Among middle-aged and elderly men worldwide, prostate cancer (PCa) stands as a significant health threat. The American Cancer Society's prognosis expects around 313,780 new prostate cancer cases in 2025, and a huge number of approximately 35,770 men are expected to die from this disease. This translates to one man being diagnosed with cancer of the prostate (CaP) every 2 minutes [1].
The current disease development rate stands at 120.2 per 100,000 men per year based on 2018-2022 data, with approximately 1 in 8 men (12.9%) developing prostate cancer (PC) during their lifetime [2]. What's really concerning is that after the number of advanced-stage cases went down from 2007-2014, things changed. Since 2014, prostate cancer rates started going up by 3% every year. The advanced-stage diagnoses are rising even faster – between 4.6-4.8% per year. When you look at survival rates, men with advanced-stage prostate cancer only have a 38% chance of surviving five years. Compare this to localized disease where it's almost 100% [2].
Therapeutic isotope programs with Lutetium-177-PSMA, Actinium-225-PSMA, and Radium-223 have been successfully used in advanced cancer therapy. These are modern drugs, in the development of which scientists have corrected the shortcomings of earlier used isotopes. With Actinium-225 isotope emerging as a promising alternative to Lutetium-177 and Radium-223 isotopes, it is crucial to understand the benefits, indications, and potential side effects of each cancer therapy.
What Patients Face When Prostate Cancer Becomes Advanced
Development of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) is about treatment options becoming more limited. The production of new-generation androgen receptor inhibitors and chemotherapeutic agents is on its way. But the resistance of tumor cells to existing medications creates a need for novel therapeutic approaches.
The mCRPC cells are heterogeneous in nature, which creates unique challenges. Around 80-90% of patients get bone metastases predominantly, others have extensive lymph node involvement, or visceral disease – and each of these needs different therapeutic considerations. Targeted radionuclide therapies changed the cancer therapy landscape significantly when they were introduced. They offer new hope to patients who already tried all conventional treatment options.
The financial burden of advanced prostate cancer (PC) includes both direct and indirect (e.g. loss of working capacity) medical costs. American Cancer Society data indicates that patient out-of-pocket expenses for cancer therapies average a huge amount of $21.1 billion annually.
Geographic differences in access to advanced cancer therapies are significant. Countries with high levels of development have nuclear medicine programs, but many men must travel abroad to undergo isotope programs with Actinium-225-PSMA and other radionuclides. This highlights the need for continued expansion of specialized treatment centers with radionuclide production.
Indications for the use of Lutetium-177, Actinium-225, and Radium-223 in Prostate Cancer
Two main parameters cause differences in the action of isotope programs with different radioactive particles:
- The physical characteristics of the radioactive particle in its composition are the type of radiation, the radiation radius of the surrounding tissues, and the half-life after production
- The characteristics of the radioactive particle carrier molecule are the reliability and targeting efficiency
| Radionuclide | Indications for use | The principle of therapeutic action |
|---|---|---|
| Lutetium-177-PSMA isotope Beta radiation production (high-energy electrons), half-life – 6.5 days | Metastatic castration-resistant P-Ca, in particular with bone metastases | Lutetium-177 isotope was the first radionuclide to receive FDA approval for use in prostate cancer treatment. The carrier molecule in this drug is PSMA, a prostate-specific membrane antigen. PSMA receptors on the surface of cancer cells serve as a unique target to which a therapeutic radionuclide binds after its intravenous administration. With its 6.5-day half-life, the radiation of Lutetium-177-PSMA extends to no more than 100-200 surrounding non-cancer cells. |
| Actinium-225-PSMA isotope Targeted alpha therapy (helium nuclei), half-life – 10 days | Metastatic castration-resistant P-Ca, in particular with bone metastases | For the metastatic prostate cancer therapy, Actinium-225 isotope binds to the same molecular carrier as Lutetium-177 – PSMA. The mechanism of action of the drug differs due to the replacement of the isotope: the action of Actinium-225 lasts 4 days longer, and the radius of action is limited to 1-2 surrounding cells. Due to this, Actinium-225 therapy is effective even in the absence of a satisfactory response to Lutetium-177 isotope. |
| Lutetium-177-DOTATATE isotope Beta radiation production (high-energy electrons), half-life – 6.5 days | Neuroendocrine P-Ca (NEPC) | In this case, the radioisotope Lutetium-177 binds to another carrier substance, namely the DOTATATE molecule. DOTATATE has a structural affinity for somatostatin receptors, which are abundant on the surface of neuroendocrine tumors. After intravenous administration, Lutetium-177-DOTATATE isotope accumulates in neuroendocrine tumors of the prostate and destroys them, preserving the normal function of the bladder and intestines. |
