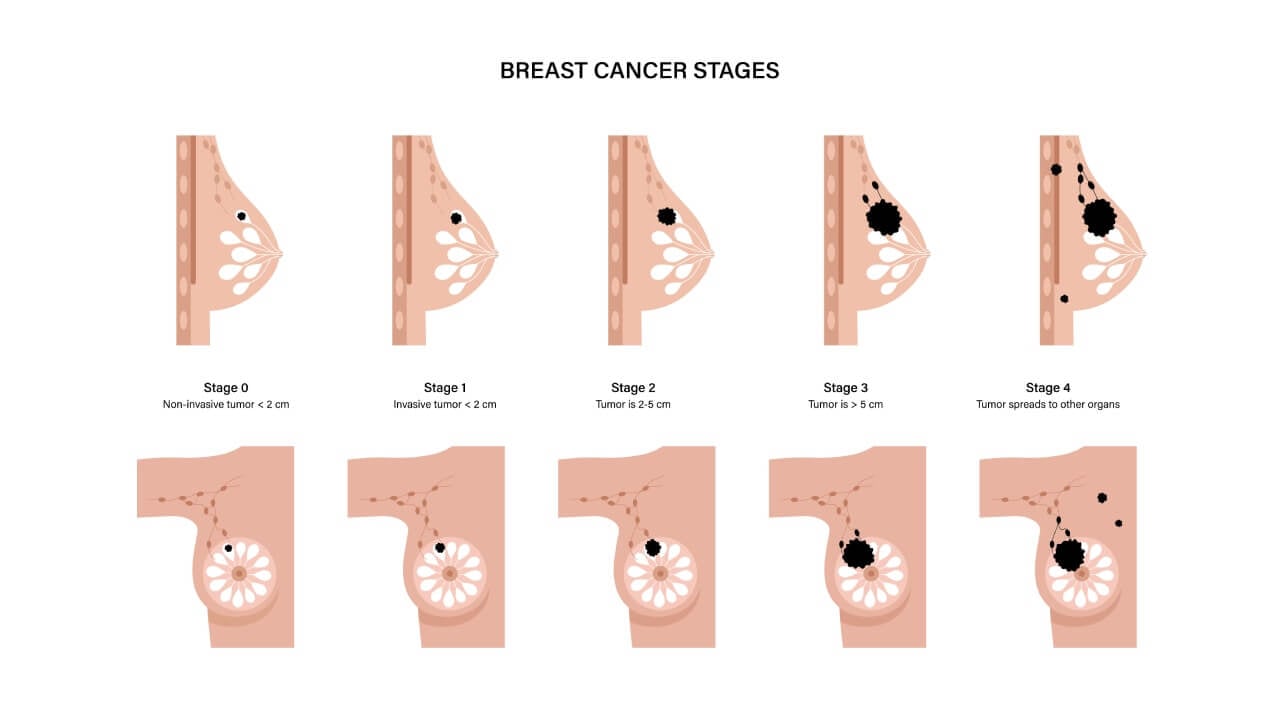
The earliest form, stage 0 breast cancer, is carcinoma in situ – the most favorable type of breast cancer. Stage 0 is described as TisN0M0.
Stage 1 breast cancer is divided into 1A and 1B. At stage 1A the tumor is small (less than 2 cm) and lymph nodes are not involved (T1N0M0). Stage 1B implies a small tumor with micrometastases in lymph nodes (T0/T1N1(mi)M0). Such early detection is possible due to modern tools that help detect breast cancer before it spreads.
Stage 2 breast cancer is also divided into 2A and 2B. In stage 2A, tumors may be small but affect axillary lymph nodes (T0/T1N1M0) or measure 2–5 cm with healthy nodes (T2N0M0). Stage 2B indicates tumors of 2–5 cm spreading to 1–3 nodes (T2N1M0), or tumors exceeding 5 cm without nodal involvement (T3N0M0). These cases show how breast cancer treatment depends on both tumor size and lymph node status.
Stage 3 breast cancer includes more advanced cases and is considered an invasive breast cancer stage.
- Stage 3A: any tumor with 4–9 axillary nodes affected, without remote metastases.
- Stage 3B: larger, more aggressive tumor invading the chest wall or skin, with possible lymph node involvement.
- Stage 3C: any tumor size with cancer spreading to 10 or more lymph nodes.
Stage IV breast cancer is the metastatic form, when the disease spreads to the bones, lungs, liver, or brain. At this point, the goal shifts from surgery to systemic treatment. Stage 4 breast cancer treatment options may include hormone therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, or chemotherapy for breast cancer. In certain clinical cases, doctors also use surgery, breast-conserving surgery, radiation therapy, or chemoembolization for breast cancer. Each case is evaluated individually, and the chosen strategy becomes part of the personalized treatment plan.
