Lung cancer remains one of the most serious and prevalent health challenges worldwide. Global statistics indicate that lung cancer is the leading cause of cancer-related deaths worldwide, accounting for approximately 25% of all cancer fatalities.
The disease progresses through four distinct stages, each influencing the choice of treatment and overall prognosis. While the five-year survival rate can reach up to 70% for stage I, it drops dramatically to around 10% for stage IV. For thousands of patients facing this diagnosis, dedicated medical teams with years of specialized experience have helped navigate the complex treatment landscape, providing hope where it once seemed lost.
Through innovative treatment approaches and comprehensive care plans, many patients have achieved improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life, even when confronting advanced disease. Each patient's unique situation requires an individualized strategy that considers not just the medical aspects but also the patient’s circumstances and preferences.
Standard Treatment Protocols for Lung Cancer
Lung cancer medical treatment typically includes surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, and targeted therapy. The choice of treatment depends on cancer type, stage, and overall patient health. In many cases, a multimodal approach is used to maximize effectiveness, especially for advanced lung cancer.
Surgery is the primary treatment modality for early-stage NSCLC, particularly Stages I and II. It involves the physical removal of the tumor and nearby affected tissue, and can result in high cure rates when the cancer is localized. Surgery may be less effective in later stages due to cancer spread but can still be used for tumor debulking or symptom relief.
Chemotherapy is a systemic therapy used across all lung cancer stages but is especially common in advanced stages (III and IV). It works by targeting rapidly dividing cancer cells throughout the body. Standard regimens typically consist of multiple cycles and may be combined with other treatments like radiation or immunotherapy. While chemotherapy can be effective, it often comes with significant side effects such as fatigue, nausea, and immune suppression.
Radiation therapy is a localized treatment that uses high-energy rays to destroy cancer cells. It is frequently used either alone or in combination with chemotherapy in both NSCLC and SCLC. In cases where surgery is not possible, radiation therapy can offer disease control and symptom relief. Side effects may include skin irritation, fatigue, and difficulty swallowing, depending on the treatment area.
Targeted therapy is designed to block specific genetic mutations and pathways involved in cancer growth. It is most effective in patients whose tumors test positive for mutations like EGFR, ALK, or ROS1. Targeted therapy generally causes fewer side effects than chemotherapy and can significantly prolong progression-free survival. It is often used in patients with advanced or recurrent lung cancer.
While conventional treatments are the foundation of lung cancer care, they are not without limitations. Challenges, such as tumor resistance, recurrence, and treatment-related toxicity, have driven the development of more innovative approaches aimed at improving outcomes and preserving quality of life.
Innovative Lung Cancer Treatment Methods
In recent years, innovative lung cancer treatment methods have emerged. These methods are designed to target cancer cells more precisely while minimizing damage to healthy tissue. They provide alternative treatment for lung cancer for patients who may not respond well to conventional therapies.
Dendritic Cell Therapy for Lung Cancer
Dendritic cell therapy for lung cancer is an advanced form of immunotherapy that activates the body’s immune system to target and destroy cancer cells. The treatment involves extracting dendritic cells from the patient’s blood, modifying them to recognize cancer-specific antigens, and reintroducing them into the body to stimulate a targeted immune response. Unlike traditional treatments, dendritic cell therapy is well-tolerated and causes minimal side effects, typically limited to mild flu-like symptoms. This therapy, pioneered by Nobel Prize winner Ralph Steinman, has shown promising results, including prolonged survival and, in some cases, complete remission. In a video interview, Professor Frank Gansauge – an expert in immunotherapy – explains how dendritic cells function as the “officers” of the immune system, organizing a precise and powerful attack on malignant cells while preserving healthy tissue. He also highlights how his clinic integrates dendritic cell therapy with conventional treatments like chemotherapy and radiation to enhance outcomes. We invite you to watch the video to learn more about the science, benefits, and real-life success stories behind this groundbreaking treatment.
Prof. Frank Gansauge: How Dendritic Cell Therapy is Transforming Modern Cancer Treatment
Interventional Radiology for Lung Cancer
Interventional radiology offers several minimally invasive procedures for managing advanced lung cancer. These image-guided techniques provide targeted treatment options with reduced damage to surrounding healthy tissues compared to conventional approaches. For patients with metastatic disease or those who cannot undergo traditional therapies, these procedures can provide effective symptom control and disease management while maintaining quality of life.