| Radium-223 isotope Natural alpha radiation production (helium nuclei), not targeted alpha therapy, half-life – 11.5 days | Metastatic castration-resistant PCa, in particular with bone metastases | In structure, radium is similar to calcium, which is the main structural element of bone tissue. Thanks to this, it integrates into the natural bone metabolism and specifically irradiates actively multiplying cancer cells of bone metastases. The alpha radiation of Radium-223 acts within 2-10 surrounding cells, and the drug, which is not absorbed by the bones, is quickly (due to its 11.5-day half-life) excreted through the intestines. According to data from clinical studies, when using the drug, cancer cells receive 8-9 times more radiation compared to healthy tissues. |
Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 isotope production was approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) for the treatment of castration-resistant metastatic prostate cancer in the summer of 2021. Clinical trials are also being conducted on Lutetium treatment in the earlier stages of prostate cancer (P-Ca). To date, indications for the use of Lutetium-177-PSMA-617 are as follows:
- Metastatic prostate cancer with the development of metastases in the bones, lymph nodes, and lungs
- Failure to respond to hormone therapy and chemotherapy
- Contraindications to hormone therapy and chemotherapy
- Sufficient number of PSMA receptors on the cell surface based on preliminary PSMA PET/CT with Gallium-68
Another modification of the isotope Lutetium-177, namely Lutetium-177-DOTATATE, is intended for patients with rare neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC). Four cycles of cancer therapy with Lutetium-177-DOTATATE, with an interval of 8 weeks between procedures, are prescribed in cases with:
- Contraindications to surgery or chemotherapy
- Ineffectiveness of previous surgery or chemotherapy
- Failure to accurately determine the characteristics of cancer cells, the presence and number of metastases
Actinium-225-PSMA isotope administration is another alternative radionuclide cancer therapy. It can be administered when Lutetium-177-PSMA isotope fails. Thus, men have a choice between 2 options, and Actinium-225 PSMA cancer treatment allows for more personalized cancer therapy development. Oncologists may administer Actinium-225 in combination with Lutetium-177 therapy, as a direct alternative, or in eligible patients, before chemotherapy. High linear energy transfer and flexibility in administration make Actinium-225 isotope a valuable part of advanced prostate cancer targeted therapy.
High-energy alpha particles of Actinium-225 isotope are a breakthrough in cancer therapy. The WARMTH Act study (you can find it in The Lancet Oncology, 2024) demonstrated exceptional outcomes in 488 patients across 7 international clinics, with a median overall survival of 15.5 months [3]. This establishes Actinium-225 isotope as a leading therapy.
High-energy alpha particles of Actinium-225 isotope have unique therapeutic advantages: a 10-day isotope half-life and tissue penetration of 1-2 cell diameters. Thus, Actinium-225 delivers radiation to PSMA-expressing cancer cells and spares healthy tissue [4].
Radium-223 isotope production has primarily been aimed at the treatment of bone metastases in advanced prostate cancer. Bone metastases with prostate cancer cells activate osteoblasts, which are non-cancer cells with intensive metabolism responsible for building bones. Osteoblasts actively accumulate calcium ions due to the structural similarity with which radioactive Radium-223 penetrates metastases. This makes Radium-223 the drug of choice for:
- Confirmed metastatic prostate cancer with osteoblastic bone metastases development
- Absence (or a small number) of metastases in internal organs (lymph nodes, liver, and lungs)
In addition to cancer therapy, radionuclides are also actively used in the diagnosis of prostate cancer. For example, diagnostic examination by means of radionuclides typically includes imaging with Gallium-68-DOTATATE (neuroendocrine prostate cancer) and PSMA PET/CT with Gallium-68 (prostate cancer).
| Therapy | Primary Indications | Disease Pattern | Prior Treatments | PSMA Expression | Key Advantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lutetium-177-PSMA | mCRPC with PSMA+ cancer cells | Bone cancer cells + soft tissue metastases | Post-ARPI, post-chemo | High SUVmax >20 | FDA approved, wide availability |
| Actinium-225-PSMA | mCRPC, post-Lu177 progression | High-volume disease development | Multiple prior lines | Moderate-high SUVmax | Superior targeted alpha therapy, salvage therapy |
| Radium-223 isotope | mCRPC with bone metastases | Osteoblastic bone lesions only | Post-ARPI | Not required | Bone-specific, pain relief |
| Lutetium-177-DOTATATE | Neuroendocrine prostate cancer | NEPC with somatostatin receptors | Surgery/chemo contraindicated | Not applicable | NEPC-specific targeting |
What is the effectiveness of the drugs in metastatic prostate cancer?