It is important to note that recurrent breast cancer may appear years later, sometimes as advanced breast cancer. In these cases, all examinations must be repeated to provide an updated cancer diagnosis and select the most effective other treatments.
Treatment Schedule and Cost of Treatment for Breast Cancer Stage 4
It is clear that only precise laboratory analyses, examination with advanced medical equipment, qualified needle biopsy, and breast cancer surgery, as well as thorough evaluation of the results by specialists, can guarantee a safe and effective treatment plan. Both medical technology and clinical expertise are equally important, as they complement each other.
As mentioned above, surgery, radiation therapy, systemic therapies such as chemotherapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, and hormone therapy are integral parts of modern cancer treatment. Doctors usually combine several methods to effectively treat breast cancer. For instance, chemoembolization may be followed by systemic drugs, while proton therapy for stage IV breast cancer may be combined with surgery.
Managing advanced breast cancer remains one of the most complex tasks. Still, new medicines and innovative techniques are improving outcomes. Current stage IV breast cancer treatment options include:
- Chemotherapy for breast cancer
- Chemoembolization for breast cancer (for selected patients)
- Targeted therapy and immunotherapy
- Hormone therapy
Rarely, stage IV breast cancer treatment also involves surgery or proton therapy. These may be performed to relieve pain, prevent fractures, reduce pressure on the spinal cord, or control solitary metastases in the brain and spinal cord. Proton therapy is considered the safest irradiation mode, as it avoids damaging the heart, lungs, and nervous system.
| Treatment | Price |
|---|---|
| Radical mastectomy | 18,750 EUR |
| Chemotherapy | 10,470 EUR |
| Radiation therapy | 28,470 EUR |
| Proton therapy | 106,440 EUR |
| Oncological rehabilitation | 1,580 EUR per day |
Effective Breast Cancer Treatments in Germany
German oncology is based on the principle of combining precise diagnosis with therapies that address the disease at every biological level—from the tumor microenvironment to systemic metastases. Each treatment not only removes or blocks breast cancer cells but also targets the mechanisms that drive tumor growth, invasion, and resistance.
Surgery for Breast Cancer: Mastectomy and Breast-Conserving Approaches
Surgery remains the fundamental way to treat breast cancer, especially in the early stages. In the event of a localized tumor, it can be removed, eliminating further spread in the blood or the lymphatic system.
- Mastectomy is performed by the total removal of the breast. This radical solution is required in the presence of a large, multifocal, or aggressive tumor (e.g., triple-negative breast cancer). It destroys the origin of the malignant breast tissue, and the chances of recurrence are minimized.
- Breast-conserving surgery (breast lumpectomy) is aimed at the removal of the tumor and the surrounding tissue of healthy tissue to keep the rest of the breast. This technique is achievable because of accurate imaging and intraoperative navigation.
Dendritic Cell Therapy (DC Therapy) for Breast Cancer
The immune system cells can naturally identify abnormal cells, and in most cases, tumors can evade immune recognition by inhibiting the immune response. This defense is reinstated by using dendritic cell therapy.
Dendritic cells are obtained using the blood of the patient and trained in a laboratory to identify tumor antigens. Re-introduced into the body, they expose T-lymphocytes to these antigens, and a cascade of immune responses is activated. Activated T-cells then assault malignant breast cancer cells throughout the body.
