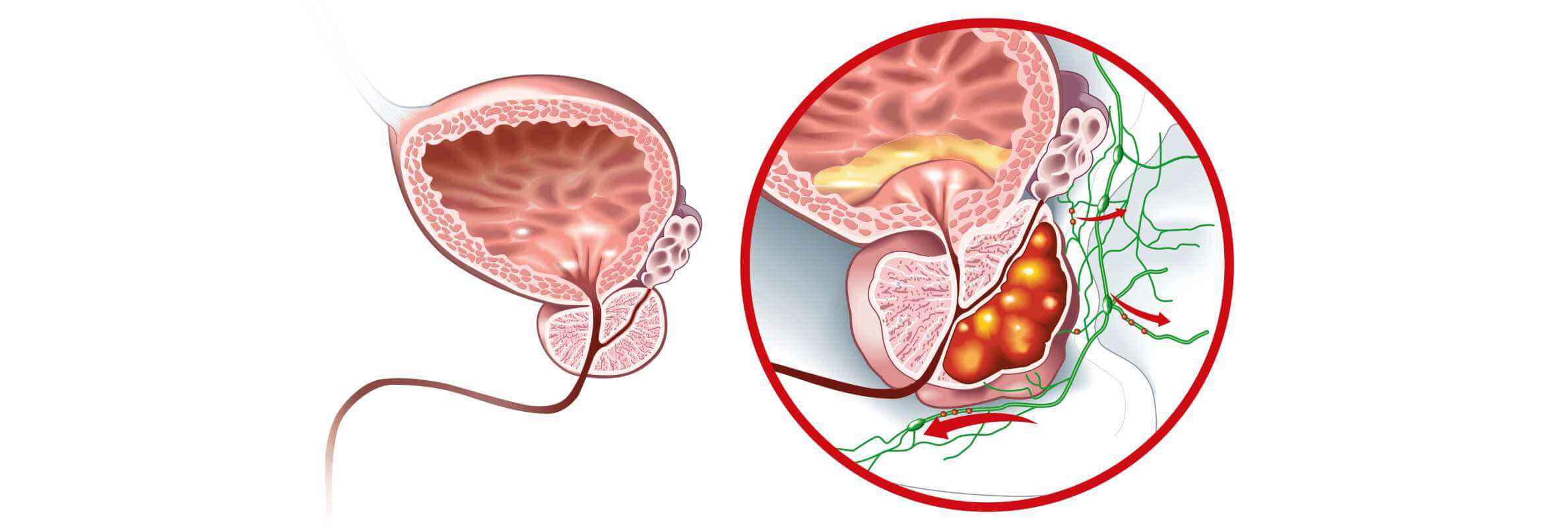
Almost any actively dividing cell of the human body can become a cancer cell. The prostate gland cells are not an exception, as they produce prostate fluid – part of the semen, which protects spermatozoids and guarantees their viability. Prostate cancer is widespread and takes second place among all oncological conditions in men [1]. Special attention should be paid to people over 65 years of age, as they account for more than 70% of all prostate cancer patients.
The good news is that localized prostate cancer usually grows slowly and does not affect one's lifestyle at all. It can be found just by accident during a general examination. Due to this, doctors have multiple choices when deciding how to treat prostate cancer, including surgical and non-surgical options.
While some patients with prostate cancer may be candidates for active surveillance or watchful waiting, surgical intervention remains the most effective curative option for many. A multidisciplinary team, including a urologist, radiation oncologist, and medical oncologist, evaluates each case individually to determine the best course of action. For patients eligible for surgery, the 5-year relative survival rate is close to 100% [2].
What Determines the Type of Prostate Cancer Treatment Choice?
Slow growth is a typical feature of localized prostate cancer, which makes it easier to detect the disease at an earlier stage. Some men with this type of cancer might never need any kind of treatment for prostate cancer, especially elderly men or those with other serious health problems.
The first and most essential aspect of treatment for prostate cancer is determining the stage of the disease at the time of diagnosis. Usually, the diagnosis starts from a preventive screening examination or examination due to the patient's complaints.