The effectiveness of treatment with radiopharmaceuticals depends on many factors:
- Characteristics of cancer cells
- Previous treatment strategy and treatment response
- Radiopharmaceutical agent and isotope program
- Duration of the isotope program and its combination with standard options
Lutetium-177-PSMA for metastatic prostate cancer
Several clinical trials explored the clinical efficacy of Lutetium-177, Actinium-225, and Radium-223 isotopes production and administration. According to the results of the VISION clinical trial, Lutetium-177-PSMA production received FDA approval and the status of "breakthrough therapy" for metastatic hormone-resistant prostate cancer in 2021. After 1 or several courses of treatment with Lutetium-177-PSMA, the 5-year survival rate of patients with metastatic prostate cancer increased to 30%. The risk of disease recurrence also decreased; in 30-40% of patients, remission persisted for 2 years.
Leading Nuclear Medicine Expert Prof. Dresel Reveals the Power of Lutetium-177 Treatment
Actinium-225-PSMA for metastatic prostate cancer
The trials on Actinium-225 PSMA as a more innovative pharmaceutical are still ongoing, but the results obtained so far show a 50-80% decrease in the number of metastases and a 90% decrease in prostate-specific antigen levels in 82% of men. A recent large-scale study, known as the WARMTH Act (Actinium-225-PSMA radioligand therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer, mCRPC), has shown encouraging results for men with advanced prostate cancer.
Recent systematic reviews established that administration of high-energy alpha particles of Actinium-225 is a superior therapeutic option. A comprehensive meta-analysis looked at 1,155 patients across multiple international studies. It reported pooled PSA50 response rates of 65% for Actinium-225 therapy. This is significantly higher than the 49-59% rates typically reported for Lutetium-177-PSMA therapy [4].
The WARMTH Act multicenter study demonstrated exceptional outcomes in heavily pretreated patients. Among 488 men treated across seven centers in Australia, India, Germany, and South Africa, median overall survival reached 15.5 months. Progression-free survival was 7.9 months [3]. What's notable is that patients without prior chemo-exposure achieved a median overall survival of 24.2 months, while those without prior Lutetium-177 isotope exposure achieved 18.8 months.
The superior efficacy of Actinium-225 comes from its unique targeted alpha therapy properties. With linear energy transfer values 500 times higher than beta radiation and tissue penetration limited to 50-80 micrometers, Actinium-225 delivers precise, high-energy radiation. This causes irreparable DNA double-strand breaks independent of cancer cell cycle phase, energy production, or oxygen status.
Actinium-225 isotope vs Lutetium-177 isotope for metastatic prostate cancer
Investigation of clinical superiority and indications for Actinium-225 / Lutetium-177 continues. Actinium-225 PSMA binds more strongly to tumor cell receptors, and its half-life is 60% longer than the half-life of Lutetium-177. Thus, it ensures production of a more long-term effect in Lutetium-177 vs Actinium-225 clinical efficacy debates. Healthy tissues are protected, as the radius of action is only 1-2 cells (as opposed to 100-200 non-cancer cells for Lutetium-177). Therefore, in a Lutetium-177 vs Actinium-225 debate, the latter seems to be superior.
In medical papers online and worldwide we see strong evidence for Actinium-225's efficacy: higher response rates of prostate-specific antigen levels in Actinium-225 (65-82%) compared to Lutetium-177 (40-60%). The advantage is more noticeable in patients with advanced disease [5].
The superiority of high-energy alpha particles of Actinium-225 becomes particularly evident in treatment-resistant settings. While Lutetium-177 response rates decline significantly after prior therapies, Actinium-225 maintains robust efficacy even in patients who have progressed on multiple prior treatments, including Lutetium-177 itself, suggesting a different mechanism of cancer cell resistance overcome.
Radium-223 for metastatic prostate cancer
Radium-223 production and administration were studied in the ALSYMPCA clinical trial in 921 men. According to the results of the trial, the drug increased the average overall survival by 3.6 months, reduced the risk of death by 30% and significantly reduced the risk of developing pathological spinal fractures. At the same time, it also reliably reduced pain syndrome developing against the background of bone metastases, which made it possible to classify it as an effective method of symptomatic therapy. The drug received FDA approval back in 2013.
Radium-223 vs Lutetium-177 for metastatic prostate cancer
Both Radium-223 and Lutetium-177 production are FDA-approved methods, which are included in the standard guidelines for the treatment of metastatic prostate cancer. However, Radium-223 has a longer half-life than Lutetium-177, which ensures a longer therapeutic effect. In addition to that, Radium-223 acts within a maximum of 10 cells as opposed to Lutetium-177. Such peculiarities help to preserve healthy tissues from being ionized.