Thermal ablation, as one of the most prominent ablation techniques, relies on increased heat to disrupt tumor structure. Two outstanding technologies in this realm are high-intensity focused ultrasound (HIFU), which concentrates ultrasound energy on tumor sites, and laser interstitial thermal therapy (LITT), which applies a laser to destroy malignant tissues.
Initially administered for locally aggressive cancer types, thermal ablation is increasingly incorporated into treatment plans for recurrent or advanced lung cancer, especially following unsuccessful radiotherapy. Thermal ablation can reduce recurrence by up to 50% while being a part of a comprehensive treatment plan.
Cryoablation presents one more minimally invasive option, which is applying extreme cold to eradicate malignant cells. This approach is actively investigated for lung cancer as it helps to preserve collagen and frozen tissues near crucial blood vessels or bronchi.
Studies for advanced forms of lung cancer demonstrated that cryoablation for non-small cell lung cancer significantly improves progression-free time (82%, 97%, and 91% at 1, 3, and 6 months follow-up period). Its favorable safety profile and minimal complication rates make cryoablation a viable and well-tolerated option for many patients.
Electrochemotherapy (ECT) merges electrical stimulation with anticancer drug administration, enhancing drug penetration into tumor cells. Delivered directly via injection, this technique is particularly useful for tumors located in strategically critical positions, such as near major vessels or in key anatomical zones.
Above its cytotoxic effects, ECT is also known to stimulate an immune response and improve local tumor control in more than 70% of cases. As a result, it makes ECT a valuable part of a complementary strategy in advanced lung cancer management, particularly for cases of metastatic secondary lesions or for health-compromised individuals after systemic treatments.
Prof. Kovács on Electrochemotherapy – How Electric Pulses Help Chemo Actually Work
Transarterial Chemoembolization (TACE) is an advanced and minimally invasive lung cancer treatment that combines localized chemotherapy with embolization – a technique that blocks the tumor’s blood supply. By delivering chemotherapy drugs directly through the arteries feeding the tumor, TACE maximizes drug concentration at the tumor site while minimizing exposure to healthy tissues, thereby reducing common side effects like nausea and hair loss.
This targeted approach has proven especially beneficial for patients with advanced lung cancer who are not candidates for surgery or have developed resistance to standard chemotherapy. Studies show that TACE can significantly improve survival rates and quality of life, with shorter recovery times compared to traditional methods.
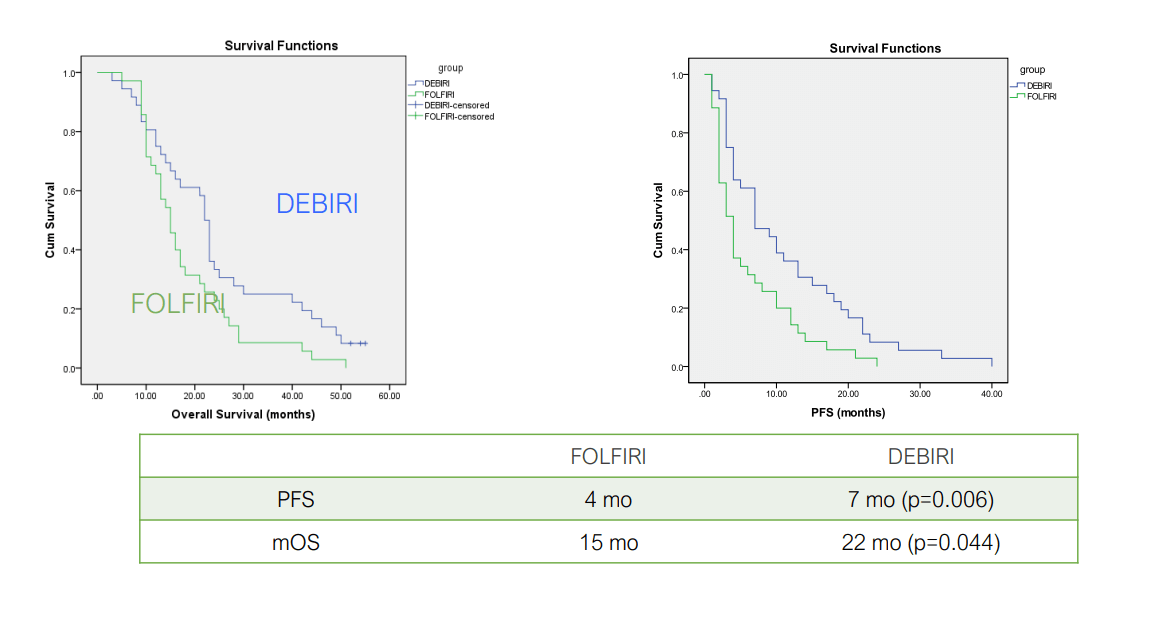
Aliberti C et al Ancancer Res 2011;31:4581
Richardson A et al J Vasc Interv Radiol 2013;24:1209
**DEBIRI = TACE, FOLFIRI = IV therapy
In a detailed video interview, Professor Attila Kovács, explains how TACE works, its dual mechanism of action, and how it can be effectively combined with systemic chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or immunotherapy to enhance outcomes. We invite you to watch this informative interview to learn more about how TACE is transforming the landscape of lung cancer treatment.