Primary diagnostic procedures include:
- Digital rectal examination (DRE) – enables the doctor to detect a tumor mechanically by palpating the prostate gland through the patient's rectum.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood test – PSA is produced only by the prostate, and its level reflects the state of the gland. A normal PSA level is below 4 ng/ml; levels between 4 and 10 ng/ml indicate a 25% likelihood of prostate cancer, while levels above 10 ng/ml suggest a 50% likelihood [3].
The PSA level plays a critical role not only in the initial diagnosis but also in determining the stage of the disease, planning further examinations, and selecting the appropriate treatment strategy, including the decision to perform radical prostatectomy or other curative procedures.
In case suspicious results of DRE and PSA blood tests are present, further and more profound examination is administered.
In addition to general analyses, a specific diagnostic plan consists of the following investigations:
- Transrectal ultrasound (TRUS) of the prostate gland
- Prostate biopsy under TRUS control (up to 12 samples of prostate tissue are usually taken)
- Bone scan (to exclude metastases presence)
- CT/MRI scan (to assess the state of nearby organs and exclude metastases in soft tissues)
- Biopsy of lymph nodes (if signs of oncological process spreading are present)
The diagnosis of prostate cancer is confirmed or excluded only by biopsy. Beyond all doubt, biopsy results are the basis of the future treatment plan.
Besides the normal picture, a biopsy may reveal precancerous conditions of the prostate tissue:
- Prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN) – in PIN, prostate cancer cells are slightly changed but do not grow into other gland parts or nearby structures. PIN might be low-grade; this state has no connection to the oncological process. Revealing a high-grade PIN means a 20% possibility of undetected cancer in another area of the prostate gland.
- Proliferative inflammatory atrophy (PIA) – in PIA, cells are smaller and show signs of the inflammatory process. PIA is not dangerous itself but can progress to high-grade PIN or cancer.
- Atypical small acinar proliferation (ASAP) or glandular atypia – in ASAP, there is a certain suspicion of cancer, but the number of changed cancer cells is not sufficient to make a conclusion. In this case, a repeat biopsy within a few months is usually recommended.
Finding precancerous conditions does not necessarily mean that prostate cancer will develop, but it does suggest an increased risk.
The final diagnosis of cancer is confirmed in case of receiving such results:
- Adenocarcinoma – the most common type of prostate cancer (over 90%). Adenocarcinomas grow slowly and may allow for postponed treatment.
- Small cell carcinoma and neuroendocrine tumors – tend to spread rapidly to lymph nodes and internal organs.
- Transitional cell carcinomas – involve features of multiple tumor types and require immediate and aggressive treatment for prostate cancer.
The next step in treatment planning is staging the prostate cancer. A comprehensive approach includes:
- Level of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) at diagnosis
- TNM classification: "T" refers to the tumor size (clinically or via prostate surgery); "N" refers to cancer spread to lymph nodes; "M" reflects the presence of distant metastases
- Grade Group (based on Gleason score): evaluates how quickly prostate cancer cells are likely to grow and spread. A higher score suggests more aggressive disease and the need for faster intervention.

What Prostate Cancer Treatment Tactics Offer the Best Results?
In case symptoms are absent, the small size of the initial tumor and its slow growth (low Gleason score), low level of prostate specific antigen, and age over 60 years, the doctor may advise postponing active treatment for prostate cancer.
According to data from clinical trials, more than 70% of all patients with localized prostate cancer will never need to go through prostate cancer surgery, radiation therapy, or hormone therapy.
In this situation, a doctor may offer you two options:
- Active surveillance – You will visit your general practitioner every 6 months and have a PSA blood test and DRE. A prostate biopsy will be repeated each year, if necessary. The results of the examination will influence further treatment options.
- Watchful waiting (observation) – A type of follow-up with fewer tests; attention is focused on complaints and clinical symptoms.