Nevertheless, some studies indicate increased mortality rates among the patients previously treated with Radium before undergoing Lutetium treatment as compared to Radium-naive individuals. Moreover, disease progression was reported slightly more frequently in Radium-223-treated patients as compared to Lutetium-177. Therefore, in a dispute between Radium vs Lutetium production and administration, the latter may win based on a number of crucial clinical indicators.
Overall, therapy with Lutetium-177, Actinium-225, and Radium-223 leads to significant improvement in the condition of most patients with advanced stages of prostate cancer. This treatment is clearly indicated for men with hormone-resistant cancer cells with metastases to the bones, lymph nodes, liver, and lungs. The ability to choose between different isotopes production and administration allows doctors to personalize the treatment for each patient and achieve excellent therapeutic results.
| Characteristics | Lutetium-177 | Actinium-225 | Radium-223 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment response | 30-80% decrease of tumor volume | 50-80% decrease of number of metastases | 30-50% |
| PSA levels | 70% decrease | 90% decrease of PSA levels | 20-30% decline |
| Disease recurrence rate | decreased in up to 40% | 40-60% decrease of progression* | 15-30% reduction of disease progression |
| Overall survival rates | increased up to 30% | 30% increase* | slightly increases survival |
| Median Overall Survival | 15.3 months (VISION trial) | 15.5 months (WARMTH Act) | 14.9 months (ALSYMPCA) |
| Progression-free Survival | 8.7 months | 7.9 months | 2.8 months |
| Time to Skeletal Events | 11.5 months | Not yet defined | 15.6 months |
| Pain Response Rate | 40-50% | 60-70% | 70-80% |
*Data may vary depending on individual patient factors.
Treatment Sequencing and Clinical Decision-Making in metastatic prostate cancer
Optimal Treatment Algorithm for Advanced Prostate Cancer
Usage of therapeutic radionuclides requires careful elaboration of treatment sequencing. Current evidence supports a personalized approach. It's based on a comprehensive assessment of disease characteristics, prior treatments, and patient performance status.
For treatment-naive mCRPC patients with high PSMA expression and mixed bone/soft tissue disease, Actinium-225-PSMA is emerging as a preferred first-line treatment option. This is due to its great prostate-specific antigen response rates and promise for stable remission. The targeted alpha therapy offers effective treatment of metastases while preserving normal tissues.
Patients with osteoblastic bone metastases are candidates for Radium-223 production and administration (as first-line therapy). Minimal soft tissue involvement is also possible. It is particularly valuable for patients prioritizing quality of life due to bone-adherent properties and proven symptomatic benefits.
Lutetium-177-PSMA serves as an important treatment option for patients with moderate disease burden who may benefit from the wider availability and established safety profile of beta-emitting therapy. The role of such isotope programs as a bridge therapy or in sequential protocols continues to evolve.
Sequential Therapy Strategies
Post-Lutetium-177 progression represents a critical decision point where Actinium-225-PSMA has demonstrated exceptional salvage efficacy. Response rates of 50-60% in Lutetium-177-refractory patients suggest that targeted alpha therapy can overcome resistance mechanisms that limit beta-emitter effectiveness [6].
Combination approaches using sequential targeted alpha therapy and beta isotope programs are under active investigation. Early results from combination trials suggest enhanced efficacy with manageable toxicity profiles, potentially representing the future of personalized radionuclide therapy.
Post-Radium-223 treatment options include both PSMA-targeted therapies, with choice dependent on PSMA expression levels and disease distribution. The bone marrow recovery period following Radium-223 may influence the optimal timing of subsequent treatments.
What reactions and side effects can occur during metastatic prostate cancer treatment?
Today, in the clinical practice of specialized centers and departments of nuclear medicine, only radioactive isotopes with an optimal safety profile and minimal side effects are in production. Isotope programs are indicated for debilitated patients with advanced stages of cancer, and therefore, doctors pay special attention not only to the effectiveness of the therapy but also to patients' tolerability to it.
The most common side effects of the isotope programs include:
- Dry mouth – 87% patients
- Nausea – 50% patients
- Fatigue – 50% patients
- Anemia – 13% patients
- Thrombocytopenia – 13% patients
- Lymphocytopenia – 37% patients
Dry mouth or xerostomia is the most common side effect, alongside fatigue. Lutetium-177 and Actinium-225 also have low myelotoxicity, that is, they do not affect the spinal cord when treating metastases in the spine and other bones (the most typical localization of metastases in prostate cancer). Most side effects are temporary and go away on their own within a few days/weeks after the end of the course of treatment. Actinium, Lutetium, and Radium therapy cause significantly less short- and long-term side effects than standard therapies due to high targeting efficiency. If necessary, doctors may prescribe symptomatic treatment, such as antiemetic drugs or drugs to improve the patient's general condition.