Prof. Kovács: Why Interventional Oncology Should Be the Fourth Pillar of Cancer Care
Why Choose Innovative Treatments for Lung Cancer?
Innovative methods offer several advantages over traditional treatments, including:
- Higher survival rates, especially for the treatment of advanced lung cancer.
- Reduced side effects and quicker recovery times.
- Targeted action that spares healthy cells and improves overall quality of life.
With the growing demand for advanced therapies, lung cancer treatment centers worldwide are adopting these innovative approaches. Patients seeking the best lung cancer treatment in the world are increasingly turning to clinics specializing in these methods.
Comparative Analysis of Treatment Methods for Lung Cancer
It is important to compare traditional and alternative treatments for lung cancer to understand their effectiveness, side effects, and costs. Traditional methods like chemotherapy and radiation are widely used but come with severe side effects and limited survival rates. Conversely, alternative treatments for lung cancer, such as immunotherapy, dendritic cell therapy, and TACE, offer higher response rates, fewer side effects, and improved survival rates, especially for advanced cases.
| CharacteristicsTherapy type | 2-Year Survival Rate | Response Rate | Duration | Side Effects |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatment | ~25% for advanced cancer | Less than 10% | Several cycles | Severe (nausea, fatigue, hair loss, immunosuppression, skin irritation) |
| Innovative Methods | ~60% for advanced cancer | 45-65% | Up to 4 sessions | Mild (localized discomfort) |
Success Stories and Lung Cancer Patient Testimonials
Real-life success stories and patient testimonials provide evidence of the effectiveness of innovative lung cancer treatments. Patients who underwent dendritic cell therapy and TACE have experienced great improvements in survival rates and quality of life. These treatments are offered at some of the best treatment centers for lung cancer, known for their advanced medical technologies and personalized care.
One such case is Anitha Cherian from Canada, who was diagnosed with Stage 4B Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer with distant metastases to the brain, liver, bones, and left adrenal gland. She was also positive for the EGFR exon 19 deletion mutation. Seeking advanced treatment, she traveled to Germany for care at LDG Laboratories Dr. Gansauge Berg, under the guidance of Professor Gansauge.
With the help of Booking Health, her medical journey was coordinated, including translation services, transportation, and appointment scheduling. She and her family praised the efficiency of the process, highlighting how these services made a challenging situation more manageable. Her experience underscores the growing reliance on specialized cancer treatment centers that offer advanced therapies, enhancing both survival and quality of life.