The opinion of the patient is important as well. Some people may strongly prefer radical prostatectomy, regardless of its risks and side effects. They have the right to such a point of view, as active surveillance may allow prostate cancer cells to grow and spread, which could restrict possible treatment options for prostate cancer. Others may prefer postponing treatment because prostate surgery may not improve their quality of life, or they wish to avoid numerous side effects.
Surgical removal of the prostate gland is the only option for radical treatment. Taking into consideration all benefits and risks of such an intervention, surgery for prostate cancer is recommended in such cases:
- Good general state of health
- Estimated life expectancy over 10 years
- High risk of cancer progression
- The localized form of cancer without spreading to lymph nodes or other organs
- No previous radiation therapy
In certain cases, radical prostatectomy may be performed before radiation therapy to reduce the volume of the tumor mass and enhance the effect of subsequent treatment. This approach is particularly beneficial for patients with locally advanced or limited metastatic prostate cancer. Studies show that combining surgery with radiation therapy can improve progression-free survival by 15-20% compared to radiation therapy alone, especially in high-risk patients. Multimodal therapy has been associated with a 5-year overall survival rate of up to 85% in selected cases.
Radical Prostatectomy: Open Approach in Prostate Cancer
Radical prostatectomy implies total and irreversible removal of the prostate gland, seminal vesicles, part of the urethra, and vas deferens. There are a few techniques for this intervention, but the first stage – preparation for prostate surgery – is common.
To make the surgery and postoperative period as safe and comfortable as possible, patients should follow these rules:
- Visit the hospital 5-7 days before the surgery to have preliminary tests done and see related specialists
- Stop taking certain drugs (warfarin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, etc.) 1-2 weeks before the procedure
- Lose weight
- Quit smoking and using other tobacco-related products
- A few days before the surgery, take medication to ensure normal stool and prevent constipation
- Do pelvic floor muscle exercises to prevent urinary problems (urinary incontinence)
- Take a vacation for 4-8 weeks before being admitted to the hospital
- Prepare comfortable clothes
- Study information about using a urinary catheter, or ask your doctor about it
- Ask somebody to stay with you and help with activities of daily living for the first few days after the surgery
The first technique of radical prostatectomy was open radical prostatectomy, which requires a long skin incision. Nowadays, the open surgery approach is used less often – mainly when the prostate volume is more than 100 grams or when laparoscopic surgery is not feasible.
In radical retropubic prostatectomy [4], the skin incision starts from the belly button and goes down to the pubic bone. Of course, the intervention is performed under general anesthesia, so the procedure is painless. Another variant is providing spinal or epidural anesthesia in combination with sedative drugs. This approach allows for pelvic lymph node dissection, as the field of view is broad. After the surgery, a urinary catheter is placed into the penis to aid urination. The catheter is typically used for the first 1-2 weeks postoperatively.
When radical perineal prostatectomy is performed, the incision is half-round and located between the anus and scrotum. This technique uses the same types of anesthesia but is less invasive and faster. However, it has downsides: a higher risk of erectile dysfunction and limited access to nearby lymph nodes, which cannot be removed via this approach. A urinary catheter is required in this case as well.
A variant of partial prostate removal is transurethral resection of the prostate (TURP), commonly indicated for benign prostatic hyperplasia and urination issues caused by urethral narrowing. In men with advanced prostate cancer, TURP may be performed to relieve similar symptoms. During this procedure, the inner part of the prostate tissue is removed using laser or electric energy through the urethra, leaving the skin intact. The surgery is painless due to general or spinal anesthesia. A urinary catheter is inserted afterward but is usually removed within 1-2 days.
Despite being minimally invasive, TURP can still result in side effects such as blood in the urine, infection, slow urine flow due to scarring, erectile dysfunction, and retrograde ejaculation. However, a skilled surgeon can significantly minimize these risks.
High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) is a minimally invasive technique used to treat prostate cancer, particularly in cases of localised prostate cancer or as a palliative option in advanced and castration resistant prostate cancer. HIFU uses precisely focused ultrasound waves to generate intense heat, which helps kill cancer cells by destroying cancerous tissue within the prostate gland without the need for incisions.