Safety Profile Comparison In Metastatic Prostate Cancer
Recent safety analyses have provided detailed insights into the tolerability profiles of different isotope programs, allowing for more informed treatment selection based on patient-specific risk factors.
Despite its potent targeted alpha therapy capabilities, Actinium-225-PSMA demonstrates a remarkably favorable safety profile. The WARMTH Act study reported grade 3-4 adverse events in only 17% of patients, with anemia (11%) and thrombocytopenia (6%) being the most common severe toxicities [3]. Notably, severe xerostomia was observed in less than 5% of patients, significantly lower than historical rates with other PSMA-targeted therapies.
The precision of targeted alpha therapy appears to result in less collateral damage to normal tissues. Renal function, a critical concern with PSMA-targeted therapies, remains stable in most patients receiving Actinium-225, with grade 3-4 nephrotoxicity reported in less than 3% of cases.
| Side Effect Category | Actinium-225-PSMA | Radium-223 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hematologic (Grade 3-4) | |||
| Anemia | 15-20% | 11% | 10-15% |
| Thrombocytopenia | 10-15% | 6% | 5-10% |
| Neutropenia | 8-12% | 4% | 2-5% |
| Non-hematologic (Any Grade) | |||
| Xerostomia (dry mouth) | 80-90% | 70-80% | 10-20% |
| Nausea | 50-60% | 40-50% | 30-40% |
| Diarrhea | 20-30% | 15-20% | 40-50% |
| Organ-specific Toxicity | |||
| Nephrotoxicity (Grade 3-4) | 5-8% | 2-3% | <1% |
| Severe xerostomia | 10-15% | <5% | <1% |
| Bone marrow suppression | Moderate | Mild | Moderate |
*Sources: Multiple clinical trials and safety analyses, 2021-2025
Risk Mitigation and Management Strategies
Proactive management of side effects has become increasingly sophisticated, with specialized protocols developed for each isotope program. For xerostomia, the most common PSMA-related side effect, preventive measures include pre-treatment salivary gland protection with cold packs and post-treatment sialagogue medications.
Hematologic monitoring follows standardized protocols with treatment delays or dose modifications based on blood count recovery. The lower myelotoxicity profile of Actinium-225 allows for more flexible scheduling and potentially improved quality of life during treatment.
Long-term surveillance programs have been established to monitor for delayed effects, particularly secondary malignancies and organ dysfunction. Current follow-up data extending to 5 years post-treatment show no increase in secondary cancer rates compared to standard therapies.
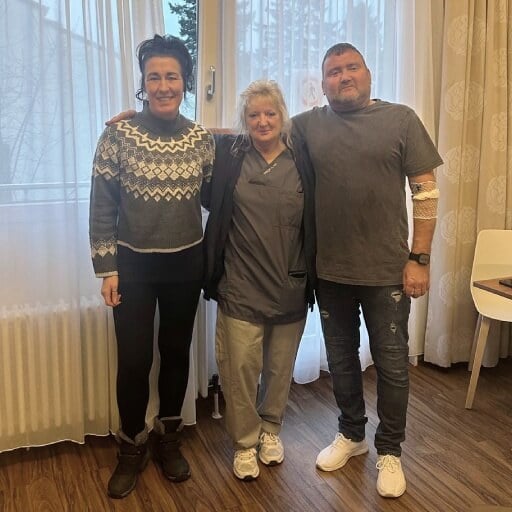
Success Stories From Prostate Cancer Patients
John Baker’s story represents strong determination and persistence in search of the best solution for his problem. John has struggled with prostate cancer for 5 years: targeted radiotherapy and heat therapy have been started immediately after the diagnosis. The effect was uninspiring though. It didn't work like he hoped.
Around that time, John found out the cancer had spread beyond the prostate. This was bad news. John and his wife faced a significant challenge. They could wait for insurance approval, which takes forever usually. Or they could explore other treatment options. It was exactly when they stumbled upon Booking Health and Lutetium-177.
John and his wife contacted the Booking Health specialists to start the treatment as soon as possible. "Everything went like clockwork", says Mr. Baker, recalling his experience of undergoing Lutetium-177 treatment in Germany. Each step of the process was well-planned and clearly communicated. "I never had to worry about where I was going", said John Baker. Treatment itself did not cause any discomfort or side effects. "The only thing that was tiring was the airplane ride", Mr. Baker said laughing. Not only the lack of adverse effects as opposed to classical chemotherapy or other protocol methods, but the efficacy of Lutetium-177 therapy convinced John that the decision to come to Germany for treatment was worthwhile. After one session of treatment, the scan showed that there were no metastatic lesions in the bones. Above that, PSA levels dropped significantly. "I would recommend it to anyone for any cancer problem, not just prostate cancer. It's pretty straightforward, pretty simple", Mr. Baker concluded.