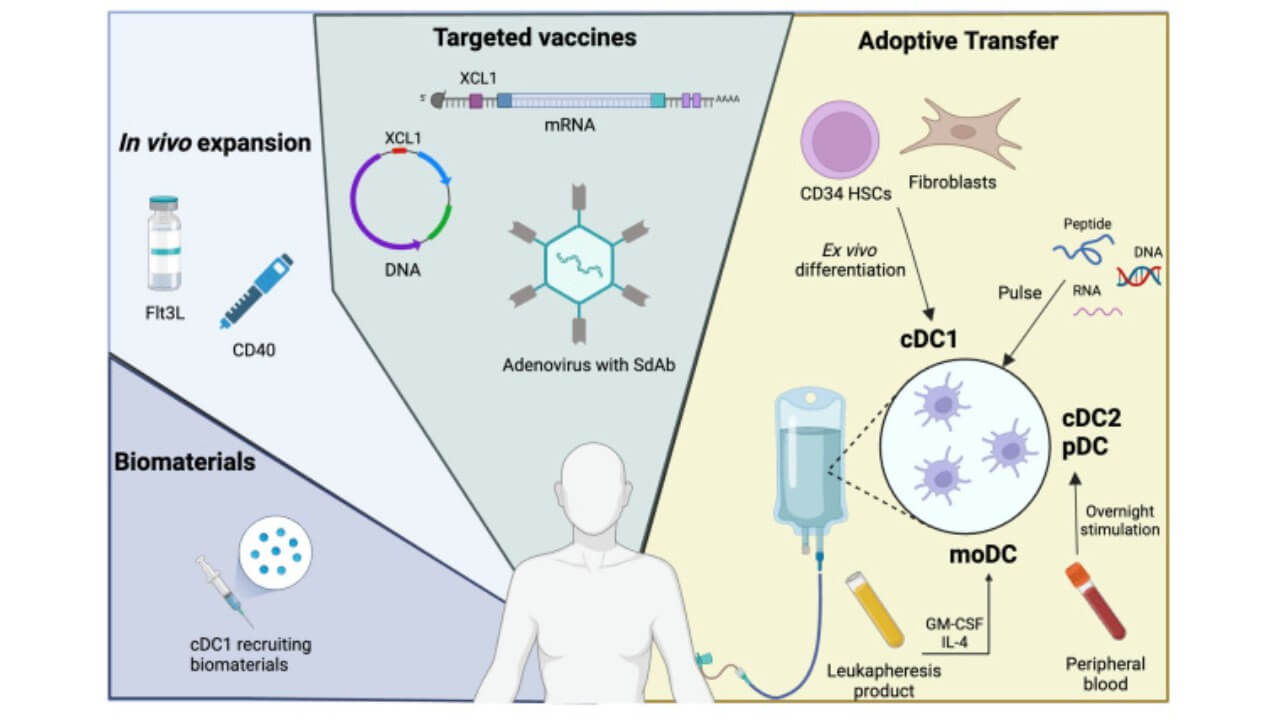
The importance of dendritic cells in orchestrating immune responses earned Ralph Steinman the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 2011. Today, this discovery allows German clinics to transform a patient’s immune system cells into a personalized weapon against advanced breast cancer and even subtypes like invasive breast cancer.
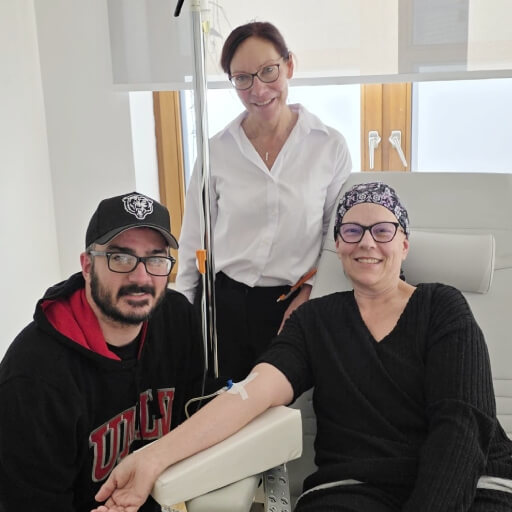
To see the real-world impact of dendritic cell therapy for advanced breast cancer, watch our patient share her personal experience with stage IV treatment. She discusses how the therapy helped improve her immune response, manage symptoms, and regain quality of life. Discover the potential of this innovative approach in the full interview:
TACE (Transarterial Chemoembolization) for Breast Cancer
TACE is a minimally invasive technique widely used in Germany for metastatic breast cancer lesions, especially in the liver.
Mechanism:
- A catheter is introduced into the artery supplying the tumor
- A concentrated chemotherapy drug is delivered directly into this vessel
- Embolic particles are injected to block blood flow
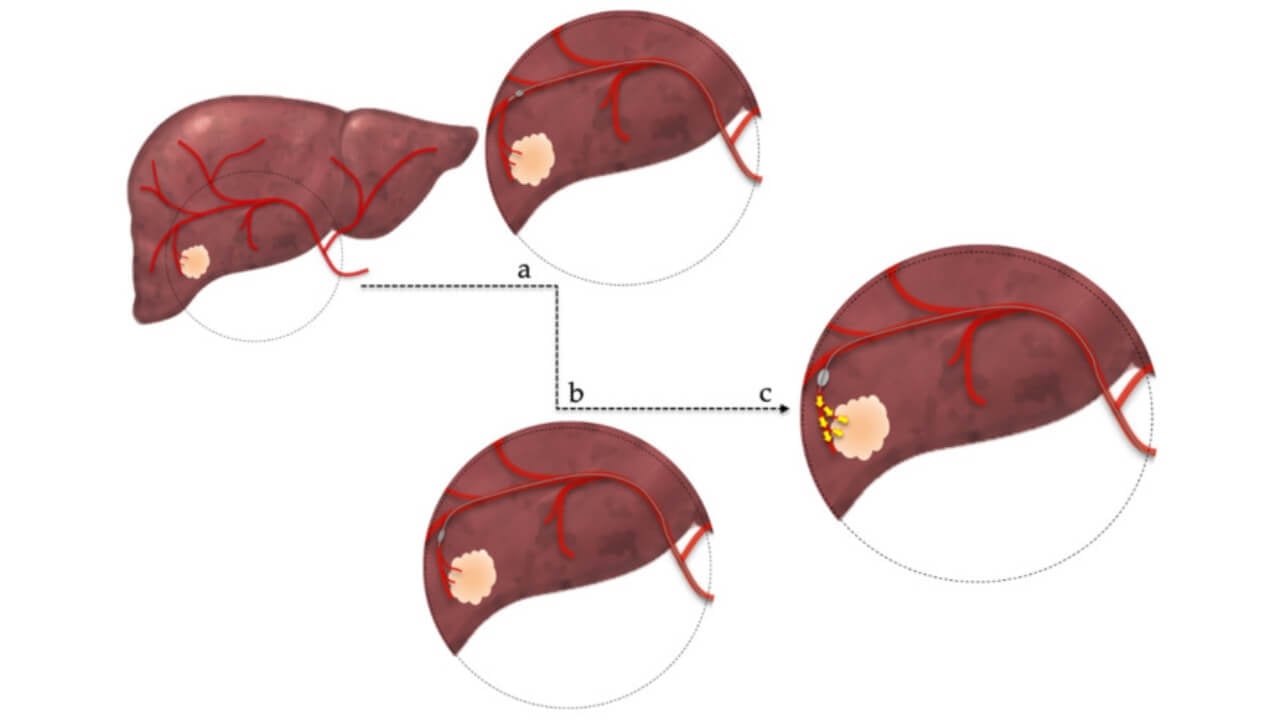
This two-step approach deprives the tumor of oxygen and nutrients while ensuring high local drug concentration. Unlike systemic chemotherapy, TACE reduces systemic toxicity and spares healthy tissues. From the pathophysiological perspective, the tumor’s angiogenesis - its ability to build new blood vessels—is interrupted. Without vascular support, cancer cannot grow or metastasize efficiently.
For patients with an invasive cancer, especially when standard therapies are exhausted, TACE offers a way to directly treat cancer without the need for extensive surgery. Since the risk of breast cancer recurrence often depends on hidden micro-metastases, such targeted local therapy significantly improves disease control. German oncologists emphasize that innovative techniques like TACE not only lower the risk of breast cancer progression but also give patients more time and a better quality of life. Moreover, in cases where systemic toxicity would be too dangerous, this method allows doctors to treat cancer effectively while protecting healthy organs. Considering that the risk of breast cancer rises with each relapse, approaches like TACE are becoming integral in advanced oncology care.
Learn about the latest advancements in minimally invasive cancer treatment as Prof. Dr. Attila Kovács discusses TACE, ablation techniques, and future innovations in oncology.