This approach can be performed under spinal or general anesthesia and is typically done on an outpatient basis. The primary benefit of HIFU is that it targets only the tumor area, helping to spare surrounding healthy cells, including those involved in sexual function and urinary control. As a result, the risk of urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction is significantly lower compared to more radical interventions like radical prostatectomy.
Although this approach cannot cure prostate cancer, HIFU is becoming more widely adopted in some German hospitals and is often used when patients are not ideal candidates for open surgery, laparoscopic prostatectomy, or robotic-assisted surgery. As with any surgical treatment, success depends on patient selection, imaging precision, and the operator's expertise with advanced technologies.
Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: Keyhole Surgery Approach in Prostate Cancer
Laparoscopic radical prostatectomy [5], or keyhole surgery, is a modern approach to performing radical prostatectomy. This technique involves removing the prostate gland through several small incisions. As a result, the laparoscopic surgery is less traumatic, blood loss is minimal, pain is significantly reduced, hospital stay is shortened to one
day, and recovery is typically faster. One limitation is that it may not be possible to convert it to open surgery if the need arises during the procedure.
It is important to note that the success of laparoscopic radical prostatectomy greatly depends on the surgeon's experience. While high-tech instruments and systems offer certain benefits, they cannot compensate for a lack of surgical expertise. A qualified professional remains the most crucial element in this surgical treatment for localised prostate cancer.
Robotic-assisted laparoscopic radical prostatectomy, also known as robotic prostatectomy, is the most recent advancement used to treat prostate cancer, introduced into clinical practice in the last two decades. This procedure uses the da Vinci Surgical System, a high-precision, four-armed robotic system that enables a minimally invasive robotic prostatectomy. As with laparoscopic procedures, the surgeon's skill is essential – ideally, the surgeon should have completed more than 100 surgeries. Many German hospitals list surgical success rates on their websites for patient transparency.
The robot assisted radical prostatectomy begins with inserting microsurgical instruments and high-definition cameras into the body. General anesthesia ensures the patient feels no pain. The surgeon then connects to the console and begins the operation. The robotic surgery system translates the surgeon's hand movements into precise actions by the instruments in real time.
It is important to understand that the robotic-assisted surgery system functions only under the surgeon's control. There is no automation or pre-programming – surgeon experience and manual control are key. The procedure ends with removal of instruments and closure of the small incisions.
During robotic radical prostatectomy, the surgeon sits comfortably at the control panel, viewing the surgical field in a magnified 3D format.
The benefits of robotic surgery include:
- Greater precision and enhanced dexterity during nerve- and vessel-sparing steps
- Improved visualization of anatomical details invisible to the naked eye
- Better access to difficult areas
- The ability to preserve healthy cells and surrounding tissues
- Improved preservation of nerves, reducing complications such as erectile dysfunction
After the procedure, the removed prostate tissue undergoes pathological examination. The pathologist assesses the tumor type, its spread beyond the prostate, and – most importantly – whether any cancer cells remain at the surgical margins.
A positive surgical margin indicates that some cancer cells may still be present. Therefore, both the rate of negative surgical margins and the number of completed prostate cancer surgeries are essential markers of a surgeon's experience.
Coping with Possible Risks and Side Effects of Radical Prostatectomy in Prostate Cancer
As with each surgical intervention, radical prostatectomy has certain risks:
- Abnormal reaction to anesthesia drugs
- Bleeding during the prostate surgery and afterward
- Thrombosis of legs and lungs
- Injury to nearby organs (this mainly happens during robotic surgery, especially if the surgeon is not skilled enough)
- Infection
- Abnormal collection of lymph in case of removal of lymph nodes
These risks can often be successfully avoided through appropriate preparation, as mentioned above, and by choosing a qualified surgeon. Side effects of radical prostatectomy also largely depend on the surgeon's experience. Some complications are temporary and resolve over time, while others may be long-term and require additional treatment for prostate cancer.
Urinary Incontinence
Urinary incontinence refers to the partial or total inability to control urination. It is one of the most common side effects after prostate cancer surgery.