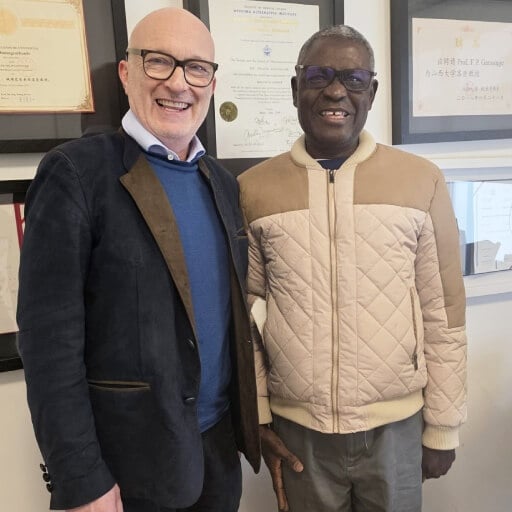
"PSA Dropped to Nothing": US Patient Shares His German Cancer Treatment Journey
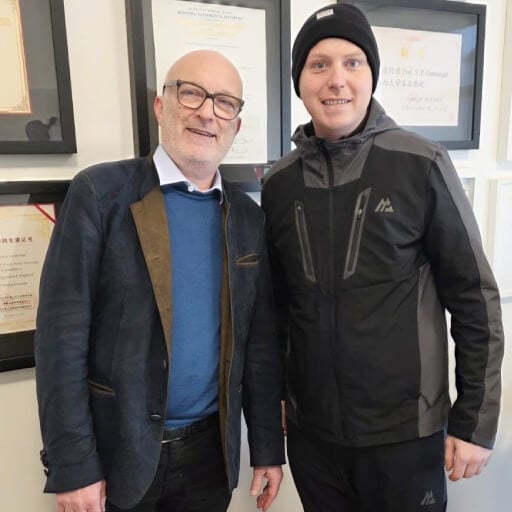
New Hope Regained with Actinium-225 PSMA Therapy for Prostate Cancer
Christopher Lambi was fighting prostate cancer for several years. He tried various standard methods, including hormones and chemotherapy. However, the disease kept progressing with little hope left when metastases were detected during another planned scan. Without much enthusiasm, Mr. Lambi decided to look for an alternative opinion abroad. This is how he found out about the Booking Health company.
After the initial communication and comprehensive analysis of the case, Mr. Lambi was recommended to start Actinium-225 PSMA therapy. "I was quite skeptical at first. I knew nothing about this Actinium: what it was and how I will take it". When the patient came, he was picked up from the airport, accompanied by a personal translator. "Everything went so smoothly: I had a personal driver, a translator, and a manager, who was literally in contact with me the whole time", said Christopher Lambi. After running medical tests and another in-person consultation, Mr. Lambi started his treatment the very next day. After going through a standard treatment protocol, Christopher Lambi was afraid of severe adverse effects that had a significant impact on his life and work. He was pleasantly surprised to have no side effects after Actinium-225 PSMA therapy. "It was unbelievable – no bleeding, no vomiting, no hair loss. The procedure was easy to go through". Mr. Lambi was even more surprised to see his next scan during the follow-up, which demonstrated that almost 90% of the metastases were gone after just one session. "I was about to lose hope after having so much struggle. Now I can even go back to work. Never dreamt of that again". Christopher Lambi is grateful he once chose to use Booking Health to organize his treatment in Germany. "My best investment so far", said Mr. Lambi with a laugh.
Where can you get Lutetium-177, Actinium-225, and Radium-223 prostate cancer treatment?
Nuclear Medicine Centers and specialized departments of large university hospitals offer radioactive isotopes treatment. This is a compilation of some of the best medical institutions anyone can reach from any part of the globe:
- University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich, Department of Nuclear Medicine. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Wolfgang Weber, whose specialization is radionuclide cancer therapy. The professor has prepared more than 250 articles for leading scientific journals, including the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- University Hospital of Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Department of Nuclear Medicine. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Matthias Brendel. He is a highly qualified expert with extensive experience in radiation oncology. Prof. Brendel has more than 200 scientific publications and regularly participates in national and international congresses devoted to radioisotope diagnosis and treatment.
- Helios Hospital Berlin-Buch, Department of Nuclear Medicine. The department is headed by Prof. Dr. med. Stefan Dresel, who has dedicated over 22 years to nuclear medicine practice. He specializes in Lu-177 PSMA therapy for advanced prostate cancer and Lu-177-DOTATOC therapy for neuroendocrine tumors. Prof. Dresel actively contributes to scientific research with numerous publications and regularly participates in international medical conferences focused on nuclear medicine advancements.