Prof. Kovács: When to Use DEB-TACE, Conventional TACE, or Radioembolization (TARE)
Regional Chemotherapy for the Treatment of Breast Cancer
Regional chemotherapy for breast cancer delivers concentrated medications directly to tumor sites through two specialized techniques. Arterial infusion threads catheters through the groin into the mammarian or subclavian artery, creating first-pass effects where drug concentrations reach levels impossible with systemic delivery. Five to seven minutes of targeted infusion floods the tumor region with therapeutic doses.
For larger masses exceeding 5 centimeters or tumors invading the chest wall, isolated thoracic perfusion provides more intensive treatment. Balloon catheters positioned in the aorta and vena cava beneath the diaphragm create complete thoracic isolation. Natural blood flow continues within this zone while concentrated chemotherapy circulates for 15 minutes – long enough for deep tissue penetration. Then comes the crucial protective step: 45 minutes of hemofiltration removes remaining drugs before systemic circulation resumes.
A retrospective study of 162 metastatic breast cancer patients receiving isolated thoracic perfusion for lung metastases achieved median overall survival of 19.5 months from metastasis diagnosis [6]. Triple-negative breast cancer patients – typically facing the bleakest prognosis – showed particularly encouraging responses. Side effects remained predominantly WHO grades I-II; serious complications occurred only in heavily pretreated patients.
Prof. Aigner has performed over 20,000 regional perfusion procedures. Breast tumors generally exhibit excellent blood supply, making them ideal candidates for regional approaches. The method proves especially valuable for locally relapsed, unresectable masses causing pain or psychological distress. In our interview below, Prof. Aigner shares detailed insights into regional chemotherapy for breast cancer applications and introduces electrochemotherapy – the innovative technique we explore in the next section.
Electrochemotherapy in Breast Cancer
Electrochemotherapy combines brief electrical pulses with concentrated medications through a process called reversible electroporation. Electrical fields create temporary pores in cancer cell membranes – microscopic gateways allowing drugs to penetrate at concentrations 80-fold higher than standard delivery achieves for certain agents.