There are several types of urinary incontinence:
- Stress incontinence – typically caused by damage to the bladder sphincter muscles or nerves, resulting in leakage when coughing or exercising
- Overflow incontinence – caused by obstruction in the urinary tract from scar tissue
- Urge incontinence – when the bladder is hypersensitive and reacts to small volumes of urine
- Continuous incontinence – a rare condition where all control over urination is lost
It usually takes several weeks to months for urination to normalize. Pelvic floor exercises before and after surgery help strengthen the relevant muscles. Temporary use of pads or pants is common during this period.
Erectile Dysfunction
Erectile dysfunction (impotence) is another frequent complication. It refers to the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse. Nerve sparing surgery is often performed if nerves are not affected by prostate cancer cells, in an effort to preserve sexual function. Still, recovery may take months or even years.
Options that may help include:
- PDE-5 inhibitors (Viagra, Cialis, Levitra)
- Vacuum erection devices
- Penile implants (a form of surgical treatment)
Sometimes, erectile dysfunction results not just from nerve damage but also from fatigue or psychological effects after treatment for prostate cancer.
Other Possible Side Effects
Changes in orgasm – Orgasm remains possible but becomes "dry" due to removal of the seminal vesicles and prostate gland, which produce seminal fluid.
Loss of fertility – As the connection between testicles and urethra is severed, ejaculation stops. However, sperm banking before prostate cancer surgery offers the option for future fertility via artificial insemination.
Lymphedema – Removal of many lymph nodes can lead to fluid buildup in the genitals or legs, which is treated with physical therapy.
Change in penis length – A slight shortening may occur due to the urethral cut and lower androgen levels. This typically does not affect sexual function.
Inguinal hernia – Risk is increased following radical prostatectomy, but regular physical activity can help prevent it.
Is It Necessary to Remove Testicles in Surgical Prostate Cancer Treatment?
Orchiectomy, or surgical castration, is a form of hormone therapy that may be helpful in treating advanced prostate cancer. This procedure permanently removes the testicles, which are the primary source of androgens – male hormones that stimulate the growth of prostate cancer. By lowering androgen levels surgically, orchiectomy achieves the same goal as chemical castration with medications, but through a one-time surgical intervention rather than ongoing drug therapy.
Androgens like testosterone and dihydrotestosterone are primarily produced by the testicles, with minor contributions from the adrenal glands. Lowering androgen levels can slow tumor growth or even shrink the mass. This strategy is known as hormone therapy. While hormone therapy alone does not cure prostate cancer, it is a vital element of comprehensive treatment regimens.
Hormone therapy is commonly administered in the following cases:
- When surgery for prostate cancer or radiation therapy are contraindicated or have failed.
- When a recurrence is detected after prior treatment
- To reduce tumor size before radiation therapy
- In combination with radiation therapy for high-risk patients
There are two primary methods of delivering hormone therapy:
- Medical treatment using several drug types:
- LHRH agonists and antagonists suppress androgen production in the testicles. Though effective, they are expensive and often cause testicular shrinkage.
- Anti-androgens block androgen receptors in the prostate tissue, preventing hormone signaling. These must be taken daily.
- Estrogen drugs are rarely used due to serious side effects, despite their ability to counteract androgens.
- Orchiectomy – a permanent surgical procedure involving the removal of both testicles. It is typically done on an outpatient basis through a small incision in the scrotum, closed with absorbable stitches. If cosmetic appearance is a concern, testicular prostheses may be inserted. Orchiectomy avoids the long-term risks and costs of medicinal therapy but may be emotionally challenging. Both approaches ultimately achieve the same goal – significant reduction of androgen levels to kill cancer cells.
Side effects of hormone therapy primarily stem from the shift in hormone balance, including:
- Erectile dysfunction
- Decreased libido
- Shrinkage of testicles and penis
- Muscle mass reduction and weight gain
- Osteoporosis
- Anemia
- Depression
- Breast tenderness or enlargement
Supportive medications are often used to mitigate these side effects during treatment for prostate cancer.