Best Treatment Centers for Lung Cancer
Selecting the best place for lung cancer treatment can significantly impact patient outcomes. The following institutions represent some of the best lung cancer treatment centers in the world. Each offers unique strengths in lung cancer new treatment through various stages and complexities.
| Hospital | Specialization | Technologies | Recognition |
|---|---|---|---|
| University Hospital RWTH Aachen | Thoracic oncology Minimally invasive surgery | Video-assisted thoracoscopy Radiofrequency ablation | Certificate ISO 9001:2015 IQM Certification Ranked among the top German medical facilities by Focus magazine
|
| Mayo Clinic (USA) | Multidisciplinary approach Precision medicine | Low-dose CT screening Robotic surgery Proton therapy | Ranked among the Best Hospitals for cancer by U.S. News & World Report |
| University Hospital Jena | Pulmonology Thoracic surgery | Hybrid interventions Robotic surgery (da Vinci system) | ISO 9001:2015 accredited DIOcert certification Ranked among the top German medical institutions for cardiothoracic surgery by Focus magazine |
| Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center | Comprehensive cancer care Clinical research | Advanced radiation therapy Immunotherapy | NCI-designated cancer center Recognized as one of the top two cancer hospitals in the U.S. for over 30 years |
| ViDia Hospital Karlsruhe | Thoracic oncology Interventional procedures | VATS Laser therapy Cryotherapy | The Department of Thoracic Surgery has been certified as a Lung Cancer Center by the German Cancer Society (DKG) since 2011 |
The Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery at University Hospital RWTH Aachen ranks among the top German medical facilities in its field. For lung cancer patients, top lung cancer doctors offer both minimally invasive approaches and conventional thoracic surgery. Their video-assisted thoracic surgery (VATS) techniques allow for atypical lung resection, anatomical resection of lung lobes, and resection of pulmonary metastases with minimal trauma to patients. The hospital's Department of Interventional Radiology complements surgical options with treatments like radiofrequency ablation and microwave ablation for lung cancer and lung metastases.
Mayo Clinic's Lung Cancer Program is one of the country's largest and most experienced practices focused on lung cancer and other thoracic cancers. What sets Mayo Clinic apart is its multidisciplinary approach, with regular Tumor Board meetings where specialists discuss complex cases to develop the best treatment strategies. Mayo Clinic doctors pioneered lung cancer screening using low-dose CT scans to detect cancer at its earliest, most treatable stage. Their treatment options include minimally invasive surgery (VATS and robotic surgery), precisely targeted radiation therapy (including proton beam therapy), and cutting-edge systemic treatments, including immunotherapy and molecularly targeted therapy.
According to the prestigious Focus magazine, the University Hospital Jena regularly ranks among the top German medical facilities for lung cancer treatment abroad. The Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery specializes in minimally invasive approaches to lung cancer treatment. The best lung cancer doctors employ cutting-edge video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) and the innovative da Vinci surgical system for robot-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (RATS), particularly for lobectomies. The department's comprehensive approach to lung cancer includes surgical treatment of primary tumors, metastases, and other thoracic conditions using laser surgery (Nd:YAG) and other sparing techniques.
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) is among the world's most respected comprehensive centers devoted exclusively to cancer. Their lung cancer specialists perform more than 1,200 operations annually, making them one of the most experienced teams in the country. MSK offers a comprehensive lung cancer screening program with low-dose CT scans for high-risk individuals between 50-80 years of age. As an NCI-designated cancer center, MSK achieves better survival rates for lung cancer patients compared to national benchmarks across all cancer stages. Their treatment approach includes surgery, precisely targeted radiation therapy, advanced chemotherapy, and immunotherapy options.
ViDia Hospital Karlsruhe combines modern medicine with a patient-centered approach. Their Department of Pulmonology offers comprehensive diagnostic services – pulmonary function tests, endoscopic procedures, and imaging studies. The Department of Thoracic Surgery has been certified by the German Cancer Society as a Lung Cancer Center since 2011, with more than 80% of surgeries performed using minimally invasive techniques. Their interventional radiologists complement surgical approaches with procedures like radiofrequency ablation for treating lung cancer and metastases. The hospital's multidisciplinary team holds weekly tumor boards to develop personalized treatment strategies and offer the best lung cancer treatment in the world.
The lung cancer hospitals in Germany set the global standard for excellence in oncological care. German medicine's reputation for superior quality is reflected in its certification protocols, specialist training programs, and patient-centered approach that prioritizes both survival rates and quality of life for lung cancer patients – here you will fing the best hospital for lung cancer, for sure.
Cost of Lung Cancer Treatment
The cost of lung cancer treatment varies significantly depending on the stage and type of therapy chosen. In Germany, a leading destination for advanced cancer treatments, patients benefit from transparent pricing and high-quality care.