Prof. Aigner's recent study of 14 patients with locally relapsed, unresectable triple-negative breast cancer demonstrates the technique's effectiveness [7]. Mean tumor size measured 7.6 centimeters. Five patients presented with ulcerated lesions. All had exhausted multiple treatment lines. Regional chemotherapy combined with reversible electroporation achieved tumor shrinkage in 13 of 14 cases, with four patients becoming candidates for complete surgical resection.
The procedure employs hexagonal electrode arrays positioned around tumor perimeters at 2.5-3 centimeter intervals. Computer-controlled pulse generators deliver synchronized electrical bursts while concentrated medications circulate through arterial infusion or isolated thoracic perfusion. Treatment duration spans only minutes, with remarkably swift recovery compared to systemic approaches.
Circulating tumor cell monitoring revealed important safety data: in 19 of 21 treatment cycles, tumor cells in bloodstream either decreased or remained stable 24 hours post-treatment, demonstrating that proper technique prevents metastatic risk [7].
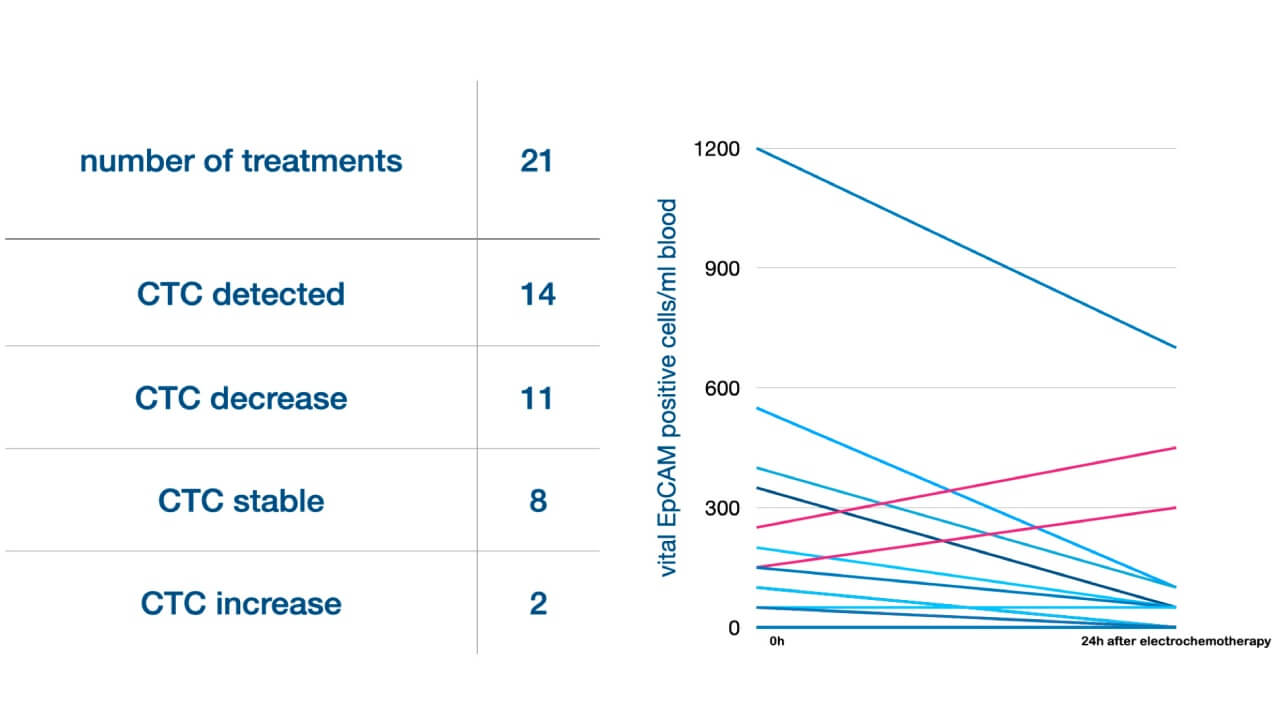
The cost of electrochemotherapy varies by institution as it requires specialized equipment available only at select centers. When evaluating electrochemotherapy cost, patients should consider that electro-chemotherapy may eliminate extensive surgery needs while achieving local control in chemotherapy-resistant cases.
The technique particularly benefits patients with chemoresistant disease, large tumor masses causing pain or bleeding, or those exhausted from multiple failed treatment lines.
Radiation Therapy and Brachytherapy for Breast Cancer
Radiation destroys cancer by damaging DNA inside malignant cells, preventing further division. German centers use both external beam radiation and brachytherapy.
- External beam therapy uses linear accelerators to direct ionizing radiation at the tumor bed. Advanced planning software allows precise targeting while sparing healthy tissue.