What happens once the surgery for prostate cancer is done?
In the absence of surgical complications, it usually takes about 6 weeks to completely return to normal life after prostate cancer surgery. Long-distance driving is generally permitted after approximately 4 weeks, though you should verify this with your insurance provider. Returning to work may also come with certain restrictions, depending on the nature of your professional duties.
You will visit your general practitioner 4-6 weeks after the radical prostatectomy. Follow-up appointments are typically scheduled every 3 to 6 months. The frequency of these visits depends on the stage of prostate cancer, results of prostate tissue analysis (including whether surgical margins are positive or negative), and whether any further treatment or medication is being administered. Side effects from such treatments may also influence visit frequency.
During follow-up care, you may discuss preventative strategies with your physician to reduce the risk of recurrence. These can include engaging in regular physical activity, avoiding weight gain, quitting smoking, and improving dietary habits. Your general practitioner can also help manage lingering side effects of radical prostatectomy, such as urinary incontinence or erectile dysfunction.
Emotional well-being is just as important as physical recovery. If needed, your doctor may refer you to a psychotherapist to provide emotional support during your treatment for prostate cancer recovery process.
Hospitals and Costs of Prostate Cancer Treatment in Germany
Surgical treatment of prostate cancer is performed at large multidisciplinary hospitals and specialized medical centers focused on urological oncology. Among the German hospitals that demonstrate high success rates in prostate cancer surgery are:
- Mayo Clinic (USA)
- Hannover Medical School (Germany)
- Hirslanden Clinic (Switzerland)
- The Martini-Klinik (Germany)
These leading clinics are recognized not only for the experience of their surgeons but also for their use of advanced technologies, such as robotic-assisted surgery, robotic prostatectomy, and robotic radical prostatectomy with the da Vinci system. Many of these centers have dedicated units for treating both localized and advanced prostate cancer, offering comprehensive care tailored to each patient.
The cost of treatment in Germany is determined individually for each patient, depending on their condition and chosen treatment method. However, average costs for major surgical treatment options for prostate cancer are as follows:
- Nerve-sparing radical prostatectomy – €25,090
- Robotic prostatectomy (using the da Vinci Surgical System) – €24,418
- High-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU) for prostate cancer – €25,266
- Transurethral electroresection for prostate cancer – €12,378
- Cancer rehabilitation – €1,576 per day
Choosing the Best Doctor for Performing a Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer
As noted above, choosing a skilled surgeon determines the success of the intervention, reduces the risk of complications in the early postoperative period, and minimizes the chance of serious side effects, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction. Even the best advanced technologies and high-end equipment used in robotic surgery, such as robotic prostatectomy, cannot replace the surgeon's expertise. Moreover, surgeons must be fully trained and experienced in using systems like the da Vinci Surgical System to ensure the effectiveness of robotic-assisted surgery. Improper use of such tools can lead to more harm than good.
Another important factor in patient recovery is the quality of nursing care. Though often underestimated, competent nurses play a vital role in easing postoperative discomfort and promoting faster healing after prostate cancer surgery.
Considering all these factors, many men choose to seek medical help abroad. Today, it is easy to compare the global ratings and qualifications of urological surgeons online, along with reading patient reviews and stories about prostate cancer treatment. As a result, numerous patients opt for treatment in Germany, particularly in world-class German hospitals located in Berlin, Cologne, and Leverkusen. However, applying directly to these hospitals often places international patients at the end of a long queue, since German citizens receive priority access to surgical treatment options using high-end medical technologies.
In addition, administrative staff handling international inquiries may not fully understand medical documentation, which is why it is highly advisable to coordinate the process through professionals.
The most effective solution is to use the trusted services of Booking Health, a medical tourism company that assists thousands of patients each year in accessing specialized healthcare abroad.