- University Hospital Carl Gustav Carus Dresden, Department of Nuclear Medicine. The head of the department is Prof. Dr. med. Jörg Kotzerke. The professor has been working with methods of radioisotope diagnostics and treatment for more than 30 years and is a board member of the German Society for Nuclear Medicine (DGN).
- University Hospital Erlangen, Department of Nuclear Medicine. The head of the department is Prof. Dr. med. Torsten Kuwert. The professor has been working in nuclear medicine institutes and university clinics for about 30 years; now he specializes in the treatment of prostate cancer and its metastases.
Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Prostate Cancer Treatment
The economic impact of radionuclide therapies goes beyond just initial treatment costs. Comprehensive economic analyses demonstrated that these advanced therapeutics have favorable cost-effectiveness profiles when you compare them to conventional treatments.
Lutetium-177-PSMA therapy has high upfront costs, that's true. But it has shown cost-effectiveness ratios when you consider quality-adjusted life years (QALYs) gained. Actinium-225 therapy is more expensive per treatment cycle. However, it may offer superior cost-effectiveness because of higher response rates and fewer treatment cycles.
| Treatment for prostate cancer | Average cost of treatment in Germany | Average cost of treatment in the USA |
|---|---|---|
| Treatment of Prostate Cancer with Metastasis by Lutetium-177-PSMA (LU-177) | €17,000 - €28,000 | starting from $55,000 per cycle |
| Treatment of Prostate Cancer with Metastasis by Actinium-225-PSMA | €15,000 - €29,000 | starting from $60,000 per cycle |
| Treatment of Prostate Cancer with Bone Metastases by Radium-223 | €21,700 - €23,700 | starting from $32,000 per cycle |
| Lutetium-177-DOTATATE (Lu-177-DOTATATE) therapy for neuroendocrine prostate cancer (NEPC) | €14,000 - €28,000 | not widely available |
Radionuclide prostate cancer treatment in the world's leading hospitals with Booking Health
Prostate cancer patients often cannot undergo treatment with Lutetium-177, Actinium-225, or Radium-223 in their home country as radioactive material production and providing high radiation shielding are technically challenging processes. That is why they look for appropriate opportunities in foreign hospitals. Booking Health is a medical tourism agent that has been organizing radionuclide treatment in leading Nuclear Medical Centers for symptomatic prostate cancer patients from 75 countries for over 12 years.
As a reputable company, Booking Health offers personalized stage 4 prostate cancer treatment plans with direct clinic booking and full support at every stage, from organizational processes to assistance during treatment. We provide:
- Assessment and analysis of medical reports
- Development of the medical care program
- Selection of a suitable treatment location
- Preparation of medical documents and forwarding to a suitable clinic
- Preparatory consultations with clinicians for the development of medical care programs
- Expert advice during the hospital stay
- Follow-up care after the patient returns to their native country after completing the medical care program
- Taking care of formalities as part of the preparation for the medical care program
- Coordination and organization of the patient's stay in a foreign country
- Assistance with visas and tickets
- A personal coordinator and interpreter with 24/7 support
- No hidden fees in your bills
Health is an invaluable aspect of our lives. Delegating management of something so fragile yet precious should be done only to experts with proven experience and a reputation. Booking Health is a trustworthy partner who assists you in pursuing stronger health and a better quality of life. Contact our medical consultant to learn more about the possibilities of personalized treatment with innovative methods for metastatic prostate cancer with leading specialists in this field.
Advanced Cancer Treatment: Patient Success Stories with Booking Health
Frequently asked questions about metastatic prostate cancer
Contact Medical SpecialistLutetium-177 and Actinium-225 isotopes are PSMA-targeted therapies using different types of radiation (beta and targeted alpha therapy, respectively). Radium-223 is more potent for bone metastases. Lutetium-177 isotope has a larger radiation range, while Actinium-225 isotope lasts longer and has a shorter radiation range, which helps to preserve healthy tissues.
These treatments are typically recommended for patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC), who have not responded well to other treatments like hormone therapy and chemotherapy. The specific choice depends on the quantity and location of metastases, previous treatments, and overall health condition.
Common side effects include fatigue, nausea, and a temporary decrease in blood cell counts. Dry mouth may occur with all PSMA-targeted therapies. Radium-223 may sometimes cause diarrhea. These side effects are generally manageable and less severe than those of traditional chemotherapy.
Clinical trials have shown promising results. For example, Lutetium-177-PSMA therapy has demonstrated PSA response rates of 40-60% and objective response rates of 40-50% in some studies. Actinium-225-PSMA has shown even higher response rates in early trials. Radium-223 has been shown to improve overall survival in patients with bone metastases.