- Brachytherapy places radioactive sources directly inside or next to the tumor bed (after breast cancer surgery). This achieves a very high radiation dose locally, destroying residual cancer at the molecular level.
Radiation creates double-strand DNA breaks in breast cancer cells, which overwhelm their already unstable repair mechanisms. Normal cells repair such damage more efficiently, so the tumor is selectively eradicated.
Integration of Therapies for Breast Cancer
The success of breast cancer treatment in Germany lies in multimodality:
- Surgery removes the malignant tissue
- Radiation and brachytherapy sterilize the surgical field
- Systemic treatments like dendritic cell therapy, hormone therapy, or TACE eliminate microscopic metastases and circulating cancer cells
This combined strategy addresses both the local tumor and the systemic risk of recurrence, making treatment effective for both early-stage breast cancer (EBC) and stage IV breast cancer.
Treatment of Early-Stage and Metastatic Breast Cancer Abroad
Oncologic disorders rarely give patients a second chance, and every repeated attempt at cancer treatment becomes more exhausting both physically and psychologically. This is why it is crucial to choose a healthcare institution with the latest technologies and highly qualified specialists. Today, patients can search for proper diagnostics and treatment for breast cancer not only in their own country but also abroad. Many investigate hospitals in Germany with the best equipment and compare doctors with high accreditation and excellent results in managing different breast cancer cases. In addition, it is possible to compare the estimated cost of stage IV breast cancer therapy in various clinics, as expenses may play a significant role in decision-making.
When it comes to accurate breast cancer diagnosis and the correct determination of breast cancer stages, Germany is among the world leaders. The country offers comprehensive examination and individualized treatment plans for both early-stage breast cancer and advanced breast cancer. German hospitals apply innovative methods that help to relieve pain, improve quality of life, and extend survival, even for patients with stage IV breast cancer. This approach has given many breast cancer survivors a real chance for longer and healthier lives.
The only challenges may include organizing the appointment in the desired hospital and handling non-medical travel details for the patient and relatives. Patient also needs to be financially prepared, as clinics tend to require a down payment besides the approximate cost of treatment for breast cancer, given the potential risks of the breast cancer progression and complicated treatment regimes. Booking Health is an important stage in this process, as it enables the management of appointments, travel logistics, and provides international patients with high-quality and timely care, which allows avoiding unnecessary delays and maximizing the treatment journey with breast cancer.
TOP Breast Cancer Hospitals
Clinical practice shows that different top rated breast cancer hospitals have three key characteristics in common. The following are peculiarities of top hospitals for breast cancer that will help you find the best breast cancer hospital in world.
Oncologists with subspecialty training in breast cancer. These board-certified specialists of a top hospital for breast cancer complete years of focused training beyond general oncology to understand breast cancer complexity.
Multidisciplinary tumor board in clinics for breast cancer that consists of:
- Medical oncologists
- Surgeons
- Radiation oncologists
- Rehabilitation specialists
Advanced technology that completes the excellence framework of breast cancer treatment hospitals. These cover modern diagnostics systems/tests, targeted interventional oncology procedures, and access to clinical trials.
Breast Cancer Hospital Rankings – Best Breast Cancer Hospitals in the World
| Hospital | Location | Key Specializations | Notable Features | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian | Munich, Germany | Comprehensive breast cancer care, early to advanced-stage treatment | German Cancer Society certification ESMO Lifetime Achievement Award recipient Advanced MR mammography capabilities |
| 2 | University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center | Houston, TX, USA | Metastatic breast cancer, clinical trials | Extensive clinical trial access Advanced Breast Cancer Clinic Brain Metastasis Specialty Clinic |
| 3 | Hannover Medical School | Hannover, Germany | Robotic surgery, oncoplastic reconstruction | Da Vinci Xi robotic system Lower Saxony's largest Cancer Center 63,000+ patients annually |
| 4 | University Hospital Greifswald | Greifswald,Germany | Complex cases, organ preservation | 180,000 patients annually Medical tradition since 1456 Focus on "hopeless" cases |
| 5 | Samsung Medical Center | Seoul, South Korea | Pregnancy-associated cancer, aesthetic reconstruction | 2,000+ breast cancer patients annually 32-channel MRI technology ASCO and ESMO memberships |
University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich
Germany is often recommended for those looking for the best hospital breast cancer treatment in Europe. FOCUS magazine ranks this German medical center as the breast cancer best hospital. The Department of Mammology treats breast cancer with German Cancer Society certified excellence standards [4].
As reported, department provides comprehensive breast cancer care from early detection to advanced-stage treatment. Doctors here practice breast-conserving surgery, minimally invasive techniques and immediate reconstruction when needed. Patients receive personalised treatment protocols with coordinated care at the Comprehensive Cancer Center Munich.