For stage 1 lung cancer treatment, video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (VATS) lobectomy can be suggested for NSCLC. Stage 2 lung cancer treatment may involve a combination of surgery and chemotherapy, whereas the treatment of stage 3 lung cancer often requires a more aggressive approach, including combined chemotherapy, radiation, and possibly immunotherapy. For the treatment of 4 stage lung cancer in Germany, innovative methods like dendritic cell therapy and TACE are frequently used.
| Treatment Method | GERMANY* | GB | USA |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Treatment | €80,000 - €150,000 full course | €90,000 - €165,000 full course | €100,000 - €180,000 full course |
| Innovative Methods | €25,000 - €60,000 full course | €70,000 - €120,000 full course | €100,000 - €150,000 full course |
*Prices may vary depending on the chemotherapeutic agents used, course of treatment, and tumor characteristics.
Compared to other countries, Germany offers competitive pricing without compromising on medical expertise or technological advancement. The transparent pricing system ensures patients are well-informed about the total cost of lung cancer treatment, including consultation fees, diagnostic tests, and post-treatment care.
A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
Finding the best treatment strategy for your clinical situation is a challenging task. Being already exhausted from multiple treatment sessions, having consulted numerous specialists, and having tried various therapeutic interventions, you may be lost in all the information given by the doctors. In such a situation, it is easy to choose a first-hand option or to follow standardized therapeutic protocols with a long list of adverse effects instead of selecting highly specialized, innovative treatment options.
To make an informed choice and get a personalized cancer management plan, which will be tailored to your specific clinical situation, consult medical experts at Booking Health. Being at the forefront of offering the latest medical innovations for already 12 years, Booking Health possesses solid expertise in creating complex cancer management programs in each case. As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized stage 4 lung cancer treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding them to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- Transparent budgeting with no hidden costs
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you on the way of pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods for metastatic lung cancer with leading specialists in this field.
Cancer Treatment Abroad: Patient Experiences with Booking Health
Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients About Lung Cancer Treatment
Send request for treatmentEarly signs include persistent cough, chest pain, shortness of breath, hoarseness, fatigue, unexplained weight loss, and coughing up blood. These symptoms are often mistaken for other respiratory conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis.
Lung cancer is diagnosed through imaging tests like X-rays, CT scans, and PET scans. A biopsy confirms the presence of cancer cells, and additional tests, such as bronchoscopy and sputum cytology, help determine the type and stage.
Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, targeted therapy, immunotherapy, dendritic cell therapy, and TACE. The choice depends on cancer type, stage, and patient health.
Survival rates vary by stage: Stage 1: 70% Stage 2: 50% Stage 3: 25% Stage 4: 10% Early diagnosis significantly improves outcomes.
Yes, non-smokers can develop lung cancer due to genetic factors, exposure to radon gas, secondhand smoke, environmental pollutants, and occupational hazards.
Risk factors include smoking, secondhand smoke, exposure to radon gas, asbestos, air pollution, genetic predisposition, and previous radiation therapy to the chest.
Quit smoking, avoid secondhand smoke, test your home for radon, minimize exposure to carcinogens at work, eat a healthy diet, and exercise regularly.
Costs vary by stage and treatment type. In Germany: Stage 1: €15,000 - €25,000 Stage 2: €25,000 - €40,000 Stage 3: €40,000 - €70,000 Stage 4 (advanced therapies): €50,000+
The best treatment depends on the cancer stage and the patient’s health. Surgery and radiation are effective for early stages, while advanced cases benefit from immunotherapy, dendritic cell therapy, and TACE.
Side effects vary by treatment type: Chemotherapy: fatigue, nausea, hair loss, immune suppression Radiation: fatigue, skin irritation Immunotherapy: fatigue, flu-like symptoms TACE: localized discomfort, mild flu-like symptoms.
Chemoembolization (TACE) delivers chemotherapy directly to the tumor and blocks its blood supply, leading to fewer systemic side effects than traditional chemotherapy, which affects the entire body.
Effectiveness is monitored through imaging tests (CT or MRI) and tumor marker analysis. Follow-up scans assess tumor size and progression.
Lung cancer can be hereditary, especially if close relatives have had it. Genetic mutations increase risk, but environmental factors like smoking play a more significant role.
Life expectancy varies by stage and treatment. With early diagnosis, patients can live for several years, while advanced stages have shorter survival rates. Innovative treatments can extend life expectancy.