In many cases 1 procedure is enough for clinical result. Repeated procedures are also possible: 4-6 for Lutetium-177-PSMA, 2-4 for Actinium-225-PSMA, and 6 for Radium-223.
Currently, Actinium-225 isotope is not as available as Lutetium-177 (Lu-177) isotope. Lu-177 preparations are accessible in many countries and in different healthcare facilities.
As a rule, Ac-225 therapy is more expensive one due to high production costs of the Ac-225 isotope. Paradoxical though, the overall treatment cost may be lower with Ac-225 as it requires fewer treatment sessions typically.
Yes, according to the conclusions of preliminary investigations. Combination therapy with Ac-225 isotope and Lu-177 isotope may improve efficacy of therapeutic protocols.
Metastatic prostate malignancies manifest themselves with bone pain, fatigue, weight loss. In the blood tests, rising PSA levels against the background of ongoing treatment are detected.
Lutetium‑177 PSMA therapy costs about €17,000-€28,000 per course, Actinium‑225 PSMA therapy – about €18,000-€29,000. You can check price in the specific hospital on the Booking Health website.
It is used in men with metastatic, castration‑resistant prostate cancer – especially when Lutetium‑177‑PSMA therapy does not work as it was expected. Currently, therapy with Actinium can even be considered as first-line option.
Caregivers and patients see a significant reduction in cancer activity, with PSA levels dropping by up to 90% (in up to 82% of cases). Assessment of PSMA level before the therapy is a must for response prediction.
Treatment with Actinium‑225 reduces cancer progression and recurrence – it offers a 40-60% improvement compared to standard protocols.
Patients treated with Actinium‑225‑PSMA have an overall survival improvement of about 30% compared to standard therapies.
University Hospital Rechts der Isar Munich, University Hospital Ludwig Maximilian Munich, Helios Berlin-Buch and University Hospital Erlangen – these hospitals specialize in radionuclide therapies.
Choose treatment abroad and you will for sure get the best results!
Authors:
This article was edited by medical experts, board-certified doctors Dr. Nadezhda Ivanisova, and Dr. Bohdan Mykhalniuk. For the treatment of the conditions referred to in the article, you must consult a doctor; the information in the article is not intended for self-medication!
Our editorial policy, which details our commitment to accuracy and transparency, is available here. Click this link to review our policies.
Sources:
[1] ZERO Prostate Cancer. Facts & Statistics. https://zerocancer.org/about-prostate-cancer/facts-statistics
[2] National Cancer Institute. SEER Cancer Stat Facts: Prostate Cancer. https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html
[3] Actinium-225-PSMA radioligand therapy of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (WARMTH Act): a multicentre, retrospective study. Sathekge, Mike M et al. The Lancet Oncology, Volume 25, Issue 2, 175 - 183. https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(23)00638-1/abstract
[4] Ninatti G, et al. Time for action: actinium-225 PSMA-targeted alpha therapy for metastatic prostate cancer - a systematic review and meta-analysis. Theranostics. 2025;15:3386-3399. DOI: 10.7150/thno.106574. [DOI]
[5] Garo ML, et al. [225Ac]Ac-PSMA for the treatment of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur J Clin Invest. 2025;55:e14358 DOI: 10.1111/eci.14358. [DOI]
[6] Benedikt Feuerecker, Robert Tauber, Karina Knorr et al. Activity and Adverse Events of Actinium-225-PSMA-617 in Advanced Metastatic Castration-resistant Prostate Cancer After Failure of Lutetium-177-PSMA, European Urology, Volume 79, Issue 3, 2021, Pages 343-350, ISSN 0302-2838, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eururo.2020.11.013. [DOI]
[7] MDPI. Review on the Increasing Role for PSMA-Based Radioligand Therapy in Prostate Cancer. https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6694/16/14/2520#
Read:
A Comprehensive Guide to Getting Prostate Cancer Treatment
Stage 4 Prostate Cancer Treatment in Germany: What You Need to Know
Article menu:
- What Patients Face When Prostate Cancer Becomes Advanced
- Indications for the use of Lutetium-177, Actinium-225, and Radium-223 in Prostate Cancer
- What is the effectiveness of the drugs in metastatic prostate cancer?
- Treatment Sequencing and Clinical Decision-Making in metastatic prostate cancer
- What reactions and side effects can occur during metastatic prostate cancer treatment?
- Safety Profile Comparison In Metastatic Prostate Cancer
- Success Stories From Prostate Cancer Patients
- Where can you get Lutetium-177, Actinium-225, and Radium-223 prostate cancer treatment?
- Cost-Effectiveness Analysis of Prostate Cancer Treatment
- Radionuclide prostate cancer treatment in the world's leading hospitals with Booking Health
- Frequently asked questions about metastatic prostate cancer
Don't know where to start?
Contact Booking Health