With the department's certification and its Head, Professor Harbeck's international recognition such as the 2020 ESMO Lifetime Achievement Award, the department is demonstrating a commitment to the highest treatment standards and best patient outcomes.
University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center
MD Anderson's Breast Medical Oncology department improves breast cancer survival due to advanced research and patient-centered care. This is another best hospital for breast cancer treatment. The Advanced Breast Cancer Clinic has top specialists on staff.
A major strength of the center is its wide range of clinical trial access – many trials are not available elsewhere. Physician, nurse and pharmacist teams coordinate care while monitoring suitable trials and helping patients with applications.
Specialized services in this best breast cancer treatment hospital include:
- Clinical trials, education, and genomic testing
- The LIMBS Clinic for internal medicine is where patients receive treatment for various medical conditions
- For brain spread, Andrew M. McDougall Brain Metastasis Clinic
- Integrative medicine: acupuncture, massage, etc.
Metastatic disease is a chronic condition that is managed to maintain a quality of life in the Advanced Breast Cancer Program. Dedicated nurse practitioners coordinate care between departments and support patients emotionally throughout treatment.
Hannover Medical School
Hannover Medical School is a top German Medical School and since 2016, it has been Lower Saxony's largest certified cancer center. The Department of Mammology is that certified by the German Cancer Society, the German Society of Senology, and DIN EN ISO 9001.
Department provides breast cancer care using advanced surgical technology, such as the da Vinci Xi robotic system. When possible, treatment approaches tend to breast conservation with options including chemotherapy, radiation therapy, hormone therapy and immunotherapy in appropriate cases.
Cancer Center's multidisciplinary protocols ensure standardized, evidence based treatment. The facility treats more than 63,000 inpatients annually and focuses on clinical excellence alongside compassionate care – understanding each patient's needs throughout treatment.
University Hospital Greifswald
The University Hospital Greifswald, ranked by Focus magazine as one of Germany's best breast cancer clinics, combines medical tradition from 1456 with modern care. It sees 180,000 patients annually – complex cases other centers consider hopeless.
The Department of Mammology is a part of the specialized Breast Center that is certified by German Cancer Society and German Society of Senology. With over 4,400 medical staff, including world-class professors, the hospital gives preference to sparing but effective treatment. Its medical team provides tailored care according to tumor characteristics and offers a human touch throughout the patient's recovery.
Samsung Medical Center
The Samsung Medical Center was founded in 1994; it maintains a presidential standard of medical care with international recognition. It has 40 departments and a comprehensive Cancer Center.
The Department of Mammology is a specialized part of the Center. It annually admits over 2,000 patients with all breast cancer types. Tumor boards are held each week; they coordinate treatment selection with breast surgery, oncology, radiation oncology, and plastic surgery healthcare professionals.
Treatment includes breast preservation and aesthetic reconstruction with access to international clinical trials for advanced cases. Worldwide memberships in ASCO and ESMO [5] assure patients internationally of recognized treatment standards.
Finding Hope with Breast Cancer in Germany: Anna’s Story
When Anna Scoric from Ukraine was diagnosed with breast cancer, she knew that choosing the right hospital and specialist would be decisive for her life. She decided to begin her treatment for breast cancer at Marien Hospital Duesseldorf under the care of Prof. Dr. Giagounidis.
Since February 2022, Anna has undergone chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and regular examinations. Her breast cancer treatment was properly scheduled, and in cases when some unforeseen circumstances, such as COVID, upset her treatment, the coordinators, Maria Stern and Natalie Korner, managed to reschedule all appointments with accuracy and consideration.
Anna highlights how much easier it was to face the challenges of breast cancer diagnosis thanks to the interpreter’s constant support. "I never felt lost. Mark Fedotov was truly professional, helping me not only during medical consultations but also with daily needs in Duesseldorf."
Anna is grateful for her travel story nowadays. She underlines that such a combination as sophisticated medicine, individual approach, and human touch helped her to win the battle against breast cancer. It was not only about treatments or interventions, such as breast cancer surgery or systemic medications for her, but the overall care of a person as a living being.
Her case shows that when international patients with breast cancer can access modern treatment in time, they can be given hope and cured.
Cancer Treatment Abroad: Patient Experiences with Booking Health
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex management programs in each individual case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized treatment plans for breast cancer with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you in pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods for breast cancer with leading specialists in this field.
Frequently Asked Questions About Breast Cancer Treatment
Send request for treatmentTreatment for breast cancer can include chemotherapy, targeted therapy, hormone therapy, and immunotherapy. However, there are cases where proton therapy, surgery, or chemoembolization may also be used in order to manage symptoms or control metastases.
Breast cancer often causes fatigue, bone pain, shortness of breath, persistent cough, weight loss, and swelling in lymph nodes. However, symptoms of this disease usually depend on where the cancer has spread.