Yes, through low-dose CT scans, especially for high-risk individuals (smokers or those with a family history). Early detection significantly improves survival rates.
Yes, symptoms like persistent cough, hoarseness, fatigue, chest pain, and unexplained weight loss are often mistaken for other conditions, leading to delayed diagnosis.
Small cell lung cancer (SCLC) is more aggressive, grows faster, and spreads more quickly than non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which is slower-growing and more common. SCLC responds better to chemotherapy and radiation but is harder to cure.
Options include second-line chemotherapy, radiation, immunotherapy, targeted therapy, and clinical trials for experimental treatments. The choice depends on previous treatments and overall health.
For advanced lung cancer, the 2-year survival rate is about 25% with standard treatment. However, it rises to around 60% with innovative methods (e.g., dendritic cell therapy, TACE, and other interventional procedures).
Standard lung cancer treatments often involve several chemotherapy or radiotherapy cycles over a few months. On the other hand, innovative therapies (e.g., TACE or immunotherapy) typically require up to four sessions.
Conventional lung cancer therapies can cause nausea, fatigue, hair loss, and immune suppression. In turn, modern targeted and interventional treatments are usually associated with mild, localized discomfort and fewer systemic effects.
The response rate for standard lung cancer treatment remains below 10%. In contrast, innovative treatments (e.g., dendritic cell therapy and TACE) achieve response rates of 45-65%.
While no single hospital claims the absolute top position worldwide, University Hospital RWTH Aachen in Germany, along with Mayo Clinic and Memorial Sloan Kettering in the US, consistently rank highest based on patient outcomes, technological capabilities, and specialist expertise.
Look for hospitals with multidisciplinary tumor boards, high surgical volumes, advanced diagnostic capabilities, and experience with your specific type of lung cancer. Consider accreditations and published survival rates. The cost of treatment for lung cancer should be a factor, but not the only consideration.
Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center reports survival rates exceeding national benchmarks in the USA, while European centers like University Hospital Jena and ViDia Karlsruhe demonstrate impressive outcomes, particularly for lung cancers treated with minimally invasive approaches.
Seek centers with board-certified thoracic oncologists, regular tumor boards, high surgical volumes, cutting-edge radiation technology, and molecular testing capabilities. The center should offer personalized treatment plans and comprehensive support services. Consider both treatment outcomes and the cost of lung cancer treatment when making your decision.
Yes, Europe offers several specialized lung cancer clinics, particularly in Germany, where the German Cancer Society certifies Lung Cancer Centers meeting strict quality criteria. University Hospital RWTH Aachen, University Hospital Jena, and ViDia Karlsruhe represent German excellence in specialized lung cancer care with a transparent lung cancer treatment price policy.
Leading hospitals provide cutting-edge treatments, including dendritic cell therapy, targeted molecular therapies, robotic surgery, and advanced radiation techniques like proton therapy.
Top hospitals approach stage 4 lung cancer with personalized treatment plans combining systemic therapies (immunotherapy, targeted therapy, chemotherapy) and treatments for symptom management. Multidisciplinary tumor boards optimize treatment sequencing, with consideration of quality of life.
Premier facilities utilize low-dose CT screening, PET-CT fusion imaging, navigational bronchoscopy, VATS (video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery), robotic systems like da Vinci, stereotactic body radiation therapy, proton therapy, and molecular diagnostic platforms.
Patients seeking advanced lung cancer care often choose Germany for its specialized centers which combine dendritic cell therapy with minimally invasive interventions. The focus is on personalizing treatment for each tumor type and stage (ensuring that complex cases receive strategies often unavailable elsewhere).
Choose treatment abroad and you will be sure to get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
Read:
Treatment of stage 4 lung cancer in Germany
Article menu:
- Standard Treatment Protocols for Lung Cancer
- Innovative Lung Cancer Treatment Methods
- Comparative Analysis of Treatment Methods for Lung Cancer
- Success Stories and Lung Cancer Patient Testimonials
- Best Treatment Centers for Lung Cancer
- Cost of Lung Cancer Treatment
- A Medical Journey: Every Step of the Way With Booking Health
- Frequently Asked Questions of Our Patients About Lung Cancer Treatment
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health