Booking Health provides comprehensive support in the following areas:
- Recommending the best doctor and clinic based on your diagnosis
- Scheduling your appointment for the earliest convenient date
- Organizing a complete preoperative examination
- Arranging transfers, an interpreter, and a medical coordinator if needed
- Providing obligatory medical insurance
- Preparing your medical reports and further treatment recommendations
- Supporting your rehabilitation process after prostate surgery
- Facilitating ongoing communication with your treating physician
To begin planning your medical journey, simply leave a request on the Booking Health website. One of our case managers or medical advisors will contact you the same day to guide you through every step. Our goal is to help you achieve a healthier and better quality of life.
Cancer Treatment Abroad: Patient Experiences with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions About Prostate Cancer Surgery
Send request for treatmentThe main types of surgical treatment for prostate cancer include radical prostatectomy, which involves the complete removal of the prostate gland. This can be performed through open surgery, laparoscopic prostatectomy, or robotic-assisted surgery, depending on the patient's condition and the facility's resources.
Yes, robotic-assisted surgery is a highly effective and minimally invasive technique for performing radical prostatectomy. It offers greater precision, reduced blood loss, faster recovery, and a lower risk of complications. The effectiveness largely depends on the surgeon's experience with the robotic system and access to advanced technologies.
Recovery after surgical treatment for prostate cancer typically takes about 4 to 6 weeks. Most patients can return to daily activities within this time. However, complete recovery may vary depending on individual health, the type of surgery performed, and whether any complications arise during the postoperative period.
Like any surgical treatment, prostate cancer surgery carries some risks. These may include infection, bleeding, injury to nearby organs, urinary incontinence, and erectile dysfunction. In some cases, if cancerous tissue is not entirely removed, additional treatment may be required.
Yes, while radical prostatectomy may cure prostate cancer in early-stage cases, recurrence is still possible, particularly if the tumor was aggressive or had spread beyond the prostate. In such cases, additional treatment options like radiation therapy may be required. Follow-up care including PSA testing is essential to detect any signs of recurrence early.
Open surgery requires a large incision and direct access to the prostate, while laparoscopic prostatectomy uses several small incisions and a camera to guide the surgeon. Laparoscopic techniques generally result in less trauma, shorter hospital stays, and quicker recovery times, especially when paired with robotic-assisted surgery.
Some of the best hospitals for prostate cancer surgery in Germany include Charité University Hospital Berlin, Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch, and LMU University Hospital Munich. These hospitals are known for their use of advanced technologies, experienced surgical teams, and high success rates in treating prostate cancer.
Preparation for surgical treatment involves medical tests, stopping certain medications, practicing pelvic floor exercises, and planning for postoperative support. Your medical team will guide you through every step to ensure a safe and effective radical prostatectomy procedure.
Choose treatment abroad and you will be sure to get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] American Cancer Society. Key Statistics for Prostate Cancer. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/types/prostate-cancer/about/key-statistics.html
[2] National Cancer Institute. Cancer Stat Facts: Prostate Cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html
[3] MedicineNet. PSA Test (Prostate Specific Antigen). https://www.medicinenet.com/prostate_specific_antigen/article.htm
[4] PubMed Central. Open Versus Laparoscopic Versus Robot-Assisted Laparoscopic Prostatectomy: The European and US Experience. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2859140/
[5] PubMed. Laparoscopic versus open radical prostatectomy: a comparative study at a single institution. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12686809/
Read:
A Comprehensive Guide to Getting Prostate Cancer Treatment
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Treatment in Germany: What You Need to Know
Article menu:
- What Determines the Type of Prostate Cancer Treatment Choice?
- What Prostate Cancer Treatment Tactics Offer the Best Results?
- Radical Prostatectomy: Open Approach in Prostate Cancer
- Laparoscopic Radical Prostatectomy: Keyhole Surgery Approach in Prostate Cancer
- Coping with Possible Risks and Side Effects of Radical Prostatectomy in Prostate Cancer
- Is It Necessary to Remove Testicles in Surgical Prostate Cancer Treatment?
- What Happens Once the Surgery for Prostate Cancer Is Done?
- Choosing the Best Doctor for Performing a Radical Prostatectomy for Prostate Cancer
- Frequently Asked Questions About Prostate Cancer Surgery
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health