The cost of breast cancer treatment can vary depending on the method and country. For example, in Germany, prices range from €10,470 for chemotherapy to €106,440 for proton therapy. In the UK and the US, treatment can cost 10-30% more. In turn, in Australia, advanced methods (e.g., proton therapy) are often unavailable or 3-4 times more expensive.
Breast cancer treatment is built around a balanced combination of established and innovative methods. In Germany surgery and radiation therapy are often complemented by dendritic cell therapy and TACE ㄧ allowing physicians to control tumor growth more precisely, and extend treatment possibilities beyond standard protocols.
The best hospitals for breast cancer treatment are centers that can combine surgery, radiation therapy and advanced interventional approaches (within one treatment plan). German oncology clinics are known for integrating dendritic cell therapy and TACE into multidisciplinary care ㄧ especially in complex or advanced cases.
Germany remains a leading destination for breast cancer treatment due to its structured oncology system. Patients gain access to surgery, modern radiation therapy, dendritic cell-based immunotherapy and interventional techniques (such as TACE) which are widely used to enhance treatment effectiveness.
The leading breast cancer centers globally are University Hospital Munich / MD Anderson cancer Center / Hannover Medical School / University Hospital Greifswald / Samsung Medical Center. All of healthcare facilities have multidisciplinary teams and innovative treatments for specific cancer types and patient needs.
Advanced technologies & innovative clinical trials are available at international top hospitals. They treat complex cases with internationally accepted treatment standards and support services.
Yes, experienced doctors at leading international cancer centers welcome second opinion consultations. Booking Health can connect you directly with top specialists, coordinate appointments, and handle travel arrangements to ensure you access world-class expertise for your specific case.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] Sergiusz Łukasiewicz, Marcin Czeczelewski, Alicja Forma et al. Breast Cancer—Epidemiology, Risk Factors, Classification, Prognostic Markers, and Current Treatment Strategies—An Updated Review. Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 25;13(17):4287. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174287. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[2] Yuyan Xu, Maoyuan Gong, Yue Wang, Yang Yang, Shu Liu, Qibing Zeng. Global trends and forecasts of breast cancer incidence and deaths. Sci Data. 2023 May 27;10:334. doi: 10.1038/s41597-023-02253-5. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[3] Hyuna Sung, Beena CR Devi, Tieng Swee Tang et al. Divergent breast cancer incidence trends by hormone receptor status in the state of Sarawak, Malaysia. Int J Cancer. Author manuscript; available in PMC: 2021 Jul 9. Published in final edited form as: Int J Cancer. 2019 Dec 23;147(3):829–837. doi: 10.1002/ijc.32812. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[4] Michael Y. Chen, Felicia Zhang, Simon Peter Goedegebuure, William E. Gillanders. Dendritic cell subsets and implications for cancer immunotherapy. Front. Immunol., 05 June 2024. Sec. Cancer Immunity and Immunotherapy. Volume 15 - 2024 | https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1393451. [DOI]
[5] Evgenia Kotsifa, Chrysovalantis Vergadis, Michael Vailas et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Why, When, How? J Pers Med. 2022 Mar 10;12(3):436. doi: 10.3390/jpm12030436. [DOI] [PMC free article]
[6] Aigner KR, Zoras O, Guadagni S, et al. Isolated thoracic perfusion in lung metastases from breast cancer: a retrospective observational study. Updates Surg. 2019;71(1):165-177. doi:10.1007/s13304-018-0613-0. [DOI]
[7] Aigner K, Selak E, Pizon M, et al. Arterial infusion and isolated perfusion in combination with reversible electroporation for locally relapsed unresectable breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2024;16(23):3991. doi:10.3390/cancers16233991. [DOI]
Read:
Breast cancer treatment with dendritic cells in Germany
Breast Cancer Treatment in Germany: Innovative Therapies and Top Clinics
Article menu:
- How Is the Stage of Breast Cancer Determined?
- Stage of Breast Cancer According to The TNM Staging System
- Additional Factors of Breast Cancer Staging: Hormone Receptor Status
- Additional Factors of Breast Cancer Staging: HER2/neu Status, Score 0–3+
- Additional Factors of Breast Cancer Staging: Determining Grade, Grade 1–3
- Comprehensive Breast Cancer Stage Grouping, Stages 0-4
- Treatment Schedule and Cost of Treatment for Breast Cancer Stage 4
- Effective Breast Cancer Treatments in Germany
- Treatment of Early-Stage and Metastatic Breast Cancer Abroad
- TOP Breast Cancer Hospitals
- Finding Hope with Breast Cancer in Germany: Anna’s Story
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
- Frequently Asked Questions About Breast Cancer Treatment
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health